1.shell编程-变量的高级用法
1.1.变量替换
变量替换的六种形式

实例:非贪婪和贪婪的区别
从头部删除
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# var_1="i love you,do you love me"
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $var_1
i love you,do you love me
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# var1=${var_1#*ov}
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $var1
e you,do you love me
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# var2=${var_1##*ov}
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $var2
e me
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]#
从尾部删除
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# var_1="i love you,do you love me"
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $var_1
i love you,do you love me
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# var3=${var_1%ov*}
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $var3
i love you,do you l
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# var4=${var_1%%ov*}
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $var4
i l
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]#
字符串替换,把bin替换成大写的BIN,单斜线和双斜线的区别
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $PATH
/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/root/bin
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]#
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# var5=${PATH/bin/BIN}
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $var5
/usr/local/sBIN:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/root/bin
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]#
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# var6=${PATH//bin//BIN}
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $var6
/usr/local/s/BIN:/usr/local//BIN:/usr/s/BIN:/usr//BIN:/root//BIN
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]#
1.2.字符串处理
计算字符串长度
方法一
${#string}
方法二
string有空格,则必须加双引号
expr length "$string"
实例
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# var1="hello world"
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# len=${#var1}
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $len
11
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# len2=`expr length "$var1"`
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $len2
11
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]#
获取子串在字符串中的索引位置
expr index $string $substring
实例
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# var1="quickstart is a app"
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# index=`expr index "$var1" start`
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $index
6
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# index2=`expr index "$var1" uniq`
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $index2
1
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# index3=`expr index "$var1" cnk`
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $index3
4
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]#
会把子串分割成一个一个字符,index是最先找到的那个字符的位置。
计算子串长度
expr match $string substr
实例
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# var1="quickstart is a app"
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# len=`expr match "$var1" quic`
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $len
4
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# len=`expr match "$var1" app`
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $len
0
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# len=`expr match "$var1" quic.*`
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $len
19
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]#
必须从开头匹配才可以
抽取子串
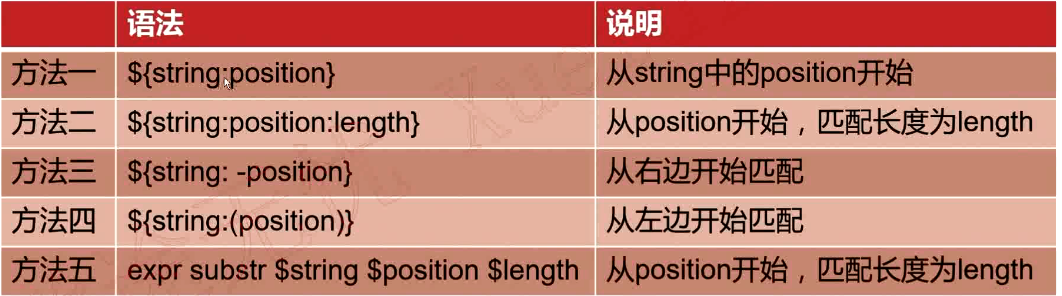
实例
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# var1="kafka hadoop yarn mapreduce"
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# sub1=${var1:10}
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $sub1
op yarn mapreduce
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# sub2=${var1:10:5}
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $sub2
op ya
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# sub3=${var1: -5}
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $sub3
educe
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# sub4=${var1:(-6)}
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $sub4
reduce
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# sub5=${var1: -5:3}
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $sub5
edu
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# sub6=`expr substr "$var1" 10 5`
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $sub6
oop y
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]#
注意:使用expr索引是从1开始计算,使用${string:position},索引从0开始计算。
1.3.字符串处理完整脚本

思路分析
1.将不同的功能模块划分,并编写函数
function print_tips
function len_of_string
function del_hadoop
function rep_hadoop_mapreduce_first
function rep_hadoop_maapreduce_all 2.实现第一步所定义的功能函数 3.程序主流程的设计
vim example.sh
#!/bin/bash string="Bigdata process framework is Hadoop,Hadoop is an open source project" function print_tips
{
echo "******************************"
echo "(1)打印string长度"
echo "(2)删除字符串中所有的Hadoop"
echo "(3)替换第一个Hadoop为Mapreduce"
echo "(4)替换全部Hadoop为Mapreduce"
echo "*******************************"
} function len_of_string
{
echo "${#string}"
} function del_hadoop
{
echo "${string//Hadoop/}"
} function rep_hadoop_mapreduce_first
{
echo "${string/Hadoop/Mapreduce}"
} function rep_hadoop_mapreduce_all
{
echo "${string//Hadoop/Mapreduce}"
} while true
do
echo "[string=$string]"
echo
print_tips
read -p "Pls input your choice(1|2|3|4|q|Q): " choice case $choice in
1)
len_of_string
;;
2)
del_hadoop
;;
3)
rep_hadoop_mapreduce_first
;;
4)
rep_hadoop_mapreduce_all
;;
q|Q)
exit
;;
*)
echo "Error,input only in {1|2|3|4|q|Q|}"
;;
esac
done
sh example.sh

1.4.命令替换
语法格式
方法一:
`command` 方法二:
$(command)
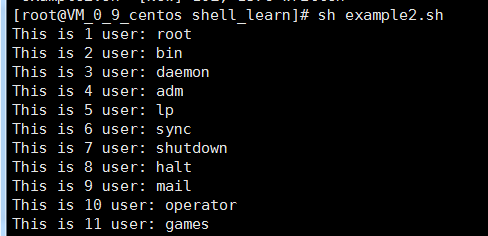
实例一:获取系统所有的用户并输出
cat /etc/passwd | cut -d ":" -f 1
vim example2.sh
#!/bin/bash
# index=1
for user in `cat /etc/passwd | cut -d ":" -f 1`
do
echo "This is $index user: $user"
index=$(($index+1)) done
结果
实例二:根据当前当前时间计算今年和明年
$(());两个括号主要用来进行整数运算
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# date
Wed Jun 26 21:58:04 CST 2019
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# date +%Y
2019
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo "This is $(date +%Y) year"
This is 2019 year
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo "This is $(($(date +%Y) + 1)) year"
This is 2020 year
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]#
实例三:根据当前时间获取今年还剩下多少星期和已经过了多少星期
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# date +%j
177
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo "This yaer have passed $(date +%j) days"
This yaer have passed 177 days
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo "This yaer have passed $(($(date +%j)/7)) weeks"
This yaer have passed 25 weeks
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo "今年还剩下$(((365 - $(date +%j))/7))星期"
今年还剩下26星期
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]#
实例四:判断nginx进程是否存在,若不存在则自动拉起该进程
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# ps -ef |grep nginx
root 6658 1 0 22:33 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx
nginx 6659 6658 0 22:33 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process
root 6891 501 0 22:35 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto nginx
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# ps -ef |grep nginx |grep -v grep |wc -l
2
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# systemctl stop nginx
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]#
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# ps -ef |grep nginx |grep -v grep |wc -l
0
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# sh example3.sh
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]#
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# ps -ef |grep nginx |grep -v grep |wc -l
2
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]#
vim example3.sh
如果nginx的进程个数为0,则拉起该进程
#!/bin.bash
# nginx_process_num=$(ps -ef | grep nginx | grep -v grep | wc -l) if [ $nginx_process_num -eq 0 ];then
systemctl start nginx
fi
1.5.有类型变量
declare和typeset命令
- declare和typeset命令两者等价
- declare和typeset命令都是用来定义变量类型的
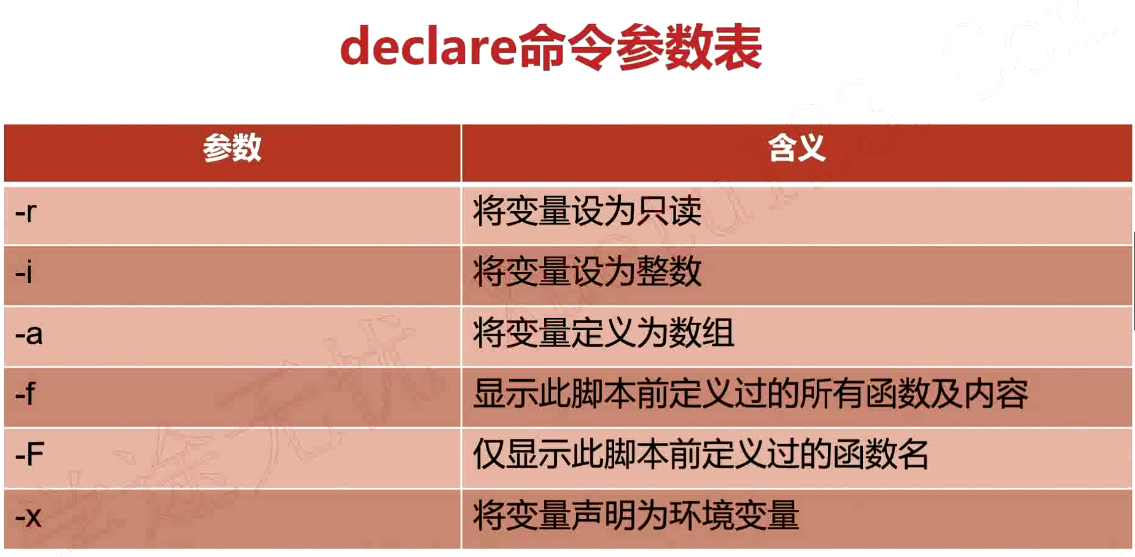
取消申明的变量
declare +r
declare +i
declare +a
declare +x
实例一:-r 将变量设为只读
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# var1="hello world"
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# var1="hello python"
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $var1
hello python
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# declare -r var1
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# var1="hello go"
-bash: var1: readonly variable
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]#
实例二:-i 将变量设为整数
shell中如果不声明,默认当做字符串处理
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# num1=10
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# num2=$num1+20
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $num2
10+20
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# declare -i num2
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# num2=$num1+20
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo $num2
30
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]#
实例三:-a 将变量定义为数组
定义数组
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# declare -a array
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# array=("jones" "mike" "kobe" "jordan")
输出数组所有的内容
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo ${array[@]}
jones mike kobe jordan
第一个元素
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo ${array[0]}
jones
数组长度
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# echo ${#array[@]}
4
删除元素
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# unset array
1.6.Bash数学运算之expr
语法格式

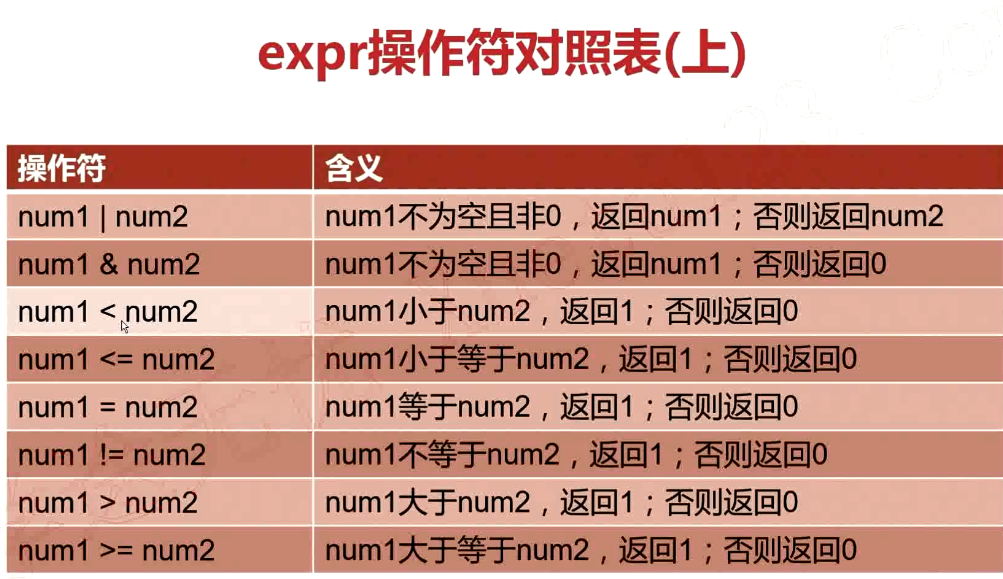
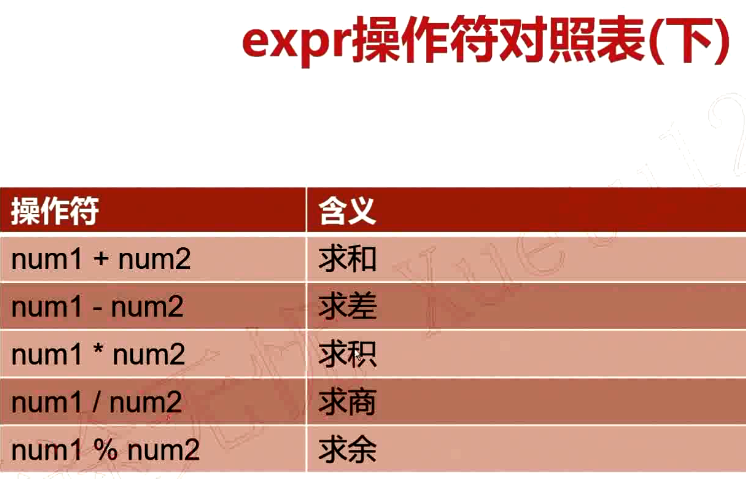
需要加转义字符“\”
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# num1=30
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# num2=40
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# expr $num1 \> $num2
0
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# expr $num1 \< $num2
1
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# expr $num1 + $num2
70
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# expr $num1 - $num2
-10
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# expr $num1 * $num2
expr: syntax error
[root@VM_0_9_centos shell_learn]# expr $num1 \* $num2
1200
1.7.Bash数学运算之bc
bc是bash内建的运算器,支持浮点数运算。内建变量scale可以设置,默认为0.
[root@VM_0_9_centos ~]# echo "23+35" | bc
58
[root@VM_0_9_centos ~]# echo "23.3+35" | bc
58.3
[root@VM_0_9_centos ~]# echo "scale=3;23.3/3.5" | bc
6.657
[root@VM_0_9_centos ~]#
1.shell编程-变量的高级用法的更多相关文章
- 2.shell编程-函数的高级用法
2.1.函数的定义和使用 函数基本使用 [root@VM_0_9_centos ~]# test() > {} -bash: syntax error near unexpected token ...
- Bash 脚本编程的一些高级用法
概述 偶然间发现 man bash 上其实详细讲解了 shell 编程的语法,包括一些很少用却很实用的高级语法.就像发现了宝藏的孩子,兴奋莫名.于是参考man bash,结合自己的理解,整理出了这篇文 ...
- Shell编程中Shift的用法
Shell编程中Shift的用法 位置参数可以用shift命令左移.比如shift 3表示原来的$4现在变成$1,原来的$5现在变成$2等等,原来的$1.$2.$3丢弃,$0不移动.不带参数的shif ...
- Shell编程中Shift的用法【转】
本文转载自:http://www.cnblogs.com/image-eye/archive/2011/08/20/2147153.html Shell编程中Shift的用法 位置参数可以用shift ...
- 详解shell编程中2>&1用法
在使用 linux 命令或者 shell 编程时,这个用法常会遇到 2>&1 下面看一个命令示例,然后分析下他是如何工作的: ls foo > /dev/null 2>&am ...
- shell编程变量赋值
[shell编程变量赋值] 1.等号两边均不能有空格存在.例, a="hello world" 2.变量和其它文字以{}或空格格开,否则会混淆.例, 有时候变量名可能会和其它文 ...
- shell 变量的高级用法
变量删除和替换 案例:从头开始匹配,将符合最短的数据删除 (#) variable_1="I love you, Do you love me" echo $variable_1 ...
- Linux_10------Linux之shell编程------变量
.-9 vim num.sh #! /bin/bash num1=$1 num2=$2 sum=$(($num1+$num2)) #变量sum是num1和num2的综合 echo $sum 执行 ./ ...
- Linux Shell编程变量赋值和引用
我们可以使用任意一种文字编辑器,比如gedit.kedit.emacs.vi等来编写shell脚本,它必须以如下行开始(必须放在文件的第一行): #!/bin/sh ... 注意:最好使用“! ...
随机推荐
- 网络分析:WireShark
安装 WireShark 官网 过滤器 类别 显示过滤器模式 捕获过滤器模式 逻辑表达式 and:&& or:|| 成组:() 过滤实例 仅监听某域名 http.host == &qu ...
- ubuntu 设置qt程序开机启动
1.建立一个桌面文件,forklift-app.desktop Name填写程序的名字 Exec执行程序的路径 [Desktop Entry] Version=1.0 Name=forklift-ap ...
- Tensorflow 保存和载入训练过程
本节涉及点: 保存训练过程 载入保存的训练过程并继续训练 通过命令行参数控制是否强制重新开始训练 训练过程中的手动保存 保存训练过程前,程序征得同意 一.保存训练过程 以下方代码为例: import ...
- VS 特殊注释
任务注释(添加此注释后,点击视图->任务列表,可以看到TODO注释的位置)://TODO: (未实现)……//UNDONE:(没有做完)……//HACK:(修改)……
- 【LeetCode】 454、四数之和 II
题目等级:4Sum II(Medium) 题目描述: Given four lists A, B, C, D of integer values, compute how many tuples (i ...
- python selenium 实战涉及很多知识点
1.iframe的切入和切出 #切入 driver.switch_to.frame(driver.find_element_by_id('iFrame_1')) # 切换出来 driver.switc ...
- NIO 编程模型
NIO 编程模型 Doug Lea 在 Scalable IO in Java 的 PPT 中描述了 Reactor 编程模型的思想,大部分 NIO 框架和一些中间件的 NIO 编程都与它一样或是它的 ...
- yum源配置、epel源配置
关键词:yum源,本地yum源,网络yum源 [1]配置本地yum源 1.挂载好光盘到/redhat/mnt/mnt下 mount /dev/cdrom /mnt 2.操作 cd /etc/yum ...
- 在Linux中,没有文件创建时间的概念。只有文件的访问时间、修改时间、状态改变时间
在Linux中,没有文件创建时间的概念.只有文件的访问时间.修改时间.状态改变时间.也就是说不能知道文件的创建时间.但如果文件创建后就没有修改过,修改时间=创建时间:如果文件创建后,状态就没有改变过, ...
- Java 类的构造器中this()和super()的困惑
关于构造器中super的使用,书本上这样写: “super是指向父类的引用,如果构造方法没有显示地调用父类的构造方法,那么编译器会自动为它加上一个默认的super()方法调用.如果父类由没有默认的无参 ...
