TCP粘包拆包场景
TCP编程底层都有粘包和拆包机制,因为我们在C/S这种传输模型下,以TCP协议传输的时候,在网络中的byte其实就像是河水,TCP就像一个搬运工,将这流水从一端转送到另一端,这时又分两种情况:
1)如果客户端的每次制造的水比较多,也就是我们常说的客户端给的包比较大,TCP这个搬运工就会分多次去搬运。
2)如果客户端每次制造的水比较少的话,TCP可能会等客户端多次生产之后,把所有的水一起再运输到另一端
上述第一种情况,就是需要我们进行粘包,在另一端接收的时候,需要把多次获取的结果粘在一起,变成我们可以理解的信息,第二种情况,我们在另一端接收的时候,就必须进行拆包处理,因为每次接收的信息,可能是另一个远程端多次发送的包,被TCP粘在一起的
我们进行上述两种情况给出具体的场景:
1)单次发送的包内容过多的情况,拆包的现象:
我们先写客户端的bootstrap:
- package com.lyncc.netty.stickpackage.myself;
- import io.netty.bootstrap.Bootstrap;
- import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
- import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
- import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
- import io.netty.channel.ChannelPipeline;
- import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
- import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
- import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
- import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioSocketChannel;
- import io.netty.handler.codec.LineBasedFrameDecoder;
- import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
- public class BaseClient {
- static final String HOST = System.getProperty("host", "127.0.0.1");
- static final int PORT = Integer.parseInt(System.getProperty("port", "8080"));
- static final int SIZE = Integer.parseInt(System.getProperty("size", "256"));
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
- EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
- try {
- Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
- b.group(group)
- .channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
- .option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY,true)
- .handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
- @Override
- public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
- ChannelPipeline p = ch.pipeline();
- // p.addLast(new LineBasedFrameDecoder(1024));
- p.addLast(new StringDecoder());
- p.addLast(new BaseClientHandler());
- }
- });
- ChannelFuture future = b.connect(HOST, PORT).sync();
- future.channel().writeAndFlush("Hello Netty Server ,I am a common client");
- future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
- } finally {
- group.shutdownGracefully();
- }
- }
- }
客户端的handler:
- package com.lyncc.netty.stickpackage.myself;
- import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
- import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
- import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
- import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
- public class BaseClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter{
- private byte[] req;
- private int counter;
- public BaseClientHandler() {
- // req = ("BazingaLyncc is learner" + System.getProperty("line.separator"))
- // .getBytes();
- req = ("In this chapter you general, we recommend Java Concurrency in Practice by Brian Goetz. His book w"
- + "ill give We’ve reached an exciting point—in the next chapter we’ll discuss bootstrapping, the process "
- + "of configuring and connecting all of Netty’s components to bring your learned about threading models in ge"
- + "neral and Netty’s threading model in particular, whose performance and consistency advantages we discuss"
- + "ed in detail In this chapter you general, we recommend Java Concurrency in Practice by Brian Goetz. Hi"
- + "s book will give We’ve reached an exciting point—in the next chapter we’ll discuss bootstrapping, the"
- + " process of configuring and connecting all of Netty’s components to bring your learned about threading "
- + "models in general and Netty’s threading model in particular, whose performance and consistency advantag"
- + "es we discussed in detailIn this chapter you general, we recommend Java Concurrency in Practice by Bri"
- + "an Goetz. His book will give We’ve reached an exciting point—in the next chapter;the counter is: 1 2222"
- + "sdsa ddasd asdsadas dsadasdas").getBytes();
- }
- @Override
- public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
- ByteBuf message = null;
- // for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
- // message = Unpooled.buffer(req.length);
- // message.writeBytes(req);
- // ctx.writeAndFlush(message);
- // }
- message = Unpooled.buffer(req.length);
- message.writeBytes(req);
- ctx.writeAndFlush(message);
- message = Unpooled.buffer(req.length);
- message.writeBytes(req);
- ctx.writeAndFlush(message);
- }
- @Override
- public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg)
- throws Exception {
- String buf = (String) msg;
- System.out.println("Now is : " + buf + " ; the counter is : "+ ++counter);
- }
- @Override
- public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
- ctx.close();
- }
- }
服务端的serverBootstrap:
- package com.lyncc.netty.stickpackage.myself;
- import io.netty.bootstrap.ServerBootstrap;
- import io.netty.channel.ChannelFuture;
- import io.netty.channel.ChannelInitializer;
- import io.netty.channel.ChannelOption;
- import io.netty.channel.EventLoopGroup;
- import io.netty.channel.nio.NioEventLoopGroup;
- import io.netty.channel.socket.SocketChannel;
- import io.netty.channel.socket.nio.NioServerSocketChannel;
- import io.netty.handler.codec.string.StringDecoder;
- import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
- public class BaseServer {
- private int port;
- public BaseServer(int port) {
- this.port = port;
- }
- public void start(){
- EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
- EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
- try {
- ServerBootstrap sbs = new ServerBootstrap().group(bossGroup,workerGroup).channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class).localAddress(new InetSocketAddress(port))
- .childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
- protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
- // ch.pipeline().addLast(new LineBasedFrameDecoder(1024));
- ch.pipeline().addLast(new StringDecoder());
- ch.pipeline().addLast(new BaseServerHandler());
- };
- }).option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128)
- .childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true);
- // 绑定端口,开始接收进来的连接
- ChannelFuture future = sbs.bind(port).sync();
- System.out.println("Server start listen at " + port );
- future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
- } catch (Exception e) {
- bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
- workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
- }
- }
- public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
- int port;
- if (args.length > 0) {
- port = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
- } else {
- port = 8080;
- }
- new BaseServer(port).start();
- }
- }
服务端的handler:
- package com.lyncc.netty.stickpackage.myself;
- import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
- import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
- public class BaseServerHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter{
- private int counter;
- @Override
- public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
- String body = (String)msg;
- System.out.println("server receive order : " + body + ";the counter is: " + ++counter);
- }
- @Override
- public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
- cause.printStackTrace();
- ctx.close();
- }
- }
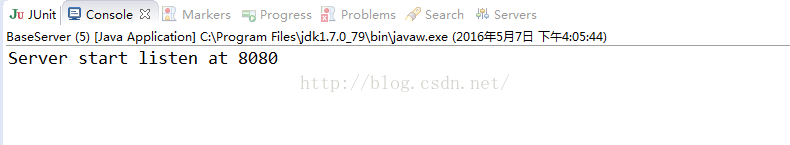
照例,我们先运行服务器端:
我们再运行客户端,客户端启动后,我们再看看服务器端的控制台打印输出:
我们可以看到服务器端分三次接收到了客户端两次发送的那段很长的信息
2)单次发送的包内容过多的情况,粘包的现象:
客户端和服务端的bootstrap不改变,我们修改一下,客户端发送信息的channelActive的代码:
- package com.lyncc.netty.stickpackage.myself;
- import io.netty.buffer.ByteBuf;
- import io.netty.buffer.Unpooled;
- import io.netty.channel.ChannelHandlerContext;
- import io.netty.channel.ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter;
- public class BaseClientHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter{
- private byte[] req;
- private int counter;
- public BaseClientHandler() {
- req = ("BazingaLyncc is learner").getBytes();
- // req = ("In this chapter you general, we recommend Java Concurrency in Practice by Brian Goetz. His book w"
- // + "ill give We’ve reached an exciting point—in the next chapter we’ll discuss bootstrapping, the process "
- // + "of configuring and connecting all of Netty’s components to bring your learned about threading models in ge"
- // + "neral and Netty’s threading model in particular, whose performance and consistency advantages we discuss"
- // + "ed in detail In this chapter you general, we recommend Java Concurrency in Practice by Brian Goetz. Hi"
- // + "s book will give We’ve reached an exciting point—in the next chapter we’ll discuss bootstrapping, the"
- // + " process of configuring and connecting all of Netty’s components to bring your learned about threading "
- // + "models in general and Netty’s threading model in particular, whose performance and consistency advantag"
- // + "es we discussed in detailIn this chapter you general, we recommend Java Concurrency in Practice by Bri"
- // + "an Goetz. His book will give We’ve reached an exciting point—in the next chapter;the counter is: 1 2222"
- // + "sdsa ddasd asdsadas dsadasdas").getBytes();
- }
- @Override
- public void channelActive(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) throws Exception {
- ByteBuf message = null;
- for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
- message = Unpooled.buffer(req.length);
- message.writeBytes(req);
- ctx.writeAndFlush(message);
- }
- // message = Unpooled.buffer(req.length);
- // message.writeBytes(req);
- // ctx.writeAndFlush(message);
- // message = Unpooled.buffer(req.length);
- // message.writeBytes(req);
- // ctx.writeAndFlush(message);
- }
- @Override
- public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) {
- ctx.close();
- }
- }
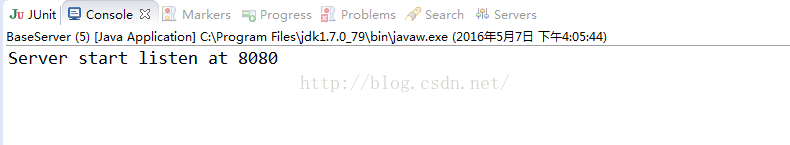
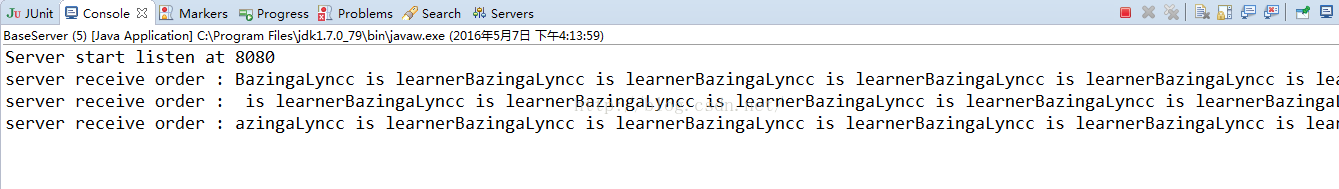
我们再次启动服务器端:
启动客户端后,依旧看服务器端的控制台:
可以看出,客户端发送100次的信息,被服务器端分三次就接收了,这就发生了粘包的现象
以上就是典型的粘包和拆包的场景
TCP粘包拆包场景的更多相关文章
- Netty(二)——TCP粘包/拆包
转载请注明出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/Joanna-Yan/p/7814644.html 前面讲到:Netty(一)--Netty入门程序 主要内容: TCP粘包/拆包的基础知 ...
- TCP粘包/拆包 ByteBuf和channel 如果没有Netty? 传统的多线程服务器,这个也是Apache处理请求的模式
通俗地讲,Netty 能做什么? - 知乎 https://www.zhihu.com/question/24322387 谢邀.netty是一套在java NIO的基础上封装的便于用户开发网络应用程 ...
- TCP 粘包拆包
一.什么是粘包拆包? 粘包拆包是TCP协议传输中一种现象概念.TCP是传输层协议,他传输的是“流”式数据,TCP并不知道传输是哪种业务数据,或者说,并不关心.它只是根据缓冲区状况将数据进行包划分,然后 ...
- Netty(三)TCP粘包拆包处理
tcp是一个“流”的协议,一个完整的包可能会被TCP拆分成多个包进行发送,也可能把小的封装成一个大的数据包发送,这就是所谓的TCP粘包和拆包问题. 粘包.拆包问题说明 假设客户端分别发送数据包D1和D ...
- TCP粘包/拆包问题
无论是服务端还是客户端,当我们读取或者发送消息的时候,都需要考虑TCP底层的粘包/拆包机制. TCP粘包/拆包 TCP是个"流"协议,所谓流,就是没有界限的一串数据.大家可以想想河 ...
- TCP 粘包/拆包问题
简介 TCP 是一个’流’协议,所谓流,就是没有界限的一串数据. 大家可以想想河里的流水,是连成一片的.期间并没有分界线, TCP 底层并不了解上层业务数据的具体含义 ,它会根据 TCP 缓冲区 ...
- TCP粘包/拆包问题的解决
TCP粘包拆包问题 一个完整的包可能被TCP拆分成多个包,或多个小包封装成一个大的数据包发送. 解决策略 消息定长,如果不够,空位补空格 在包尾增加回车换行符进行分割,例如FTP协议 将消息分为消息头 ...
- 第四章 TCP粘包/拆包问题的解决之道---4.1---
4.1 TCP粘包/拆包 TCP是一个“流”协议,所谓流,就是没有界限的一串数据.TCP底层并不了解上层业务数据的具体含义,它会根据TCP缓冲区的实际情况进行包的划分,所以在业务上认为,一个完整的包可 ...
- Java网络编程基础之TCP粘包拆包
TCP是个"流"协议,所谓流,就是没有界限的一串数据.大家可以想象河里的流水,他们是连成一片的,其间并没有分界线.TCP底层并不了解上层业务数据的具体含义,他会根据TCP缓冲区的实 ...
随机推荐
- 【剑指offer-21】调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面,C++实现(冒泡排序)
1.题目 输入一个整数数组,实现一个函数来调整该数组中数字的顺序,使得所有的奇数位于数组的前半部分,所有的偶数位于位于数组的后半部分. 2.思路 本题有两种解法,一种是不保证数组稳定性的解法,一种是保 ...
- VC dimension and Model complexity
可以把growth function m_H(N)的upper bound用N^(k-1)来限制, for N large, k>=3 Thus, 定义: VC Dimension: maxim ...
- js 值和引用
js对值和引用的赋值/传递在语法上没有区别,完全根据值得类型决定 简单值(即标量基本类型值),总是通过值复制的方式来赋值/传递,包括null,undefined,字符串,数字,布尔值和ES6中的sym ...
- Uoj 129 寿司晚宴
Uoj 129 寿司晚宴 显然合法性只与每个数所含的质因子有关,考虑状压 \(dp\) 若记录所有质因子状态显然爆炸,注意到每个数最多有一个超过 \(\sqrt 500\) 的大质因子,而其他的小质因 ...
- python ctypes 和windows DLL互相调用
图片项目
- 网站使用QQ登录问题小结
关于网站如何使用QQ登陆这个问题就不多说了,很简单,登陆connect.qq.com找到相应的SDK,下载下来,里面会有demo,将相应的appid,appkey和回调地址callback改成自己的就 ...
- Nginx配置(需要把nginx的根目录指向ftp上传文件的目录。)
改成
- 最最基本的SQL常用命令
2015-12-01 18:08:52 1.启动/关闭mysql 开始菜单搜索cmd,右击,以管理员身份运行,输入net start mysql启动mysql,输入net stop mysql关闭my ...
- psd文件导出为图片教程
美术给过来PSD文件好多层啊.怎么挨个把需要的图片导出来呢. 1. 选中 要导出的图片的图层 2.ctrl+N 新建个文档 然后把图片拉到 新的里面 然后点图像-裁剪 确定就行了,然后ctrl+s保 ...
- [LeetCode系列] 二叉树最大深度求解问题(C++递归解法)
问: 给定二叉树, 如何计算二叉树最大深度? 算法描述如下: 如果当前节点为空, 返回0(代表此节点下方最大节点数为0) 如果当前节点不为空, 返回(其左子树和右子树下方最大节点数中的最大值+1) 上 ...