2023-10-21:用go语言,一共有三个服务A、B、C,网络延时分别为a、b、c 并且一定有:1 <= a <= b <= c <= 10^9 但是具体的延时数字丢失了,只有单次调用的时间 一次调
2023-10-21:用go语言,一共有三个服务A、B、C,网络延时分别为a、b、c
并且一定有:1 <= a <= b <= c <= 10^9
但是具体的延时数字丢失了,只有单次调用的时间
一次调用不可能重复使用相同的服务,
一次调用可能使用了三个服务中的某1个、某2个或者全部3个服务
比如一个调用的时间,T = 100
100的延时可能来自以下7种情况:
a = 100,这次调用可能单独使用了A
b = 100,这次调用可能单独使用了B
c = 100,这次调用可能单独使用了C
a + b = 100,这次调用可能组合使用了A、B
a + c = 100,这次调用可能组合使用了A、C
b + c = 100,这次调用可能组合使用了B、C
a + b + c = 100,这次调用可能组合使用了A、B、C全部服务
那么可想而知,如果给的调用时间足够多,是可以猜测出a、b、c的
给定一个数组times,长度为n,并且一定有4 <= n <= 7
times[i] = s,表示i号调用用时s,而且times中一定都是正数且没有重复值。
请根据n次调用,猜测出a、b、c三元组可能的情况数。
如果任何a、b、c都无法匹配上给定的调用耗时,返回0,
测试的次数T <= 100,
也就是说,一共最多给定100个数组,每一次让你返回a、b、c三元组可能的情况数。
来自招商银行。
来自左程云。
答案2023-10-21:
为什么用讯飞星火?
这次代码生成用的讯飞星火,生成完后,要略微修改下代码才能通过。另外c代码的生成,一直有问题,索性就不管了。
之前一直用的chatgpt,但那个地址不能用了,所以用讯飞星火试水。
文心一言以及其他产品,我也试了下,java代码太多,文心一言无法转换成其他代码,都有各自的问题,所以只能放弃。
大体过程如下:
1.首先,定义一个函数ways,接受一个整数数组times作为参数,并返回可能的情况数。
2.在ways函数中,创建一个长度为7的整数数组status,用于记录服务的延时情况。初始化为全0。
3.创建一个空的mapans,用于存储可能的三元组情况。
4.调用process函数,传入times、0、status和ans作为参数。
5.返回ans的长度,即为可能的情况数。
6.在process函数中,判断是否已经遍历完了times数组,如果是,则进行下面的操作:
6.1.创建三个变量a、b、c,用于存储可能的延时情况。
6.2.调用counts函数,获取当前status数组中非零元素的个数,存储在变量count中。
6.3.根据count的值,进行不同的情况判断:
6.3.1.如果count为0,说明三个服务都没有使用过,根据给定的关系式计算出a、b、c的值。
6.3.2.如果count为1,说明只有一个服务被使用过,根据给定的关系式计算出a、b、c的值。
6.3.3.如果count为2,说明有两个服务被使用过,根据给定的关系式计算出a、b、c的值。
6.3.4.如果count为3,说明三个服务都被使用过,直接将status数组中的值赋给a、b、c。
6.4.调用verify函数,判断当前的a、b、c是否满足条件,如果满足,则将其作为键存入ans中。
7.如果没有遍历完times数组,则进行递归操作:
7.1.遍历status数组,找到第一个为0的位置。
7.2.将当前遍历到的times元素赋值给status数组的该位置。
7.3.递归调用process函数,传入更新后的status数组,i+1,ans作为参数。
7.4.将status数组的该位置重新置为0,进行下一次遍历。
8.在counts函数中,遍历status数组,统计非零元素的个数,并返回该个数。
9.在verify函数中,根据给定的条件,判断a、b、c是否满足条件,如果满足则返回true,否则返回false。
go完整代码如下:
package main
import "fmt"
func ways(times []int) int {
status := []int{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}
ans := make(map[string]struct{})
process(times, 0, status, ans)
return len(ans)
}
func process(times []int, i int, status []int, ans map[string]struct{}) {
if i == len(times) {
a, b, c := 0, 0, 0
count := counts(status)
if count == 0 {
a = (status[3] + status[4] - status[5]) / 2
b = (status[3] + status[5] - status[4]) / 2
c = (status[4] + status[5] - status[3]) / 2
} else if count == 1 {
if status[0] != 0 {
a = status[0]
if status[3] != 0 {
b = status[3] - a
}
if status[4] != 0 {
c = status[4] - a
}
if status[5] != 0 {
if b != 0 && c == 0 {
c = status[5] - b
}
if c != 0 && b == 0 {
b = status[5] - c
}
}
} else if status[1] != 0 {
b = status[1]
if status[3] != 0 {
a = status[3] - b
}
if status[5] != 0 {
c = status[5] - b
}
if status[4] != 0 {
if a != 0 && c == 0 {
c = status[4] - a
}
if c != 0 && a == 0 {
a = status[4] - c
}
}
} else {
c = status[2]
if status[4] != 0 {
a = status[4] - c
}
if status[5] != 0 {
b = status[5] - c
}
if status[3] != 0 {
if a != 0 && b == 0 {
b = status[3] - a
}
if b != 0 && a == 0 {
a = status[3] - b
}
}
}
} else if count == 2 {
if status[0] != 0 {
a = status[0]
}
if status[1] != 0 {
b = status[1]
}
if status[2] != 0 {
c = status[2]
}
if a == 0 {
if status[3] != 0 {
a = status[3] - b
} else if status[4] != 0 {
a = status[4] - c
} else {
a = status[6] - b - c
}
} else if b == 0 {
if status[3] != 0 {
b = status[3] - a
} else if status[5] != 0 {
b = status[5] - c
} else {
b = status[6] - a - c
}
} else {
if status[4] != 0 {
c = status[4] - a
} else if status[5] != 0 {
c = status[5] - b
} else {
c = status[6] - a - b
}
}
} else {
a = status[0]
b = status[1]
c = status[2]
}
if verify(status, a, b, c) {
ans[fmt.Sprint(a)+"_"+fmt.Sprint(b)+"_"+fmt.Sprint(c)] = struct{}{}
}
} else {
for j := 0; j < 7; j++ {
if status[j] == 0 {
status[j] = times[i]
process(times, i+1, status, ans)
status[j] = 0
}
}
}
}
func counts(status []int) int {
count := 0
for i := 0; i < 3; i++ {
if status[i] != 0 {
count++
}
}
return count
}
func verify(status []int, a, b, c int) bool {
if a <= 0 || b <= 0 || c <= 0 || a > b || b > c {
return false
}
if status[0] != 0 && status[0] != a {
return false
}
if status[1] != 0 && status[1] != b {
return false
}
if status[2] != 0 && status[2] != c {
return false
}
if status[3] != 0 && status[3] != a+b {
return false
}
if status[4] != 0 && status[4] != a+c {
return false
}
if status[5] != 0 && status[5] != b+c {
return false
}
if status[6] != 0 && status[6] != a+b+c {
return false
}
return true
}
func main() {
times := []int{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}
fmt.Println(ways(times))
}
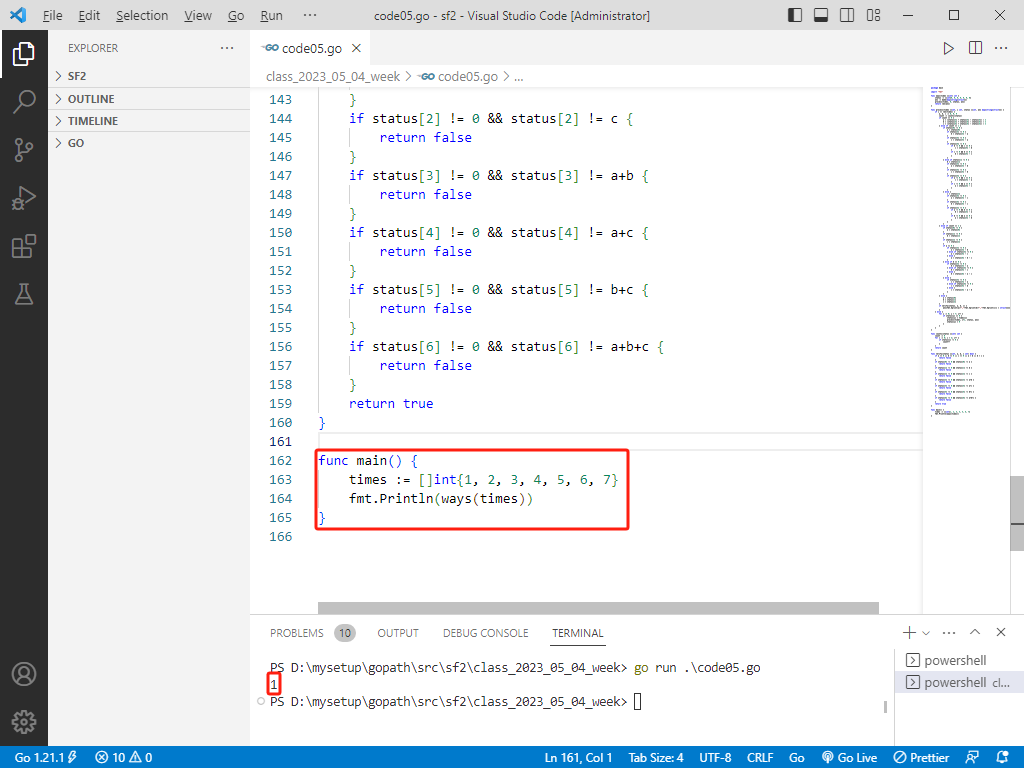
rust完整代码如下:
use std::collections::HashSet;
fn main() {
let status = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7];
let ans = ways(&status);
println!("Hello, World {}", ans);
}
fn ways(times: &[i32]) -> usize {
let mut status = [0; 7];
let mut ans = std::collections::HashSet::new();
process(times, 0, &mut status, &mut ans);
ans.len()
}
fn process(times: &[i32], i: usize, status: &mut [i32], ans: &mut HashSet<String>) {
if i == times.len() {
let a = if status[0] != 0 {
status[0]
} else {
(status[3] + status[4] - status[5]) / 2
};
let b = if status[1] != 0 {
status[1]
} else {
(status[3] + status[5] - status[4]) / 2
};
let c = if status[2] != 0 {
status[2]
} else {
(status[4] + status[5] - status[3]) / 2
};
if verify(status, a, b, c) {
let a_str = a.to_string();
let b_str = b.to_string();
let c_str = c.to_string();
ans.insert(format!("{}-{}-{}", a_str, b_str, c_str));
}
} else {
for j in 0..7 {
if status[j] == 0 {
status[j] = times[i];
process(times, i + 1, status, ans);
status[j] = 0;
}
}
}
}
fn verify(s: &[i32], a: i32, b: i32, c: i32) -> bool {
if a <= 0 || b <= 0 || c <= 0 || a > b || b > c {
return false;
}
if s[0] != 0 && s[0] != a {
return false;
}
if s[1] != 0 && s[1] != b {
return false;
}
if s[2] != 0 && s[2] != c {
return false;
}
if s[3] != 0 && s[3] != a + b {
return false;
}
if s[4] != 0 && s[4] != a + c {
return false;
}
if s[5] != 0 && s[5] != b + c {
return false;
}
if s[6] != 0 && s[6] != a + b + c {
return false;
}
true
}
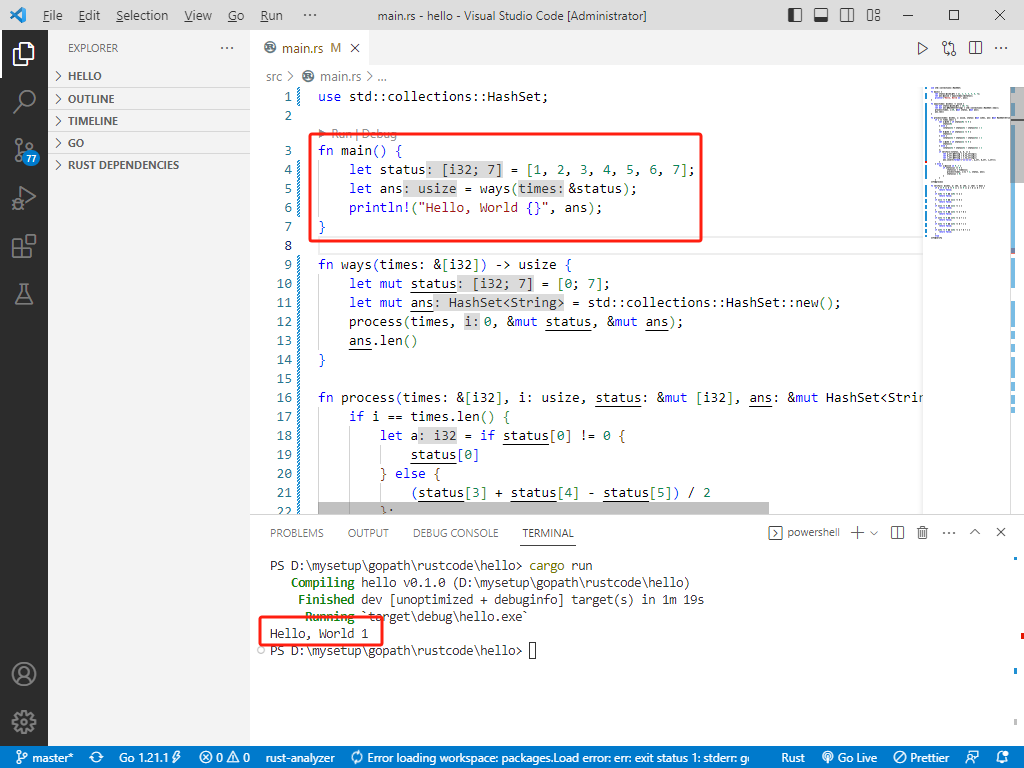
c++完整代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <unordered_set>
using namespace std;
bool verify(std::vector<int> s, int a, int b, int c);
int counts(vector<int> status);
void process(vector<int> times, int i, vector<int>& status, unordered_set<string>& ans);
int ways(vector<int> times) {
vector<int> status(7);
unordered_set<string> ans;
process(times, 0, status, ans);
return ans.size();
}
void process(vector<int> times, int i, vector<int>& status, unordered_set<string>& ans) {
if (i == times.size()) {
int a = 0;
int b = 0;
int c = 0;
int cnt = counts(status);
if (cnt == 0) {
a = (status[3] + status[4] - status[5]) / 2;
b = (status[3] + status[5] - status[4]) / 2;
c = (status[4] + status[5] - status[3]) / 2;
}
else if (cnt == 1) {
if (status[0] != 0) {
a = status[0];
if (status[3] != 0) {
b = status[3] - a;
}
if (status[4] != 0) {
c = status[4] - a;
}
if (status[5] != 0) {
if (b != 0 && c == 0) {
c = status[5] - b;
}
if (c != 0 && b == 0) {
b = status[5] - c;
}
}
}
else if (status[1] != 0) {
b = status[1];
if (status[3] != 0) {
a = status[3] - b;
}
if (status[5] != 0) {
c = status[5] - b;
}
if (status[4] != 0) {
if (a != 0 && c == 0) {
c = status[4] - a;
}
if (c != 0 && a == 0) {
a = status[4] - c;
}
}
}
else {
c = status[2];
if (status[4] != 0) {
a = status[4] - c;
}
if (status[5] != 0) {
b = status[5] - c;
}
if (status[3] != 0) {
if (a != 0 && b == 0) {
b = status[3] - a;
}
if (b != 0 && a == 0) {
a = status[3] - b;
}
}
}
}
else if (cnt == 2) {
if (status[0] != 0) {
a = status[0];
}
if (status[1] != 0) {
b = status[1];
}
if (status[2] != 0) {
c = status[2];
}
if (a == 0) {
if (status[3] != 0) {
a = status[3] - b;
}
else if (status[4] != 0) {
a = status[4] - c;
}
else {
a = status[6] - b - c;
}
}
else if (b == 0) {
if (status[3] != 0) {
b = status[3] - a;
}
else if (status[5] != 0) {
b = status[5] - c;
}
else {
b = status[6] - a - c;
}
}
else {
if (status[4] != 0) {
c = status[4] - a;
}
else if (status[5] != 0) {
c = status[5] - b;
}
else {
c = status[6] - a - b;
}
}
if (verify(status, a, b, c)) {
ans.insert(to_string(a) + "_" + to_string(b) + "_" + to_string(c));
}
}
else {
a = status[0];
b = status[1];
c = status[2];
}
if (verify(status, a, b, c)) {
ans.insert(to_string(a) + "_" + to_string(b) + "_" + to_string(c));
}
}
else {
for (int j = 0; j < 7; j++) {
if (status[j] == 0) {
status[j] = times[i];
process(times, i + 1, status, ans);
status[j] = 0;
}
}
}
}
int counts(vector<int> status) {
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
if (status[i] != 0) {
cnt++;
}
}
return cnt;
}
bool verify(std::vector<int> s, int a, int b, int c) {
if (a <= 0 || b <= 0 || c <= 0 || a > b || b > c) {
return false;
}
if (s[0] != 0 && s[0] != a) {
return false;
}
if (s[1] != 0 && s[1] != b) {
return false;
}
if (s[2] != 0 && s[2] != c) {
return false;
}
if (s[3] != 0 && s[3] != a + b) {
return false;
}
if (s[4] != 0 && s[4] != a + c) {
return false;
}
if (s[5] != 0 && s[5] != b + c) {
return false;
}
if (s[6] != 0 && s[6] != a + b + c) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
int main() {
std::vector<int> status = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 };
int ans = ways(status);
std::cout << "Hello, World " << ans << std::endl;
return 0;
}
2023-10-21:用go语言,一共有三个服务A、B、C,网络延时分别为a、b、c 并且一定有:1 <= a <= b <= c <= 10^9 但是具体的延时数字丢失了,只有单次调用的时间 一次调的更多相关文章
- 【转载】经典10道c/c++语言经典笔试题(含全部所有参考答案)
经典10道c/c++语言经典笔试题(含全部所有参考答案) 1. 下面这段代码的输出是多少(在32位机上). char *p; char *q[20]; char *m[20][20]; int (*n ...
- Golang优秀开源项目汇总, 10大流行Go语言开源项目, golang 开源项目全集(golang/go/wiki/Projects), GitHub上优秀的Go开源项目
Golang优秀开源项目汇总(持续更新...)我把这个汇总放在github上了, 后面更新也会在github上更新. https://github.com/hackstoic/golang-open- ...
- 背水一战 Windows 10 (21) - 绑定: x:Bind 绑定, x:Bind 绑定之 x:Phase, 使用绑定过程中的一些技巧
[源码下载] 背水一战 Windows 10 (21) - 绑定: x:Bind 绑定, x:Bind 绑定之 x:Phase, 使用绑定过程中的一些技巧 作者:webabcd 介绍背水一战 Wind ...
- 数据结构与算法分析——C语言描述 第三章的单链表
数据结构与算法分析--C语言描述 第三章的单链表 很基础的东西.走一遍流程.有人说学编程最简单最笨的方法就是把书上的代码敲一遍.这个我是头文件是照抄的..c源文件自己实现. list.h typede ...
- 21世纪C语言(影印版)
<21世纪C语言(影印版)> 基本信息 原书名:21st Century C 作者: Ben Klemens 出版社:东南大学出版社 ISBN:9787564142056 上架时间:201 ...
- Daily Scrum 10.21
然后由于服务器端有变化,另外具体IDE已经确定,接下来对已经分配下去的任务做些细节补充: 10.20日晚所有人必须完成AS的配置,统一版本为1.3.2,安卓版本为4.4.0,可视化界面手机为Nexus ...
- 第9次Scrum会议(10/21)【欢迎来怼】
一.小组信息 队名:欢迎来怼小组成员队长:田继平成员:李圆圆,葛美义,王伟东,姜珊,邵朔,冉华小组照片 二.开会信息 时间:2017/10/21 17:20~17:45,总计25min.地点:东北师范 ...
- GridView导出成Excel字符"0"丢失/数字丢失的处理方式 收藏
GridView导出成Excel字符"0"丢失/数字丢失的处理方式 收藏 GridView 导出成Excel文件,这个代码在网上比较多.但是发现存在一个问题,导出的数据中如果有&q ...
- Clover KextsToPatch 使用方法 2015.10.21
Clover KextsToPatch 使用方法 2015.10.21 前些天,因为 Thinkpad X230 BIOS 白名单限制,给她换了一块 ar9285 无线网卡,只是因为这块网卡正好可 ...
- MySQL开启binlog无法启动ct 10 21:27:31 postfix/pickup[4801]: warning: 6BD991A0039: message has been queue
1 详细异常 ct 10 21:27:31 postfix/pickup[4801]: warning: 6BD991A0039: message has been queue Oct 10 21:2 ...
随机推荐
- C++面试八股文:什么是空指针/野指针/悬垂指针?
某日二师兄参加XXX科技公司的C++工程师开发岗位第30面: 面试官:什么是空指针? 二师兄:一般我们将等于0/NULL/nullptr的指针称为空指针.空指针不能被解引用,但是可以对空指针取地址. ...
- Android BottomNavigation底部导航栏使用
原文地址: Android BottomNavigation底部导航栏使用 - Stars-One的杂货小窝 基本使用 本文侧重点记录一些特殊的样式设置,所以基本使用这里就简单概述一下,详细图文可以去 ...
- 【git】基于JGit通过ssh-url拉取指定commit-id的代码
实现 1️⃣ pom依赖: <dependency> <groupId>org.eclipse.jgit</groupId> <artifactId>o ...
- T-star高校挑战赛部分wp
web-1签到 checkin还是很基础的 网站上传存在js检测,禁用js即可上传 写PHP一句话木马上传,http://588f25a5.yunyansec.com/upload/test.php连 ...
- 今日ERROR
树莓派插卡发烫严重 首先,我们要知道: 树莓派的指示灯可以告诉用户系统的工作状态,常见的指示灯有四个,分别是红色电源灯.绿色SD卡读写灯.黄色ACT指示灯和蓝色网络连接指示灯(仅适用于某些型号的树莓派 ...
- Oracle分区表设置详解
Oracle分区表详解 Oracle建议单表超过2G就需要进行分表,一万数据大概3MB,单表最多分区为1024*1024-1个分区,我感觉够我们使用了哈 废话不多说,上示例,Oracle分表具体sql ...
- 利用Python爬取免费代理IP
# 2019/9/8 # 思路: 1.找到一个免费的ip代理网站(如:西刺代理) # # 2.爬取ip(常规爬取requests+BeautifulSoup) # # 3.验证ip有效性(携带爬取到的 ...
- Linux: rsyslog.conf 配置
refer to: https://www.debian.org/doc/manuals/debian-handbook/sect.syslog.en.html 日志子系统 Each log mess ...
- quarkus依赖注入之八:装饰器(Decorator)
欢迎访问我的GitHub 这里分类和汇总了欣宸的全部原创(含配套源码):https://github.com/zq2599/blog_demos 本篇概览 本篇是<quarkus依赖注入> ...
- 使用kubeadm部署kubernetes
k8s版本:1.15.0 前期准备 节点: master:172.50.13.103(2核2G) node-1:172.50.13.104(2核2G) node-2:172.50.13.105(2核2 ...
