SpringBoot从入门到精通教程(四)
前端时间整合SSM ,发现了一个现象,在整合的时候 配置文件过于复杂.
1.建工程,建目录,导入jar包。
2.配置 数据源 映射信息 等等 。。。
3. 还有 各种 拦截器,控制器 ,头都大了。。。。。。。。。
4.于是 今天我们就来解决 SSM 的配置问题,所以我们今天就来讲讲 SpringBoot 整合MyBatis
框架的优点和缺点
mybatis的优缺点:
优点 :
- sql写在xml文件中,便于统一管理和优化,解除sql和程序代码的耦合。
- 提供映射标签,支持对象和和数据库orm字段关系的映射,支持对象关系映射标签,支持对象关系的组建
- 提供xml标签,支持编写动态sql。
缺点
工作量较大,特别是在表的字段多,关联表多的情况下
sql语句的编写依赖于数据库,移植性差。
不支持级联删除,级联更新,需要自己对表进行删除。
spring的优点:
优点 :
通过Spring的IOC特性,将对象之间的依赖关系交给了Spring控制,方便解耦,简化了 开发。
通过Spring的AOP特性,很容易实现事务,日志,权限的控制。
提供了对其他优秀开源框架的集成支持。
低侵入式。
缺点
jsp中要写很多代码、控制器过于灵活,缺少一个公用控制器
Spring不支持分布式,这也是EJB仍然在用的原因之一。
今天自己搭建了下Spring boot+Mybatis,比原来的Spring+SpringMVC+Mybatis简
单好多。其实只用Spring boot也可以开发,但是对于多表多条件分页查询,Spring boot就有点力不从心了,所以 把Mybatis整合进去,不得不说,现在的框架搭建真的是方便。话不多说,进入正题。
Spring boot搭建
1、Intellij idea菜单栏File->new->project。
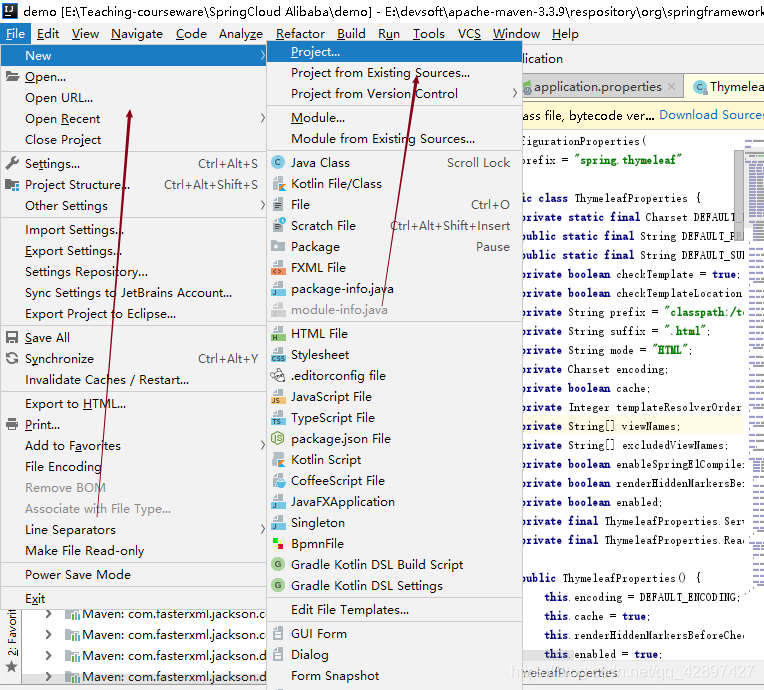
2、选择左侧栏中spring initializr,右侧选择jdk版本,以及默认的Service URL,点击next,大家也可以选择Custom (自定义)。
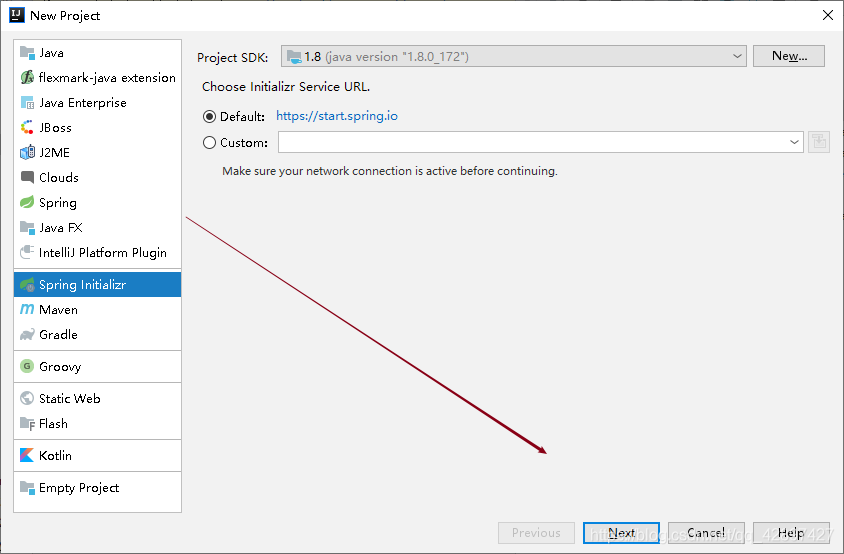
3、然后填写项目的Group(包名)、Artifact(组织名称)等信息,helloworld()阶段选默认就可以了,点击next。
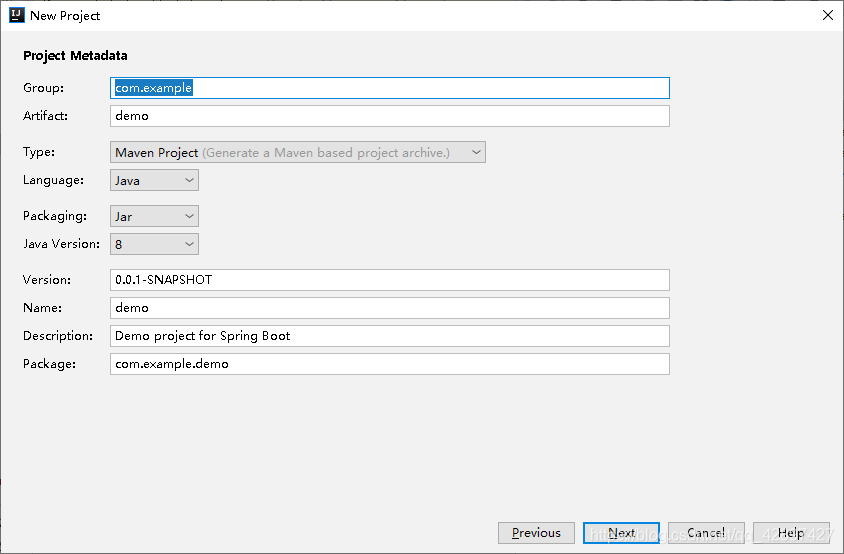
4、左侧点击Web,中间一侧选择Web,然后左侧选择SQL,中间一侧选择 Mybatis、MYSQL(LZ数据库用的是mysql,大家可以选择其他DB),点击next
5、填写Project name 等信息,然后点击Finish。
至此,一个maven web项目就创建好了,目录结构如下:
这样,Spring boot就搭建好了,pom.xml里已经有了Spring boot的jar包,包括我们的
mysql数据连接的jar包。Spring boot内置了类似tomcat这样的中间件,所以,只要运行
DemoApplication中的main方法就可以启动项目了。我们测试一下。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
- 在src/main/java下新建目录
com/spiritmark/boot/entity/User。 (实体类)
package com.spiritmark.boot.entity;
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
private String password;
private String number;
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public String getNumber() {
return number;
}
public void setNumber(String number) {
this.number = number;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", password=" + password + ", number=" + number + "]";
}
- 相同目录下新建
com/spiritmark/boot/controller/TestBootController。
package com.spiritmark.boot.controller;
import com.spiritmark.boot.entity.User;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@RequestMapping("/testboot")
public class TestBootController {
@RequestMapping("getuser")
public User getUser() {
User user = new User();
user.setName("test");
return user;
}
}
最终的目录结构如下,
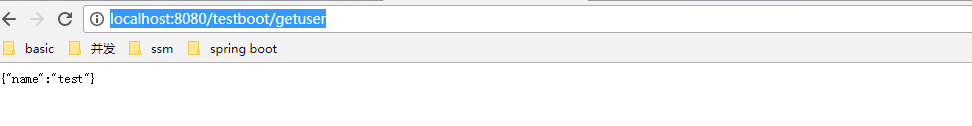
启动DemoApplication的main方法,访问http://localhost:8080/testboot/getuser即可。
mapper层的UserMapper类:
package com.spiritmark.boot.mapper;
import java.util.List;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.Mapper;
import com.spiritmark.boot.entity.User;
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper {
List<User> findUserByName(String name);
public List<User> ListUser();
public int insertUser(User user);
public int delete(int id);
public int Update(User user);
}
service层的实现类Userservice:
package com.spiritmark.boot.service;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.spiritmark.boot.entity.User;
import com.example.demo.mapper.UserMapper;
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
public List<User> findByName(String name) {
return userMapper.findUserByName(name);
}
public User insertUser(User user) {
userMapper.insertUser(user);
return user;
}
public List<User> ListUser(){
return userMapper.ListUser();
}
public int Update(User user){
return userMapper.Update(user);
}
public int delete(int id){
return userMapper.delete(id);
}
}
controller层 的访问类CRUD:
package com.spiritmark.boot.controller;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import com.spiritmark.boot.entity.User;
import com.example.demo.service.UserService;
@RestController
@RequestMapping(value = "/CRUD", method = { RequestMethod.GET, RequestMethod.POST })
public class CRUD {
@Autowired
private UserService userservice;
@RequestMapping(value = "/delete", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String delete(int id) {
int result = userservice.delete(id);
if (result >= 1) {
return "删除成功";
} else {
return "删除失败";
}
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/update", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String update(User user) {
int result = userservice.Update(user);
if (result >= 1) {
return "修改成功";
} else {
return "修改失败";
}
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/insert", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public User insert(User user) {
return userservice.insertUser(user);
}
@RequestMapping("/ListUser")
@ResponseBody
public List<User> ListUser(){
return userservice.ListUser();
}
@RequestMapping("/ListUserByname")
@ResponseBody
public List<User> ListUserByname(String name){
return userservice.findByName(name);
}
}
接着:
在src/main/resources/mapper 下写UserMapper的映射文件xml.
UserMapper.xml
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC
"-//mybatis.org//DTD com.example.Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.spiritmark.boot.mapper.UserMapper">
<resultMap id="result" type="User">
<result property="name" column="name" />
<result property="password" column="password" />
<result property="number" column="number"/>
</resultMap>
<select id="ListUser" resultMap="result">
SELECT * FROM user
</select>
<select id="findUserByName" resultMap="result">
SELECT * FROM user where name=#{name}
</select>
<insert id="insertUser" parameterType="User"
keyProperty="id" useGeneratedKeys="true">
INSERT INTO user
(
id,name,password,number
)
VALUES (
#{id},
#{name, jdbcType=VARCHAR},
#{password, jdbcType=VARCHAR},
#{number}
)
</insert>
<delete id="delete" parameterType="int">
delete from user where id=#{id}
</delete>
<update id="Update" parameterType="User">
update user set user.name=#{name},user.password=#{password},user.number=#{number} where user.id=#{id}
</update>
</mapper>
在配置文件中配置了 别名扫描的包,会自动拼接实体类
application.yml:
#默认使用配置
#公共配置与profiles选择无关
mybatis:
typeAliasesPackage: com.spiritmark.boot.entity # 实体的包名
mapperLocations: classpath:mapper/*.xml # mapper.xml 的地址
---
#开发配置
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?characterEncoding=utf8
username: root
password: root
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
启动程序的入口类:SpringbootApplication.java
我们在postmain这个工具中测试:
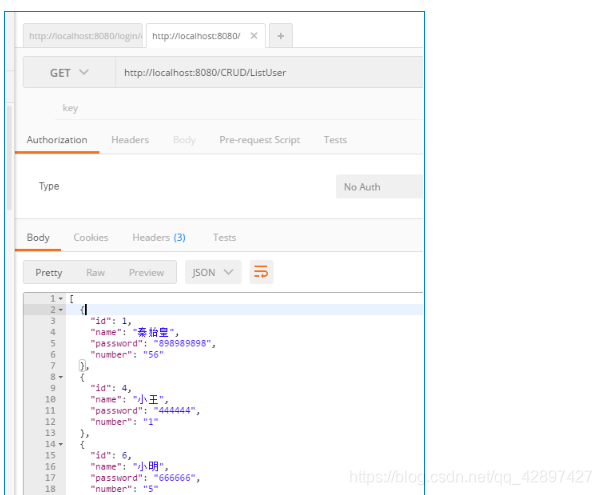
注解版
有人说SpringBoot XML 太麻烦了,这个时候,可以使用 注解版
我们把 XML 删除src/main/resources/mapper/*xml修改成下面这样
package com.spiritmark.boot.mapper;
import com.spiritmark.boot.entity.User;
import org.apache.ibatis.annotations.*;
import java.util.List;
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper {
@Insert("insert into user(name,age) values(#{name},#{age})")
int addUser(@Param("name") String name, @Param("age") String age);
@Select("select * from user where id =#{id}")
User findById(@Param("id") String id);
@Update("update user set name=#{name} where id=#{id}")
void updataById(@Param("id") String id, @Param("name") String name);
@Delete("delete from user where id=#{id}")
void deleteById(@Param("id") String id);
@Select("select * from user")
List<User> findAllUser();
}
SpringBoot从入门到精通教程(四)的更多相关文章
- SpringBoot从入门到精通教程(二)
SpringBoot 是为了简化 Spring 应用的创建.运行.调试.部署等一系列问题而诞生的产物,自动装配的特性让我们可以更好的关注业务本身而不是外部的XML配置,我们只需遵循规范,引入相关的依赖 ...
- SpringBoot从入门到精通教程(八)
本主要介绍ElasticSearch 和 SpringBoot 的整合 ,对您有帮助的话,点个关注哦 ElastSearch 介绍 ElasticSearch是一个基于Lucene的搜索服务器.它提供 ...
- SpringBoot从入门到精通教程(七)
今天,我们继续讲SpringBoot整合Redis ,也就缓存,它将与我们的Springboot整合 Redis 简介 Redis 是当前比较热门的NOSQL系统之一,它是一个开源的使用ANSI c语 ...
- SpringBoot从入门到精通教程(六)
之前学了,这么多东西 thyemeaf .MyBatis 还有 配置文件等等,今天我们就来做一个小案例 CRUD,程序员的必备 项目结构 pom.xml <!-- mybatis 相关依赖 -- ...
- SpringBoot从入门到精通教程(三)
在上一篇中,我们已经讲了,SpringBoot 如何构建项目,和SpringBoot的HelloWorld, 那这一节我们继续讲 Thymeleaf Thymeleaf 官网: Thymeleaf T ...
- SpringBoot从入门到精通教程(一)
写在前面的话: 在很早之前,记笔记时候,我就一直在思考一个问题,我记笔记是为了什么,我一直想不明白 ,后面发现技术跟新迭代的速度实在太快了,笔记刚纪完,技术又跟新了,于是我想了想干脆边写博客,边记笔记 ...
- SpringBoot从入门到精通教程(五)
上节,我们讲了 SpringBoot 如何使用MyBatis 今天我们讲讲 Springboot Logo自定义的问题, 我们在启动 SpringBoot 时,控制台会打印 SpringBoot Lo ...
- 深入浅出!springboot从入门到精通,实战开发全套教程!
前言 之前一直有粉丝想让我出一套springboot实战开发的教程,我这边总结了很久资料和经验,在最近总算把这套教程的大纲和内容初步总结完毕了,这份教程从springboot的入门到精通全部涵盖在内, ...
- GPU 编程入门到精通(四)之 GPU 程序优化
博主因为工作其中的须要,開始学习 GPU 上面的编程,主要涉及到的是基于 GPU 的深度学习方面的知识,鉴于之前没有接触过 GPU 编程.因此在这里特地学习一下 GPU 上面的编程.有志同道合的小伙伴 ...
随机推荐
- 337. 打家劫舍 III(树上dp)
在上次打劫完一条街道之后和一圈房屋后,小偷又发现了一个新的可行窃的地区.这个地区只有一个入口,我们称之为"根". 除了"根"之外,每栋房子有且只有一个" ...
- K8ssandra——专为Kubernetes云原生数据而生
DataStax最近发布了K8ssandra--一个开源的.部署于Kubernetes上的Apache Cassandra全新发行版本.K8ssandra一站式集合了在Kubernetes上部署开源版 ...
- C++基础练习1
1 /* 2 //读入一个双精度浮点数,保留12位小数输出这个浮点数. 3 #include<iostream> 4 #include <iomanip> 5 using na ...
- FPGA PS2协议
VerilogHDL那些事儿_建模篇(黑金FPGA开发板配套教程) 作者:akuei2 说明:参照该书将部分程序验证学习一遍 学习时间:2014年5月3号 主要收获: 1. 对PS2接口有初步了解: ...
- Django的下载及命令
安装 命令行 pip3 install django==1.11.11 测试是否安装成功 django-admin 创建django项目 django-admin startproject 项目名称( ...
- NOIP 2020 退役记
躲进你的身体. 哈哈 没想到这么快就轮到我退役啦 以前想想还感觉挺遥远的 这是我最后的机会啦! day-1 晚上照例吃了断头饭 但是没有蛋糕/kk 恭喜 Luckyblock 逃过一劫! (照照片的时 ...
- Flink实战(102):配置(一)管理配置
来源:http://www.54tianzhisheng.cn/2019/03/28/flink-additional-data/ 前言 如果你了解 Apache Flink 的话,那么你应该熟悉该如 ...
- RabbitMQ,想说爱你不容易(附详细安装教程)
前言 本文讲述的只是主要是 RabbitMQ 的入门知识,学习本文主要可以掌握以下知识点: MQ 的发展史 AMQP 协议 Rabbit MQ 的安装 Rabbit MQ 在 Java API 中的使 ...
- moviepy音视频剪辑:AudioClip的max_volume方法报TypeError: bad operand type for abs(): ‘list‘错
☞ ░ 前往老猿Python博文目录 ░ 一.环境 操作系统:win7 64位 moviepy:1.0.3 numpy:1.19.0 Python:3.7.2 二.应用代码及报错信息 应用代码 imp ...
- 第15.41节、PyQt(Python+Qt)入门学习:输入部件QComboBox组合框功能详解
专栏:Python基础教程目录 专栏:使用PyQt开发图形界面Python应用 专栏:PyQt入门学习 老猿Python博文目录 一.概述 Designer中输入工具部件中的Combo Box组合框与 ...
