解析SwiftUI布局细节(三)地图的基本操作
前言
前面的几篇文章总结了怎样用 SwiftUI 搭建基本框架时候的一些注意点(和这篇文章在相同的分类里面,有需要了可以点进去看看),这篇文章要总结的东西是用地图数据处理结合来说的,通过这篇文章我们能总结到的点有下面几点:
1、SwiftUI怎样使用UIKit的控件
2、网络请求到的数据我们怎样刷新页面(模拟)
3、顺便总结下系统地图的一些基本使用(定位、地图显示、自定义大头针等等)
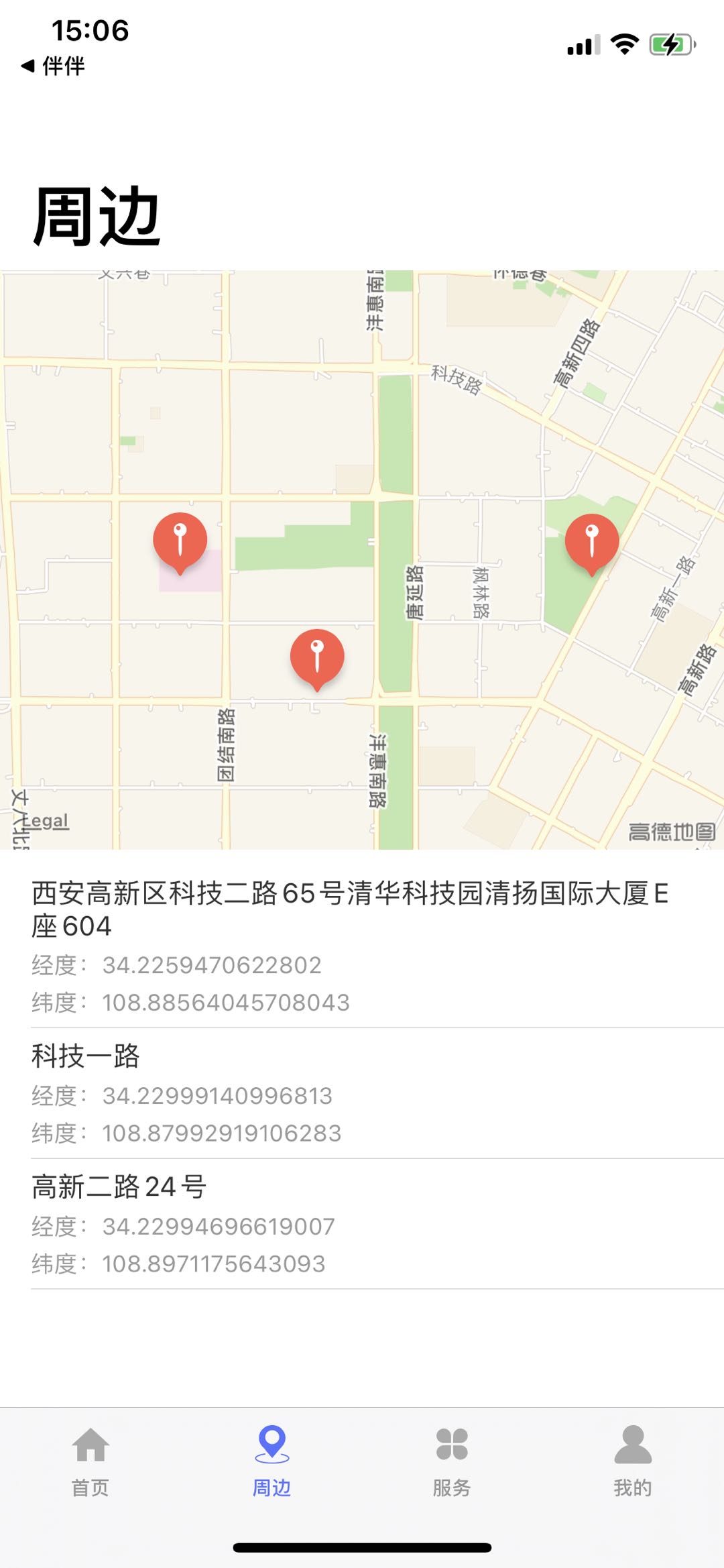
(点击地图位置会获取经纬度,反地理编译得到具体的位置信息,显示在列表中)
SwiftUI怎样使用UIKit的控件
我们来总结一下,SwiftUI怎么使用UIKit的控件,中间的连接就是 UIViewRepresentable,UIViewRepresentable 是一个协议。我们结合他的源码来具体看看它的内容:
@available(iOS 13.0, tvOS 13.0, *)
@available(macOS, unavailable)
@available(watchOS, unavailable)
public protocol UIViewRepresentable : View where Self.Body == Never { /// The type of view to present.
associatedtype UIViewType : UIView /// Creates the view object and configures its initial state.
///
/// You must implement this method and use it to create your view object.
/// Configure the view using your app's current data and contents of the
/// `context` parameter. The system calls this method only once, when it
/// creates your view for the first time. For all subsequent updates, the
/// system calls the ``UIViewRepresentable/updateUIView(_:context:)``
/// method.
///
/// - Parameter context: A context structure containing information about
/// the current state of the system.
///
/// - Returns: Your UIKit view configured with the provided information.
func makeUIView(context: Self.Context) -> Self.UIViewType /// Updates the state of the specified view with new information from
/// SwiftUI.
///
/// When the state of your app changes, SwiftUI updates the portions of your
/// interface affected by those changes. SwiftUI calls this method for any
/// changes affecting the corresponding UIKit view. Use this method to
/// update the configuration of your view to match the new state information
/// provided in the `context` parameter.
///
/// - Parameters:
/// - uiView: Your custom view object.
/// - context: A context structure containing information about the current
/// state of the system.
func updateUIView(_ uiView: Self.UIViewType, context: Self.Context) static func dismantleUIView(_ uiView: Self.UIViewType, coordinator: Self.Coordinator) /// A type to coordinate with the view.
associatedtype Coordinator = Void func makeCoordinator() -> Self.Coordinator typealias Context = UIViewRepresentableContext<Self>
}
上面的代码可以分析出 UIViewRepresentable 是一个协议,它也是遵守了 View 这个协议的,条件就是内容不能为空,它有一个关联类型 (associatedtype UIViewType : UIView) , 看看源码你知道这个 UIViewType 是个关联类型之后也明白后面中使用的一些问题( 还是得理解不能去记它的用法 ),里面的下面两个方法是我们使用的:
func makeUIView(context: Self.Context) -> Self.UIViewType func updateUIView(_ uiView: Self.UIViewType, context: Self.Context)
按照我的理解,第一个方法就像一个初始化方法,返回的就是你SwiftUI想用的UIKit的控件对象。
第二个方法是我们用来更新UIKit控件的方法
理解前面加我们提的关联类型,那我们在第一个方法返回的对象类型就是你要使用的UIKit的类型,第二个方法更新的View也就是我们UIKit的控件。在我们的Demo中就是 MKMapView 。
接下来还有一点,我们既然点击地图之后需要给我们点击的位置添加一个大头针并且去获取这个点的经纬度,那我们首先第一步就是必须得给地图添加一个单击手势,具体的我们怎么做呢?首先有一点,在SwiftUI中我们创建的View都是Struct类型,但手势的事件是#selector(),本质上还是OC的东西,所以在事件前面都是带有@Obic的修饰符的,但你要是Struct类型肯定是行不通的,那怎么办呢?其实 UIViewRepresentable 已经帮我们把这步预留好了,就是下面的这个关联类型:
/// A type to coordinate with the view.
associatedtype Coordinator = Void
具体的返回就是在下面方法,大家具体的看看这个方法给的简介说明,就明白了:
/// Creates the custom instance that you use to communicate changes from
/// your view to other parts of your SwiftUI interface.
///
/// Implement this method if changes to your view might affect other parts
/// of your app. In your implementation, create a custom Swift instance that
/// can communicate with other parts of your interface. For example, you
/// might provide an instance that binds its variables to SwiftUI
/// properties, causing the two to remain synchronized. If your view doesn't
/// interact with other parts of your app, providing a coordinator is
/// unnecessary.
///
/// SwiftUI calls this method before calling the
/// ``UIViewRepresentable/makeUIView(context:)`` method. The system provides
/// your coordinator either directly or as part of a context structure when
/// calling the other methods of your representable instance. func makeCoordinator() -> Self.Coordinator
再具体点的使用我们这里不详细说明了,大家直接看Demo中的代码,我们添加完点击事件之后要做的就是一个点击坐标的转换了,你获取到你点击的地图的Point,你就需要通过MKMapView的点击职位转换经纬度的方法去获取点击位置的经纬度信息,下面这个方法:
open func convert(_ point: CGPoint, toCoordinateFrom view: UIView?) -> CLLocationCoordinate2D
获取到点击位置的经纬度,就可以继续往下看了,下面会说明把点击的这个位置添加到数据源之后怎样去更新地图上面的信息。
网络请求到的数据我们怎样刷新页面(模拟)
关于刷新数据这个是比较简单的,用到的就是我们前面提的绑定数据的模式,这点真和Rx挺像的,你创建了一个列表,然后给列表绑定了一个数组数据源,等你网络请求到数据之后,你需要处理的就是去改变这个数据源的数据,它就能去刷新它绑定的UI。
在前面第一小节我们提到了地图获取到点击的经纬度之后怎样更新地图上面的信息,其实用的也是这点,绑定数据刷新!我们在初始化AroundMapView的时候给它绑定了 userLocationArray 这个数据,具体的就没必要细说了,看代码能理解这部分的东西!
其实在我们使用UIKit的时候如许多的复用问题我们基本上都是通过写数据再Model里面去解决的,SwiftUI 也不例外。我们来看看我们 List 绑定部分的代码:
/// 地址List
List(aroundViewModel.userLocationArray, id: \.self){ model in /// List 里面的具体View内容
}.listStyle(PlainListStyle())
我们给List绑定的是 AroundViewModel 的 userLocationArray 数组,那这个数组我们又是怎样定义的呢?
///
@Published var userLocationArray:Array<UserLocation> = Array()
我们使用的是 @Published 关键字,如果你用 @ObservedObject 来修饰一个对象 (Demo中用的是 @EnvironmentObject ),那么那个对象必须要实现 ObservableObject 协议( AroundViewModel 实现了 ObservableObject 协议 ),然后用 @Published 修饰对象里属性,表示这个属性是需要被 SwiftUI 监听,这句话就能帮我们理解它的用法。
那接下来我们只需要关心这个数据源的增删就可以了。就像我们在定位成功之后添加数据一样,代码如下:
init() {
/// 开始定位
userLocation { (plackMark) in
/// mkmapView监听了这个属性的,这里改变之后是会刷新地图内容的
/// 在AroundMapView里面我们以这个点为地图中心点
self.userLocationCoordinate = plackMark.location!.coordinate
print("aroundLocationIndex-1:",aroundLocationIndex)
let locationModel = UserLocation(id: aroundLocationIndex,
latitude: plackMark.location?.coordinate.latitude ?? 0.000000,
longitude: plackMark.location?.coordinate.longitude ?? 0.000000,
location: plackMark.thoroughfare ?? "获取位置出错啦~")
self.userLocationArray.append(locationModel)
print("aroundLocationIndex-1:",self.userLocationArray)
/// 加1
aroundLocationIndex += 1
}
}
通过上面的解析应该了解了请求到数据之后我们怎样去刷新UI的问题。
地图使用
我们结合SwiftUI总结一下地图的使用,这部分的代码去Demo看比较有效果,地图我们使用 CoreLocation 框架,在这个 Demo 中我们使用到的关于 CoreLocation 的东西主要有下面几点:
1、CLLocationManager & CLLocationManagerDelegate(定位)
2、CLGeocoder (地理编码和反地理编码)
3、CLPlacemark、CLLocation、CLLocationCoordinate2D (几个位置类)和 MKAnnotationView (大头针)
我们先来看看 CLLocationManager & CLLocationManagerDelegate
/// manager
lazy var locationManager: CLLocationManager = { let locationManager = CLLocationManager()
locationManager.delegate = self
/// 导航级别
/*
kCLLocationAccuracyBestForNavigation /// 适合导航
kCLLocationAccuracyBest /// 这个是比较推荐的综合来讲,我记得百度也是推荐
kCLLocationAccuracyNearestTenMeters /// 10m
kCLLocationAccuracyHundredMeters /// 100m
kCLLocationAccuracyKilometer /// 1000m
kCLLocationAccuracyThreeKilometers /// 3000m
*/
locationManager.desiredAccuracy = kCLLocationAccuracyBest
/// 隔多少米定位一次
locationManager.distanceFilter = 10
return locationManager
}()
上面我们定义了一个 CLLocationManager,加下来就是开始定位了,在开始定位之前我们要做的一件事就肯定是判断用户位置信息有没有开启,具体的是否开启权限判断和判断后的回调方法代码如下所示,代码注释写的很详细,我们这里也不做累赘。
判断有没有开始获取位置权限:
/// 先判断用户定位是否可用 默认是不启动定位的
if CLLocationManager.locationServicesEnabled() { /// userLocationManager.startUpdatingLocation()
/// 单次获取用户位置
locationManager.requestLocation()
}else{ /// plist添加 NSLocationWhenInUseUsageDescription NSLocationAlwaysUsageDescription
/// 提个小的知识点,以前我们写这个内容的时候都比较随意,但现在按照苹果的审核要求
/// 你必须得明确说明他们的使用意图,不然会影响审核的,不能随便写个需要访问您的位置
/// 请求使用位置 前后台都获取
locationManager.requestAlwaysAuthorization()
/// 请求使用位置 前台都获取
/// userLocationManager.requestWhenInUseAuthorization()
}
获取权限之后的回调方法以及各种状态的判断代码如下:
/// 用户授权回调
/// - Parameter manager: manager description
/// open > public > interal > fileprivate > private
func locationManagerDidChangeAuthorization(_ manager: CLLocationManager) { /// CLAuthorizationStatus
switch manager.authorizationStatus { case .notDetermined:
print("用户没有决定")
case .authorizedWhenInUse:
print("使用App时候允许")
case .authorizedAlways:
print("用户始终允许")
case.denied:
print("定位关闭或者对此APP授权为never")
/// 这种情况下你可以判断是定位关闭还是拒绝
/// 根据locationServicesEnabled方法
case .restricted:
print("访问受限")
@unknown default:
print("不确定的类型")
}
}
当定位权限打开之后我们就开始了获取位置,单次获取具体位置的方法调用上面代码有,就是 requestLocation() 方法,接下来就是成功和失败的方法处理了,下面两个方法:
/// 获取更新到的用户位置
/// - Parameters:
/// - manager: manager description
/// - locations: locations description
func locationManager(_ manager: CLLocationManager, didUpdateLocations locations: [CLLocation]) { print("纬度:" + String(locations.first?.coordinate.latitude ?? 0))
print("经度:" + String(locations.first?.coordinate.longitude ?? 0))
print("海拔:" + String(locations.first?.altitude ?? 0))
print("航向:" + String(locations.first?.course ?? 0))
print("速度:" + String(locations.first?.speed ?? 0)) /*
纬度34.227653802098665
经度108.88102549186357
海拔410.17602920532227
航向-1.0
速度-1.0
*/
/// 反编码得到具体的位置信息
guard let coordinate = locations.first else { return }
reverseGeocodeLocation(location: coordinate )
} /// 获取失败回调
/// - Parameters:
/// - manager: manager description
/// - error: error description
func locationManager(_ manager: CLLocationManager, didFailWithError error: Error) { print("定位Error:" + error.localizedDescription)
guard let locationFail = self.locationFail else{return}
locationFail(error.localizedDescription)
}
这样我们就拿到你的具体位置信息,回到给你的就是一个元素是 CLLocation 类型的数组,我们在Demo中只取了First,你拿到的是经纬度,你要想获取这个经纬度的具体位置信息就得经过反地理编码,拿到某某市区某某街道某某位置的信息,在CoreLocation中做地理编码和反地理编码的就是 CLGeocoder 这个类,它的 reverseGeocodeLocation 就是反地理编码方法, 地理拜纳姆的方法就是 geocodeAddressString 。具体的我们看看Demo中的方法:
地理编码方法:(具体位置信息 -> 经纬度)
/// 地理编码
/// - Parameter addressString: addressString description
private func geocodeUserAddress(addressString:String) { locationGeocoder.geocodeAddressString(addressString){(placeMark, error) in print("地理编码纬度:",placeMark?.first?.location?.coordinate.latitude ?? "")
print("地理编码经度:",placeMark?.first?.location?.coordinate.longitude ?? "")
}
}
反地理编码方法:( 经纬度 -> 具体位置信息 )
/// 反地理编码定位得到的位置信息
/// - Parameter location: location description
private func reverseGeocodeLocation(location:CLLocation){ locationGeocoder.reverseGeocodeLocation(location){(placemark, error) in /// city, eg. Cupertino
print("反地理编码-locality:" + (placemark?.first?.locality ?? ""))
/// eg. Lake Tahoe
print("反地理编码-inlandWater:" + (placemark?.first?.inlandWater ?? ""))
/// neighborhood, common name, eg. Mission District
print("反地理编码-subLocality:" + (placemark?.first?.subLocality ?? ""))
/// eg. CA
print("反地理编码-administrativeArea:" + (placemark?.first?.administrativeArea ?? ""))
/// eg. Santa Clara
print("反地理编码-subAdministrativeArea:" + (placemark?.first?.subAdministrativeArea ?? ""))
/// eg. Pacific Ocean
print("反地理编码-ocean:" + (placemark?.first?.ocean ?? ""))
/// eg. Golden Gate Park
print("反地理编码-areasOfInterest:",(placemark?.first?.areasOfInterest ?? [""]))
/// 具体街道信息
print("反地理编码-thoroughfare:",(placemark?.first?.thoroughfare ?? "")) /// 回调得到的位置信息
guard let locationPlacemark = placemark?.first else{return}
guard let locationSuccess = self.locationSuccess else{return}
locationSuccess(locationPlacemark)
/// 地理编码位置,看能不能得到正确经纬度
self.geocodeUserAddress(addressString: (placemark?.first?.thoroughfare ?? ""))
}
}
最后我们梳理一下关于大头针的几个类,我们在项目中使用的是 MKPointAnnotation
MKPointAnnotation 继承与 MKShape 遵守了 MKAnnotation 协议 , MKAnnotation 就是底层的协议了,像它里面的title,image这些属性我们就不提了,大家可以点进去看看源码。
MKMapView 有个 MKMapViewDelegate 代理方法,它具体的方法可以点进这个协议去看,里面有个方法是
- (nullable MKAnnotationView *)mapView:(MKMapView *)mapView viewForAnnotation:(id <MKAnnotation>)annotation;
它返回的是一个 MKAnnotationView ,这个方法也为每个 大头针 MKAnnotation 提供了一个自定义的View,也就是我们自定义大头针的位置。这样地图基本的东西我们也就说的差不多了,最后要提的一点是获取到位置的经纬度类型,我们经常使用的百度、高德等的地图它们定位得到的经纬度坐标类型是不一样的,它们之间的联系我们再梳理一下。
什么是国测局坐标、百度坐标、WGS84坐标 ?三种坐标系说明如下:
* WGS84:表示GPS获取的坐标;
** GCJ02:是由中国国家测绘局制订的地理信息系统的坐标系统。由WGS84坐标系经加密后的坐标系。
*** BD09:为百度坐标系,在GCJ02坐标系基础上再次加密。其中bd09ll表示百度经纬度坐标,bd09mc表示百度墨卡托米制坐标;百度地图SDK在国内(包括港澳台)使用的是BD09坐标;在海外地区,统一使用WGS84坐标。
参考文章:
解析SwiftUI布局细节(三)地图的基本操作的更多相关文章
- 解析SwiftUI布局细节(二)循环轮播+复杂布局
前言 上一篇我们总结的主要是VStack里面的东西,由他延伸到 @ViewBuilder, 接着我们上一篇总结的我们这篇内容主要说的是下面的几点,在这些东西说完后我准备解析一下苹果在SiwftUI文档 ...
- 解析SwiftUI布局细节(一)
前言 在前面的文章中谈了谈对SwiftUI的基本的认识,以及用我们最常见的TB+NA的方式搭建了一个很基本的场景来帮助认识了一下SwiftUI,具体的文章可以在SwiftUI分类部分查找,这篇我准备在 ...
- MeteoInfo-Java解析与绘图教程(三)
MeteoInfo-Java解析与绘图教程(三) 上文我们说到简单绘制色斑图(卫星云图),但那种效果可定不符合要求,一般来说,客户需要的是在地图上色斑图的叠加,或者是将图片导出分别是这两种效果 当然还 ...
- 解析Xml文件的三种方式及其特点
解析Xml文件的三种方式 1.Sax解析(simple api for xml) 使用流式处理的方式,它并不记录所读内容的相关信息.它是一种以事件为驱动的XML API,解析速度快,占用内存少.使用 ...
- 三、Redis基本操作——List
小喵的唠叨话:前面我们介绍了Redis的string的数据结构的原理和操作.当时我们提到Redis的键值对不仅仅是字符串.而这次我们就要介绍Redis的第二个数据结构了,List(链表).由于List ...
- css常见的各种布局下----三列布局
css 三列布局,左右固定宽度右边自适应 1不使用定位,只使用浮动可以实现左右固定,中间宽度自适应布局 1.1.1 自适应部分一定要放第一个位子,使用浮动,并且设置宽度为100%,不设置浮动元素内容不 ...
- TiKV 源码解析系列文章(三)Prometheus(上)
本文为 TiKV 源码解析系列的第三篇,继续为大家介绍 TiKV 依赖的周边库 rust-prometheus,本篇主要介绍基础知识以及最基本的几个指标的内部工作机制,下篇会介绍一些高级功能的实现原理 ...
- react解析: render的FiberRoot(三)
react解析: render的FiberRoot(三) 感谢 yck: 剖析 React 源码解析,本篇文章是在读完他的文章的基础上,将他的文章进行拆解和加工,加入我自己的一下理解和例子,便于大家理 ...
- arcgis api for javascript 学习(四) 地图的基本操作
1.文章讲解的为地图的平移.放大.缩小.前视图.后视图以及全景视图的基本功能操作 2.主要用到的是arcgis api for javascript中Navigation的用法,代码如下: <! ...
随机推荐
- Python模块学习遇到的问题
Python使用import导入模块时报ValueError: source code string cannot contain null bytes的解决方案 Python使用import导入模块 ...
- Django链接mysql数据库报错1064
D:\PycharmProjects\autotest>python manage.py makemigrations django.db.utils.ProgrammingError: (10 ...
- Day7 【Scrum 冲刺博客】
每日会议总结 昨天已完成的工作 方晓莹(PIPIYIng) 对接车位管理接口 处理对接接口遇到的bug和错误 方子茵(Laa-L) 暂无 黄芯悦(Sheaxx) 完成住户车位查询页面 完成住户物业报修 ...
- 调用windows系统下的cmd命令窗口处理文件
从后缀名为grib2的文件中查询相关的信息,并将查出来的信息保存起来. 主要是学习java中调用windows下的cmd平台,并进行执行相关的命令. package com.wis.wgrib2; i ...
- STL——容器(Set & multiset)之 仿函数(函数对象)functor 的用法
Set/multiset 中元素的存储数据总是会按照从大到小或者从小到大排列,这个是怎么实现的?这就要说 "仿函数" 这个概念了. 仿函数概念 1. 尽管函数指针被广泛用于实现函数 ...
- Hyper-v 虚拟机使用NAT方式连接网络
最近因为搞docker的原因,卸掉了vb和vm,用上了hyper. 其实一直挺喜欢hyper-v的,但是一直都受虚拟网络的影响--hyper-v创建不了vm和vb使用的那种NAT连接方式. 默认使用外 ...
- Kubernetes弃用Docker后怎么办?
本文转自Rancher Labs 近期,Kubernetes在其最新的Changelog中宣布,自Kubernetes 1.20之后将弃用Docker作为容器运行时.这一消息在云原生领域激起了不小的水 ...
- Struts2-059 漏洞复现
0x00 漏洞简介 Apache Struts框架, 会对某些特定的标签的属性值,比如id属性进行二次解析,所以攻击者可以传递将在呈现标签属性时再次解析的OGNL表达式,造成OGNL表达式注入.从而可 ...
- Centos7.6上部署Supervisor来监控和操作各类服务
supervisor 是用Python开发的一个client/server服务,是Linux/Unix系统下的一个进程管理工具,不支持Windows系统.它可以很方便的监听.启动.停止.重启一个 ...
- Vue 打包部署上线
1,VUE逻辑编写完成后在当前项目下打包 npm run build 需要注意的是,当打包完毕后,需要将入口的index.html的项目dist路径改成相对路径 另外需要注意的一点是,一旦打包vue. ...
