C++进程间通信之共享内存
转载:http://blog.csdn.net/taily_duan/article/details/51692999
转载:http://blog.csdn.net/fengrx/article/details/4069088
转载:http://www.cnblogs.com/xuandi/p/5673917.html
// ServerCom.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.
// #include "stdafx.h" #include <stdio.h>
#include <windows.h>
#pragma endregion
#define MAP_PREFIX L"Local\\"
#define MAP_NAME L"SampleMap"
#define FULL_MAP_NAME MAP_PREFIX MAP_NAME // Max size of the file mapping object.
#define MAP_SIZE 65536 // File offset where the view is to begin.
#define VIEW_OFFSET 0 // The number of bytes of a file mapping to map to the view. All bytes of the
// view must be within the maximum size of the file mapping object (MAP_SIZE).
// If VIEW_SIZE is 0, the mapping extends from the offset (VIEW_OFFSET) to
// the end of the file mapping.
#define VIEW_SIZE 1024 // Unicode string message to be written to the mapped view. Its size in byte
// must be less than the view size (VIEW_SIZE).
#define MESSAGE L"Message from the first process." int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
HANDLE hMapFile = NULL;
PVOID pView = NULL; // Create the file mapping object.
hMapFile = CreateFileMapping(
INVALID_HANDLE_VALUE, // Use paging file - shared memory
NULL, // Default security attributes
PAGE_READWRITE, // Allow read and write access
, // High-order DWORD of file mapping max size
MAP_SIZE, // Low-order DWORD of file mapping max size
FULL_MAP_NAME // Name of the file mapping object
);
if (hMapFile == NULL)
{
wprintf(L"CreateFileMapping failed w/err 0x%08lx\n", GetLastError());
goto Cleanup;
}
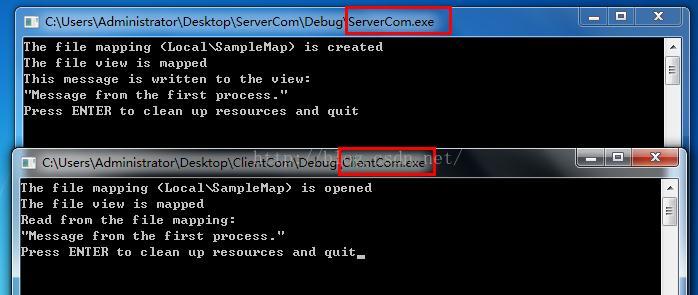
wprintf(L"The file mapping (%s) is created\n", FULL_MAP_NAME); // Map a view of the file mapping into the address space of the current
// process.
pView = MapViewOfFile(
hMapFile, // Handle of the map object
FILE_MAP_ALL_ACCESS, // Read and write access
, // High-order DWORD of the file offset
VIEW_OFFSET, // Low-order DWORD of the file offset
VIEW_SIZE // The number of bytes to map to view
);
if (pView == NULL)
{
wprintf(L"MapViewOfFile failed w/err 0x%08lx\n", GetLastError());
goto Cleanup;
}
wprintf(L"The file view is mapped\n"); // Prepare a message to be written to the view.
PWSTR pszMessage = MESSAGE;
DWORD cbMessage = (wcslen(pszMessage) + ) * sizeof(*pszMessage); // Write the message to the view.
memcpy_s(pView, VIEW_SIZE, pszMessage, cbMessage); wprintf(L"This message is written to the view:\n\"%s\"\n",
pszMessage); // Wait to clean up resources and stop the process.
wprintf(L"Press ENTER to clean up resources and quit");
getchar(); Cleanup: if (hMapFile)
{
if (pView)
{
// Unmap the file view.
UnmapViewOfFile(pView);
pView = NULL;
}
// Close the file mapping object.
CloseHandle(hMapFile);
hMapFile = NULL;
} return ;
}
// ClientCom.cpp : Defines the entry point for the console application.
// #include "stdafx.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include <windows.h>
#pragma endregion
#define MAP_PREFIX L"Local\\"
#define MAP_NAME L"SampleMap"
#define FULL_MAP_NAME MAP_PREFIX MAP_NAME // File offset where the view is to begin.
#define VIEW_OFFSET 0 // The number of bytes of a file mapping to map to the view. All bytes of the
// view must be within the maximum size of the file mapping object. If
// VIEW_SIZE is 0, the mapping extends from the offset (VIEW_OFFSET) to the
// end of the file mapping.
#define VIEW_SIZE 1024 int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
HANDLE hMapFile = NULL;
PVOID pView = NULL; // Try to open the named file mapping identified by the map name.
hMapFile = OpenFileMapping(
FILE_MAP_READ, // Read access
FALSE, // Do not inherit the name
FULL_MAP_NAME // File mapping name
);
if (hMapFile == NULL)
{
wprintf(L"OpenFileMapping failed w/err 0x%08lx\n", GetLastError());
goto Cleanup;
}
wprintf(L"The file mapping (%s) is opened\n", FULL_MAP_NAME); // Map a view of the file mapping into the address space of the current
// process.
pView = MapViewOfFile(
hMapFile, // Handle of the map object
FILE_MAP_READ, // Read access
, // High-order DWORD of the file offset
VIEW_OFFSET, // Low-order DWORD of the file offset
VIEW_SIZE // The number of bytes to map to view
);
if (pView == NULL)
{
wprintf(L"MapViewOfFile failed w/err 0x%08lx\n", GetLastError());
goto Cleanup;
}
wprintf(L"The file view is mapped\n"); // Read and display the content in view.
wprintf(L"Read from the file mapping:\n\"%s\"\n", (PWSTR)pView); // Wait to clean up resources and stop the process.
wprintf(L"Press ENTER to clean up resources and quit");
getchar(); Cleanup: if (hMapFile)
{
if (pView)
{
// Unmap the file view.
UnmapViewOfFile(pView);
pView = NULL;
}
// Close the file mapping object.
CloseHandle(hMapFile);
hMapFile = NULL;
} return ;
}
注:运行的时候先运行写入的进程,再运行读出的进程
C++进程间通信之共享内存的更多相关文章
- 浅析Linux下进程间通信:共享内存
浅析Linux下进程间通信:共享内存 共享内存允许两个或多个进程共享一给定的存储区.因为数据不需要在客户进程和服务器进程之间复制,所以它是最快的一种IPC.使用共享内存要注意的是,多个进程之间对一给定 ...
- Linux环境进程间通信(五): 共享内存(下)
linux下进程间通信的几种主要手段: 管道(Pipe)及有名管道(named pipe):管道可用于具有亲缘关系进程间的通信,有名管道克服了管道没有名字的限制,因此,除具有管道所具有的功能外,它还允 ...
- Linux环境进程间通信(五): 共享内存(上)
linux下进程间通信的几种主要手段: 管道(Pipe)及有名管道(named pipe):管道可用于具有亲缘关系进程间的通信,有名管道克服了管道没有名字的限制,因此,除具有管道所具有的功能外,它还允 ...
- Linux进程IPC浅析[进程间通信SystemV共享内存]
Linux进程IPC浅析[进程间通信SystemV共享内存] 共享内存概念,概述 共享内存的相关函数 共享内存概念,概述: 共享内存区域是被多个进程共享的一部分物理内存 多个进程都可把该共享内存映射到 ...
- Linux进程间通信—使用共享内存
Linux进程间通信-使用共享内存 转自: https://blog.csdn.net/ljianhui/article/details/10253345 下面将讲解进程间通信的另一种方式,使用共享内 ...
- Linux进程间通信——使用共享内存
一.什么是共享内存 顾名思义,共享内存就是允许两个不相关的进程访问同一个逻辑内存.共享内存是在两个正在运行的进程之间共享和传递数据的一种非常有效的方式.不同进程之间共享的内存通常安排为同一段物理内存. ...
- linux进程间通信之共享内存篇
本文是对http://www.cnblogs.com/andtt/articles/2136279.html中共享内存(上)的进一步阐释说说明 1 共享内存的实现原理 共享内存是linux进程间通讯的 ...
- linux内核剖析(十一)进程间通信之-共享内存Shared Memory
共享内存 共享内存是进程间通信中最简单的方式之一. 共享内存是系统出于多个进程之间通讯的考虑,而预留的的一块内存区. 共享内存允许两个或更多进程访问同一块内存,就如同 malloc() 函数向不同进程 ...
- Linux进程间通信——使用共享内存(转)
一.什么是共享内存 顾名思义,共享内存就是允许两个不相关的进程访问同一个逻辑内存.共享内存是在两个正在运行的进程之间共享和传递数据的一种非常有效的方式.不同进程之间共享的内存通常安排为同一段物理内存. ...
- Python进程间通信之共享内存
前一篇博客说了怎样通过命名管道实现进程间通信,但是要在windows是使用命名管道,需要使用python调研windows api,太麻烦,于是想到是不是可以通过共享内存的方式来实现.查了一下,Pyt ...
随机推荐
- 使用Pytorch进行图像分类,AI challenger 农作物病害分类竞赛源码解读
1.首先对给的数据进行划分,类型为每个类单独放在一个文件夹中 import json import shutil import os from glob import glob from tqdm i ...
- linux c语言开发工具
---恢复内容开始--- C语言编译全过程剖析 编译的概念:编译程序读取源程序(字符流),对之进行词法和语法的分析,将高级语言指令转换为功能等效的汇编代码,再由汇编程序转换为机器语言,并且按照操作系统 ...
- UVA 11178 Morley's Theorem(几何)
Morley's Theorem [题目链接]Morley's Theorem [题目类型]几何 &题解: 蓝书P259 简单的几何模拟,但要熟练的应用模板,还有注意模板的适用范围和传参不要传 ...
- python pandas模块,nba数据处理(1)
pandas提供了使我们能够快速便捷地处理结构化数据的大量数据结构和函数.pandas兼具Numpy高性能的数组计算功能以及电子表格和关系型数据(如SQL)灵活的数据处理能力.它提供了复杂精细的索引功 ...
- Python - 1. Built-in Atomic Data Types
From:http://interactivepython.org/courselib/static/pythonds/Introduction/GettingStartedwithData.html ...
- scu 4439 Vertex Cover
题意: 给出n个点,m条边,将若干个点染色,使得每个边至少有一点染色,问至少染多少个点. 思路: 如果是二分图,那就是最小点覆盖,但是这是一般图. 一般图的最小覆盖是npc问题,但是这题有一个条件比较 ...
- 32个使用python代码片段
1.冒泡排序 lis = [56,12,1,8,354,10,100,34,56,7,23,456,234,-58] def sortport(): for i in range(len(lis ...
- centos安装angr
1.angr环境 yum install -y python-dev libffi-dev build-essential virtualenvwrapper mkvirtualenv angr 问题 ...
- 51Nod 2020 排序相减
题目链接:https://www.51nod.com/onlineJudge/questionCode.html#!problemId=2020 思路:排序 水水 #include<iostre ...
- 大数据学习路线:Zookeeper集群管理与选举
大数据技术的学习,逐渐成为很多程序员的必修课,因为趋势也是因为自己的职业生涯.在各个技术社区分享交流成为很多人学习的方式,今天很荣幸给我们分享一些大数据基础知识,大家可以一起学习! 1.集群机器监控 ...
