有向图的基本算法-Java实现
有向图
有向图同无向图的区别为每条边带有方向,表明从一个顶点至另一个顶点可达。有向图的算法多依赖深度搜索算法。
本文主要介绍有向图的基本算法,涉及图的表示、可达性、检测环、图的遍历、拓扑排序以及强连通检测等算法。
1 定义有向图
采用邻接表结构存储边信息,同时提供reverse接口生成反向图,倒置每个边的方向,该接口在后续其他算法中会用到。
/*** 采用邻接表表示的有向图*/public class DiGraph {private final int V;private int E;private ArrayList<Integer>[] adj;public DiGraph(int V){this.V = V;E = 0;adj = new ArrayList[V];for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {adj[i] = new ArrayList<>();}}public DiGraph(Scanner scanner){this(scanner.nextInt());int E = scanner.nextInt();for (int i = 0; i < E; i++) {int v = scanner.nextInt();int w = scanner.nextInt();addEdge(v, w);}}public void addEdge(int v, int w){// 添加一条v指向w的边adj[v].add(w);E++;}/*** 返回有向图的反向图, 将每条边的方向反转*/public DiGraph reverse(){DiGraph diGraph = new DiGraph(V);for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) {for (int w : adj[v]) {diGraph.addEdge(w, v);}}return diGraph;}public void show() {System.out.println("V: " + V);System.out.println("E: " + E);for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {System.out.print(i + ": ");for (Integer integer : adj[i]) {System.out.print(integer + " ");}System.out.println();}}public static void main(String[] args) {Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);// 输入用例参加附录1DiGraph diGraph = new DiGraph(scanner);// 输入结果见附录2diGraph.show();}}
2 有向图的可达性
有向图的可达性是指给定一个或一组顶点,判断是否可以到达图中其他顶点。垃圾清除常见算法“标记-清除”算法中,采用有向图的可达性算法
标记所有可以被访问的对象,然后在回收阶段,仅仅回收那些未被标记的对象。
/*** 基于深度优先的有向图可达性算法* 求出给定顶点或一组顶点,有向图中能到达的点*/public class DirectedDFS {private boolean[] marked; // 标记每个顶点是否可到达public DirectedDFS(DiGraph G, int s){marked = new boolean[G.V()];dfs(G, s);}public DirectedDFS(DiGraph G, Iterable<Integer> sources){marked = new boolean[G.V()];for (int v : sources) {if(!marked[v]){dfs(G, v);}}}private void dfs(DiGraph G, int v){marked[v] = true;for (int w : G.adj(v)) {if(!marked[w])dfs(G, w);}}public boolean marked(int v) { return marked[v]; }public static void main(String[] args) {// 输入用例参加附录1DiGraph diGraph = new DiGraph(new Scanner(System.in));// 输出结果参加附录3// 测试顶点2到达的点System.out.println("顶点2到达的点");DirectedDFS reachable = new DirectedDFS(diGraph, 2);for (int i = 0; i < diGraph.V(); i++)if(reachable.marked(i)) System.out.print(i + " ");System.out.println();// 测试一组点:1,2,6能够到达的点System.out.println("1,2,6能够到达的点");DirectedDFS reachable2 = new DirectedDFS(diGraph, Arrays.asList(1, 2, 6));for (int i = 0; i < diGraph.V(); i++)if(reachable2.marked(i)) System.out.print(i + " ");System.out.println();}}
3 单点有向路径和单点最短有向路径
分别采用深度优先搜索和广度优先搜索实现
有向图的路径
/*** 单点有向路径,给定顶点v,确定对于图中任一点w;* 是否存在v到w的路径,并输出路径;* 注意,深度优先搜索的路径无法保证是最短路径*/public class DigraghDepthFirstPaths {// 标记点是否可达private boolean[] marked;// 记录到达点的那条边private int[] edge;private final int s;public DigraghDepthFirstPaths(DiGraph G, int s){this.s = s;marked = new boolean[G.V()];edge = new int[G.V()];edge[s] = s;dfs(G, s);}private void dfs(DiGraph G, int v){marked[v] = true;for (int w : G.adj(v)) {if(!marked[w]){edge[w] = v;dfs(G, w);}}}public boolean hasPathTo(int v){ return marked[v]; }public Stack<Integer> pathTo(int v){Stack<Integer> paths = new Stack<>();for (int x=v; x!=s; x=edge[x]){paths.add(x);}paths.add(s);return paths;}public static void main(String[] args) {// 输入用例参加附录1DiGraph diGraph = new DiGraph(new Scanner(System.in));// 输出结果参加附录4// 构建顶点0到其他顶点的有向路径DigraghDepthFirstPaths depthFirstPaths = new DigraghDepthFirstPaths(diGraph, 0);System.out.print("顶点0可达的点: ");for (int i = 0; i < diGraph.V(); i++) {if (depthFirstPaths.hasPathTo(i)) System.out.print(i + " ");}System.out.println();// 是否存在有向路径if(depthFirstPaths.hasPathTo(12))System.out.println("0至12存在有向路径");elseSystem.out.println("0至12不存在有向路径");// 顶点0到顶点3的一条有向路径System.out.print("0至3的一条有向路径: ");Stack<Integer> pathTo = depthFirstPaths.pathTo(3);while (!pathTo.isEmpty()){if (pathTo.size() == 1)System.out.print(pathTo.pop());elseSystem.out.print(pathTo.pop() + " -> ");}System.out.println();}}
有向图的最短路径,基于广度优先算法
/*** 基于广度优先搜索的单向路径算法;* 在此方法下,求得的路径为最短路径(忽略边权重)*/public class DigraphBreadthFirstPaths {private boolean[] marked;// 采用队列保持带访问的顶点private ArrayDeque<Integer> enqueue;private int[] edge;private final int s;public DigraphBreadthFirstPaths(DiGraph G, int s){this.s = s;marked = new boolean[G.V()];edge = new int[G.V()];enqueue = new ArrayDeque<>();enqueue.add(s);bfs(G);}private void bfs(DiGraph G){while (!enqueue.isEmpty()){int v = enqueue.poll();for (int w : G.adj(v)) {if(!marked[w]){edge[w] = v;marked[w] = true;enqueue.add(w);}}}}public boolean hasPathTo(int v){ return marked[v]; }public Stack<Integer> pathTo(int v){Stack<Integer> paths = new Stack<>();for (int x=v; x!=s; x=edge[x]){paths.add(x);}paths.add(s);return paths;}public static void main(String[] args) {// 输入用例参加附录1DiGraph diGraph = new DiGraph(new Scanner(System.in));// 输出结果参加附录5// 构建顶点0到其他顶点的有向路径DigraphBreadthFirstPaths breadthFirstPaths = new DigraphBreadthFirstPaths(diGraph, 0);System.out.print("顶点0可达的点: ");for (int i = 0; i < diGraph.V(); i++) {if (breadthFirstPaths.hasPathTo(i)) System.out.print(i + " ");}System.out.println();// 是否存在有向路径if(breadthFirstPaths.hasPathTo(12))System.out.println("0至12存在有向路径");elseSystem.out.println("0至12不存在有向路径");// 顶点0到顶点3的最短路径System.out.print("0至3的一条有向路径: ");Stack<Integer> pathTo = breadthFirstPaths.pathTo(3);while (!pathTo.isEmpty()){if (pathTo.size() == 1)System.out.print(pathTo.pop());elseSystem.out.print(pathTo.pop() + " -> ");}System.out.println();}}
4 检测有向图的环
检测有向图是否包含环,检测图没有环是拓扑排序的前提条件。
多数情况下,需要知道有向图是否包含环,并且输出够成环的边。
/*** 基于深度优先搜索检测图中是否包含环*/public class DirectedCycle {private boolean[] onStack;private Stack<Integer> cycle;private int[] edge;private boolean[] marked;public DirectedCycle(DiGraph G){onStack = new boolean[G.V()];edge = new int[G.V()];marked = new boolean[G.V()];for (int i = 0; i < G.V(); i++) {if(!marked[i])dfs(G, i);}}private void dfs(DiGraph G, int v){onStack[v] = true;marked[v] = true;for (int w : G.adj(v)) {if (this.hasCycle()) return;else if (!marked[w]){edge[w] = v; dfs(G, w); }// onStack[w]为true表明,当前v节点是一条经过w的抵达,表明w -> v有路径// 由于v -> w有边,因此必为环else if(onStack[w]){cycle = new Stack<>();for (int x = v; x != w; x=edge[x])cycle.push(x);cycle.push(w);cycle.push(v);}}onStack[v] = false;}public boolean hasCycle(){ return cycle != null; }public Iterable<Integer> cycle() { return cycle; }public static void main(String[] args) {// 输入用例参加附录1DiGraph diGraph = new DiGraph(new Scanner(System.in));// 输出结果参加附录6DirectedCycle directedCycle = new DirectedCycle(diGraph);System.out.println("有向图是否包含环: " + (directedCycle.hasCycle() ? "是" : "否"));if (directedCycle.hasCycle()){System.out.print("其中一条环为:");for (int i : directedCycle.cycle()) {System.out.print(i + " ");}}System.out.println();}}
5 顶点的深度优先次序
顶点的深度优先次序分为前序、后序和逆后续,区别是记录点的时机发生在递归调用的前还是后。该算法产生的pre、post和reversePost
顺序在图的高级算法中十分有用。
public class DepthFirstOrder {private boolean[] marked;private ArrayDeque<Integer> pre; // 保存前序遍历的结果private ArrayDeque<Integer> post; // 保存后序的遍历结果private ArrayDeque<Integer> reversePost; //保存逆后序的遍历结果public DepthFirstOrder(DiGraph G){marked = new boolean[G.V()];pre = new ArrayDeque<>();post = new ArrayDeque<>();reversePost = new ArrayDeque<>();for (int v=0; v<G.V(); v++)if (!marked[v]) dfs(G, v);}private void dfs(DiGraph G, int v){marked[v] = true;pre.add(v);for (int w : G.adj(v))if(!marked[w])dfs(G, w);post.add(v);// 按post的倒序保存reversePost.addFirst(v);}public Iterable<Integer> pre(){ return pre; }public Iterable<Integer> post(){ return post; }public Iterable<Integer> reversePost(){ return reversePost; }public static void main(String[] args) {// 构造无环图的输入参见附录7DiGraph diGraph = new DiGraph(new Scanner(System.in));DepthFirstOrder depthFirstOrder = new DepthFirstOrder(diGraph);// 输出结果参加附录8// 注意:对于同一幅图,构造图的输入顺序不一致// 会导致输出不相同System.out.print("前序节点顺序: ");for (int v : depthFirstOrder.pre())System.out.print(v + " ");System.out.println();System.out.print("后续节点顺序:");for (int v : depthFirstOrder.post())System.out.print(v + " ");System.out.println();System.out.print("逆后序节点顺序:");for (int v : depthFirstOrder.reversePost())System.out.print(v + " ");}}
6 拓扑排序
给定一幅有向图,给出一组顶点排序,在有向图中,所有的边均是前面的点指向后面的点。
拓扑排序依赖图的环检测和逆后序遍历算法。
/*** 计算有向无环图中的所有顶点的拓扑排序,* 通常用于解决优先级限制下的调度问题*/public class Topological {private Iterable<Integer> order;public Topological(DiGraph G){DirectedCycle directedCycle = new DirectedCycle(G);if(!directedCycle.hasCycle())order = new DepthFirstOrder(G).reversePost();}public boolean isDAG(){ return order == null; }public Iterable<Integer> order(){ return order; }public static void main(String[] args) {// 输入用例参考附录7DiGraph diGraph = new DiGraph(new Scanner(System.in));Topological topological = new Topological(diGraph);// 输出结果参见附录9if (topological.isDAG())System.out.println("有向图带有环,无法进行拓扑排序");else{System.out.print("拓扑排序结果:");for (int v : topological.order()) {System.out.print(v + " ");}}}}
7 强联通检测
如果存在从v至w的路径,同时还存在从w至v的路径,则称v和w之间是强连通;如果一幅有向图中任意两点间都
是强连通,则这幅有向图也是强连通的。检测强连通算法依赖图的反转和逆后序遍历算法。算法比较简洁,但是
理解起来比较难,需要仔细分析理解。
/*** 有向图的强连通性,该算法依赖逆后序排序、图的反转、无向图的联通性算法*/public class SCC {private int[] id;private int count;private boolean[] marked;public SCC(DiGraph G){id = new int[G.V()];marked = new boolean[G.V()];DepthFirstOrder depthFirstOrder = new DepthFirstOrder(G.reverse());for (int v : depthFirstOrder.reversePost())if(!marked[v]) {dfs(G, v);count++;}}private void dfs(DiGraph G, int v){id[v] = count;marked[v] = true;for (int w : G.adj(v))if(!marked[w])dfs(G, w);}// 两点是否是强连通public boolean stronglyConnected(int v, int w){ return id[v] == id[w]; }// 强联通分量数public int count(){ return count; }// 节点所在的联通分量标识符public int id(int v){ return id[v]; }public static void main(String[] args) {// 带环的图,输入用例参见附录1DiGraph diGraph = new DiGraph(new Scanner(System.in));// 输出结果参见附录10SCC scc = new SCC(diGraph);System.out.println("有向图中强连通分量数:" + scc.count());System.out.println("节点6与12是否是强连通:" + (scc.stronglyConnected(6, 12) ? "是" : "否"));System.out.println("节点9与12是否是强连通:" + (scc.stronglyConnected(9, 12) ? "是" : "否"));System.out.println("输出联通分量");for (int i = 0; i < scc.count(); i++) {for (int v = 0; v < diGraph.V(); v++) {if(scc.id[v] == i)System.out.print(v + " ");}System.out.println();}}}
附录1,有向图构造数据
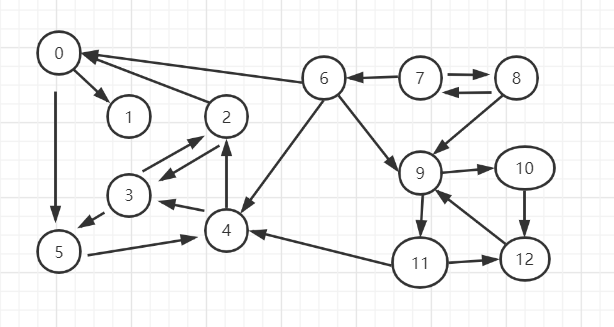
13224 22 33 26 00 12 011 1212 99 109 118 910 1211 44 33 57 88 75 40 56 46 97 6
附录2,有向图输出
V: 13E: 220: 1 51:2: 3 03: 2 54: 2 35: 46: 0 4 97: 8 68: 9 79: 10 1110: 1211: 12 412: 9
附录3:有向图的可达性测试
顶点2到达的点0 1 2 3 4 51,2,6能够到达的点0 1 2 3 4 5 6 9 10 11 12
附录4:基于深度优先搜索的单向路径测试结果
顶点0可达的点: 0 1 2 3 4 50至12不存在有向路径0至3的一条有向路径: 0 -> 5 -> 4 -> 2 -> 3
附录5:基于广度优先搜索的最短路径测试结果
顶点0可达的点: 0 1 2 3 4 50至12不存在有向路径0至3的一条有向路径: 0 -> 5 -> 4 -> 3
附录6:检测环算法的测试输出
有向图是否包含环: 是其中一条环为:3 2 4 5 3
附录7:构造无环图的输入用例
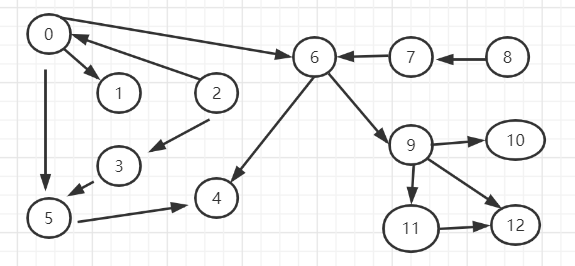
13150 10 50 62 02 33 55 46 46 97 68 79 109 119 1211 12
附录8:深度优先遍历图的输出结果
前序节点顺序: 0 1 5 4 6 9 10 11 12 2 3 7 8后续节点顺序:1 4 5 10 12 11 9 6 0 3 2 7 8逆后序节点顺序:8 7 2 3 0 6 9 11 12 10 5 4 1
附录9:拓扑排序测试输出结果
拓扑排序结果:8 7 2 3 0 6 9 11 12 10 5 4 1
附录10:带环有向图的强连通性测试输出结果
有向图中强连通分量数:5节点6与12是否是强连通:否节点9与12是否是强连通:是输出联通分量10 2 3 4 59 10 11 1267 8
有向图的基本算法-Java实现的更多相关文章
- 无向图的最短路径算法JAVA实现
一,问题描述 给出一个无向图,指定无向图中某个顶点作为源点.求出图中所有顶点到源点的最短路径. 无向图的最短路径其实是源点到该顶点的最少边的数目. 本文假设图的信息保存在文件中,通过读取文件来构造图. ...
- 无向图的最短路径算法JAVA实现(转)
一,问题描述 给出一个无向图,指定无向图中某个顶点作为源点.求出图中所有顶点到源点的最短路径. 无向图的最短路径其实是源点到该顶点的最少边的数目. 本文假设图的信息保存在文件中,通过读取文件来构造图. ...
- 归并排序算法 java 实现
归并排序算法 java 实现 可视化对比十多种排序算法(C#版) [直观学习排序算法] 视觉直观感受若干常用排序算法 算法概念 归并排序是建立在归并操作上的一种有效的排序算法,该算法是采用分治法(Di ...
- 快速排序算法 java 实现
快速排序算法 java 实现 快速排序算法Java实现 白话经典算法系列之六 快速排序 快速搞定 各种排序算法的分析及java实现 算法概念 快速排序是C.R.A.Hoare于1962年提出的一种划分 ...
- 堆排序算法 java 实现
堆排序算法 java 实现 白话经典算法系列之七 堆与堆排序 Java排序算法(三):堆排序 算法概念 堆排序(HeapSort)是指利用堆积树(堆)这种数据结构所设计的一种排序算法,可以利用数组的特 ...
- Atitit 电子商务订单号码算法(java c# php js 微信
Atitit 电子商务订单号码算法(java c# php js 微信 1.1. Js版本的居然钱三爷里面没有..只好自己实现了. 1.2. 订单号标准化...长度16位 1.3. 订单号的结构 前 ...
- 基于FP-Tree的关联规则FP-Growth推荐算法Java实现
基于FP-Tree的关联规则FP-Growth推荐算法Java实现 package edu.test.ch8; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util ...
- 双色球机选算法java实现
双色球机选算法java实现 一.代码 package com.hdwang; import java.util.Random; /** * Created by admin on 2017/1/10. ...
- Floyd算法java实现demo
Floyd算法java实现,如下: https://www.cnblogs.com/Halburt/p/10756572.html package a; /** * ┏┓ ┏┓+ + * ┏┛┻━━━ ...
随机推荐
- 7.hbase shell命令 cmd
$HADOOP_USER_NAME #创建命名空间create_namespace 'bd1902' #展示所有命名空间 list_namespace #删除命名空间,The namespace mu ...
- HDFS的数据流读写数据 (面试开发重点)
1 HDFS写数据流程 1.1 剖析文件写入 HDFS写数据流程,如图所示 1)客户端通过Distributed FileSystem模块向NameNode请求上传文件,NameNode检查目标文件是 ...
- SwitchyOmega 配置
1.google 扩展程序里面的chrome 网上应用店里面安装Proxy SwitchyOmega 2.新建情景模式 3.配置代理 4.自动切换添加新建的情景模式,最后保存
- Overcoming Forgetting in Federated Learning on Non-IID Data
郑重声明:原文参见标题,如有侵权,请联系作者,将会撤销发布! 以下是对本文关键部分的摘抄翻译,详情请参见原文. NeurIPS 2019 Workshop on Federated Learning ...
- wordpress个人常用标签调用
wordpress常见标签调用,老是容易忘记,又要找半天,干脆搬到网站上. <?php bloginfo('name');?>网站名称 url <?php echo home_url ...
- 推荐一款万能抓包神器:Fiddler Everywhere
搞IT技术的同行,相信没有几个人是不会抓包这项技能的(如果很不幸你中枪了,那希望这篇文章给你一些动力),市面上的抓包工具也有很多,常用的有:Charles.Fiddler.Burpsuite.Wire ...
- oracle再回首
第一章 Oracle 数据库的使用 一. 数据库相关概念 1 什么是数据库 所谓的数据库其实就是数据的集合.用户可以对集合中的数据进行新增.查询.更新. 删除等操作.数据库是以一定方式储存在一 ...
- 用rspec执行自动化测试用例
rspec是一款行为驱动开发(BDD)的工具,不过在这里用于测试,准确来说应该是测试驱动开发(TDD)吧.事实上我也没搞清楚.作为初学者不清楚就不清楚吧,以后会知道的.写博客无非就是写写学习笔记,不纠 ...
- Lua C API的正确用法
http://blog.codingnow.com/2015/05/lua_c_api.html http://blog.csdn.net/oilcode/article/details/510861 ...
- nginx server_name 多个
nginx server_name 多个 nginx server_name 多个的话,空格隔开就行 server_name baidu.com baidu.me; 如果很多的话可以用正则,我的需求, ...
