Java_Day8
Java learning_Day8
本人学习视频用的是马士兵的,也在这里献上
<链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1qKNGJNh0GgvlJnitTJGqgA>
提取码:fobs
内容
- 容器
- 泛型
容器
Java API 所提供的一系列类的实例,用于在程序中存放对象。
容器 API
- JDK 所提供的容器 API 位于 java.util 包内。
- 容器 API 的类图结构如下图所示:
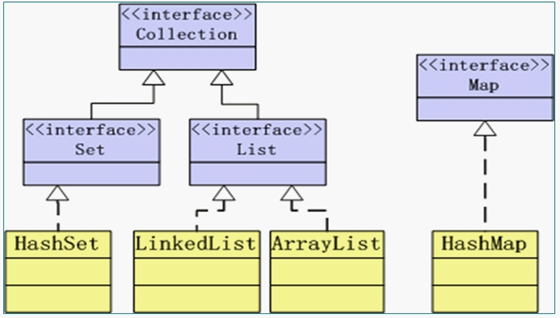
- Collection 接口:定义了存取一组对象的方法,其子接口 Set 和 List 分别定义了存储方式。
- Set 中的数据对象没有顺序且不可以重复。
- List 中的数据对象有顺序且可以重复。
- Map 接口定义了存储“键(key)—— 值(value)映射对”的方法。
Collection
Collection接口所定义的方法:

Collection 方法举例
- 容器类对象在调用 remove、contains 等方法时需要比较对象是否相等,这回涉及到对象类型的 equals 方法和 hashCode 方法;对于自定义的类型,需要重写 equals 和 hashCode 方法以实现自定义的对象相等规则。
- 注意:相等的对象应该具有相等的 hashCodes。
Iterator 接口
- 所有实现了 Collection 接口的容器类都有一个 iterator 方法用以返回一个实现了 Iterator 接口的对象。
- iterator 对象称作迭代器,用以方便地实现对容器内元素的遍历操作。
- Iterator 接口定义了如下方法:

方法举例一
import java.util.*;
public class IteratorTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Collection c = new HashSet();
c.add(new Name("f1", "l1"));
c.add(new Name("f2", "l2"));
c.add(new Name("f3", "l3"));
Iterator i = c.iterator();
while (i.hasNext()) {
//next()的返回值为object类型,需要转换为相应类型
Name n = (Name)i.next();
System.out.println(n.getFirstName());
}
}
}
class Name {
String firstName, lastName;
public Name(String firstName, String lastName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public String getFirstName() {
return firstName;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
}
输出
f3
f1
f2
注意:由于哈希值没有固定的顺序,因此输出内容的顺序可能有所不同
方法举例二
... ... ...
Collection c = new HashSet();
c.add(new Name("fff1", "lll1"));
c.add(new Name("f2", "l2"));
c.add(new Name("fff3", "lll3"));
for (Iterator i = c.iterator(); i.hasNext();) {
Name name = (Name)i.Next();
if (name.getFirstName().length() < 3) {
i.remove();
//如果换成 c.remove(name);会产生例外(线程锁定)
}
}
增强 for 循环
- 增强的 for 循环对于遍历 array 或 Collection 的时候相当简便
- 缺陷:
- 数组:不能方便地访问下标值
- 集合:
- 与使用 Iterator 相比,不能方便地删除集合中的内容
- 在内部也是调用 Iterator
- 总结:除了简单遍历并读出其中的内容外(只读),不建议使用增强 for
举例
import java.util.*;
public class EnhancedFor {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
for(int i : arr) {
System.out.println(i);
}
Collection c = new ArrayList();
c.add(new String("aaa"));
c.add(new String("bbb"));
c.add(new String("ccc"));
for(Object o : c) {
System.out.println(o);
}
}
}
Set 接口
- Set 接口是 Collection 的子接口,Set 接口没有提供额外的方法,但实现 Set 接口的容器类中的元素是没有顺序的,而且不可以重复。
- Set 容器可以与数学中“集合”的概念相对应。
- JDK API 中所提供的的 Set 容器类有 HashSet,TreeSet 等。
List 接口
- List 接口是 Collection 的子接口,实现 List 接口的容器类的元素是有顺序的,而且可以重复。
- List 容器中的元素都对应一个整数型的序号记载其在容器中的位置,可以根据序号存取容器中的元素。
- JDK 所提供的 List 容器类有 ArrayList,LinkList 等。

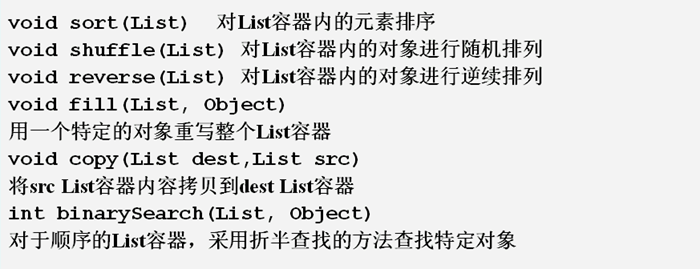
List 常用算法
类 java.util.Collections 提供了一些静态方法实现了基于 List 容器的一些常用算法。
Comparable 接口
- 所有可以“排序”的类都实现了 java.lang.Comparable 接口,Comparable 接口中只有一个方法:
public int compareTo(Object obj);
该方法:- 返回0表示 this == obj
- 返回正数表示 this > obj
- 返回负数表示 this < obj
- 实现了 Comparable 接口的类通过实现 comparaTo 方法从而确定该类对象的排序方式。
如何选择数据结构*
- 衡量标准:读的效率和改的效率
- Array 读快改慢
- Linked 改快读慢
- Hash 两者之间
Map 接口
- 实现 Map 接口的类用来存储键——值对。
- Map 接口的实现类有 HashMap 和 TreeMap 等。
- Map 类中存储的键——值对通过键来标识,所以键值不能重复。

示例
import java.util.*;
public class TestMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map m1 = new HashMap();
Map m2 = new TreeMap();
m1.put("one", new Integer(1));
m1.put("two", new Integer(2));
m1.put("three", new Integer(3));
m2.put("A", new Character('A'));
m2.put("B", new Character('B'));
System.out.println(m1.size()); //3
System.out.println(m1.containsKey("one")); //true
System.out.println(m2.containsValue(new Character('A'))); //true
if (m2.containsKey("A")) {
char i = ((Character)m2.get("A")).charValue();
System.out.println(i); //A
}
Map m3 = new HashMap(m1);
m3.putAll(m2);
System.out.println(m3);
}
}
输出
3
true
true
A
{A=A, B=B, two=2, three=3, one=1}
Auto-boxing/unboxing
- 在合适的时机自动打包、解包
- 自动将基础类型转换为对象
- 自动将对象转换为基础类型
对上一处的程序进行改进
import java.util.*;
public class TestMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Map m1 = new HashMap();
Map m2 = new TreeMap();
m1.put("one", 1); //Autoboxing
//m1.put("one", new Integer(1));
m1.put("two", 2); //Autoboxing
//m1.put("two", new Integer(2));
m1.put("three", 3); //Autoboxing
//m1.put("three", new Integer(3));
m2.put("A", 'A'); //Autoboxing
//m2.put("A", new Character('A'));
m2.put("B", 'B'); //Autoboxing
//m2.put("B", new Character('B'));
System.out.println(m1.size()); //3
System.out.println(m1.containsKey("one")); //true
System.out.println(m2.containsValue('A')); //Autoboxing
//System.out.println(m2.containsValue(new Character('A'))); //true
if (m2.containsKey("A")) {
char i = (Character)m2.get("A"); //Autoboxing
//char i = ((Character)m2.get("A")).charValue();
System.out.println(i); //A
}
Map m3 = new HashMap(m1);
m3.putAll(m2);
System.out.println(m3);
}
}
编译通过,可见编译器会自动执行打包和解包工作。
泛型(generic)
- 起因:
- JDK1.4 以前类型不明确;
- 装入集合的类型都被当做 Object 对待,从而失去自己的实际类型。
- 从集合中取出时往往需要转型,效率低,容易产生错误。
- JDK1.4 以前类型不明确;
- 解决办法:在定义集合的时候同时定义集合中对象的类型
- 好处:增强程序的可读性和稳定性
对上一个程序应用泛型
import java.util.*;
public class TestMap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Map m1 = new HashMap();
Map<String, Integer> m1 = new HashMap<String, Integer>(); //generic
//Map m2 = new TreeMap();
Map<String, Character> m2 = new TreeMap<String, Character>(); //generic
m1.put("one", 1); //Autoboxing
//m1.put("one", new Integer(1));
m1.put("two", 2); //Autoboxing
//m1.put("two", new Integer(2));
m1.put("three", 3); //Autoboxing
//m1.put("three", new Integer(3));
m2.put("A", 'A'); //Autoboxing
//m2.put("A", new Character('A'));
m2.put("B", 'B'); //Autoboxing
//m2.put("B", new Character('B'));
System.out.println(m1.size()); //3
System.out.println(m1.containsKey("one")); //true
System.out.println(m2.containsValue('A')); //Autoboxing
//System.out.println(m2.containsValue(new Character('A'))); //true
if (m2.containsKey("A")) {
char i = m2.get("A"); //generic
//*char i = (Character)m2.get("A"); //Autoboxing
//char i = ((Character)m2.get("A")).charValue();
System.out.println(i); //A
}
Map<String, Object> m3 = new HashMap<String, Object>(m1);
m3.putAll(m2);
System.out.println(m3);
}
}
Java_Day8的更多相关文章
随机推荐
- SLF4j 居然不是编译时绑定?日志又该如何正确的分文件输出?——原理与总结篇
各位新年快乐,过了个新年,休(hua)息(shui)了三周,不过我又回来更新了,经过前面四篇想必小伙伴已经了解日志的使用以及最佳实践了,这个系列的文章也差不多要结束了,今天我们来总结一下. 概览 这篇 ...
- MongoDB -> kafka 高性能实时同步(采集)mongodb数据到kafka解决方案
写这篇博客的目的 让更多的人了解 阿里开源的MongoShake可以很好满足mongodb到kafka高性能高可用实时同步需求(项目地址:https://github.com/alibaba/Mong ...
- 面试官:你说你熟悉jvm?那你讲一下并发的可达性分析
这是why技术的第35篇原创文章 上面这张图是我还是北漂的时候,在鼓楼附近的胡同里面拍的. 那天刚刚下完雨,路过这个地方的时候,一瞬间就被这五颜六色的门板和自行车给吸引了,于是拍下了这张图片.看到这张 ...
- Failed to get convolution algorithm解决
蒸腾了两天,终于搞定了 是cudnn版本的问题 更新cudnn的时候,首先要删除/usr/local/cuda-10.0/targets/x86_64-linux/lib路径下所有之前cudnn版本的 ...
- B树(B-树) 、B+树
B树(B-树) 1.B-树(B树)的基本概念B-树中所有结点中孩子结点个数的最大值成为B-树的阶,通常用m表示,从查找效率考虑,一般要求m>=3.一棵m阶B-树或者是一棵空树,或者是满足以下条件 ...
- Go语言SQL注入和防注入
Go语言SQL注入和防注入 一.SQL注入是什么 SQL注入是一种注入攻击手段,通过执行恶意SQL语句,进而将任意SQL代码插入数据库查询,从而使攻击者完全控制Web应用程序后台的数据库服务器.攻击者 ...
- .net 微服务实践
l 前言 本文记录了我的一次.net core 微服务架构实践经验,以及所用到的技术 l 优点 每个服务聚焦于一块业务,无论在开发阶段或是部署阶段都是独立的,更适合被各个小团队开发维护,团队对服务 ...
- java设计模式学习笔记——里氏替换原则
oo中的继承性的思考和说明 1.继承包含这样一层含义:父类中凡是已经实现好的方法,实际上是在设定规范和契约,虽然它不强制要求所有的子类必须遵循这些七月,但是如果子类对这些已经实现的方法任意修改,就会对 ...
- Python3.7+Pycharm+cuda10.0+tensorflow GPU版本 安装
处理器:I5-7500 显卡 :GTX1050Ti 系统 :Win10 1. 首先搭建Python环境. 官网https://www.python.org/downloads/下载Python ...
- docker笔记(2)
docker笔记(2) 常用命令和操作 1. 镜像操作 操作 命令 说明 检索 docker search 关键字 eg:docker search redis 我们经常去docker hub上检索镜 ...
