Arduino 串口库函数
库函数目录
begin()
end()
find()
flush()
parseInt()
peek()
print()
println()
read()
write()
库函数详解
if (Serial)
Description 指示串行口是否准备好
Indicates if the specified Serial port is ready.
On 32u4 based boards (Leonardo, Yùn, ecc) , if (Serial) indicates wether or not the USB CDC serial connection is open. For all other instances, including if (Serial1) on the Leonardo, this will always returns true.
This was introduced in Arduino 1.0.1.
Syntax
All boards:
if (Serial)
Arduino Leonardo specific:
if (Serial1)
Arduino Mega specific:
if (Serial1)
if (Serial2)
if (Serial3)
Parameters
none
Returns
boolean : returns true if the specified serial port is available. This will only return false if querying the Leonardo's USB CDC serial connection before it is ready.
Serial.available()
Description 得到从串行口读回的字节数
Get the number of bytes (characters) available for reading from the serial port. This is data that's already arrived and stored in the serial receive buffer (which holds 64 bytes). available() inherits from the Stream utility class.
Syntax
Serial.available()
Arduino Mega only:
Serial1.available()
Serial2.available()
Serial3.available()
Parameters
none
Returns
the number of bytes available to read
Example
1 int incomingByte = 0; // for incoming serial data
2
3 void setup()
4
5 {
6 Serial.begin(9600); // opens serial port, sets data rate to 9600 bps
7 }
8 void loop()
9
10 {
11 // send data only when you receive data:
12 if (Serial.available() > 0)
13
14 {
15 // read the incoming byte:
16 incomingByte = Serial.read();
17 // say what you got:
18 Serial.print("I received: ");
19 Serial.println(incomingByte, DEC);
20 }
21 }
Arduino Mega example:
1 void setup()
2
3 {
4 Serial.begin(9600);
5 Serial1.begin(9600);
6 }
7
8 void loop()
9
10 {
11 // read from port 0, send to port 1:
12 if (Serial.available())
13
14 {
15 int inByte = Serial.read();
16 Serial1.print(inByte, BYTE);
17 }
18 // read from port 1, send to port 0:
19 if (Serial1.available())
20
21 {
22 int inByte = Serial1.read();
23 Serial.print(inByte, BYTE);
24 }
25 }
availableForWrite()
Description 得到缓存中可以写出的字节数
Get the number of bytes (characters) available for writing in the serial buffer without blocking the write operation.
Syntax
Serial.availableForWrite()
Arduino Mega only:
Serial1.availableForWrite()
Serial2.availableForWrite()
Serial3.availableForWrite()
Parameters
none
Returns
the number of bytes available to write
begin()
Description 设置波特率
Sets the data rate in bits per second (baud) for serial data transmission. For communicating with the computer, use one of these rates: 300, 600, 1200, 2400, 4800, 9600, 14400, 19200, 28800, 38400, 57600, or 115200. You can, however, specify other rates - for example, to communicate over pins 0 and 1 with a component that requires a particular baud rate.
An optional second argument configures the data, parity, and stop bits. The default is 8 data bits, no parity, one stop bit.
Syntax
Serial.begin(speed)
Serial.begin(speed, config)
Arduino Mega only:
Serial1.begin(speed)
Serial2.begin(speed)
Serial3.begin(speed)
Serial1.begin(speed, config)
Serial2.begin(speed, config)
Serial3.begin(speed, config)
Parameters
speed: in bits per second (baud) - long
config: sets data, parity, and stop bits. 设置数据长度,极性,停止位。Valid values are :
SERIAL_5N1
SERIAL_6N1
SERIAL_7N1
SERIAL_8N1 (the default) 缺省配置:8位数据,无校验位,1个停止位
SERIAL_5N2
SERIAL_6N2
SERIAL_7N2
SERIAL_8N2
SERIAL_5E1
SERIAL_6E1
SERIAL_7E1
SERIAL_8E1
SERIAL_5E2
SERIAL_6E2
SERIAL_7E2
SERIAL_8E2
SERIAL_5O1
SERIAL_6O1
SERIAL_7O1
SERIAL_8O1
SERIAL_5O2
SERIAL_6O2
SERIAL_7O2
SERIAL_8O2
Returns
nothing
Example:
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600); // opens serial port, sets data rate to 9600 bps
}
void loop() { }
Arduino Mega example:
1 // Arduino Mega using all four of its Serial ports
2 // (Serial, Serial1, Serial2, Serial3),
3 // with different baud rates:
4 void setup()
5
6 {
7 Serial.begin(9600);
8 Serial1.begin(38400);
9 Serial2.begin(19200);
10 Serial3.begin(4800);
11
12 Serial.println("Hello Computer");
13 Serial1.println("Hello Serial 1");
14 Serial2.println("Hello Serial 2");
15 Serial3.println("Hello Serial 3");
16 }
17
18 void loop() { }
Thanks to Jeff Gray for the mega example
end()
Description 禁止串行通信,释放RX和TX引脚
Disables serial communication, allowing the RX and TX pins to be used for general input and output. To re-enable serial communication, call Serial.begin().
Syntax
Serial.end()
Arduino Mega only:
Serial1.end()
Serial2.end()
Serial3.end()
Parameters
none
Returns
nothing
Serial.find()
Description 从串行缓存中读数据直到找到目标字符串
Serial.find() reads data from the serial buffer until the target string of given length is found. The function returns true if target string is found, false if it times out.
Serial.find() inherits from the Stream utility class.
Syntax
Serial.find(target)
Parameters
target : the string to search for (char)
Returns
boolean
Serial.findUntil()
Description 从串行缓存中读数据直到找到目标字符串或停止符
Serial.findUntil() reads data from the serial buffer until a target string of given length or terminator string is found.
The function returns true if the target string is found, false if it times out.
Serial.findUntil() inherits from the Stream utility class.
Syntax
Serial.findUntil(target, terminal)
Parameters
target : the string to search for (char)
terminal : the terminal string in the search (char)
Returns
boolean
flush()
Description 等待数据发送完成
Waits for the transmission of outgoing serial data to complete. (Prior to Arduino 1.0, this instead removed any buffered incoming serial data.)
flush() inherits from the Stream utility class.
Syntax
Serial.flush()
Arduino Mega only:
Serial1.flush()
Serial2.flush()
Serial3.flush()
Parameters
none
Returns
nothing
parseFloat()
Description 从缓冲区返回第一个有效浮点数据
Serial.parseFloat() returns the first valid floating point number from the Serial buffer. Characters that are not digits (or the minus sign) are skipped. parseFloat() is terminated by the first character that is not a floating point number.
Serial.parseFloat() inherits from the Stream utility class.
Syntax
Serial.parseFloat()
Parameters
none
Returns
float
parseInt()
Description 从新到的串口数据中查找下一个有效的整数
Looks for the next valid integer in the incoming serial stream. parseInt() inherits from the Stream utility class.
In particular:
Initial characters that are not digits or a minus sign, are skipped;
Parsing stops when no characters have been read for a configurable time-out value, or a non-digit is read;
If no valid digits were read when the time-out (see Serial.setTimeout()) occurs, 0 is returned;
Syntax
Serial.parseInt()
Serial.parseInt(char skipChar)
Arduino Mega only:
Serial1.parseInt()
Serial2.parseInt()
Serial3.parseInt()
Parameters
skipChar: used to skip the indicated char in the search. Used for example to skip thousands divider.
Returns
long : the next valid integer
peek()
Description 读取下一个字节的数据,读取后不从缓存中删除
Returns the next byte (character) of incoming serial data without removing it from the internal serial buffer. That is, successive calls to peek() will return the same character, as will the next call to read(). peek() inherits from the Stream utility class.
Syntax
Serial.peek()
Arduino Mega only:
Serial1.peek()
Serial2.peek()
Serial3.peek()
Parameters
None
Returns
the first byte of incoming serial data available (or -1 if no data is available) - int
print()
Description 以ASCII形式输出数据到串口。发送方式为:数据转为字符,发送该字符对应的ASCII码,显示时再转换为字符。
Prints data to the serial port as human-readable ASCII text. This command can take many forms. Numbers are printed using an ASCII character for each digit. Floats are similarly printed as ASCII digits, defaulting to two decimal places. Bytes are sent as a single character. Characters and strings are sent as is. For example:
Serial.print(78) gives "78"
Serial.print(1.23456) gives "1.23"
Serial.print('N') gives "N"
Serial.print("Hello world.") gives "Hello world."
An optional second parameter specifies the base (format) to use; permitted values are BIN (binary, or base 2), OCT (octal, or base 8), DEC (decimal, or base 10), HEX (hexadecimal, or base 16). For floating point numbers, this parameter specifies the number of decimal places to use. For example:
Serial.print(78, BIN) gives "1001110"
Serial.print(78, OCT) gives "116"
Serial.print(78, DEC) gives "78"
Serial.print(78, HEX) gives "4E"
Serial.println(1.23456, 0) gives "1"
Serial.println(1.23456, 2) gives "1.23"
Serial.println(1.23456, 4) gives "1.2346"
You can pass flash-memory based strings to Serial.print() by wrapping them with F(). For example :
Serial.print(F(“Hello World”))
To send a single byte, use Serial.write().
Syntax
Serial.print(val)
Serial.print(val, format)
Parameters
val: the value to print - any data type
format: specifies the number base (for integral data types) or number of decimal places (for floating point types)
Returns
size_t (long): print() returns the number of bytes written, though reading that number is optional
Example
1 /*
2 Uses a FOR loop for data and prints a number in various formats.
3 */
4 int x = 0; // variable
5
6 void setup()
7 {
8 Serial.begin(9600); // open the serial port at 9600 bps:
9 }
10 void loop()
11 {
12 // print labels
13 Serial.print("NF"); // prints a label no format
14 Serial.print("\t"); // prints a tab
15
16 Serial.print("DEC");
17 Serial.print("\t");
18
19 Serial.print("HEX");
20 Serial.print("\t");
21
22 Serial.print("OCT");
23 Serial.print("\t");
24
25 Serial.print("BIN");
26 Serial.print("\t");
27
28 Serial.println(); 加一个回车符切换到下一行
29
30 for(x=0; x<16; x++)
31 { // only part of the ASCII chart, change to suit
32
33 // print it out in many formats:
34 Serial.print(x); // print as an ASCII-encoded decimal - same as "DEC"
35 Serial.print("\t"); // prints a tab
36
37 Serial.print(x, DEC); // print as an ASCII-encoded decimal
38 Serial.print("\t"); // prints a tab
39
40 Serial.print(x, HEX); // print as an ASCII-encoded hexadecimal
41 Serial.print("\t"); // prints a tab
42
43 Serial.print(x, OCT); // print as an ASCII-encoded octal
44 Serial.print("\t"); // prints a tab
45
46 Serial.println(x, BIN); // print as an ASCII-encoded binary
47 // then adds the carriage return with "println"
48 delay(200); // delay 200 milliseconds
49 }
50 Serial.println(""); // prints another carriage return 加一个回车符切换到下一行
51 while(1)
52 { }
53 }
运行结果如下图
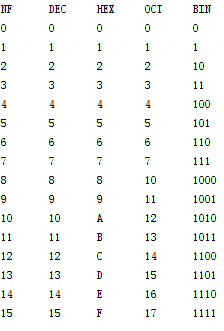
Programming Tips
As of version 1.0, serial transmission is asynchronous; Serial.print() will return before any characters are transmitted.
println()
Description 以ASCII文本行书输出数据到串口,跟着一个回车换行
Prints data to the serial port as human-readable ASCII text followed by a carriage return character (ASCII 13, or '\r') and a newline character (ASCII 10, or '\n'). This command takes the same forms as Serial.print().
Syntax
Serial.println(val)
Serial.println(val, format)
Parameters
val: the value to print - any data type
format: specifies the number base (for integral data types) or number of decimal places (for floating point types)
Returns
size_t (long): println() returns the number of bytes written, though reading that number is optional
Example
1 /*
2 Analog input
3 reads an analog input on analog in 0, prints the value out.
4 created 24 March 2006
5 by Tom Igoe
6 */
7 int analogValue = 0; // variable to hold the analog value
8
9 void setup()
10 {
11 // open the serial port at 9600 bps:
12 Serial.begin(9600);
13 }
14 void loop()
15 {
16 // read the analog input on pin 0:
17 analogValue = analogRead(0);
18
19 // print it out in many formats:
20 Serial.println(analogValue); // print as an ASCII-encoded decimal
21 Serial.println(analogValue, DEC); // print as an ASCII-encoded decimal
22 Serial.println(analogValue, HEX); // print as an ASCII-encoded hexadecimal
23 Serial.println(analogValue, OCT); // print as an ASCII-encoded octal
24 Serial.println(analogValue, BIN); // print as an ASCII-encoded binary
25
26 // delay 10 milliseconds before the next reading:
27 delay(10);
28 }
read()
Description 从串口中读取数据,每次读1个字节。读取后将该数据从缓存删除。
Reads incoming serial data. read() inherits from the Stream utility class.
Syntax
Serial.read()
Arduino Mega only:
Serial1.read()
Serial2.read()
Serial3.read()
Parameters
None
Returns
the first byte of incoming serial data available (or -1 if no data is available) - int
Example
1 int incomingByte = 0; // for incoming serial data
2
3 void setup()
4
5 {
6 Serial.begin(9600); // opens serial port, sets data rate to 9600 bps
7 }
8
9 void loop()
10
11 {
12 // send data only when you receive data:
13 if (Serial.available() > 0)
14
15 {
16 // read the incoming byte:
17 incomingByte = Serial.read();
18 // say what you got:
19 Serial.print("I received: ");
20 Serial.println(incomingByte, DEC);
21 }
22 }
Serial.readBytes()
Description 从缓冲区读取指定长度的字符
Serial.readBytes() reads characters from the serial port into a buffer. The function terminates if the determined length has been read, or it times out (see Serial.setTimeout()).
Serial.readBytes() returns the number of characters placed in the buffer. A 0 means no valid data was found.
Serial.readBytes() inherits from the Stream utility class.
Syntax
Serial.readBytes(buffer, length)
Parameters
buffer: the buffer to store the bytes in (char[] or byte[])
length : the number of bytes to read (int)
Returns
byte
Serial.readBytesUntil()
Description 读取指定长度的字符到一个数组中
Serial.readBytesUntil() reads characters from the serial buffer into an array. The function terminates if the terminator character is detected, the determined length has been read, or it times out (see Serial.setTimeout()).
Serial.readBytesUntil() returns the number of characters read into the buffer. A 0 means no valid data was found.
Serial.readBytesUntil() inherits from the Stream utility class.
Syntax
Serial.readBytesUntil(character, buffer, length)
Parameters
character : the character to search for (char)
buffer: the buffer to store the bytes in (char[] or byte[])
length : the number of bytes to read (int)
Returns
byte
readString()
Description 读取字符到一个字符串,直到超时
Serial.readString() reads characters from the serial buffer into a string. The function terminates if it times out (see setTimeout()).
This function is part of the Stream class, and is called by any class that inherits from it (Wire, Serial, etc). See the Stream class main page for more information.
Syntax
Serial.readString()
Parameters
none
Returns
A string read from the serial buffer
readStringUntil()
Description 读取字符到一个字符串,遇到停止符停止读取
readStringUntil() reads characters from the serial buffer into a string. The function terminates if the terminator character is detected or it times out (see setTimeout()).
This function is part of the Stream class, and is called by any class that inherits from it (Wire, Serial, etc). See the Stream class main page for more information.
Syntax
Serial.readStringUntil(terminator)
Parameters
terminator : the character to search for (char)
Returns
The entire string
Serial.setTimeout()
Description 等待读数据时的最大时间(单位为毫秒),缺省值为1000
Serial.setTimeout() sets the maximum milliseconds to wait for serial data when using Serial.readBytesUntil(), Serial.readBytes(), Serial.parseInt() or Serial.parseFloat(). It defaults to 1000 milliseconds.
Serial.setTimeout() inherits from the Stream utility class.
Syntax
Serial.setTimeout(time)
Parameters
time : timeout duration in milliseconds (long).
Returns
None
write()
Description 输出二进制数据到串口。发送数据本身,收到数据后显示时会将该数据当作ASCII码而显示其对应的字符
Writes binary data to the serial port. This data is sent as a byte or series of bytes; to send the characters representing the digits of a number use the print() function instead.
Syntax
Serial.write(val)
Serial.write(str)
Serial.write(buf, len)
Arduino Mega also supports: Serial1, Serial2, Serial3 (in place of Serial)
Parameters
val: a value to send as a single byte
str: a string to send as a series of bytes
buf: an array to send as a series of bytes
len: the length of the buffer
Returns
byte
write() will return the number of bytes written, though reading that number is optional
Example
1 byte BYTE[3]={49,50,51};
2
3 void setup()
4
5 {
6
7 Serial.begin(9600);
8
9 }
10
11 void loop()
12
13 {
14
15 Serial.write(45); // send a byte with the value 45
16
17 Serial.println();
18
19 Serial.write(BYTE,3); // send a byte with the value 45
20
21 Serial.println();
22
23 int bytesSent = Serial.write("hello"); //send the string “hello” and return the length of the string.
24
25 Serial.println();
26
27 while(1)
28
29 { }
30
31 }
运行结果如下图
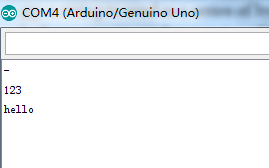
十进制数45对应的ASCII字符为“-”,十进制数49,50,51对应的ASCII字符为1,2,3,字符“HELLO”原码输出。
serialEvent()
Description 串口缓冲区有数据则执行该函数
Called when data is available. Use Serial.read() to capture this data.
NB : Currently, serialEvent() is not compatible with the Esplora, Leonardo, or Micro
Syntax
void serialEvent()
{
//statements
}
Arduino Mega only:
void serialEvent1()
{
//statements
}
void serialEvent2()
{
//statements
}
void serialEvent3()
{
//statements
}
Parameters
statements: any valid statements
Arduino 串口库函数的更多相关文章
- Arduino 串口通讯参考笔记 - Serial 类库及相关函数介绍
声明: 本ID发布的所有文章及随笔均为原创,可随意转载,单转载文章必须注明作者 aiyauto 及包含原文出处地址 http://www.cnblogs.com/aiyauto/p/7071712.h ...
- win10上使用php与python实现与arduino串口通信
注意: php 需要php7,安装及开启php_dio.dll com口按照实际的进行设置,如果不知道可以打开arduino编辑器进行查看 可以与用户实现命令行交互,但是效率过慢,不清楚如何优化,使用 ...
- Arduino串口的一些高级用法
1.配置串口通信数据位.校验位.停止位通常我们使用Serial.begin(speed)来完成串口的初始化,这种方式,只能配置串口的波特率.而使用Serial.begin(speed, config) ...
- Arduino 串口的一些高级用法
来源: 1.配置串口通信数据位.校验位.停止位 通常我们使用Serial.begin(speed)来完成串口的初始化,这种方式,只能配置串口的波特率. 而使用Serial.begin(speed, c ...
- Arduino - 串口操作函数与示例代码大全
来源:https://blog.csdn.net/iracer/article/details/50334041 Arduino - 串口操作函数与示例代码大全 本文总结了Arduino常用串口操作函 ...
- arduino 串口实时绘图(以mpu9250为例)
兴趣之余,利用晚上的时间,做一些个人兴趣方面的开发. 之前没接触过 arduino, 无意之中买了个开发板做一些小开发, 这里利用python 读取 mpu9250 数据实时绘图. 下位机代码 C++ ...
- ASCIITable: 演示 Arduino 串口输出的进阶功能
原文地址 - https://www.arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/ASCIITable ASCII字符表 本例展示了高级的串口打印功能,通过本功能可以在Arduino软件(IDE)的 ...
- 修改Arduino串口缓冲区大小(转)
本帖节选自<Arduino程序设计基础>第二版5.1.6串口缓冲区 在之前的示例程序中,我们都是采用人工输入测试数据的方式检验程序效果,Arduino每接收到一次数据,就会将数 ...
- Arduino 串口篇 Arduino发送二进制 send binary via RS232-to-USB to PC
有用的链接在这里:http://hi.baidu.com/mizuda/item/06b7fdc1d0e45a0ec710b2dd 更加详细的内容请查阅Arduino官方:http://arduino ...
随机推荐
- Apache Pulsar 社区周报:08-08 ~ 08-14
关于 Apache Pulsar Apache Pulsar 是 Apache 软件基金会顶级项目,是下一代云原生分布式消息流平台,集消息.存储.轻量化函数式计算为一体,采用计算与存储分离架构设计,支 ...
- C++轻量级跨平台文件系统API
http://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/experimental/fs https://www.starmessagesoftware.com/cpcclibrary htt ...
- Pandoanload涅槃重生,小白羊重出江湖?
Pandoanload涅槃重生,小白羊重出江湖? 科技是把双刃剑,一方面能够砸烂愚昧和落后,另一方面也可能带给人类无尽的灾难. 原子物理理论的发展是的人类掌握了核能技术但是也带来了广岛和长崎的核灾难, ...
- Activiti7 学习总结
什么是工作流? 就是通过计算机对业务流程进行自动化处理,实现多个参与者按照预定义的流程去自动执行业务流程 什么是Activiti? Activiti是一个工作流引擎,开源的架构,基于BPMN2.0标准 ...
- Python3 字典浅析
Python 字典 字典(Dictionary) 字典是一个无序.可变和有索引的集合.在 Python 中,字典用花括号编写,拥有键和值. 实例 创建并打印字典: thisdict = { " ...
- C:算术表达式求值
代码: // fgets2.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点. // #include "stdafx.h" #include <stdio.h> #includ ...
- Sentinel使用
Sentinel控制台的功能主要包括:流量控制.降级控制.热点配置.系统规则和授权规则等 # 安装sentinel的控制台 ## 下载地址 Sentinel控制台下载地址: https://githu ...
- leetcode刷题-60第k个队列
题目 给出集合 [1,2,3,…,n],其所有元素共有 n! 种排列. 按大小顺序列出所有排列情况,并一一标记,当 n = 3 时, 所有排列如下: "123""132& ...
- 【GDKOI2004】汉诺塔
题目描述 古老的汉诺塔问题是这样的:用最少的步数将N个半径互不相等的圆盘从1号柱利用2号柱全部移动到3号柱,在移动的过程中小盘要始终在大盘的上面. 现在再加上一个条件:不允许直接把盘从1号柱移动到3号 ...
- 动手编写—动态数组(Java实现)
目录 数组基础回顾 自定义动态数组 动态数组的设计 抽象父类接口设计 抽象父类设计 动态数组之DynamicArray 补充数组缩容 全局的关系图 声明 数组基础回顾 1.数组是一种常见的数据结构,用 ...
