linux内核的双链表list_head、散列表hlist_head
一、双链表list_head
1、基本概念
linux内核提供的标准链表可用于将任何类型的数据结构彼此链接起来。
不是数据内嵌到链表中,而是把链表内嵌到数据对象中。
即:加入链表的数据结构必须包含一个类型为list_head的成员,其中包含了正向和反向指针。
struct list_head {
struct list_head *next, *prev;
};
由此可见,内核的链表具备双链表功能,实际上,通常它都组织成双循环链表。
该成员可以如下放置到数据结构中:
struct task_struct{
...
struct list_head run_list;
...
};
链表的起点同样是list_head的实例,如果作为数据成员,则struct list_head被称作链表元素;若用于链表起点,则被称作表头。
标准双链表如下:
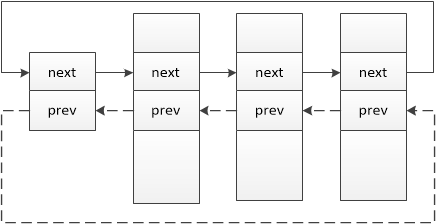
2、 链表操作函数(linux/list.h)
(1)声明和初始化
通常用LIST_HEAD(list_name)宏来声明并初始化:
#define LIST_HEAD_INIT(name) { &(name), &(name) }
#define LIST_HEAD(name) \
struct list_head name = LIST_HEAD_INIT(name)
它的next、prev指针都初始化为指向自己,这样就有了一个空链表。
除了用LIST_HEAD()宏在声明的时候初始化一个链表以外,Linux还提供了一个INIT_LIST_HEAD宏用于运行时初始化链表:
static inline void INIT_LIST_HEAD(struct list_head *list)
{
list->next = list;
list->prev = list;
}
(2)插入
对链表的插入操作有两种:
在表头插入:
static inline void __list_add(struct list_head *new,
struct list_head *prev,
struct list_head *next)
{//在两个连续的链表项之间添加一个新项,适用于已知前后两个链表项的情况
next->prev = new;
new->next = next;
new->prev = prev;
prev->next = new;
} /**
* list_add - add a new entry
* @new: new entry to be added
* @head: list head to add it after
*
* Insert a new entry after the specified head.
* This is good for implementing stacks.
*/
static inline void list_add(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head)
{//添加节点到head后。若把最后一个节点当head,则实现了一个栈
__list_add(new, head, head->next);
}
在表尾插入:
/**
* list_add_tail - add a new entry
* @new: new entry to be added
* @head: list head to add it before
*
* Insert a new entry before the specified head.
* This is useful for implementing queues.
*/
static inline void list_add_tail(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head)
{//添加到head前,即尾部。把第一个元素当head,则实现了一个队列
__list_add(new, head->prev, head);
}
(3)删除
/*
* Delete a list entry by making the prev/next entries
* point to each other.
*
* This is only for internal list manipulation where we know
* the prev/next entries already!
*/
static inline void __list_del(struct list_head * prev, struct list_head * next)
{//链表项指向彼此
next->prev = prev;
prev->next = next;
} /**
* list_del - deletes entry from list.
* @entry: the element to delete from the list.
* Note: list_empty() on entry does not return true after this, the entry is
* in an undefined state.
*/
static inline void __list_del_entry(struct list_head *entry)
{
__list_del(entry->prev, entry->next);
} static inline void list_del(struct list_head *entry)
{//删除节点(仅将其从链表中移走,而不会释放entry或释放包含entry的数据结构
__list_del(entry->prev, entry->next);
entry->next = LIST_POISON1;//用于调试,以便在内存中检测已经删除的链表元素
entry->prev = LIST_POISON2;
}
(4)合并
static inline void __list_splice(const struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *prev,
struct list_head *next)
{
struct list_head *first = list->next;
struct list_head *last = list->prev; first->prev = prev;
prev->next = first; last->next = next;
next->prev = last;
} /**
* list_splice - join two lists, this is designed for stacks
* @list: the new list to add.
* @head: the place to add it in the first list.
*/
static inline void list_splice(const struct list_head *list,
struct list_head *head)
{//list指向链表插入到指定链表head后
if (!list_empty(list))
__list_splice(list, head, head->next);
}
(5)遍历
/**
* list_for_each_entry - iterate over list of given type
* @pos: the type * to use as a loop cursor.
* @head: the head for your list.
* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.
pos是一个指向包含list_head节点对象的指针,可看做list_entry的返回值
head是一个指向头结点的指针,即开始遍历位置
member是实际数据结构内部list_head实例的名称
*/
#define list_for_each_entry(pos, head, member) \
for (pos = list_entry((head)->next, typeof(*pos), member); \
&pos->member != (head); \
pos = list_entry(pos->member.next, typeof(*pos), member))
a.举例
遍历与一个超级块(struct super_block)相关联的所有文件(通过struct file表示),这些file实例包含在一个双链表中,表头位于超级块实例中:
struct super_block *sb = get_some_sb();
struct file *f;
list_for_each_entry(f, &sb->s_files, f_list){
/*用于处理f中成员的代码*/
}
super_block->s_files用作链表起始点,其中存储了file类型的链表项,file->f_list用作链表元素,用于建立各链表项之间的关联:
struct file{
...
struct list_head f_list;
...
}
struct super_block {
...
struct list_head s_files;
...
}
b.讲解
链表元素遍历分为两个阶段:查找下一项list_head实例。这与链表中保存的具体数据结构无关。内核通过反引用当前链表元素的next成员,就可以找到下一个链表元素位置;查找链表元素的容器对象实例(链表的实现基于容器机制,用于将对象嵌入到其他对象中,如果结构A包含一个子结构B,则A称为B的一个容器)。其中包含了有用数据,通过list_entry宏查找。
/**
* list_entry - get the struct for this entry
* @ptr: the &struct list_head pointer.
* @type: the type of the struct this is embedded in.
* @member: the name of the list_struct within the struct.
ptr指向链表元素指针
type制定了容器对象类型(上例struct file)
member定义了容器的哪个元素表示当前链表的链表元素(上例是f_list,因为链表元素由file->f_list表示)
*/
#define list_entry(ptr, type, member) \
container_of(ptr, type, member)
其中:
#define offsetof(TYPE, MEMBER) ((size_t) &((TYPE *)0)->MEMBER)
/**
* container_of - cast a member of a structure out to the containing structure
* @ptr: the pointer to the member.
* @type: the type of the container struct this is embedded in.
* @member: the name of the member within the struct.
*
从结构成员来获得包含成员的结构类型
ptr指向成员数据的指针
type所嵌入到容器结构的类型
member成员在结构内的名称
*/
#define container_of(ptr, type, member) ({ \
const typeof( ((type *))->member ) *__mptr = (ptr); \
(type *)( (char *)__mptr - offsetof(type,member) );})
在本例中,将offset宏展开:
(size_t) &((struct file *)0)->f_list
通过空指针将0转换为一个指向struct file的指针,然后执行的->和&获得的地址,计算出了f_list成员相对于struct file实例的偏移量。
将上例展开:
const (struct list_head*) __mptr = (ptr);
(struct file *)((char *)__mptr - offset);
ptr指向容器元素中的list_head实例。内核首先创建一个指针__mptr,其值与ptr相同,指向所要求的目标数据类型struct list_head。接下来,使用此前计算的偏移量来移动__mptr,使之不再指向链表元素,而是指向容器对象实例。为确保指针运算是按字节执行,先将__mptr转换为char *指针。但在计算完成后的赋值操作中,又转换回原来的数据类型。
二、散列表hlist_head
1、基本定义
散列表(Hash table,也叫哈希表),是根据关键码值(Key value)而直接进行访问的数据结构。也就是说,它通过把关键码值映射到表中一个位置来访问记录,以加快查找的速度。这个映射函数叫做散列函数,存放记录的数组叫做散列表。
struct hlist_head{
struct hlist_node *first;
}
struct hlist_node {
struct hlist_node *next,**pprev;
}
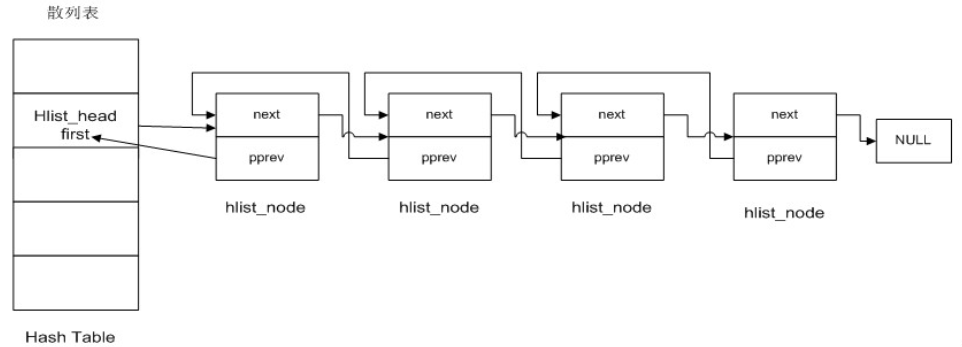
(1)hlist_head表示哈希表的头结点。哈希表中每一个entry(list_entry)所对应的都是一个链表(hlist)。hlist_head结构体只有一个域,即first,first指针指向该hlist链表的第一个结点。
(2)hlist_node结构体有两个域,next和pprev:
a.next指向下个hlist_node结点,倘若该结点是链表的最后一个节点,next则指向NULL
b.pprev是一个二级指针,它指向前一个节点的next指针。
2、解说
(1)Linux 中的hlist(哈希表)和list是不相同的,在list中每个结点都是一样的,不管头结点还是其它结点,使用同一个结构体表示,但是在hlist中,头结点使用的是struct hlist_head来表示的,而对于其它结点使用的是strcuct hlist_node这个数据结构来表示的。还有list是双向循环链表,而hlist不是双向循环链表,因为hlist头结点中没有prev变量。为什么要这样设计呢?
--因为哈希散列表在内核中使用的非常多,这样的头节点定义能使包含hlist_head的结构稍微变小一点,节省一半的内存空间。
(2)hlist的结点有两个指针,但是pprev是指针的指针,它指向的是前一个结点的next指针,为什么要采用pprev,而不采用一级指针?
--由于hlist不是一个完整的循环链表,在list中,表头和结点是同一个数据结构,直接用prev是ok的。在hlist中,表头中没有prev,只有一个first。
1>为了能统一地修改表头的first指针,即表头的first指针必须修改指向新插入的结点,hlist就设计了pprev。hlist结点的pprev不再是指向前一个结点的指针,而是指向前一个节点(可能是表头)中的next(对于表头则是first)指针,从而在表头插入的操作中可以通过一致的node->pprev访问和修改前结点的next(或first)指针。
2>还解决了数据结构不一致,hlist_node巧妙的将pprev指向上一个节点的next指针的地址,由于hlist_head和hlist_node指向的下一个节点的指针类型相同,就解决了通用性。
(3)内核采用的解决哈希冲突的方法是:拉链法
--拉链法解决冲突的做法是:将所有关键字为同义词的结点链接在同一个链表中。若选定的散列表长度为m,则可将散列表定义为一个由m个头指针(struct hlist_head name)组成的指针数组T[0..m-1]。凡是散列地址为i的结点,均插入到以T[i]为头指针的链表中。T中各分量的初值均应为空指针。在拉链法中,装填因子α(装填的元素个数/数组长度)可以大于 1,但一般均取α≤1。当然,用拉链法解决hash冲突也是有缺点的,指针需要额外的空间。
(红黑树、基数树这种用到再说吧....)
参考:
《深入linux内核架构》
https://blog.csdn.net/tigerjibo/article/details/8450995
linux内核的双链表list_head、散列表hlist_head的更多相关文章
- linux内核数据结构之链表
linux内核数据结构之链表 1.前言 最近写代码需用到链表结构,正好公共库有关于链表的.第一眼看时,觉得有点新鲜,和我之前见到的链表结构不一样,只有前驱和后继指针,而没有数据域.后来看代码注释发现该 ...
- linux内核数据结构之链表【转】
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/Anker/p/3475643.html 1.前言 最近写代码需用到链表结构,正好公共库有关于链表的.第一眼看时,觉得有点新鲜,和我之前见到的链表结 ...
- 拒绝造轮子!如何移植并使用Linux内核的通用链表(附完整代码实现)
在实际的工作中,我们可能会经常使用链表结构来存储数据,特别是嵌入式开发,经常会使用linux内核最经典的双向链表 list_head.本篇文章详细介绍了Linux内核的通用链表是如何实现的,对于经常使 ...
- linux内核中的链表
1.内核中的链表 linux内核链表与众不同,他不是把将数据结构塞入链表,而是将链表节点塞入数据,在2.1内核中引入了官方链表,从此内核中所有的链表使用都采用此链表,千万不要在重复造车轮子了!链表实现 ...
- pta L2-002 链表去重 +散列表知识小普及+二进制取反补码运算
题目链接:https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/994805046380707840/problems/994805072641245184: 废话:今天忙着学习新知识了,没怎 ...
- 学习/linux/list.h_双链表实现
linux-3.5/include/linux/list.h 使用只含指针域的双向循环链表进行链表的操作. 下面是我选取部分list.h中代码: #ifndef _LINUX_LIST_H #defi ...
- Linux内核之旅 链表实现
#include "stdio.h" #include "stdlib.h" struct list_head{ struct list_head *prev; ...
- Linux内核之数据双链表
导读 Linux 内核中自己实现了双向链表,可以在 include/linux/list.h 找到定义.我们将会首先从双向链表数据结构开始介绍内核里的数据结构.为什么?因为它在内核里使用的很广泛,你只 ...
- linux内核之链表操作解析
本文只是对linux内核中的链表进行分析.内核版本是linux-2.6.32.63.文件在:linux内核/linux-2.6.32.63/include/linux/list.h.本文对list.h ...
随机推荐
- 报错解决——pytesseract.pytesseract.TesseractError: (1,’Error opening data file /usr/local/share/tessdata/eng.traineddata’)
解决方法:(原文地址http://stackoverflow.com/questions/14800730/tesseract-running-error) $ wget https://tesser ...
- 打开Delphi 10.1 berlin提示脚本错误的解决方法
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Embarcadero\BDS\18.0\Known IDE Packages $(BDS)\Bin\CommunityToolbar240.bp ...
- python线程中的join(转)
Python多线程与多进程中join()方法的效果是相同的. 下面仅以多线程为例: 首先需要明确几个概念: 知识点一:当一个进程启动之后,会默认产生一个主线程,因为线程是程序执行流的最小单元,当设置多 ...
- 算法 -- 四种方法获取的最长“回文串”,并对时间复杂进行分析对比&PHP
https://blog.csdn.net/hongyuancao/article/details/82962382 “回文串”是一个正读和反读都一样的字符串,比如“level”或者“noon”等等就 ...
- Linux用户群组权限恢复
/etc/passwd:该文件用于存放用户详细信息:例如 root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash 用户id 0:就表示root用户 bin下的bash:表示可以登入操作系统 s ...
- Linux下fork机制详解(以PHP为例)
考:https://blog.csdn.net/jason314/article/details/5640969 1.fork简介 一个进程,包括代码.数据和分配给进程的资源.fork()函数通过系统 ...
- JS通过类名判断是否都必填
//判断class='required' 是否都必填 function required() { var flag = true; $(".required").each(func ...
- 使用VS2013自带的PreEmptive Dotfuscator and Analytis来混淆C#代码
1. 使用VS2013编译你要打包的程序,会在文件夹中的 ..\bin\Release中 2. 点击VS2013中的TOOLS -> PreEmptive Dotfuscator and Ana ...
- python threading acquire release
线程同步 //test.py import threading import time exitFlag = 0 class myThread (threading.Thread): def __in ...
- cocos2d-x JS 富文本(为一段文本中的个别字体上颜色)
setWinText : function (levelStr1,levelStr2,levelStr3,color1,color2) { var imgRankingBG = this.contai ...
