[Testing] Config jest to test Javascript Application -- Part 3
Run Jest Watch Mode by default locally with is-ci-cli
In CI, we don’t want to start the tests in watch mode, but locally we normally want to run the tests in watch mode. We can have separate scripts, but it’d be great to not have to remember which script to run locally. Let’s use is-ci-cli to run the right script in the right environment when running the test script.
install:
- npm i -D is-ci-cli
scripts:
- "test": "is-ci \"test:coverage\" \"test:watch\"",
- "test:coverage": "jest --coverage",
- "test:watch": "jest --watch",
- "test:debug": "node --inspect-brk ./node_modules/jest/bin/jest.js --runInBand --watch",
So when we run:
- npm t
It will check our enviorment, if it is running in CI mode, it will run coverage, otherwise it running in node, it runs watch mode.
Filter which Tests are Run with Typeahead Support in Jest Watch Mode
Jest’s watch mode is pluggable and jest-watch-typeahead is one plugin that you definitely don’t want to live without. It enhances the watch mode experience to help you know which tests will be run based on your filter. Making it even easier to run only the tests you’re concerned with running as you develop your codebase.
Install:
- npm install --save-dev jest-watch-typeahead
jest.config.js:
- const path = require('path');
- module.exports = {
- testEnvironment: 'jest-environment-jsdom', //'jest-environment-node',
- moduleDirectories: [
- 'node_modules',
- path.join(__dirname, 'src'),
- 'shared',
- path.join(__dirname, 'test'),
- ],
- moduleNameMapper: {
- '\\.module\\.css$': 'identity-obj-proxy',
- '\\.css$': require.resolve('./test/style-mock.js')
- },
- snapshotSerializers: ['jest-serializer-path'],
- // after jest is loaded
- setupTestFrameworkScriptFile: require.resolve('./test/setup-tests.js'),
- collectCoverageFrom: ['**/src/**/*.js'],
- coverageThreshold: {
- global: {
- statements: 80,
- branchs: 80,
- lines: 80,
- functions: 80,
- },
- './src/shared/utils.js': {
- statements: 100,
- branchs: 80,
- lines: 100,
- functions: 100,
- }
- },
- watchPlugins: [
- 'jest-watch-typeahead/filename',
- 'jest-watch-typeahead/testname',
- ]
- }

Run tests with a different configuration using Jest’s --config flag and testMatch option
Sometimes you may have situations where configuration needs to be different for certain tests. In this lesson we’ll take a look at how we could create a custom configuration for tests that are intended to run in a node environment.
We might want to test server side rendering code, which doesn't need DOM, and some other configurations for client side. For that we need to split current jest config, to need the requirements.
test/jest-common.js:
- const path = require('path');
- module.exports = {
- rootDir: path.join(__dirname, '..'), // find tests in src folder
- moduleDirectories: [
- 'node_modules',
- path.join(__dirname, '../src'),
- 'shared',
- __dirname,
- ],
- moduleNameMapper: {
- '\\.module\\.css$': 'identity-obj-proxy',
- '\\.css$': require.resolve('./style-mock.js')
- },
- snapshotSerializers: ['jest-serializer-path'],
- collectCoverageFrom: ['**/src/**/*.js'],
- }
test/jest-client.js
- module.exports = {
- ...require('./jest-common'),
- testEnvironment: 'jest-environment-jsdom', //'jest-environment-node',
- // after jest is loaded
- setupTestFrameworkScriptFile: require.resolve('./setup-tests.js'),
- coverageThreshold: {
- global: {
- statements: 80,
- branchs: 80,
- lines: 80,
- functions: 80,
- },
- './src/shared/utils.js': {
- statements: 100,
- branchs: 80,
- lines: 100,
- functions: 100,
- }
- },
- watchPlugins: [
- 'jest-watch-typeahead/filename',
- 'jest-watch-typeahead/testname',
- ]
- }
test/jest-server.js
- const path = require('path')
- module.exports = {
- ...require('./jest-common'),
- coverageDirectory: path.join(__dirname, '../coverage/server'),
- testEnvironment: 'jest-environment-node',
- testMatch: ['**/__server_tests__/**/*.js']
- }
With that we can create new script for running the jest:
- "test": "is-ci \"test:coverage\" \"test:watch:client\" # CI=1 npm t run in ci mode",
- "test:coverage": "npm run test:coverage:client && npm run test:coverage:server",
- "test:coverage:client": "jest --config test/jest-client.js --coverage",
- "test:coverage:server": "jest --config test/jest-server.js --coverage",
- "test:watch:client": "jest --config test/jest-client.js --watch",
- "test:watch:server": "jest --config test/jest-server.js --watch",
- "test:debug:client": "node --inspect-brk ./node_modules/jest/bin/jest.js --config test/jest-client.js --runInBand --watch",
- "test:debug:server": "node --inspect-brk ./node_modules/jest/bin/jest.js --config test/jest-server.js --runInBand --watch",
The hightlighted code in script is how we run jest with the configuration file.
Support Running Multiple Configurations with Jest’s Projects Feature
Sometimes you may find it useful to have more than one configuration in a project (for example, running some tests in a node environment and others in the jsdom environment). In this lesson we’ll learn about Jest’s projects feature to have jest run both of these configurations at once.
Now we have lots of scripts for client and server:
- "test": "is-ci \"test:coverage\" \"test:watch:client\" # CI=1 npm t run in ci mode",
- "test:coverage": "npm run test:coverage:client && npm run test:coverage:server",
- "test:coverage:client": "jest --config test/jest-client.js --coverage",
- "test:coverage:server": "jest --config test/jest-server.js --coverage",
- "test:watch:client": "jest --config test/jest-client.js --watch",
- "test:watch:server": "jest --config test/jest-server.js --watch",
- "test:debug:client": "node --inspect-brk ./node_modules/jest/bin/jest.js --config test/jest-client.js --runInBand --watch",
- "test:debug:server": "node --inspect-brk ./node_modules/jest/bin/jest.js --config test/jest-server.js --runInBand --watch",
Those are not ideal, in fact we prefer:
- "test": "is-ci \"test:coverage\" \"test:watch\"",
- "test:coverage": "jest --coverage",
- "test:watch": "jest --watch",
- "test:debug": "node --inspect-brk ./node_modules/jest/bin/jest.js --runInBand --watch",
Jest provides '--projects' options we can use to run mutiplue scripts:
- npx jest --projects ./test/jest-client.js ./test/jest-server.js
It runs based on both client config and server config.
Now we can config '--projects' inside jest.config.js:
- /*Mainly for global jest config*/
- // npx jest --showConifg --config ./test/jest-client.js
- module.exports = {
- ...require('./test/jest-common'),
- projects: ['./test/jest-client.js', './test/jest-server.js'],
- coverageThreshold: {
- global: {
- statements: 80,
- branchs: 80,
- lines: 80,
- functions: 80,
- },
- './src/shared/utils.js': {
- statements: 100,
- branchs: 80,
- lines: 100,
- functions: 100,
- }
- },
- collectCoverageFrom: ['**/src/**/*.js'],
- }
Coverage reports will be combine by jest automaticlly for both client and server side.
./test/jest-clinet.js
- module.exports = {
- ...require('./jest-common'),
- displayName: 'dom',
- testEnvironment: 'jest-environment-jsdom', //'jest-environment-node',
- // after jest is loaded
- setupTestFrameworkScriptFile: require.resolve('./setup-tests.js'),
- watchPlugins: [
- 'jest-watch-typeahead/filename',
- 'jest-watch-typeahead/testname',
- ]
- }
./test/jest-server.js:
- const path = require('path')
- module.exports = {
- ...require('./jest-common'),
- displayName: 'server',
- testEnvironment: 'jest-environment-node',
- testMatch: ['**/__server_tests__/**/*.js']
- }
./test/jest-common.js:
- const path = require('path');
- module.exports = {
- rootDir: path.join(__dirname, '..'), // find tests in src folder
- moduleDirectories: [
- 'node_modules',
- path.join(__dirname, '../src'),
- 'shared',
- __dirname,
- ],
- moduleNameMapper: {
- '\\.module\\.css$': 'identity-obj-proxy',
- '\\.css$': require.resolve('./style-mock.js')
- },
- snapshotSerializers: ['jest-serializer-path'],
- }
We added 'displayName':
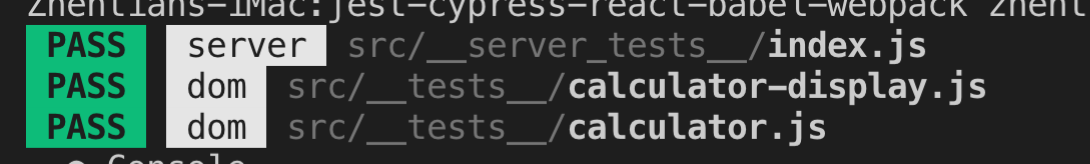
So it is clear, tests are from which part.
If you just want run client test, you still can do:
- npx jest --config ./test/jest-client.js --watch
Test specific projects in Jest Watch Mode with jest-watch-select-projects
It’s great that we can run multiple projects in our watch mode and that we can scope the tests down to specific tests, but sometimes it’s nice to be able to quickly switch between projects in watch mode. Let’s see how this works with jest-watch-select-projects.
After we refactor our scripts, now if we want to just run client tests, we need to do:
- npx jest --config ./test/jest-client.js --watch
It is not so good approach.
Install:
- npm i -D jest-watch-select-projects
In the 'watchPlugins':
- watchPlugins: [
- 'jest-watch-typeahead/filename',
- 'jest-watch-typeahead/testname',
- 'jest-watch-select-projects',
- ],
Now, if we run:
- jest--watch
It will give a new options, which is 'P', we can select the project we want to run against.
Run ESLint with Jest using jest-runner-eslint
Jest is more than a testing framework. It’s a highly optimized, blazing fast platform with incredible parallelization for running tasks across many files in our project. It has a capability to run more than just tests. We can bring these features to our linting as well. Let’s see how we can bring our favorite Jest features (like watch mode) to ESLint with jest-runner-eslint.
Idea is using jest to run eslint as well though jest-runner
Install:
- npm i -D jest-runner-eslint
Create test/jest-lint.js
- const {rootDir} = require('./jest-common')
- module.exports = {
- rootDir,
- displayName: 'lint',
- runner: 'jest-runner-eslint',
- testMatch: ['<rootDir>/**/*.js'],
- testPathIgnorePatterns: ['/node_modules/', '/coverage/', '/dist/', '/other/']
- }
To run the lint, we can do:
- npx jest --config test/jest-lint.js
We want to include 'lint' into the default tests runner:
jest.config.js:
- module.exports = {
- ...require('./test/jest-common'),
- projects: ['./test/jest-lint.js', './test/jest-client.js', './test/jest-server.js'],
- coverageThreshold: {
- global: {
- statements: 80,
- branchs: 80,
- lines: 80,
- functions: 80,
- },
- './src/shared/utils.js': {
- statements: 100,
- branchs: 80,
- lines: 100,
- functions: 100,
- }
- },
- collectCoverageFrom: ['**/src/**/*.js'],
- }
Now everytime, we run test, the lint will be also running.
Last, we can update our scripts to run the lint:
- "lint": "jest --config test/jest-lint.js",
Run only relevant Jest tests on git commit to avoid breakages
Running the project tests on commit is a great way to avoid breaking the application accidentally and leverage the mechanism for confidence you have from your testbase. However, as the testbase grows this can take a very long time and slow productivity down. Let’s see how Jest is capable of running only the tests and linting only the files that are affected by the files we’re committing with husky and lint-staged to speed up our local test runs as well as help us avoid accidentally committing code that breaks our application.
You can target one file to run all the tests which are related:
- npx jest --findRelatedTests src/shared/util.js
Install:
- npm i -D husky lint-staged
Add lint-staged.config.js file:
- module.exports = {
- linters: {
- '**/*.js': ['jest --findRelatedTests'] // any file which jest find related tests found will be added to the lint-staged
- }
- }
In package.json:
- "precommit": "lint-staged",
Then if we were going to change one file and break the tests, then after we do git commit, husky will kick in and run the tests which are related to the file we have changed. If the tests faild, we are not able to commit the code.
[Testing] Config jest to test Javascript Application -- Part 3的更多相关文章
- [Testing] Config jest to test Javascript Application -- Part 1
Transpile Modules with Babel in Jest Tests Jest automatically loads and applies our babel configurat ...
- [Testing] Config jest to test Javascript Application -- Part 2
Setup an afterEach Test Hook for all tests with Jest setupTestFrameworkScriptFile With our current t ...
- Web.config Transformation Syntax for Web Application Project Deployment
Web.config Transformation Syntax for Web Application Project Deployment Other Versions Updated: Ma ...
- JavaScript Application Architecture On The Road To 2015
JavaScript Application Architecture On The Road To 2015 I once told someone I was an architect. It’s ...
- 转:Transform Web.Config when Deploying a Web Application Project
Introduction One of the really cool features that are integrated with Visual Studio 2010 is Web.Conf ...
- spring cloud config的bootstrap.yml与application.proterties的区别
bootstrap.yml 和application.yml 都可以用来配置参数 bootstrap.yml可以理解成系统级别的一些参数配置,这些参数一般是不会变动的 application.ym ...
- Unit Testing a zend-mvc application
Unit Testing a zend-mvc application A solid unit test suite is essential for ongoing development in ...
- JavaScript Web Application summary
Widget/ HTML DOM (CORE) (local dom) DOM, BOM, Event(Framework, UI, Widget) function(closure) DATA (c ...
- JavaScript Libraries In A TypeScript Application, Revisited
If you haven’t already gotten involved with it, you’ll probably know that TypeScript is becoming inc ...
随机推荐
- leepcode作业解析 - 5-19
18.两数之和II -输入有序数组 给定一个已按照升序排列 的有序数组,找到两个数使得它们相加之和等于目标数. 函数应该返回这两个下标值 index1 和 index2,其中 index1 必须小于 ...
- Python的第3堂课
20181119笔记 一.内存管理相关 ①Cpython解释器的垃圾回收机制 什么是垃圾:当一个值没有被绑定任何变量名(即该值的引用计数为零时),该值就是垃圾. 垃圾回收是收回值占用的内存空间. 引用 ...
- selenium之定位以及切换frame
总有人看不明白,以防万一,先在开头大写加粗说明一下: frameset不用切,frame需层层切! 很多人在用selenium定位页面元素的时候会遇到定位不到的问题,明明元素就在那儿,用firebug ...
- 【LeetCode】Design Linked List(设计链表)
这道题是LeetCode里的第707到题.这是在学习链表时碰见的. 题目要求: 设计链表的实现.您可以选择使用单链表或双链表.单链表中的节点应该具有两个属性:val 和 next.val 是当前节点的 ...
- Clickomania(区间DP)
描述 Clickomania is a puzzle in which one starts with a rectangular grid of cells of different colours ...
- PAT天梯赛练习题——L3-005. 垃圾箱分布(暴力SPFA)
L3-005. 垃圾箱分布 时间限制 200 ms 内存限制 65536 kB 代码长度限制 8000 B 判题程序 Standard 作者 陈越 大家倒垃圾的时候,都希望垃圾箱距离自己比较近,但是谁 ...
- SPOJ GSS1 Can you answer these queries I ——线段树
[题目分析] 线段树裸题. 注意update的操作,写结构体里好方便. 嗯,没了. [代码] #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #inc ...
- leetcode 349 map
只需要用map来标记1,今儿通过map的值来得到重叠的部分 class Solution { public: vector<int> intersection(vector<int& ...
- Modular Production Line
Modular Production Line 时空限制: 1000ms /65536K An automobile factory has a car production line. Now ...
- Find that single one.(linear runtime complexity0
public class Solution { public int singleNumber(int[] nums) { int temp = 0; for (int i=0;i<nums.l ...
