JAVA定时任务Timer
故事起因
因业务需要,写了一个定时任务Timer,任务将在每天的凌晨2点执行,代码顺利码完,一切就绪,开始测试。运行程序,为了节省时间,将系统时间调整为第二天凌晨1点59分,看着秒针滴答滴答的转动,期盼着到2点时程序能正确运行,正暗暗欣喜之时,时间滑过2点,但是程序没有任何反应,啊哦,难道是我程序写错了。悲剧。
二次测试
首先检查自己写的程序没有什么问题。再次测试,先将时间调整为1点59分,打上断点,再运行程序,2点到来,程序运行到断点处,一步一步往下走,一切正常。为何,刚刚不是还是不能运行吗。又重复测试了几次,发现一个规律,先调整好时间后再运行程序一切正常,但是先运行程序再调整时间就什么没有任何反应。没办法了,只能研究一下JDK的Timer源码,看看内部有什么玄机。
了解内幕
我们先看看类的关系,见下图:
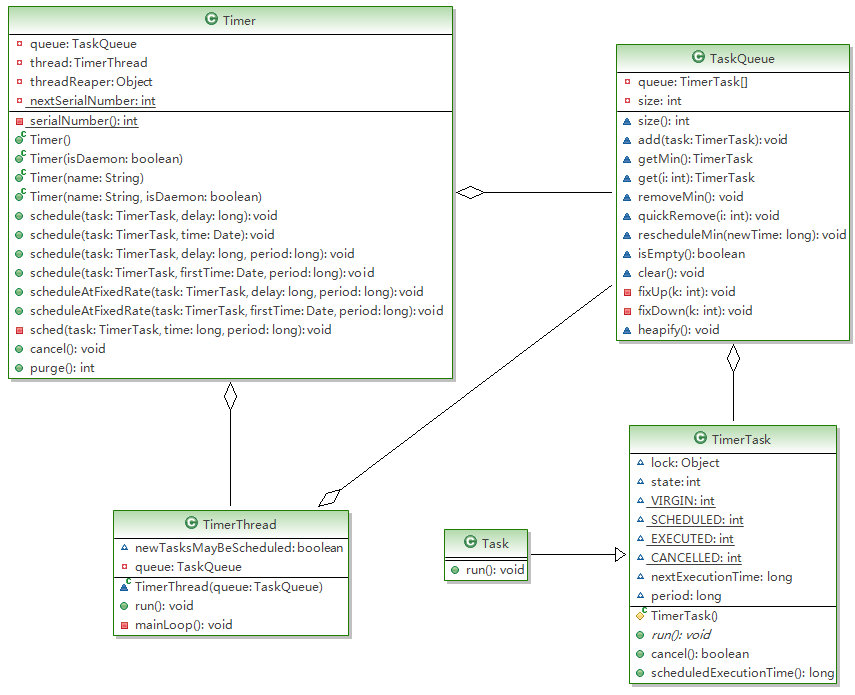
图1
其中Task是我自己写的任务类,这个类需要继承TimerTask,并且实现run()抽象方法,需要将任务执行的相关代码写在run方法中。
public class Task extends TimerTask {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("do task...");
}
}
执行任务的方法如下:
public class TimerManager {
public TimerManager() {
……
Timer timer = new Timer();
Task task = new Task();
// 安排指定的任务在指定的时间开始进行重复的固定延迟执行。
timer.schedule(task, date, ConfigData.getDeltaTime() * 1000);
}
}
在执行任务的时候,我们只跟Timer打交道,所以先来了解一下Timer.
Timer的构造函数如下,又调用了自己的另一个构造函数 :
public Timer() {
this("Timer-" + serialNumber());
}
public Timer(String name) {
thread.setName(name);
thread.start();
}
到了这一步,我们需要了解thread是个什么玩意儿,我们来看看他的定义:
private TimerThread thread = new TimerThread(queue);
此时我们需要了解的对象成了TimerThread了,顺藤摸瓜,接着往下看吧:
class TimerThread extends Thread {
boolean newTasksMayBeScheduled = true;
private TaskQueue queue;
TimerThread(TaskQueue queue) {
this.queue = queue;
}
public void run() {
try {
mainLoop();
} finally {
// Someone killed this Thread, behave as if Timer cancelled
synchronized(queue) {
newTasksMayBeScheduled = false;
queue.clear(); // Eliminate obsolete references
}
}
}
/**
* The main timer loop. (See class comment.)
*/
private void mainLoop() {
while (true) {
try {
TimerTask task;
boolean taskFired;
synchronized(queue) {
// Wait for queue to become non-empty
while (queue.isEmpty() && newTasksMayBeScheduled)
queue.wait();
if (queue.isEmpty())
break; // Queue is empty and will forever remain; die
// Queue nonempty; look at first evt and do the right thing
long currentTime, executionTime;
task = queue.getMin();
synchronized(task.lock) {
if (task.state == TimerTask.CANCELLED) {
queue.removeMin();
continue; // No action required, poll queue again
}
currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
executionTime = task.nextExecutionTime;
if (taskFired = (executionTime<=currentTime)) {
if (task.period == 0) { // Non-repeating, remove
queue.removeMin();
task.state = TimerTask.EXECUTED;
} else { // Repeating task, reschedule
queue.rescheduleMin(
task.period<0 ? currentTime - task.period
: executionTime + task.period);
}
}
}
if (!taskFired) // Task hasn't yet fired; wait
queue.wait(executionTime - currentTime);
}
if (taskFired) // Task fired; run it, holding no locks
task.run();
} catch(InterruptedException e) {
}
}
}
}
我们可以看到TimerThread主要就是mianLoop()方法,在mainLoop方法中有这么两行代码:
while (queue.isEmpty() && newTasksMayBeScheduled)
queue.wait();
当我们 new Timer(),然后两次调用Timer()的构造函数,并调用thread.start()时,就到了mainLoop方法的这两行代码了,此时的queue.isEmpty()为true,所以线程就wait在这个地方了。什么时候将他notify呢?我们接着往下看我们自己的代码,new Timer(),new Task()之后就到了下面的这行代码了:
timer.schedule(task, date, ConfigData.getDeltaTime() * 1000);
继续摸索一下timer.schedule()是怎么工作的:
public void schedule(TimerTask task, Date firstTime, long period) {
if (period <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Non-positive period.");
sched(task, firstTime.getTime(), -period);
}
private void sched(TimerTask task, long time, long period) {
if (time < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal execution time.");
synchronized(queue) {
if (!thread.newTasksMayBeScheduled)
throw new IllegalStateException("Timer already cancelled.");
synchronized(task.lock) {
if (task.state != TimerTask.VIRGIN)
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Task already scheduled or cancelled");
task.nextExecutionTime = time;
task.period = period;
task.state = TimerTask.SCHEDULED;
}
queue.add(task);
if (queue.getMin() == task)
queue.notify();
}
}
当我们跟踪到方法sched时可以看到,这方法中设置了任务的下一次执行时间为传入的时间task.nextExecutionTime = time,然后把添加任务到队列中并notify队列。
到了这里我们要回到之前的wait位置了:
while (queue.isEmpty() && newTasksMayBeScheduled)
queue.wait();
现在queue.isEmpty()为false了,得继续往下运行,
currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
executionTime = task.nextExecutionTime;
if (taskFired = (executionTime<=currentTime))
程序取得当前的时间和任务下一次执行的时间,比较如果执行的时间还未到则任务执行为false,即taskFired=false。
if (!taskFired) // Task hasn't yet fired; wait
queue.wait(executionTime - currentTime);
所以程序为进入wait状态,要wait多久呢?时间为executionTime – currentTime
而如果当前执行程序的时间在任务执行的时间之后了,则任务执行为true,即taskFired=true。
if (taskFired) // Task fired; run it, holding no locks
task.run();
任务立即会被执行。
豁然开朗
到这里我们就清楚了为什么之前的测试是那样一个现象,当我们先运行程序再将时间调整为1点59分后,程序一直处于queue.wait(executionTime - currentTime)状态,需要wait的时间为executionTime – currentTime,所以刚过2点时程序是不会马上运行的,必须要等待 executionTime – currentTime的时间后才能执行任务。
JAVA定时任务Timer的更多相关文章
- Java定时任务Timer、TimerTask与ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor详解
定时任务就是在指定时间执行程序,或周期性执行计划任务.Java中实现定时任务的方法有很多,本文从从JDK自带的一些方法来实现定时任务的需求. 一.Timer和TimerTask Timer和Tim ...
- 详解java定时任务---Timer篇
一.简介 在java的jdk中提供了Timer.TimerTask两个类来做定时任务. Timer是一种定时器工具,用来在一个后台线程计划执行指定任务,而TimerTask一个抽象类,它的子 ...
- java定时任务Timer与ScheduledExecutorService<转>
在我们编程过程中如果需要执行一些简单的定时任务,无须做复杂的控制,我们可以考虑使用JDK中的Timer定时任务来实现.下面LZ就其原理.实例以及Timer缺陷三个方面来解析java Timer定时器. ...
- java定时任务Timer/scheduleAtFixedRate
Timer类是用来执行任务的类,定时器 scheduleAtFixedRate模式可以用,在这个模式下,Timer会尽量的让任务在一个固定的频率下运行. 参考:http://swiftlet.net/ ...
- Java基础--定时任务Timer
Java基础--定时任务Timer 一.Timer介绍 java.util.Timer java.util.TimerTask Timer是一个定时器类,通过该类可以为指定的定时任务进行配置.Time ...
- Java 中Timer和TimerTask 定时器和定时任务使用的例子
转自:http://blog.csdn.net/kalision/article/details/7692796 这两个类使用起来非常方便,可以完成我们对定时器的绝大多数需求 Timer类是用来执行任 ...
- Java基础--定时任务Timer(转载)
Java基础--定时任务Timer 一.Timer介绍 java.util.Timer java.util.TimerTask Timer是一个定时器类,通过该类可以为指定的定时任务进行配置.Time ...
- Java之旅--定时任务(Timer、Quartz、Spring、LinuxCron)
在Java中,实现定时任务有多种方式,本文介绍4种,Timer和TimerTask.Spring.QuartZ.Linux Cron. 以上4种实现定时任务的方式,Timer是最简单的,不需要任何框架 ...
- Java定时任务:利用java Timer类实现定时执行任务的功能
一.概述 在java中实现定时执行任务的功能,主要用到两个类,Timer和TimerTask类.其中Timer是用来在一个后台线程按指定的计划来执行指定的任务. TimerTask一个抽象类,它的子类 ...
随机推荐
- IO 流之字节流和转换流
基本读取操作: InputStream(); OutputStream(); // 直接写入目的地中, 不需要 flush() 刷新 write(byte[] b); // 参数为 byte 数组 字 ...
- FastReports_4.14.1 _Cliff手动安装
首次编译frx15.dproj包的时候,会出错: [DCC Fatal Error] fs15.dpk(59): F1026 File not found: 'fs_ipascal.dcu'原因是因为 ...
- 对protected函数的简单理解 good
对于protected提供的函数和属性,除非想扩充这个类的功能,否则是完全用不到的.外部函数main()永远只能调用public的那些函数.所以从拖拉控件编程的角度来讲,只需要学习public的函数和 ...
- sklearn.svm包中的SVC(kernel=”linear“)和LinearSVC的区别
参考:https://stackoverflow.com/questions/45384185/what-is-the-difference-between-linearsvc-and-svckern ...
- delphi 模拟POST提交数据
unit GetHttpInfo; interface uses Classes, WinINet, Sysutils, windows, IDURI, IdSSLOpenSSL , IdBaseCo ...
- JavaScript数据类型转换汇总
ECMAScirpt中的数据类型:undefined.Null.Boolean.Number.String.Object 对一个值使用typeof操作符可能返回下列某个字符串: number(数字). ...
- 洛谷 P2467 [SDOI2010]地精部落
洛谷 我讲的应该没有这个[https://www.luogu.org/blog/user55639/solution-p2467]清楚. 贴个代码算了: #include <bits/stdc+ ...
- BZOJ2648: SJY摆棋子&&2716: [Violet 3]天使玩偶
BZOJ2648: SJY摆棋子 BZOJ2716: [Violet 3]天使玩偶 BZOJ氪金无极限... 其实这两道是同一题. 附上2648的题面: Description 这天,SJY显得无聊. ...
- 自动更新SVN项目
@echo off@echo =================================@echo 定时在SVN上自动更新项目内容,可用于项目放在web服务器没有hudson的时候@echo ...
- 我的Android进阶之旅------>Android Activity的singleTask加载模式和onActivityResult方法之间的冲突
今天调试一个bug的时候,情景如下: 一个Activity A,需要用startActivityForResult方法开启Activity B.Activity B的launch mode被设置为si ...
