Java改写重构第2版第一个示例
写在前面
《重构:改善既有代码的设计》是一本经典的软件工程必读书籍。作者马丁·福勒强调重构技术是以微小的步伐修改程序。
但是,从国内的情况来而论,“重构”的概念表里分离。大家往往喜欢打着“重构”的名号,实际上却干的是“刀劈斧砍”的勾当。产生这种现象的原因,一方面是程序员希望写出可维护,可复用,可拓展,灵活性好的代码,使系统具长期生命力;另一方面,重构的扎实功夫要学起来、做起来,颇不是一件轻松的事,且不说详尽到近乎琐碎的重构手法,光是单元测试一事,怕是已有九成同行无法企及。所以,重构变质为重写,研发团队拿着公司的经费,干着“重复造轮子”的事儿,最终“重构”后的软件仍然不能使人满意,反倒是一堆问题,用户不愿意买单,程序员不愿意继续维护,管理人员也担着巨大的压力。痛苦的滋味在心底蔓延。
转头来看,Martin Fowler 时隔 20 年后的第 2 版,没有照搬第一版,而是把工夫做得更加扎实了,我有幸发现这本书,解我之惑,实属幸事一件。由于第 2 版中使用 javascript 作为展现重构手法的语言,可是本人惯用的语言却是 Java,因此本着 “实践出真知” 的原则,我想尝试用 Java 语言来对示例进行改写,在分享思路的同时,也希望能够有人与我讨论,甚至指出我的错误,在此深表感谢。
废话不多说了,我们赶紧开始
项目地址
git clone https://gitee.com/kendoziyu/code-refactoring-example.git
起点
有些看到文章的小伙伴,可能还没拿到这本《重构2》,所以我先把原文需求贴出来,另外在改写时,我会参考并结合《重构》第 1 版中的代码。
设想有一个戏剧演出团,演员们经常要去各种场合表演戏剧。通常客户(customer)会指定几出剧目,而剧团则根据观众(audience)人数及剧目类型向客户收费。该团目前出演两种戏剧:悲剧(tragedy)和喜剧(comedy)。给客户发出账单时,剧团还根据到场观众的数量给出“观众量积分”(volume credit)优惠,下次客户再请剧团表演时,可以使用积分获得折扣————你可以把它看作一种提升客户忠诚度的方式。
该剧团将 剧目 的数据存储在一个简单的 JSON 文件中。
plays.json...
{
"hamlet":{"name":"Hamlet", "type":"tragedy"},
"as-like":{"name":"As You Like It", "type":"comedy"},
"othello":{"name":"Othello", "type":"tragedy"}
}
他们开出的 账单 也存储在一个 JSON 文件里。
invoices.json...
{
"customer":"BigCo",
"performances":[
{
"playId":"hamlet",
"audience":55
},
{
"playId":"as-like",
"audience":35
},
{
"playId":"othello",
"audience":40
}
]
}
等下我要来解析这两组 JSON 对象,不妨先来分析一下实体类之间的关系:

发票(Invoice)
public class Invoice {
private String customer;
private List<Performance> performances;
public String getCustomer() {
return customer;
}
public void setCustomer(String customer) {
this.customer = customer;
}
public List getPerformances() {
return performances;
}
public void setPerformances(List performances) {
this.performances = performances;
}
}
表演(Performance)
public class Performance {
private String playId;
private int audience;
public String getPlayId() {
return playId;
}
public void setPlayId(String playId) {
this.playId = playId;
}
public int getAudience() {
return audience;
}
public void setAudience(int audience) {
this.audience = audience;
}
}
剧目(Play)
public class Play {
private String name;
private String type;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getType() {
return type;
}
public void setType(String type) {
this.type = type;
}
}
接着,书中直接就给出了 打印账单信息 的函数 function statement(invoice, plays) {}。注意,《重构2》书中有提到,
当我在代码块上方使用了斜体(中文对应楷体)标记的题头 “function xxx” 时,表明该代码位于题头所在函数、文件或类的作用域内。
所以,结合《重构(第 1 版)》中的 Java 示例,我对第二版的示例做了一些改造:
Statement.java...
public class Statement {
private Invoice invoice;
private Map<String, Play> plays;
public Statement(Invoice invoice, Map<String, Play> plays) {
this.invoice = invoice;
this.plays = plays;
}
public String show() {
int totalAmount = 0;
int volumeCredits = 0;
String result = String.format("Statement for %s\n", invoice.getCustomer());
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder(result);
Locale locale = new Locale("en", "US");
NumberFormat format = NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance(locale);
for (Performance performance : invoice.getPerformances()) {
Play play = plays.get(performance.getPlayId());
int thisAmount = 0;
switch (play.getType()) {
case "tragedy":
thisAmount = 40000;
if (performance.getAudience() > 30) {
thisAmount += 1000 * (performance.getAudience() - 30);
}
break;
case "comedy":
thisAmount = 30000;
if (performance.getAudience() > 20) {
thisAmount += 10000 + 500 *(performance.getAudience() - 20);
}
thisAmount += 300 * performance.getAudience();
break;
default:
throw new RuntimeException("unknown type:" + play.getType());
}
volumeCredits += Math.max(performance.getAudience() - 30, 0);
if ("comedy".equals(play.getType())) {
volumeCredits += Math.floor(performance.getAudience() / 5);
}
stringBuilder.append(String.format(" %s: %s (%d seats)\n", play.getName(), format.format(thisAmount/100), performance.getAudience()));
totalAmount += thisAmount;
}
stringBuilder.append(String.format("Amount owed is %s\n", format.format(totalAmount/100)));
stringBuilder.append(String.format("You earned %s credits\n", volumeCredits));
return stringBuilder.toString();
}
}
值得一提的有:
从 Java 1.7 开始,switch 开始支持字符串了
NumberFormat.getCurrencyInstance 这个 API,可以为我们打印货币信息
Main.java...
public class Main {
static final String plays = "{" +
"\"hamlet\":{\"name\":\"Hamlet\",\"type\":\"tragedy\"}," +
"\"as-like\":{\"name\":\"As You Like It\",\"type\":\"comedy\"}," +
"\"othello\":{\"name\":\"Othello\",\"type\":\"tragedy\"}" +
"}";
static final String invoices = "[{" +
"\"customer\":\"BigCo\",\"performances\":[" +
"{\"playId\":\"hamlet\",\"audience\":55}" +
"{\"playId\":\"as-like\",\"audience\":35}" +
"{\"playId\":\"othello\",\"audience\":40}" +
"]" +
"}]";
public static void main(String[] args) {
TypeReference<Map<String, Play>> typeReference = new TypeReference<Map<String, Play>>(){};
Map<String, Play> playMap = JSONObject.parseObject(plays, typeReference);
List<Invoice> invoiceList = JSONObject.parseArray(invoices, Invoice.class);
for (Invoice invoice : invoiceList) {
Statement statement = new Statement(invoice, playMap);
String result = statement.show();
System.out.println(result);
}
}
}
运行上面的 Main 主类,会得到如下输出:
Statement for BigCo
Hamlet: $650.00 (55 seats)
As You Like It: $580.00 (35 seats)
Othello: $500.00 (40 seats)
Amount owed is $1,730.00
You earned 47 credits
新需求
在这个例子里,我们的用户希望对系统做几个修改。首先,他们希望以 HTML 格式输出详单。另外,他们还希望增加表演(Play)的类型,虽然还没决定增加哪种以及何时试演。这对戏剧场次的计费方式、积分方式都有影响。在这样的需求前提下,如果你不想以后面对一堆莫名奇妙的 BUG,被逼着各种加班,那我们现在就要着手重构上面的示例了。
如果你要给程序增加一个特性,但是发现代码因缺乏良好的结构而不易于进行更改,那就先重构哪个程序,使其比较容易添加该特性,然后再添加该特性。
重构第一步
重构前,先检查自己是否有一套可靠的测试集。这些测试必须有自我检验能力。
所以,我把 Main.java 稍微改变了一下,设计成了一个简单的测试:
点击查看 StatementTest.java
- 基于 Junit 的单元测试
public class StatementTest {
@Test
public void test() {
String expected = "Statement for BigCo\n" +
" Hamlet: $650.00 (55 seats)\n" +
" As You Like It: $580.00 (35 seats)\n" +
" Othello: $500.00 (40 seats)\n" +
"Amount owed is $1,730.00\n" +
"You earned 47 credits\n";
final String plays = "{" +
"\"hamlet\":{\"name\":\"Hamlet\",\"type\":\"tragedy\"}," +
"\"as-like\":{\"name\":\"As You Like It\",\"type\":\"comedy\"}," +
"\"othello\":{\"name\":\"Othello\",\"type\":\"tragedy\"}" +
"}";
final String invoices = "{" +
"\"customer\":\"BigCo\",\"performances\":[" +
"{\"playId\":\"hamlet\",\"audience\":55}" +
"{\"playId\":\"as-like\",\"audience\":35}" +
"{\"playId\":\"othello\",\"audience\":40}" +
"]" +
"}";
TypeReference> typeReference = new TypeReference>(){};
Map playMap = JSONObject.parseObject(plays, typeReference);
Invoice invoice = JSONObject.parseObject(invoices, Invoice.class);
Statement statement = new Statement(invoice, playMap);
String result = statement.show();
Assert.assertEquals(expected, result);
}
}
接下来的可以照着书上的要求执行,以微小的步伐开始你的重构之旅了,如果有不明白的也可以参考一下我的例子 code-refactoring-example
拆分计算阶段和格式化阶段
我们希望同样的计算函数可以被 文本版 详单和 HTML版 详单共用。
实现复用有许多种方法,而我最喜欢的技术是 拆分阶段。这里我们的目标是将逻辑分成两部分:一部分计算详单所需的数据,另一部分将数据渲染成文本或者HTML。第一阶段会创建一个中转数据结构,再它传递给第二阶段。
我们可以创建一个 StatementData 作为两个阶段间传递的中间数据结构。建议大家根据书上的讲解实际操练,这里仅仅提供一种思路,我的实操过程已经放在了 Gitee 上面,有兴趣的可以参考和修改。
我们这里拆分函数时有一个目标:让 renderPlainText 只操作通过 data 传递进来的数据(data 就是 StatementData 的实例对象),经过一系列搬移函数之后,我们可以达成这个目标:
/**
* 使用纯文本渲染
* @param data 详单数据
* @return
*/
private String renderPlainText(StatementData data) {
String result = String.format("Statement for %s\n", data.getCustomer());
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder(result);
for (Performance performance : data.getPerformances()) {
stringBuilder.append(String.format(" %s: %s (%d seats)\n", performance.getPlay().getName(), usd(performance.getAmount()), performance.getAudience()));
}
stringBuilder.append(String.format("Amount owed is %s\n", usd(data.getTotalAmount())));
stringBuilder.append(String.format("You earned %s credits\n", data.getTotalVolumeCredits()));
return stringBuilder.toString();
}
按计算过程重组计算过程
接下来我们将注意力集中到下一个特性改动:支持更多类型的戏剧,以及支持他们各自的价格计算和观众量积分计算。而改动的核心在 enrichPerformance 函数就是关键所在,因为正是它用每场演出的数据来填充中转数据结构。目前它直接调用了计算价格函数 amountFor,和计算观众量积分函数 volumeCreditsFor 。我们需要创建一个类,通过这个类来调用这些函数。由于这个类存放了与每场演出相关数据的计算函数,于是我们把它称为演出计算器 PerformanceCalculator。
我们把 amountFor, volumeCredits 都搬到了 PerformanceCalculator 中。play 字段严格来说,是不需要搬移的,因为它并未体现出多态性。但是这样可以把所有数据转换集中到一处地方,保证了代码的一致性和清晰度。改动后如下:
private Performance enrichPerformance(Performance performance) {
PerformanceCalculator calculator = new PerformanceCalculator(performance, playFor(performance));
performance.setPlay(calculator.play());
performance.setAmount(calculator.amount());
performance.setVolumeCredits(calculator.volumeCredits());
return performance;
}
以工厂函数取代构造函数
private Performance enrichPerformance(Performance performance) {
PerformanceCalculator calculator = createPerformanceCalculator(performance, playFor(performance));
...(同上)
return performance;
}
private PerformanceCalculator createPerformanceCalculator(Performance performance, Play play) {
return new PerformanceCalculator(performance, play);
}
以子类取代类型码,新建 ComedyCalculator 和 TragedyCalculator 并且让他们继承 PerformanceCalculator
private PerformanceCalculator createPerformanceCalculator(Performance performance, Play play) {
switch (play.getType()) {
case "tragedy": return new TragedyCalculator(performance, play);
case "comedy": return new ComedyCalculator(performance, play);
default:
throw new RuntimeException("unknown type:" + play.getType());
}
}
以多态取代条件表达式
public class ComedyCalculator extends PerformanceCalculator {
public ComedyCalculator(Performance performance, Play play) {
super(performance, play);
}
@Override
public int amount() {
int result = 30000;
if (performance.getAudience() > 20) {
result += 10000 + 500 *(performance.getAudience() - 20);
}
result += 300 * performance.getAudience();
return result;
}
@Override
public int volumeCredits() {
return (int) (super.volumeCredits() + Math.floor(performance.getAudience() / 5));
}
}
public class TragedyCalculator extends PerformanceCalculator {
public TragedyCalculator(Performance performance, Play play) {
super(performance, play);
}
@Override
public int amount() {
int result = 40000;
if (performance.getAudience() > 30) {
result += 1000 * (performance.getAudience() - 30);
}
return result;
}
}
总结
以一张图总结本文内容:
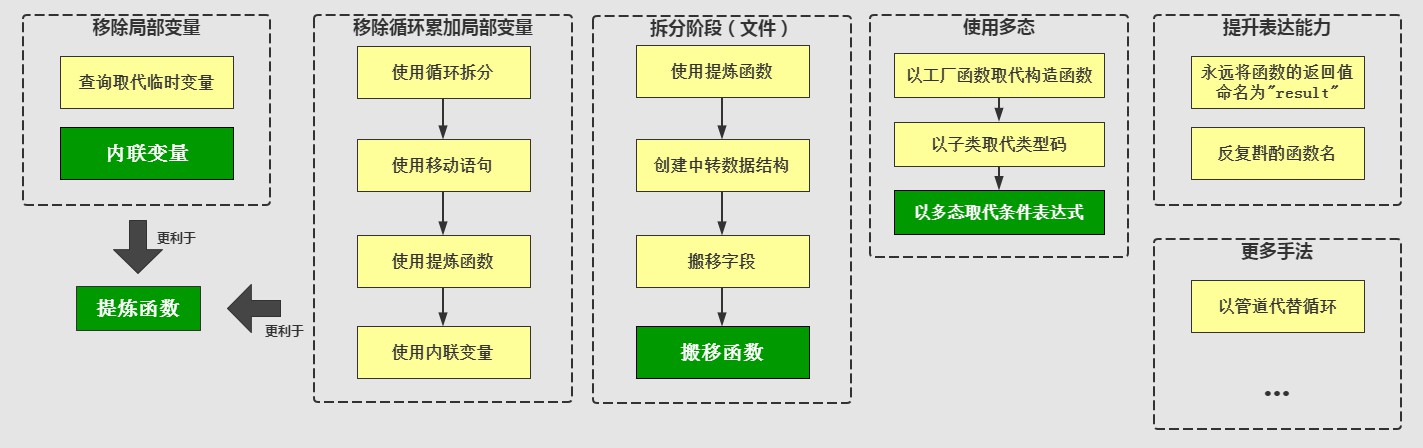
- 例中我们用到了数种重构手法。包括提炼函数,内联变量,搬移函数,以多态取代条件表达式等。
- 我们用 拆分阶段 的技术分离计算逻辑与输出格式化的逻辑。
好代码的检验标准就是人们能否轻而易举地修改它!
与君共勉
编程时,需要遵循营地法则:希望我们都可以“保证你离开时的代码库一定比你来时更健康”。
Java改写重构第2版第一个示例的更多相关文章
- SkylineGlobe TerraExplorer Pro 7.0 Web 控件版 第一行示例代码
SkylineGlobe TerraExplorer Pro 7.0 是原生的64位应用程序,在Web端用插件方式开发的第一行示例代码如下: 常规代码,需要IE64位: <!DOCTYPE ht ...
- java版第一个代码——HelloWorld!
java版第一个代码--HelloWorld! 今天来接触一下java代码: 事前准备 jdk的配置(推荐jdk8或jdk11) notepad++或idea软件 开始编写 建立文件夹存放代码 建立j ...
- 《Java学习笔记(第8版)》学习指导
<Java学习笔记(第8版)>学习指导 目录 图书简况 学习指导 第一章 Java平台概论 第二章 从JDK到IDE 第三章 基础语法 第四章 认识对象 第五章 对象封装 第六章 继承与多 ...
- 《Java编程思想第四版》附录 B 对比 C++和 Java
<Java编程思想第四版完整中文高清版.pdf>-笔记 附录 B 对比 C++和 Java “作为一名 C++程序员,我们早已掌握了面向对象程序设计的基本概念,而且 Java 的语法无疑是 ...
- 阿里正式发布《Java开发手册》终极版!
摘要: 本文讲的是阿里正式发布<Java开发手册>终极版!,别人都说我们是码农,但我们知道,自己是个艺术家.也许我们不过多在意自己的外表和穿着,但我们不羁的外表下,骨子里追求着代码的美.质 ...
- 0038 Java学习笔记-多线程-传统线程间通信、Condition、阻塞队列、《疯狂Java讲义 第三版》进程间通信示例代码存在的一个问题
调用同步锁的wait().notify().notifyAll()进行线程通信 看这个经典的存取款问题,要求两个线程存款,两个线程取款,账户里有余额的时候只能取款,没余额的时候只能存款,存取款金额相同 ...
- 《阿里巴巴Java开发手册(正式版》读记
前几天,阿里巴巴发布了<阿里巴巴Java开发手册(正式版>,第一时间下载阅读了一番. 不同于一般大厂内部的代码规范,阿里巴巴的这本Java开发手册,可谓包罗万象,几乎日常Java开发中方方 ...
- 20165205 2017-2018-2《Java程序设计》结对编程一 第一周总结
20165205 2017-2018-2<Java程序设计>结对编程一 第一周总结 需求分析 对输入的算式进行计算,要求满足一下条件: 支持整数运算,如2+5,47+7865. 支持多运算 ...
- 阿里巴巴Java开发手册(详尽版)-个人未注意到的知识点(转)
转自 https://blog.csdn.net/u013039395/article/details/86528164 一.编程规约 (一) 命名风格 [强制]代码中的命名只可用英文方式 [强制]类 ...
随机推荐
- html基础:基本标签
一.html简介 html是一个长的字符串,它能够被浏览器解析.html分为三块:html代码,css,js. html的注释可以用<!-- --> 或者ctrl+? html页面打开以后 ...
- LeetCode.518 零钱兑换Ⅱ(记录)
518题是背包问题的变体,也称完全背包问题. 解法参考了该篇文章,然后对自己困惑的地方进行记录. 下面是该题的描述: 有一个背包,最大容量为 amount,有一系列物品 coins,每个物品的重量为 ...
- Lua GC机制
说明 分析lua使用的gc算法,如何做到分步gc,以及测试结论 gc算法分析 lua gc采用的是标记-清除算法,即一次gc分两步: 从根节点开始遍历gc对象,如果可达,则标记 遍历所有的gc对象,清 ...
- 面向对象--有参数的__init__方法
有参数的__init__()方法 class Hero(object): """定义了一个英雄类,可以移动和攻击""" def __init ...
- windows下nginx的配置
这里做的nginx的配置主要的功能是: 能够用localhost访问本地文件夹中的项目 输入ip地址访问本地文件夹中的项目 反向代理其他地址访问本地文件 1.nginx安装地址 2.解压之后的文件如下 ...
- Vue iview可收缩多级菜单的实现
递归组件实战 views/layout.vue <template> <div class="layout-wrapper"> <Layout cla ...
- netty学习心得2内存池
http://frankfan915.iteye.com/blog/2199600 https://www.jianshu.com/p/13f72e0395c8:一个性能调优的文档,还有一些linux ...
- 虚拟机Ubuntu(18.04.2)下安装配置Hadoop(2.9.2)(伪分布式+Java8)
[本文结构] [1]安装Hadoop前的准备工作 [1.1] 创建新用户 [1.2] 更新APT [1.3] 安装SSH [1.4] 安装Java环境 [2]安装和配置hadoop [2.1] Had ...
- 趣图:普通人讲故事 VS 程序员讲故事
扩展阅读 趣图:我说自己菜 vs 大佬说自己菜 趣图:客户需求VS客户预算 趣图:在外行人眼中的程序员 如何处理前任程序员留下的代码 一个故事讲清楚NIO
- MyBatis学习(一)初识MyBatis
一.MyBatis简介 MyBatis 本是apache的一个开源项目iBatis, 2010年这个项目由apache software foundation 迁移到了google code,并且改名 ...
