源码跟读,Spring是如何解析和加载xml中配置的beans
1、配置启动Spring所需的监听器
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener><listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
ContextLoaderListener.java extends ContextLoader implements ServletContextListener
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
this.contextLoader = createContextLoader();
if (this.contextLoader == null) {
this.contextLoader = this;
}
this.contextLoader.initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}ContextLoaderListener.java extends ContextLoader implements ServletContextListener
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
this.contextLoader = createContextLoader();
if (this.contextLoader == null) {
this.contextLoader = this;
}
this.contextLoader.initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}
- 基于 XML 文件的配置方式
- 基于 Annotation 的配置方式
- 基于 Java Code 的配置方式
- 用户自定义的配置方式
2、监听器都做了些什么?
ContextLoader.java
static {
// Load default strategy implementations from properties file.
// This is currently strictly internal and not meant to be customized
// by application developers.
try {
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH, ContextLoader.class);
//private static final String DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH = "ContextLoader.properties";
defaultStrategies = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not load 'ContextLoader.properties': " + ex.getMessage());
}
}ContextLoader.java
static {
// Load default strategy implementations from properties file.
// This is currently strictly internal and not meant to be customized
// by application developers.
try {
ClassPathResource resource = new ClassPathResource(DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH, ContextLoader.class);
//private static final String DEFAULT_STRATEGIES_PATH = "ContextLoader.properties";
defaultStrategies = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Could not load 'ContextLoader.properties': " + ex.getMessage());
}
}
ContextLoader.properties
org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext=org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContextContextLoader.properties
org.springframework.web.context.WebApplicationContext=org.springframework.web.context.support.XmlWebApplicationContext
ContextLoader.java
// Store context in local instance variable, to guarantee that
// it is available on ServletContext shutdown.
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext, parent);ContextLoader.java
// Store context in local instance variable, to guarantee that
// it is available on ServletContext shutdown.
this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext, parent);
ContextLoader.java
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc, ApplicationContext parent) {
//step1
Class<?> contextClass = determineContextClass(sc);
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Custom context class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type [" + ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.getName() + "]");
}
//step2
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac =
(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
// Assign the best possible id value.
if (sc.getMajorVersion() == 2 && sc.getMinorVersion() < 5) {
// Servlet <= 2.4: resort to name specified in web.xml, if any.
String servletContextName = sc.getServletContextName();
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(servletContextName));
}
else {
// Servlet 2.5's getContextPath available!
try {
String contextPath = (String) ServletContext.class.getMethod("getContextPath").invoke(sc);
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(contextPath));
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to invoke Servlet 2.5 getContextPath method", ex);
}
}
//step3
wac.setParent(parent);
wac.setServletContext(sc);
wac.setConfigLocation(sc.getInitParameter(CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM));
customizeContext(sc, wac);
//step4
wac.refresh();
return wac;
}ContextLoader.java
protected WebApplicationContext createWebApplicationContext(ServletContext sc, ApplicationContext parent) {
//step1
Class<?> contextClass = determineContextClass(sc);
if (!ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.isAssignableFrom(contextClass)) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("Custom context class [" + contextClass.getName() +
"] is not of type [" + ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.class.getName() + "]");
}
//step2
ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac =
(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
// Assign the best possible id value.
if (sc.getMajorVersion() == 2 && sc.getMinorVersion() < 5) {
// Servlet <= 2.4: resort to name specified in web.xml, if any.
String servletContextName = sc.getServletContextName();
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(servletContextName));
}
else {
// Servlet 2.5's getContextPath available!
try {
String contextPath = (String) ServletContext.class.getMethod("getContextPath").invoke(sc);
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(contextPath));
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to invoke Servlet 2.5 getContextPath method", ex);
}
}
//step3
wac.setParent(parent);
wac.setServletContext(sc);
wac.setConfigLocation(sc.getInitParameter(CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM));
customizeContext(sc, wac);
//step4
wac.refresh();
return wac;
}
3、createWebApplicationContext
3.1 //step1
ContextLoader.java
protected Class<?> determineContextClass(ServletContext servletContext) {
String contextClassName = servletContext.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM); //CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM = "contextClass"
if (contextClassName != null) {
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Failed to load custom context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
else {
contextClassName = defaultStrategies.getProperty(WebApplicationContext.class.getName());
//defaultStrategies = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource); defaultStrategies也就是静态代码块中初始化的默认工具类XmlWebApplicationContext
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Failed to load default context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
}ContextLoader.java
protected Class<?> determineContextClass(ServletContext servletContext) {
String contextClassName = servletContext.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM); //CONTEXT_CLASS_PARAM = "contextClass"
if (contextClassName != null) {
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Failed to load custom context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
else {
contextClassName = defaultStrategies.getProperty(WebApplicationContext.class.getName());
//defaultStrategies = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource); defaultStrategies也就是静态代码块中初始化的默认工具类XmlWebApplicationContext
try {
return ClassUtils.forName(contextClassName, ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader());
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException(
"Failed to load default context class [" + contextClassName + "]", ex);
}
}
}
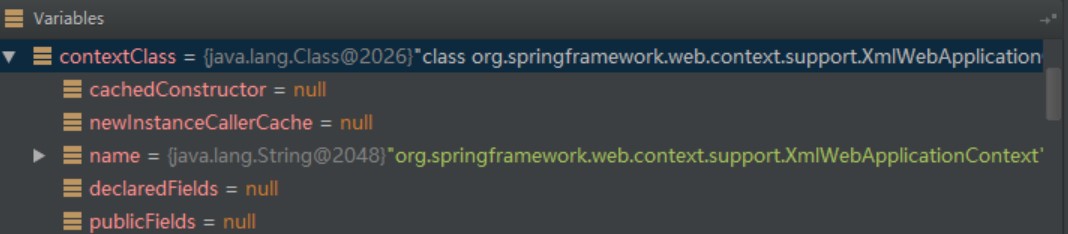
3.2 //step2
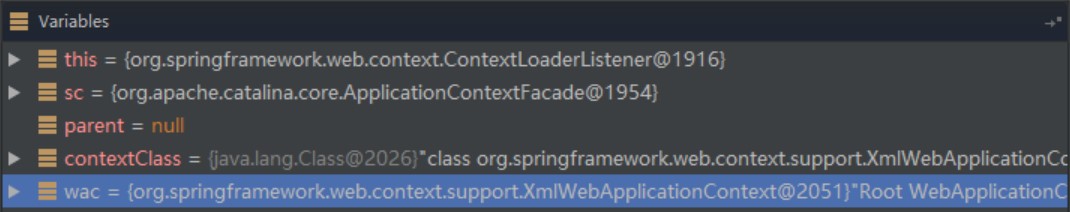
3.3 //step3
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</context-param><context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
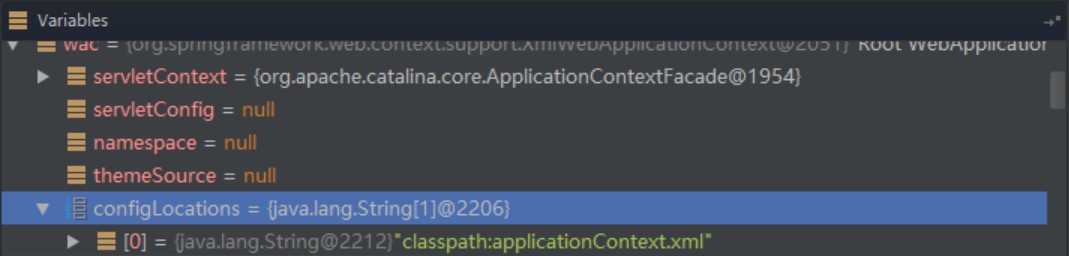
3.4 //step4
AbstractApplicationContext.java
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
//此方法做一些准备工作,如记录开始时间,输出日志,initPropertySources();和getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties();一般没干什么事
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
//step4.1
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
//step4.2
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - cancelling refresh attempt", ex);
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
}
}AbstractApplicationContext.java
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
//此方法做一些准备工作,如记录开始时间,输出日志,initPropertySources();和getEnvironment().validateRequiredProperties();一般没干什么事
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
//step4.1
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
//step4.2
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - cancelling refresh attempt", ex);
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
}
}
3.4.1 //step4.1 refresh()的核心 obtainFreshBeanFactory()
AbstractApplicationContext.java
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
refreshBeanFactory();
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Bean factory for " + getDisplayName() + ": " + beanFactory);
}
return beanFactory;
}AbstractApplicationContext.java
protected ConfigurableListableBeanFactory obtainFreshBeanFactory() {
refreshBeanFactory();
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = getBeanFactory();
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Bean factory for " + getDisplayName() + ": " + beanFactory);
}
return beanFactory;
}
AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext.java
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
destroyBeans();
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext.java
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
destroyBeans();
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}
AbstractXmlApplicationContext.java
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException {
// Create a new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given BeanFactory.
XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
// Configure the bean definition reader with this context's
// resource loading environment.
beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment());
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);
beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this));
// Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader,
// then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions.
initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader);
loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);
}AbstractXmlApplicationContext.java
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException {
// Create a new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given BeanFactory.
XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
// Configure the bean definition reader with this context's
// resource loading environment.
beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment());
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);
beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this));
// Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader,
// then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions.
initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader);
loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);
}
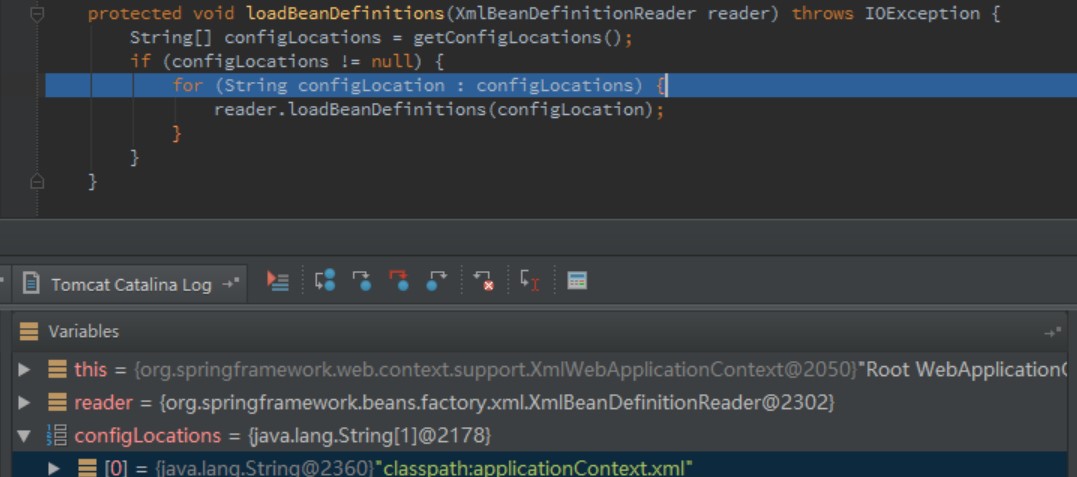
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws IOException {
String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations();
if (configLocations != null) {
for (String configLocation : configLocations) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocation);
}
}
}protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws IOException {
String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations();
if (configLocations != null) {
for (String configLocation : configLocations) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocation);
}
}
}
DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.java
protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) {
// Any nested <beans> elements will cause recursion in this method. In
// order to propagate and preserve <beans> default-* attributes correctly,
// keep track of the current (parent) delegate, which may be null. Create
// the new (child) delegate with a reference to the parent for fallback purposes,
// then ultimately reset this.delegate back to its original (parent) reference.
// this behavior emulates a stack of delegates without actually necessitating one.
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate;
this.delegate = createDelegate(this.readerContext, root, parent);
if (this.delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) {
Assert.state(this.environment != null, "Environment must be set for evaluating profiles");
String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(
profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
if (!this.environment.acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) {
return;
}
}
}
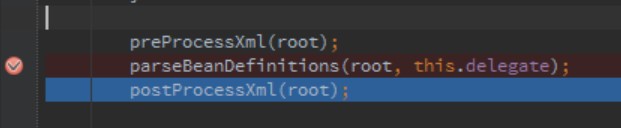
preProcessXml(root);
//xml解析和加载类
parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate);
postProcessXml(root);
this.delegate = parent;
}DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.java
protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) {
// Any nested <beans> elements will cause recursion in this method. In
// order to propagate and preserve <beans> default-* attributes correctly,
// keep track of the current (parent) delegate, which may be null. Create
// the new (child) delegate with a reference to the parent for fallback purposes,
// then ultimately reset this.delegate back to its original (parent) reference.
// this behavior emulates a stack of delegates without actually necessitating one.
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate;
this.delegate = createDelegate(this.readerContext, root, parent);
if (this.delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) {
Assert.state(this.environment != null, "Environment must be set for evaluating profiles");
String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(
profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
if (!this.environment.acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) {
return;
}
}
}
preProcessXml(root);
//xml解析和加载类
parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate);
postProcessXml(root);
this.delegate = parent;
}
...
public static final String PROPERTY_ELEMENT = "property";
public static final String REF_ATTRIBUTE = "ref";
public static final String VALUE_ATTRIBUTE = "value";
......
public static final String PROPERTY_ELEMENT = "property";
public static final String REF_ATTRIBUTE = "ref";
public static final String VALUE_ATTRIBUTE = "value";
...
DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.java
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes(); //将节点获取存入collection
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) { //对collection中存储的节点进行依次遍历
Node node = nl.item(i); //返回当前序号的节点
if (node instanceof Element) { //判断节点是否属于元素类(我们不需要文本型)(参考文章《Java是如何解析xml文件的(DOM)》)
Element ele = (Element) node;
//判断是否为默认的命名空间,其实就是根据配置文件的命名空间来判定
//如果是beans下的则认为是默认的命名空间,如果不是则认为是自定义的,我们使用的Aop、Tx等都是属于自定义标签的范畴
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate); //进行解析
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);
}
}
}
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(root);
}
}DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.java
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes(); //将节点获取存入collection
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) { //对collection中存储的节点进行依次遍历
Node node = nl.item(i); //返回当前序号的节点
if (node instanceof Element) { //判断节点是否属于元素类(我们不需要文本型)(参考文章《Java是如何解析xml文件的(DOM)》)
Element ele = (Element) node;
//判断是否为默认的命名空间,其实就是根据配置文件的命名空间来判定
//如果是beans下的则认为是默认的命名空间,如果不是则认为是自定义的,我们使用的Aop、Tx等都是属于自定义标签的范畴
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate); //进行解析
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);
}
}
}
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(root);
}
}
DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.java
private void parseDefaultElement(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, IMPORT_ELEMENT)) {
importBeanDefinitionResource(ele);
}
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, ALIAS_ELEMENT)) {
processAliasRegistration(ele);
}
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, BEAN_ELEMENT)) {
processBeanDefinition(ele, delegate);
}
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, NESTED_BEANS_ELEMENT)) {
// recurse
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(ele);
}
}DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.java
private void parseDefaultElement(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, IMPORT_ELEMENT)) {
importBeanDefinitionResource(ele);
}
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, ALIAS_ELEMENT)) {
processAliasRegistration(ele);
}
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, BEAN_ELEMENT)) {
processBeanDefinition(ele, delegate);
}
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, NESTED_BEANS_ELEMENT)) {
// recurse
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(ele);
}
}
DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.java
protected void processBeanDefinition(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder = delegate.parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele);
if (bdHolder != null) {
bdHolder = delegate.decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, bdHolder);
try {
// Register the final decorated instance.
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry());
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to register bean definition with name '" +
bdHolder.getBeanName() + "'", ele, ex);
}
// Send registration event.
getReaderContext().fireComponentRegistered(new BeanComponentDefinition(bdHolder));
}
}DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.java
protected void processBeanDefinition(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder = delegate.parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele);
if (bdHolder != null) {
bdHolder = delegate.decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, bdHolder);
try {
// Register the final decorated instance.
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry());
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to register bean definition with name '" +
bdHolder.getBeanName() + "'", ele, ex);
}
// Send registration event.
getReaderContext().fireComponentRegistered(new BeanComponentDefinition(bdHolder));
}
}
- 把beanName放到队列里
- 把BeanDefinition放到map中
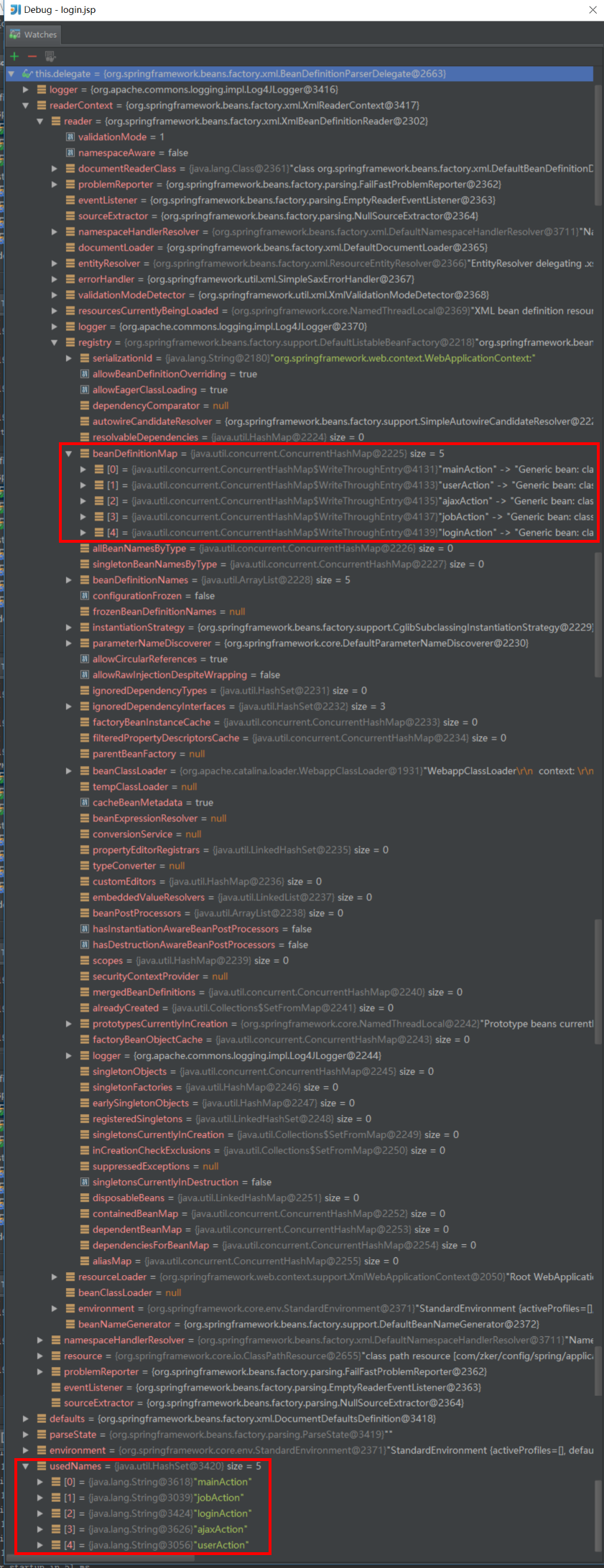
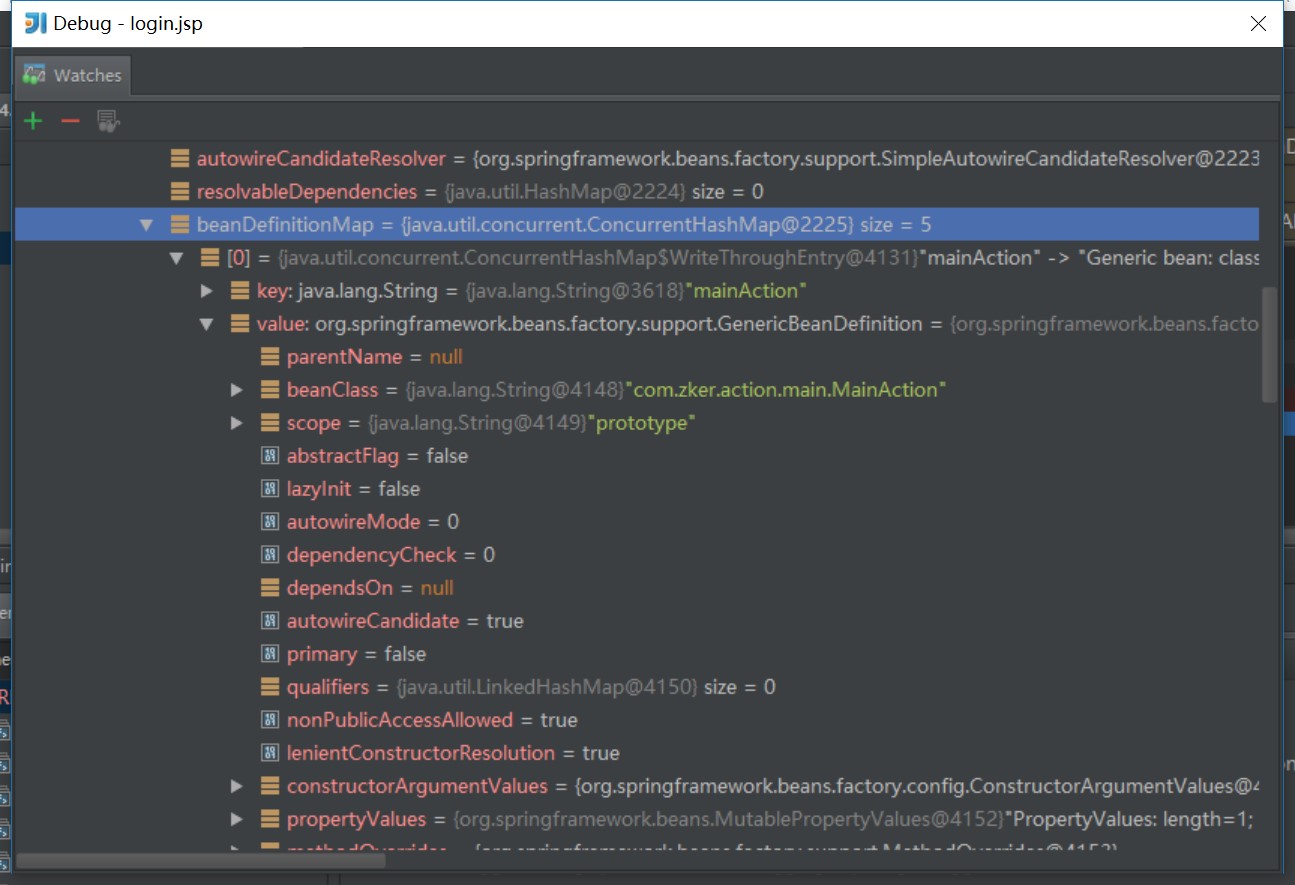
3.4.2 //step4.2 refresh()的核心finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
AbstractApplicationContext.java
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Initialize conversion service for this context.
if (beanFactory.containsBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)) {
beanFactory.setConversionService(
beanFactory.getBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class));
}
// Initialize LoadTimeWeaverAware beans early to allow for registering their transformers early.
String[] weaverAwareNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(LoadTimeWeaverAware.class, false, false);
for (String weaverAwareName : weaverAwareNames) {
getBean(weaverAwareName);
}
// Stop using the temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(null);
// Allow for caching all bean definition metadata, not expecting further changes.
beanFactory.freezeConfiguration();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
}AbstractApplicationContext.java
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Initialize conversion service for this context.
if (beanFactory.containsBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME) &&
beanFactory.isTypeMatch(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class)) {
beanFactory.setConversionService(
beanFactory.getBean(CONVERSION_SERVICE_BEAN_NAME, ConversionService.class));
}
// Initialize LoadTimeWeaverAware beans early to allow for registering their transformers early.
String[] weaverAwareNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(LoadTimeWeaverAware.class, false, false);
for (String weaverAwareName : weaverAwareNames) {
getBean(weaverAwareName);
}
// Stop using the temporary ClassLoader for type matching.
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(null);
// Allow for caching all bean definition metadata, not expecting further changes.
beanFactory.freezeConfiguration();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
}
DefaultListableBeanFactory.java
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
List<String> beanNames;
synchronized (this.beanDefinitionMap) {
// Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.
// While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.
beanNames = new ArrayList<String>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
}
// Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) { //将加载进来的beanDefinitionNames循环分析
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) { //如果不是抽象类, 且是单例, 且不是延迟加载
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
final FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Boolean>() {
@Override
public Boolean run() {
return ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit();
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit());
}
if (isEagerInit) {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
else {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
// Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) {
final SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() {
@Override
public Object run() {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
return null;
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
}
}
}
}DefaultListableBeanFactory.java
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
List<String> beanNames;
synchronized (this.beanDefinitionMap) {
// Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.
// While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.
beanNames = new ArrayList<String>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
}
// Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) { //将加载进来的beanDefinitionNames循环分析
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) { //如果不是抽象类, 且是单例, 且不是延迟加载
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
final FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Boolean>() {
@Override
public Boolean run() {
return ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit();
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit());
}
if (isEagerInit) {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
else {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
// Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans...
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) {
final SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() {
@Override
public Object run() {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
return null;
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
}
}
}
}
for (String beanName : beanNames) { //将加载进来的beanDefinitionNames循环分析
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) { //如果不是抽象类, 且是单例, 且不是延迟加载
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) { //是否实现FactoryBean接口
final FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Boolean>() {
@Override
public Boolean run() {
return ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit();
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit());
}
if (isEagerInit) {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
else {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}for (String beanName : beanNames) { //将加载进来的beanDefinitionNames循环分析
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) { //如果不是抽象类, 且是单例, 且不是延迟加载
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) { //是否实现FactoryBean接口
final FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Boolean>() {
@Override
public Boolean run() {
return ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit();
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
}
else {
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit());
}
if (isEagerInit) {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
else {
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
- 判断这个bean是否是抽象类,是否是单例,是否延迟加载
- 如果不是抽象类, 且是单例, 且不是延迟加载,那么判断是否实现 FactoryBean 接口
- 如果实现了 FactoryBean,则 getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName),否则 getBean(beanName)
- 创建一个bean的实例
- 将这个实例封装到BeanWrapper中
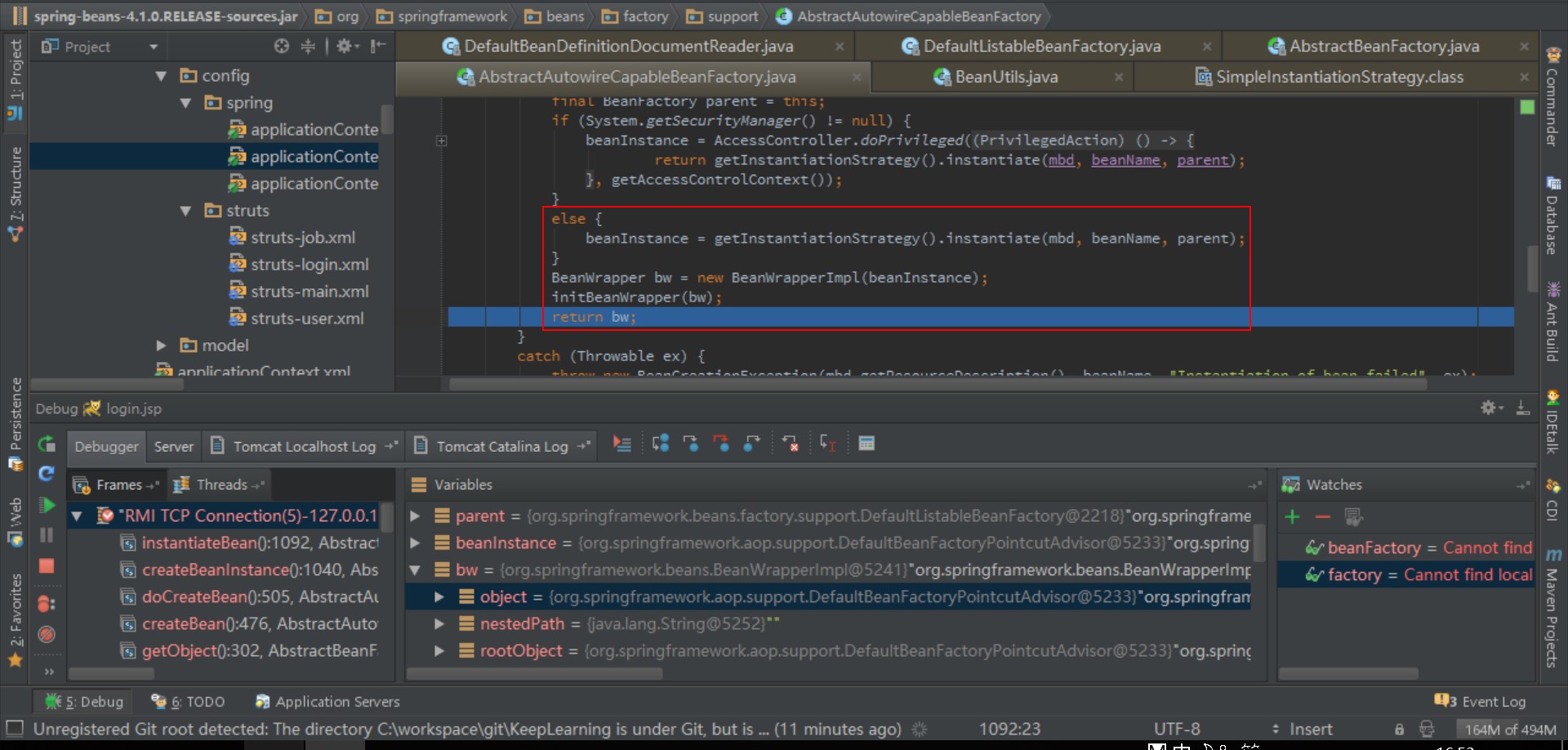
4、参考链接
源码跟读,Spring是如何解析和加载xml中配置的beans的更多相关文章
- 【spring源码学习】spring的IOC容器之自定义xml配置标签扩展namspaceHandler向IOC容器中注册bean
[spring以及第三方jar的案例]在spring中的aop相关配置的标签,线程池相关配置的标签,都是基于该种方式实现的.包括dubbo的配置标签都是基于该方式实现的.[一]原理 ===>sp ...
- Spring源码情操陶冶-自定义节点的解析
本文承接前文Spring源码情操陶冶-DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader#parseBeanDefinitions,特开辟出一块新地来啃啃这块有意思的骨头 自定义节 ...
- spring IoC源码分析 (3)Resource解析
引自 spring IoC源码分析 (3)Resource解析 定义好了Resource之后,看到XmlFactoryBean的构造函数 public XmlBeanFactory(Resource ...
- Spring源码情操陶冶-ComponentScanBeanDefinitionParser文件扫描解析器
承接前文Spring源码情操陶冶-自定义节点的解析,本文讲述spring通过context:component-scan节点干了什么事 ComponentScanBeanDefinitionParse ...
- 专治不会看源码的毛病--spring源码解析AOP篇
昨天有个大牛说我啰嗦,眼光比较细碎,看不到重点.太他爷爷的有道理了!要说看人品,还是女孩子强一些.原来记得看到一个男孩子的抱怨,说怎么两人刚刚开始在一起,女孩子在心里就已经和他过完了一辈子.哥哥们,不 ...
- 框架源码系列六:Spring源码学习之Spring IOC源码学习
Spring 源码学习过程: 一.搞明白IOC能做什么,是怎么做的 1. 搞明白IOC能做什么? IOC是用为用户创建.管理实例对象的.用户需要实例对象时只需要向IOC容器获取就行了,不用自己去创建 ...
- 结合源码浅谈Spring容器与其子容器Spring MVC 冲突问题
容器是整个Spring 框架的核心思想,用来管理Bean的整个生命周期. 一个项目中引入Spring和SpringMVC这两个框架,Spring是父容器,SpringMVC是其子容器,子容器可以看见父 ...
- 【源码讲解】Spring事务是如何应用到你的业务场景中的?
初衷 日常开发中经常用到@Transaction注解,那你知道它是怎么应用到你的业务代码中的吗?本篇文章将从以下两个方面阐述Spring事务实现原理: 解析并加载事务配置:本质上是解析xml文件将标签 ...
- spring-cloud-square源码速读(spring-cloud-square-okhttp篇)
欢迎访问我的GitHub https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos 内容:所有原创文章分类汇总及配套源码,涉及Java.Docker.Kubernetes.DevOPS ...
随机推荐
- APP跨进程数据通信-访问手机联系人
1. 简述 在实际开发中,常常需要进行不同应用程序之间的数据通信,例如读取联系人列表等等,ContentProvider就是Android提供的用于实现不同进程之间进行数据通信的类. ContentP ...
- Python网络爬虫与信息提取(一)
学习 北京理工大学 嵩天 课程笔记 课程体系结构: 1.Requests框架:自动爬取HTML页面与自动网络请求提交 2.robots.txt:网络爬虫排除标准 3.BeautifulSoup框架:解 ...
- [2017-08-16]ABP系列——QuickStartB:正确理解Abp解决方案的代码组织方式、分层和命名空间
本系列目录:Abp介绍和经验分享-目录 介绍ABP的文章,大多会提到ABP框架吸收了很多最佳实践,比如: 1.N层 (复用一下上篇的图) 展现层(Personball.Demo.Web):asp.ne ...
- 一只菜鸟的瞎J8封装系列的目录
因为这是一个系列...也就是我们所说的依赖关系.后面很多方法都是基于我前面封装的工具来进行的,所以我列一个目录供大家参考... 一只菜鸟的瞎J8封装系列 一.手把手封装数据层之DButil数据库连接 ...
- 中科微北斗定位模组ATGM336H简介
36H系列卫星定位模块 产品介绍 ATGM336H是高灵敏度,支持BDS/GPS/GLONASS卫星导航系统的单系统定位,以及任意组合的多系统联合定位的接收机模块.ATGM336H基于本公司自主独立研 ...
- MongoDB聚合
--------------------MongoDB聚合-------------------- 1.aggregate(): 1.概念: 1.简介 ...
- 【搬运工】——初识Lua(转)
使用 Lua 编写可嵌入式脚本 Lua 提供了高级抽象,却又没失去与硬件的关联. 虽然编译性编程语言和脚本语言各自具有自己独特的优点,但是如果我们使用这两种类型的语言来编写大型的应用程序会是什么样子呢 ...
- Spring Cloud官方文档中文版-服务发现:Eureka服务端
官方文档地址为:http://cloud.spring.io/spring-cloud-static/Dalston.SR3/#spring-cloud-eureka-server 文中例子我做了一些 ...
- Android studio 1.x 安装完毕后无法打开问题解决方案
Android Studio 1.0正式发布,给Android开发者带来了不小的惊喜,再也不用为繁琐的环境配置而烦恼,从某一层面上说这降低了android开发门槛. 不过貌似只能开心一会儿,因为and ...
- Eclipse注释模板设置方法
设置注释模板的入口:Window->Preference->Java->Code Style->Code Template 然后展开Comments节点就是所有需设置注释的元素 ...
