推荐 的FPGA设计经验(2)-时钟策略优化
Optimizing Clocking Schemes
Avoid using internally generated clocks (other than PLLs) wherever possible because they can cause functional and timing problems in the design.
Use clock setting assignments on any derived or internal clocks to specify their relationship to the base clock.
Use global device-wide, low-skew dedicated routing for all internally-generated clocks, instead of
routing clocks on regular routing lines.
Avoid data transfers between different clocks wherever possible. If you require a data transfer between different clocks, use FIFO circuitry.
You can use the clock uncertainty features in the Quartus Prime software to compensate for the variable delays between clock domains. Consider setting a clock setup uncertainty and clock hold uncertainty value of 10% to 15% of the clock delay.
Register Combinational Logic Outputs
If you use the output from combinational logic as a clock signal or as an asynchronous reset signal, you can expect to see glitches in your design. In a synchronous design, glitches on data inputs of registers are normal events that have no consequences. However, a glitch or a spike on the clock input (or an asynchronous input) to a register can have significant consequences.
To avoid these problems, you should always register the output of combinational logic before you use it as a clock signal.

Avoid Asyncrhonous Clock Division
Using dedicated PLL circuitry can help you to avoid many of the problems that can be introduced by asynchronous clock division logic.
When you must use logic to divide a master clock, always use synchronous counters or state machines. Additionally, create your design so that registers always directly generate divided clock signals, and route the clock on global clock resources. To avoid glitches, do not decode the outputs of a counter or a state machine to generate clock signals.
Avoid Ripple Counters
Ripple counters use cascaded registers, in which the output pin of one register feeds the clock pin of the register in the next stage. This cascading can cause problems because the counter creates a ripple clock at each stage. These ripple clocks must be handled properly during timing analysis, which can be difficult and may require you to make complicated timing assignments in your synthesis and placement and routing tools.
Use Multiplexed Clocks
Use clock multiplexing to operate the same logic function with different clock sources. In these designs, multiplexing selects a clock source.
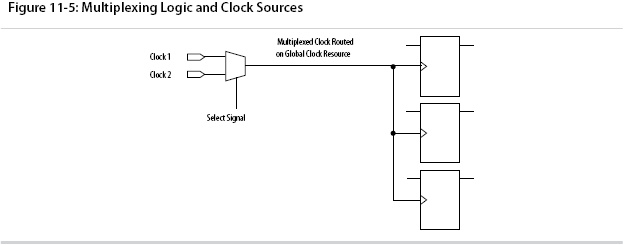
Adding multiplexing logic to the clock signal can create the problems addressed in the previous sections, but requirements for multiplexed clocks vary widely, depending on the application. Clock multiplexing is acceptable when the clock signal uses global clock routing resources and if the following criteria are met:
• The clock multiplexing logic does not change after initial configuration
• The design uses multiplexing logic to select a clock for testing purposes
• Registers are always reset when the clock switches
• A temporarily incorrect response following clock switching has no negative consequences
Use Gated Clocks
Gated clocks turn a clock signal on and off using an enable signal that controls gating circuitry.
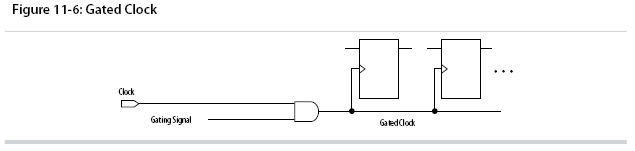
You can use gated clocks to reduce power consumption in some device architectures by effectively shutting down portions of a digital circuit when they are not in use. When a clock is gated, both the clock network and the registers driven by it stop toggling, thereby eliminating their contributions to power consumption. However, gated clocks are not part of a synchronous scheme and therefore can significantly increase the effort required for design implementation and verification. Gated clocks contribute to clock skew and make device migration difficult. These clocks are also sensitive to glitches, which can cause design failure.
Use dedicated hardware to perform clock gating rather than an AND or OR gate.
From a functional point of view, you can shut down a clock domain in a purely synchronous manner using a synchronous clock enable signal.
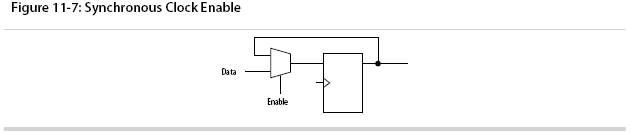
Use Synchronous Clock Enables
To turn off a clock domain in a synchronous manner, use a synchronous clock enable signal. FPGAs efficiently support clock enable signals because there is a dedicated clock enable signal available on all device registers.
This scheme does not reduce power consumption as much as gating the clock at the source because the clock network keeps toggling, and performs the same function as a gated clock by disabling a set of registers. Insert a multiplexer in front of the data input of every register to either load new data, or copy the output of the register.
Recommended Clock-Gating Methods
Use gated clocks only when your target application requires power reduction and when gated clocks are able to provide the required reduction in your device architecture.
If you must use clocks gated by logic, implement these clocks using the robust clock-gating technique and ensure that the gated clock signal uses dedicated global clock routing.
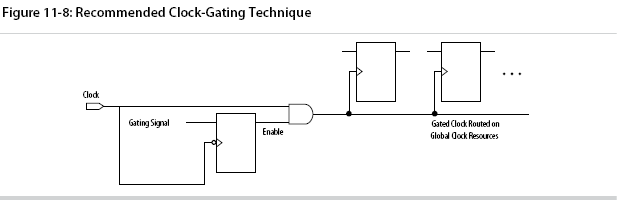
The register that generates the enable signal is triggered on the inactive edge of the clock to be gated. Use the falling edge when gating a clock that is active on the rising edge. Using this technique, only one input of the gate that turns the clock on and off changes at a time. This prevents glitches or spikes on the output.
推荐 的FPGA设计经验(2)-时钟策略优化的更多相关文章
- 推荐 的FPGA设计经验(4) 时钟和寄存器控制架构特性使用
Use Clock and Register-Control Architectural Features FPGAs provide device-wide clocks and register ...
- 推荐 的FPGA设计经验(3) 物理实现和时间闭环优化
Optimizing Physical Implementation and Timing Closure Planning Physical Implementation When planning ...
- 推荐 的FPGA设计经验(1)组合逻辑优化
主要内容摘自Quartus prime Recommended Design Practices For optimal performance, reliability, and faster ti ...
- 【转载】如何在FPGA设计环境中添加加时序约束
转自:http://bbs.ednchina.com/BLOG_ARTICLE_198929.HTM 如何在FPGA设计环境中加时序约束 在给FPGA做逻辑综合和布局布线时,需要在工具中设定时序 ...
- FPGA异步时钟设计中的同步策略
1 引言 基于FPGA的数字系统设计中大都推荐采用同步时序的设计,也就是单时钟系统.但是实际的工程中,纯粹单时钟系统设计的情况很少,特别是设计模块与外围芯片的通信中,跨时钟域的情况经常不可避免. ...
- 影响FPGA设计中时钟因素的探讨。。。转
http://www.fpga.com.cn/advance/skill/speed.htm http://www.fpga.com.cn/advance/skill/design_skill3.ht ...
- FPGA分频与倍频的简单总结(涉及自己设计,调用时钟IP核,调用MMCM原语模块)
原理介绍 1.分频 FPGA设计中时钟分频是重要的基础知识,对于分频通常是利用计数器来实现想要的时钟频率,由此可知分频后的频率周期更大.一般而言实现偶数系数的分频在程序设计上较为容易,而奇数分频则相对 ...
- FPGA设计思想与技巧(转载)
题记:这个笔记不是特权同学自己整理的,特权同学只是对这个笔记做了一下完善,也忘了是从那DOWNLOAD来的,首先对整理者表示感谢.这些知识点确实都很实用,这些设计思想或者也可以说是经验吧,是很值得每一 ...
- 【设计经验】2、ISE中ChipScope使用教程
一.软件与硬件平台 软件平台: 操作系统:Windows 8.1 开发套件:ISE14.7 硬件平台: FPGA型号:XC6SLX45-CSG324 二.ChipScope介绍 ChipScope是X ...
随机推荐
- WSDM 2014推荐系统论文
Xiao Yu, Hao Ma, Paul Hsu, Jiawei Han On Building Entity Recommender Systems Using User Click Log an ...
- python UI自动化实战记录七:页面2用例编写
使用python自带的unittest测试框架,用例继承自unittest.TestCase类. 1 引入接口类和页面类 2 setUp函数中打开页面,定义接口对象 3 tearDown函数中关闭页面 ...
- CSAPP Bomb Lab记录
记录关于CSAPP 二进制炸弹实验过程 (CSAPP配套教学网站Bomb Lab自学版本,实验地址:http://csapp.cs.cmu.edu/2e/labs.html) (个人体验:对x86汇编 ...
- JPA注解实现联合主键
当表中一个主键不能唯一标识一条记录的时候,就需要使用联合主键了,下面是使用JPA注解实现联合主键的代码 1 首先需要建立一个复合主键类,用来存放需要生产联合主键的属性,该类需要实现序列化. packa ...
- swift的clourse:字面量化的函数、将函数字面量化-与函数的类型签名相同
1.clourse的签名与函数的签名相同: 所以两者可以相互赋值: 2.可以将函数(表达式)字面量化: 因为可以字面量化,所以和其它的值(变量)没有任何区别,可以存在变量存在的任何地方: 3.clou ...
- 汇编试验四:[bx] 和 loop 的使用
预备知识: 段前缀的使用: ffff:0~ffff:b 和 0020:0~0020:b 的数据: 一次循环的复制效果: 但是,这种方式DS的数据得修改: Source Code: assume cs: ...
- MySQL数据库------常用函数
一.数学函数 数学函数主要用于处理数字,包括整型.浮点数等. [1]ABS(x) 返回x的绝对值 例子:SELECT ABS(-1) -- 返回1 [2]CEIL(x),CEILING( ...
- cmd进入指定的文件夹
怎么利用cmd进入指定的文件夹呢? 1:win+r ——cmd 2:进入要到达的盘符 (比如我要进入d盘) 3:然后通过 cd d:\project 进入指定的文件夹
- 【题解】洛谷P4391 [BOI2009] Radio Transmission(KMP)
洛谷P4391:https://www.luogu.org/problemnew/show/P4391 思路 对于给定的字符串 运用KMP思想 设P[x]为前x个字符前缀和后缀相同的最长长度 则对于题 ...
- Java 分支结构
Java 分支结构 - if...else/switch 顺序结构只能顺序执行,不能进行判断和选择,因此需要分支结构. Java 有两种分支结构: if 语句 switch 语句 if 语句 一个 i ...
