leveldb 学习记录(四) skiplist补与变长数字
在leveldb 学习记录(一) skiplist 已经将skiplist的插入 查找等操作流程用图示说明
这里在介绍 下skiplist的代码
里面有几个模块
template<typename Key, class Comparator>
class SkipList {......}
class Arena;(内存池模块 暂时不介绍)
struct Node;(节点 存储key 和指向其他Node的指针)
- //Node 构造函数 KEY赋值
- // Implementation details follow
- template<typename Key, class Comparator>
- struct SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Node {
- explicit Node(const Key& k) : key(k) { }
- Key const key;
- // Accessors/mutators for links. Wrapped in methods so we can
- // add the appropriate barriers as necessary.
- // 访问修改器使用 包装在方法中 可以使用内存屏障
- // Node指向的另一层?
- Node* Next(int n) {
- assert(n >= 0);
- // Use an 'acquire load' so that we observe a fully initialized
- // version of the returned Node.
- return reinterpret_cast<Node*>(next_[n].Acquire_Load());
- }
- //设置下层Node指向
- void SetNext(int n, Node* x) {
- assert(n >= 0);
- // Use a 'release store' so that anybody who reads through this
- // pointer observes a fully initialized version of the inserted node.
- next_[n].Release_Store(x);
- }
- // No-barrier variants that can be safely used in a few locations.
- // 读取本Node在N层的NODE指向 非内存屏蔽操作
- Node* NoBarrier_Next(int n) {
- assert(n >= 0);
- return reinterpret_cast<Node*>(next_[n].NoBarrier_Load());
- }
- //设置Node 在N层的Node指向 非内存屏蔽操作
- void NoBarrier_SetNext(int n, Node* x) {
- assert(n >= 0);
- next_[n].NoBarrier_Store(x);
- }
- private:
- // Array of length equal to the node height. next_[0] is lowest level link.
- // 原子指针数组 指向其他Node 创建时候动态确认数组长度
- port::AtomicPointer next_[1];
- };
结构示意图如下
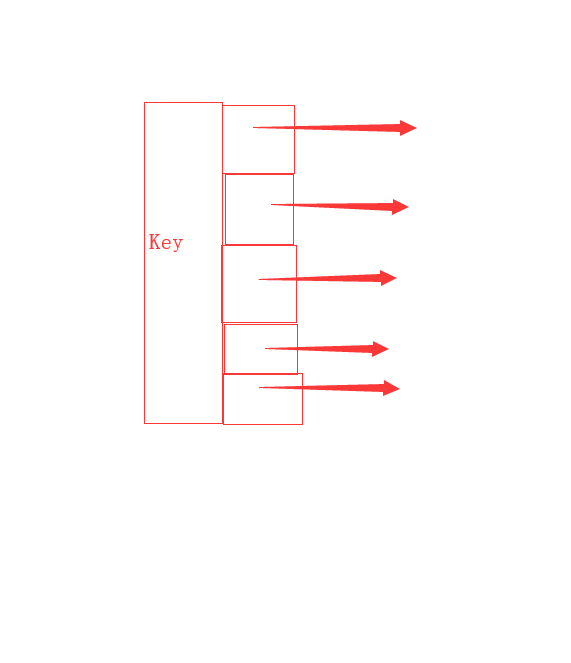
其他操作可参见系列文章一
最后附上我注释的代码
- #include <assert.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include "port/port.h"
- #include "util/arena.h"
- #include "util/random.h"
- namespace leveldb {
- class Arena;
- template<typename Key, class Comparator>
- class SkipList {
- private:
- struct Node;
- public:
- // Create a new SkipList object that will use "cmp" for comparing keys,
- // and will allocate memory using "*arena". Objects allocated in the arena
- // must remain allocated for the lifetime of the skiplist object.
- explicit SkipList(Comparator cmp, Arena* arena);
- // Insert key into the list.
- // REQUIRES: nothing that compares equal to key is currently in the list.
- void Insert(const Key& key);
- // Returns true iff an entry that compares equal to key is in the list.
- bool Contains(const Key& key) const;
- // Iteration over the contents of a skip list
- class Iterator {
- public:
- // Initialize an iterator over the specified list.
- // The returned iterator is not valid.
- explicit Iterator(const SkipList* list);
- // Returns true iff the iterator is positioned at a valid node.
- bool Valid() const;
- // Returns the key at the current position.
- // REQUIRES: Valid()
- const Key& key() const;
- // Advances to the next position.
- // REQUIRES: Valid()
- void Next();
- // Advances to the previous position.
- // REQUIRES: Valid()
- void Prev();
- // Advance to the first entry with a key >= target
- void Seek(const Key& target);
- // Position at the first entry in list.
- // Final state of iterator is Valid() iff list is not empty.
- void SeekToFirst();
- // Position at the last entry in list.
- // Final state of iterator is Valid() iff list is not empty.
- void SeekToLast();
- private:
- const SkipList* list_;
- Node* node_;
- // Intentionally copyable
- };
- private:
- enum { kMaxHeight = };
- // Immutable after construction
- Comparator const compare_;
- Arena* const arena_; // Arena used for allocations of nodes
- Node* const head_;
- // Modified only by Insert(). Read racily by readers, but stale
- // values are ok.
- port::AtomicPointer max_height_; // Height of the entire list
- inline int GetMaxHeight() const {
- return reinterpret_cast<intptr_t>(max_height_.NoBarrier_Load());
- }
- // Read/written only by Insert().
- Random rnd_;
- Node* NewNode(const Key& key, int height);
- int RandomHeight();
- bool Equal(const Key& a, const Key& b) const { return (compare_(a, b) == ); }
- // Return true if key is greater than the data stored in "n"
- bool KeyIsAfterNode(const Key& key, Node* n) const;
- // Return the earliest node that comes at or after key.
- // Return NULL if there is no such node.
- //
- // If prev is non-NULL, fills prev[level] with pointer to previous
- // node at "level" for every level in [0..max_height_-1].
- Node* FindGreaterOrEqual(const Key& key, Node** prev) const;
- // Return the latest node with a key < key.
- // Return head_ if there is no such node.
- Node* FindLessThan(const Key& key) const;
- // Return the last node in the list.
- // Return head_ if list is empty.
- Node* FindLast() const;
- // No copying allowed
- SkipList(const SkipList&);
- void operator=(const SkipList&);
- };
- //Node 构造函数 KEY赋值
- // Implementation details follow
- template<typename Key, class Comparator>
- struct SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Node {
- explicit Node(const Key& k) : key(k) { }
- Key const key;
- // Accessors/mutators for links. Wrapped in methods so we can
- // add the appropriate barriers as necessary.
- // 访问修改器使用 包装在方法中 可以使用内存屏障
- // Node指向的另一层?
- Node* Next(int n) {
- assert(n >= );
- // Use an 'acquire load' so that we observe a fully initialized
- // version of the returned Node.
- return reinterpret_cast<Node*>(next_[n].Acquire_Load());
- }
- //设置下层Node指向
- void SetNext(int n, Node* x) {
- assert(n >= );
- // Use a 'release store' so that anybody who reads through this
- // pointer observes a fully initialized version of the inserted node.
- next_[n].Release_Store(x);
- }
- // No-barrier variants that can be safely used in a few locations.
- // 读取本Node在N层的NODE指向 非内存屏蔽操作
- Node* NoBarrier_Next(int n) {
- assert(n >= );
- return reinterpret_cast<Node*>(next_[n].NoBarrier_Load());
- }
- //设置Node 在N层的Node指向 非内存屏蔽操作
- void NoBarrier_SetNext(int n, Node* x) {
- assert(n >= );
- next_[n].NoBarrier_Store(x);
- }
- private:
- // Array of length equal to the node height. next_[0] is lowest level link.
- // 原子指针数组 指向其他Node 创建时候动态确认数组长度
- port::AtomicPointer next_[];
- };
- //创建一个NODE 内存池arena_分配内存 height确认该NODE的Node指向数量
- template<typename Key, class Comparator>
- typename SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Node*
- SkipList<Key,Comparator>::NewNode(const Key& key, int height) {
- char* mem = arena_->AllocateAligned(
- sizeof(Node) + sizeof(port::AtomicPointer) * (height - ));
- return new (mem) Node(key);
- }
- //根据输入的SkipList指针构造一个 iterator
- template<typename Key, class Comparator>
- inline SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Iterator::Iterator(const SkipList* list) {
- list_ = list;
- node_ = NULL;
- }
- //
- template<typename Key, class Comparator>
- inline bool SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Iterator::Valid() const {
- return node_ != NULL;
- }
- //返回iterator指向的Node的key
- template<typename Key, class Comparator>
- inline const Key& SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Iterator::key() const {
- assert(Valid());
- return node_->key;
- }
- //获取iterator指向的下一个node 在第0层获取(Node第0层均有记录)
- template<typename Key, class Comparator>
- inline void SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Iterator::Next() {
- assert(Valid());
- node_ = node_->Next();
- }
- //寻找该node上一个node
- template<typename Key, class Comparator>
- inline void SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Iterator::Prev() {
- // Instead of using explicit "prev" links, we just search for the
- // last node that falls before key.
- assert(Valid());
- node_ = list_->FindLessThan(node_->key);
- if (node_ == list_->head_) {
- node_ = NULL;
- }
- }
- //调用 FindGreaterOrEqual 查找
- template<typename Key, class Comparator>
- inline void SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Iterator::Seek(const Key& target) {
- node_ = list_->FindGreaterOrEqual(target, NULL);
- }
- //重置到head Node 第0层 第一个Node
- template<typename Key, class Comparator>
- inline void SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Iterator::SeekToFirst() {
- node_ = list_->head_->Next();
- }
- //重置到last Node
- template<typename Key, class Comparator>
- inline void SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Iterator::SeekToLast() {
- node_ = list_->FindLast();
- if (node_ == list_->head_) {
- node_ = NULL;
- }
- }
- //返回height 随机增加1
- template<typename Key, class Comparator>
- int SkipList<Key,Comparator>::RandomHeight() {
- // Increase height with probability 1 in kBranching
- static const unsigned int kBranching = ;
- int height = ;
- while (height < kMaxHeight && ((rnd_.Next() % kBranching) == )) {
- height++;
- }
- assert(height > );
- assert(height <= kMaxHeight);
- return height;
- }
- //调用 cmp 比较是大小
- template<typename Key, class Comparator>
- bool SkipList<Key,Comparator>::KeyIsAfterNode(const Key& key, Node* n) const {
- // NULL n is considered infinite
- return (n != NULL) && (compare_(n->key, key) < );
- }
- //寻找比key大或者等于的Node
- template<typename Key, class Comparator>
- typename SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Node* SkipList<Key,Comparator>::FindGreaterOrEqual(const Key& key, Node** prev)
- const {
- Node* x = head_;
- int level = GetMaxHeight() - ;
- // k在Next后面 则在本level寻找 否则 在下一层level寻找
- while (true) {
- Node* next = x->(level);
- if (KeyIsAfterNode(key, next)) {
- // Keep searching in this list
- x = next;
- } else {
- if (prev != NULL) prev[level] = x;
- if (level == ) {
- return next;
- } else {
- // Switch to next list
- level--;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- //寻找小于等于KEY的第一个NODE
- template<typename Key, class Comparator>
- typename SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Node*
- SkipList<Key,Comparator>::FindLessThan(const Key& key) const {
- Node* x = head_;
- int level = GetMaxHeight() - ;
- while (true) {
- assert(x == head_ || compare_(x->key, key) < );
- Node* next = x->Next(level);
- if (next == NULL || compare_(next->key, key) >= ) {
- if (level == ) {
- return x;
- } else {
- // Switch to next list
- level--;
- }
- } else {
- x = next;
- }
- }
- }
- //在最高层 寻找最后一个Node
- template<typename Key, class Comparator>
- typename SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Node* SkipList<Key,Comparator>::FindLast()
- const {
- Node* x = head_;
- int level = GetMaxHeight() - ;
- while (true) {
- Node* next = x->Next(level);
- if (next == NULL) {
- if (level == ) {
- return x;
- } else {
- // Switch to next list
- level--;
- }
- } else {
- x = next;
- }
- }
- }
- //构建函数 第一个head Node key是0 后继Node指针最大kMaxHeight
- template<typename Key, class Comparator>
- SkipList<Key,Comparator>::SkipList(Comparator cmp, Arena* arena)
- : compare_(cmp),
- arena_(arena),
- head_(NewNode( /* any key will do */, kMaxHeight)),
- max_height_(reinterpret_cast<void*>()),
- rnd_(0xdeadbeef) {
- for (int i = ; i < kMaxHeight; i++) {
- head_->SetNext(i, NULL);
- }
- }
- //insert算法
- template<typename Key, class Comparator>
- void SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Insert(const Key& key) {
- // TODO(opt): We can use a barrier-free variant of FindGreaterOrEqual()
- // here since Insert() is externally synchronized.
- Node* prev[kMaxHeight];
- Node* x = FindGreaterOrEqual(key, prev);
- // Our data structure does not allow duplicate insertion
- assert(x == NULL || !Equal(key, x->key));
- int height = RandomHeight();
- if (height > GetMaxHeight()) {
- for (int i = GetMaxHeight(); i < height; i++) {
- prev[i] = head_;
- }
- //fprintf(stderr, "Change height from %d to %d\n", max_height_, height);
- // It is ok to mutate max_height_ without any synchronization
- // with concurrent readers. A concurrent reader that observes
- // the new value of max_height_ will see either the old value of
- // new level pointers from head_ (NULL), or a new value set in
- // the loop below. In the former case the reader will
- // immediately drop to the next level since NULL sorts after all
- // keys. In the latter case the reader will use the new node.
- max_height_.NoBarrier_Store(reinterpret_cast<void*>(height));
- }
- x = NewNode(key, height);
- for (int i = ; i < height; i++) {
- // NoBarrier_SetNext() suffices since we will add a barrier when
- // we publish a pointer to "x" in prev[i].
- x->NoBarrier_SetNext(i, prev[i]->NoBarrier_Next(i));
- prev[i]->SetNext(i, x);
- }
- }
- //寻找等于KEY 即可确认是否包含与KEY相等的Node
- template<typename Key, class Comparator>
- bool SkipList<Key,Comparator>::Contains(const Key& key) const {
- Node* x = FindGreaterOrEqual(key, NULL);
- if (x != NULL && Equal(key, x->key)) {
- return true;
- } else {
- return false;
- }
- }
- }
varint变长数
leveldb使用了Protocol Buffers的变长字节整形编码 每个字节中使用7位来表示数字 最高位用作他处
300的编码,编码后是两个字节:
- 1010 1100 0000 0010
它这个例子是每个字节左边是高位,可以看到每个字节的最高位是一个标识位,从左到右第一个字节是10101100,最高位是1,说明后面还有字节需要解码,然后第二个字节是00000010,最高位是0,后面没字节了。所以这两个字节就需要解码成一个整数,再往下看。
- 代码
- 1010 1100 0000 0010
- → 010 1100 000 0010 //每个字节去掉最高位
- → 000 0010 010 1100 //字节序转换,两个字节互换位置
- → 000 0010 ++ 010 1100 //两个字节进行链接操作(不是相加)
- → 100101100 //合并后的结果,高位位0的部分截取掉
- → 256 + 32 + 8 + 4 = 300 //每个值为1的bit位乘以以2为底的幂,得出编码后的值
主要函数在
coding.h
extern void PutFixed32(std::string* dst, uint32_t value);
extern void PutFixed64(std::string* dst, uint64_t value);
extern void PutVarint32(std::string* dst, uint32_t value);
extern void PutVarint64(std::string* dst, uint64_t value);
extern void PutLengthPrefixedSlice(std::string* dst, const Slice& value);
extern bool GetVarint32(Slice* input, uint32_t* value);
extern bool GetVarint64(Slice* input, uint64_t* value);
extern bool GetLengthPrefixedSlice(Slice* input, Slice* result);
extern const char* GetVarint32Ptr(const char* p,const char* limit, uint32_t* v);
extern const char* GetVarint64Ptr(const char* p,const char* limit, uint64_t* v);
extern int VarintLength(uint64_t v);
extern void EncodeFixed32(char* dst, uint32_t value);
extern void EncodeFixed64(char* dst, uint64_t value);
extern char* EncodeVarint32(char* dst, uint32_t value);
extern char* EncodeVarint64(char* dst, uint64_t value);
参考
https://www.cnblogs.com/onlytiancai/archive/2010/10/16/1853003.html
leveldb 学习记录(四) skiplist补与变长数字的更多相关文章
- leveldb 学习记录(四)Log文件
前文记录 leveldb 学习记录(一) skiplistleveldb 学习记录(二) Sliceleveldb 学习记录(三) MemTable 与 Immutable Memtablelevel ...
- leveldb 学习记录(一) skiplist
leveldb LevelDb是一个持久化存储的KV系统,并非完全将数据放置于内存中,部分数据也会存储到磁盘上. 想了解这个由谷歌大神编写的经典项目. 可以从数据结构以及数据结构的处理下手,也可以从示 ...
- leveldb 学习记录(三) MemTable 与 Immutable Memtable
前文: leveldb 学习记录(一) skiplist leveldb 学习记录(二) Slice 存储格式: leveldb数据在内存中以 Memtable存储(核心结构是skiplist 已介绍 ...
- JavaScript学习记录四
title: JavaScript学习记录四 toc: true date: 2018-09-16 20:31:22 --<JavaScript高级程序设计(第2版)>学习笔记 要多查阅M ...
- 4.VUE前端框架学习记录四:Vue组件化编码2
VUE前端框架学习记录四:Vue组件化编码2文字信息没办法描述清楚,主要看编码Demo里面,有附带完整的代码下载地址,有需要的同学到脑图里面自取.脑图地址http://naotu.baidu.com/ ...
- leveldb 学习记录(五)SSTable格式介绍
本节主要记录SSTable的结构 为下一步代码阅读打好基础,考虑到已经有大量优秀博客解析透彻 就不再编写了 这里推荐 https://blog.csdn.net/tankles/article/det ...
- leveldb 学习记录(七) SSTable构造
使用TableBuilder构造一个Table struct TableBuilder::Rep { // TableBuilder内部使用的结构,记录当前的一些状态等 Options options ...
- leveldb 学习记录(八) compact
随着运行时间的增加,memtable会慢慢 转化成 sstable. sstable会越来越多 我们就需要进行整合 compact 代码会在写入查询key值 db写入时等多出位置调用MaybeSche ...
- Linux 学习记录 四(Bash 和 Shell scirpt)
一.什么是 Shell? 狭义的shell指的是指令列方面的软件,包括基本的Linux操作窗口Bash等,广义的shell则包括 图形接口的软件,因为图形接口其实也可以操作各种驱动程序来呼叫核心进行工 ...
随机推荐
- centos7下安全访问远程服务器
1. 添加普通账号 众所周知,linux下的root拥有最高权限,可以执行任何命令.在使用root身份操作时,有时的一个不注意就可能将非常重要的删除(最可怕的是 rm -rf /).而linux不像w ...
- 2017-07-06 eclipse在线安装SVN1.9插件
1,百度搜索subeclipse,点击第一个: 2,官网说,文档已移动到github wiki上: 3,打开github wiki,复制最新发布版本地址: 4,在eclipse里面,打开help-&g ...
- JVM内部细节之一:synchronized关键字及实现细节(轻量级锁Lightweight Locking)
在C程序代码中我们可以利用操作系统提供的互斥锁来实现同步块的互斥访问及线程的阻塞及唤醒等工作.然而在Java中除了提供Lock API外还在语法层面上提供了synchronized关键字来实现互斥同步 ...
- jquery:获取checked复选框的问题
jquery:获取checked复选框的问题 功能描述:要完成一个全选的功能,但总是获取不到复选框的被选中的个数,究其原因,是Jquery中length和checked使用不当所造成的. // 获取所 ...
- echarts属性的设置(完整大全)
// 全图默认背景 // backgroundColor: ‘rgba(0,0,0,0)’, // 默认色板 color: ['#ff7f50','#87cefa','#da70d6','#32cd ...
- @Bean 的用法
@Bean是一个方法级别上的注解,主要用在@Configuration注解的类里,也可以用在@Component注解的类里.添加的bean的id为方法名 定义bean 下面是@Configuratio ...
- leetcode647
class Solution { public: ][],int i,int j){ if(i>=j){ return true; } else{ return DP[i][j]; } } in ...
- springBoot框架的搭建
1新建一个项目: 2.注意选择JDK1.8,和选择spring initializr加载springBoot相关jar包: 3.下一步next: 4.下一步next,选择Web和MyBatis然后ne ...
- mysql连接测试java脚本
JDBC.java import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; import java.sql.*; import java.uti ...
- Linux网络编程学习(六) ----- 管道(第四章)
1.管道的定义 管道就是将一个程序的输出和另外一个程序的输入连接起来的单向通道,比如命令: ls -l|more,就建立了一个管道,获取ls -l的输出作为more的输入,数据就沿着管道从管道的左边流 ...
