[转]Implementing User Authentication in ASP.NET MVC 6
本文转自:http://www.dotnetcurry.com/aspnet-mvc/1229/user-authentication-aspnet-mvc-6-identity
In this article we will be implementing User Authentication in an ASP.NET MVC 6 application. Just like MVC 5, we have an Authentication Action Filter in MVC 6.
The following diagram gives an idea of Authentication when the end-user makes a call to an MVC 6 application.
Download an ASP.NET MVC CMS - Free Trial
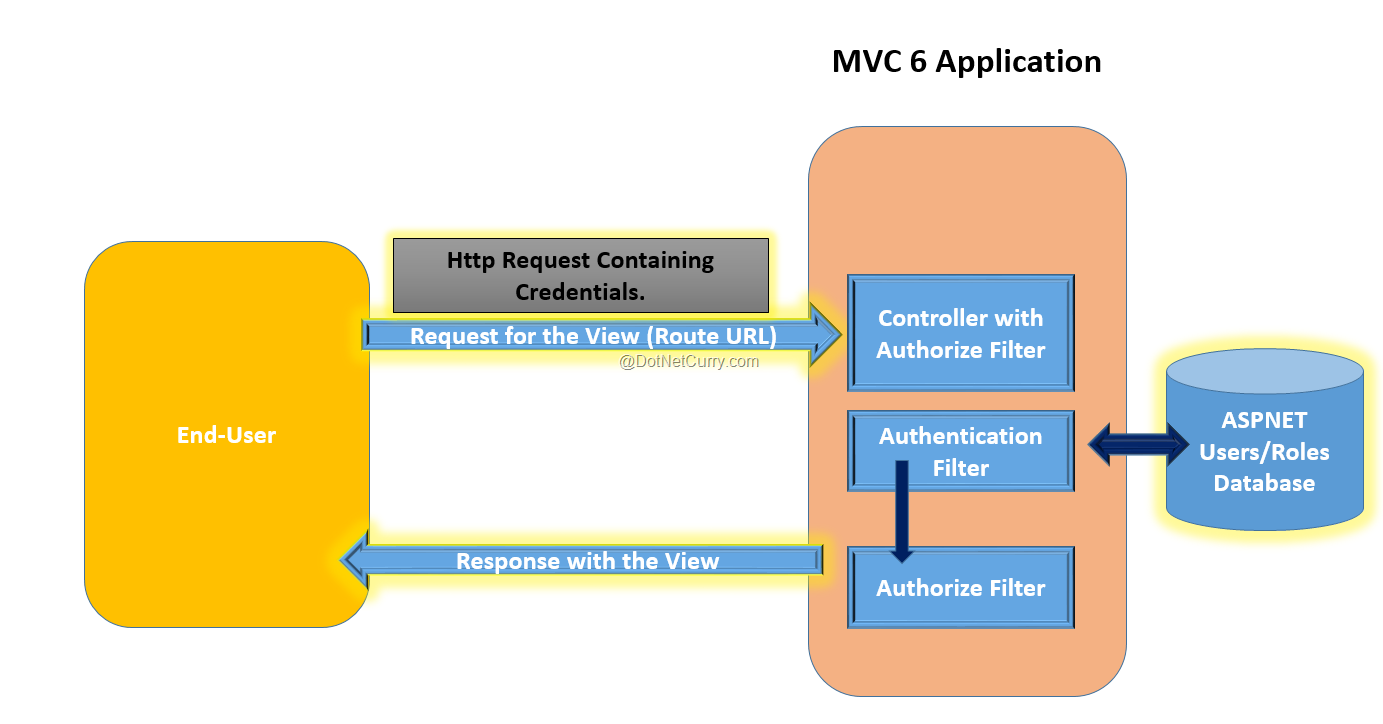
When the end-user makes a call to an MVC 6 application requesting a View, a response in the form of a View is returned when the action is executed. However if the Controller or the Action is applied with the Authorize attribute, then the request processing on the server sends the Login Page response to the client. Once the end-user sends the request with credentials, the Authentication Filter is executed which is responsible for validating Credentials against the Database server where the application users are stored. If the credentials are validated, then the Users will be Logged In and response of the View will be sent back to the user.
Implementing Authentication in ASP.NET MVC
To implement this application, we will be using Visual Studio 2015 Community Edition and ASP.NET 5 RC1. ASP.NET 5 RC 1 can be downloaded from this link.
Step 1: Open Visual Studio 2015 and create a new ASP.NET application of name ASPNET5_Auth as shown in the following Image

Click on OK and from the next window select ASP.NET Empty application from ASP.NET 5 templates as shown in the following image

Step 2: We need to add the following dependencies for using MVC, Identity, EntityFramework, etc. as shown here:
"dependencies": { "EntityFramework.Commands": "7.0.0-rc1-final", "EntityFramework.MicrosoftSqlServer": "7.0.0-rc1-final", "Microsoft.AspNet.Identity": "3.0.0-rc1-final", "Microsoft.AspNet.Identity.EntityFramework": "3.0.0-rc1-final", "Microsoft.AspNet.IISPlatformHandler": "1.0.0-rc1-final", "Microsoft.AspNet.Mvc": "6.0.0-rc1-final", "Microsoft.AspNet.Server.Kestrel": "1.0.0-rc1-final", "Microsoft.Framework.ConfigurationModel.Json": "1.0.0-beta4", "Microsoft.AspNet.Authentication.Cookies": "1.0.0-rc1-final", "Microsoft.AspNet.Mvc.TagHelpers": "6.0.0-rc1-final", "Microsoft.AspNet.StaticFiles": "1.0.0-rc1-final", "Microsoft.Extensions.CodeGenerators.Mvc": "1.0.0-rc1-final", "Microsoft.AspNet.Tooling.Razor": "1.0.0-rc1-final" }, "commands": { "web": "Microsoft.AspNet.Server.Kestrel", "ef": "EntityFramework.Commands" } |
The above dependencies will add necessary assemblies in the project.
Step 3: Since we need to store the Application users information in a SQL Server database, open Sql Server and create database of the name Security.
Step 4: In the project, add a new ASP.NET Configuration file, this will add appSettings.json file in the project. In this file add the following connection string
{ "Data": { "DefaultConnection": { "ConnectionString": "Server=.;Database=Security; Trusted_Connection=True;" } }} |
Step 5: In the project add Models, Views and Controllers folder. In the Models folder add the following class files.
Register.cs
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;namespace ASPNET5_Auth.Models{ public class Register { [Required] [EmailAddress] [Display(Name = "Email")] public string Email { get; set; } [Required] [StringLength(100, ErrorMessage = "The {0} must be at least {2} characters long.", MinimumLength = 6)] [DataType(DataType.Password)] [Display(Name = "Password")] public string Password { get; set; } [DataType(DataType.Password)] [Display(Name = "Confirm password")] [Compare("Password", ErrorMessage = "The password and confirmation password do not match.")] public string ConfirmPassword { get; set; } }} |
The above class contains properties for registering new user.
Login.cs
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;namespace ASPNET5_Auth.Models{ public class Login { [Required] [EmailAddress] public string Email { get; set; } [Required] [DataType(DataType.Password)] public string Password { get; set; } }} |
The above class contains properties for User Login.
ApplicationUser.cs
using Microsoft.AspNet.Identity.EntityFramework;namespace ASPNET5_Auth.Models{ public class ApplicationUser :IdentityUser { }} |
The above class is IdentityUser. This is used to manage application users. This class is used to store application user name based on unique email.
AppDbContext.cs
using Microsoft.AspNet.Identity.EntityFramework;using Microsoft.Data.Entity;namespace ASPNET5_Auth.Models{ public class AppDbContext : IdentityDbContext<ApplicationUser> { protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder builder) { base.OnModelCreating(builder); } }} |
The above class uses the Connection string to connect to database server and generate tables for storing the application user information in it. The IdentityDbContext<T> class uses EntityFramework to connect to database server.
ModelClasses.cs
using System.Collections.Generic;namespace ASPNET5_Auth.Models{ public class Person { public int PersonId { get; set; } public string PersonName { get; set; } } public class PersonDatabase : List<Person> { public PersonDatabase() { Add(new Person() { PersonId=1,PersonName="MS"}); Add(new Person() { PersonId = 2, PersonName = "SA" }); Add(new Person() { PersonId = 3, PersonName = "VP" }); } }} |
The above code is used to define Person entity class and the PersonDatabase class for storing person data.
Step 6: To generate the tables for storing Application users, right-click on the project name and select the Open Folder in File Explorer option. This will open the Explorer window. Right-click on any folder in the explorer window with ctrl+shift > and select option Open Command Window from Here. This will open the command prompt. Run following commands from the command prompt
dnu restorednvm use 1.0.0-rc1-final -pdnx ef migrations add Initialdnx ef database update |
Details for this commands can be read from this link.
This will add the following tables in Sql Server Security database

The command also adds Migration folder in the project containing AppDbContextModelSnapshot class. This contains logic for DB migration. The Initial class contains logic for Creating table using the Migration Command.
Step 7: In the Controllers folder, add a new item of type MVC Controller class of name AccountController. In this class, add the following code
using System.Threading.Tasks;using Microsoft.AspNet.Mvc;using Microsoft.AspNet.Authorization;using ASPNET5_Auth.Models;using Microsoft.AspNet.Identity; namespace ASPNET5_Auth.Controllers{ public class AccountController : Controller { //1 private readonly UserManager<ApplicationUser> _securityManager; private readonly SignInManager<ApplicationUser> _loginManager; //2 public AccountController(UserManager<ApplicationUser> secMgr, SignInManager<ApplicationUser> loginManager) { _securityManager = secMgr; _loginManager = loginManager; } //3 [HttpGet] [AllowAnonymous] public IActionResult Register() { return View(); } //4 [HttpPost] [AllowAnonymous] [ValidateAntiForgeryToken] public async Task<IActionResult> Register(Register model) { if (ModelState.IsValid) { var user = new ApplicationUser { UserName = model.Email, Email = model.Email }; var result = await _securityManager.CreateAsync(user, model.Password); if (result.Succeeded) { await _loginManager.SignInAsync(user, isPersistent: false); return RedirectToAction(nameof(HomeController.Index), "Home"); } } return View(model); } //5 [HttpGet] [AllowAnonymous] public IActionResult Login(string returnUrl = null) { ViewData["ReturnUrl"] = returnUrl; return View(); } //6 [HttpPost] [AllowAnonymous] [ValidateAntiForgeryToken] public async Task<IActionResult> Login(Login model, string returnUrl = null) { ViewData["ReturnUrl"] = returnUrl; if (ModelState.IsValid) { var result = await _loginManager.PasswordSignInAsync(model.Email, model.Password, false, lockoutOnFailure: false); if (result.Succeeded) { return RedirectToReturnUrl(returnUrl); } } return View(model); } //7 [HttpPost] [ValidateAntiForgeryToken] public async Task<IActionResult> LogOff() { await _loginManager.SignOutAsync(); return RedirectToAction(nameof(HomeController.Index), "Home"); } //8 private IActionResult RedirectToReturnUrl(string returnUrl) { if (Url.IsLocalUrl(returnUrl)) { return Redirect(returnUrl); } else { return RedirectToAction(nameof(HomeController.Index), "Home"); } } }} |
This above code has the following specifications:
1. It declares objects of UserManager<T> and SignInManager<T> classes. The UserManager<T> is used to manage users from the persistent store i.e. database and the SignInManager<T> class is used to manager APIs for user Sign In. The T here is the ApplicationUser class which contains user information.
2. The constructor of the controller class is injected with the UserManager and SignInManager dependencies. These dependencies will be registered in future steps.
3. Step for responding with the Register view.
4. HttpPost Register method which accepts the Register model object. This method will create an application method by using CreateAsync() method of the SignInManager class. If the user is registered successfully then the user will be signed using SignAsync() method of the UserManager class.
5. The HttpGet Login() method which responds with a Login View.
6. The Login() HttpPost method is used for the model containing the Email and password. If the Login is successful, then it will redirect to the page from which the request for Login initiated.
7. The LogOff () method.
8. A private method to redirect to the url from where the login request initiated.
Step 8: In the Controllers folder, add the following new controllers
PersonController.cs
using Microsoft.AspNet.Mvc;using ASPNET5_Auth.Models;using Microsoft.AspNet.Authorization;namespace ASPNET5_Auth.Controllers{ [Authorize] public class PersonController : Controller { // GET: /<controller>/ public IActionResult Index() { var persons = new PersonDatabase(); return View(persons); } }} |
The above controller contains the Index method to return Person Collection.
HomeController.cs
using Microsoft.AspNet.Mvc;namespace ASPNET5_Auth.Controllers{ public class HomeController : Controller { // GET: /<controller>/ public IActionResult Index() { return View(); } }} |
The Home Controllers contains Index method.
Step 9: Since we need to use Bootstrap styles in the project for view, in the Project add Bower.json and add the following dependencies in it
"dependencies": { "jQuery": "2.1.4", "bootstrap": "3.3.6" } |
This will install jQuery and Bower dependencies in the wwwroot section of the project.
Step 10: In the View folder, Add Shared folder. In this folder, using Add New Item, add the MVC View Layout Page. This will be _Layout.cshtml page. Add the following Markup and script references in it:
<!DOCTYPE html><html><head> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width" /> <link rel="stylesheet" href="~/lib/bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css" /> <title>@ViewBag.Title</title></head><body> <div class="navbar-collapse collapse"><ul class="nav navbar-nav"> <li><a target="_blank" rel="nofollow">Home</a></li> <li><a target="_blank" rel="nofollow">Person</a></li> <li><a target="_blank" rel="nofollow">Register</a></li> <li><a target="_blank" rel="nofollow">Login</a></li> </ul></div> <div>@RenderBody()</div> <a href="http://~/lib/jQuery/dist/jquery.js" target="_blank" rel="nofollow">http://~/lib/jQuery/dist/jquery.js</a> <a href="http://~/lib/bootstrap/dist/js/bootstrap.js" target="_blank" rel="nofollow">http://~/lib/bootstrap/dist/js/bootstrap.js</a></body></html> |
We have links for Home, Register, Login, Person controllers.
Step 11: In the Views folder, using add new item, add MVC View Imports Page and in this page add the following imports
@using Microsoft.AspNet.Identity@addTagHelper "*, Microsoft.AspNet.Mvc.TagHelpers" |
This will be used to activate tag helpers from the MVC Views. This will be used in Model binding.
Step 12: In the Views folder, add a new folder of the name Person. In this folder add a new MVC View using add new item. This will add Index.cshtml. Add the following markup in the view:
@model IEnumerable<ASPNET5_Auth.Models.Person>@{ Layout = "_Layout"; ViewData["Title"] = "Index";}<h2>Index</h2> <table class="table"> <tr> <th> @Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.PersonId) </th> <th> @Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.PersonName) </th> </tr> @foreach (var item in Model) { <tr> <td> @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.PersonId) </td> <td> @Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.PersonName) </td> </tr> }</table> |
Add the Home folder, in the View folder with the Index.cshtml view with markup as per your need.
In the Views folder, add a new MVC View of name Register.cshtml with the following markup code:
@model ASPNET5_Auth.Models.Register@{ Layout = "_Layout"; ViewData["Title"] = "Register";}<h2>@ViewData["Title"].</h2><form asp-controller="Account" asp-action="Register" method="post" class="form-horizontal" role="form"> <h4>Create a new account.</h4> <hr /> <div class="text-danger"> </div> <div class="form-group"><div class="col-md-10"> </div> </div> <div class="form-group"><div class="col-md-10"> </div> </div> <div class="form-group"><div class="col-md-10"> </div> </div> <div class="form-group"><div class="col-md-offset-2 col-md-10">Register</div> </div> </form></div></div></div></div> |
This view contains Textboxes for accepting user registration information. This view uses new MVC 6 tags like asp-controller, asp-action, asp-for etc. These tags will be processed by Microsoft.AspNet.Mvc.TagHelpers.
The same folder will contain Login.cshtml with the following code:
@model ASPNET5_Auth.Models.Login @{ Layout = "_Layout"; ViewData["Title"] = "Log in";}<div class="row"><div class="col-md-8"><section> <h4>Use a local account to log in.</h4> <hr> <div class="text-danger"> </div> <div class="form-group"><div class="col-md-10"> </div> </div> <div class="form-group"><div class="col-md-10"> </div> </div> <div class="form-group"><div class="col-md-offset-2 col-md-10">Log in</div> </div> <p> <a asp-action="Register">Register as a new user?</a> </p> </form> </section> </div> </div></div></div></div></section></div></div> |
All above steps completes the application design. Now we need to complete the Identity registration.
Identity Registration
Step 13: In Startup.cs, add the following code:
Add References in the Class
using Microsoft.AspNet.Builder;using Microsoft.AspNet.Hosting;using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;using ASPNET5_Auth.Models;using Microsoft.Data.Entity;using Microsoft.AspNet.Identity.EntityFramework;using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration; |
The Constructor
public Startup(IHostingEnvironment env){ var builder = new ConfigurationBuilder() .AddJsonFile("appsettings.json") .AddJsonFile($"appsettings.{env.EnvironmentName}.json", optional: true); builder.AddEnvironmentVariables(); Configuration = builder.Build();} |
The above code loads and reads json files in the project.
The rest of the code
public IConfigurationRoot Configuration { get; set; }// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to add services to the container.// For more information on how to configure your application, visit http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=398940public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services){ services.AddEntityFramework() .AddSqlServer() .AddDbContext<AppDbContext>(options => options.UseSqlServer(Configuration["Data:DefaultConnection:ConnectionString"])); services.AddIdentity<ApplicationUser, IdentityRole>() .AddEntityFrameworkStores<AppDbContext>() .AddDefaultTokenProviders(); services.AddMvc();}// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline.public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app){ app.UseIISPlatformHandler(); app.UseStaticFiles(); app.UseIdentity(); // To configure external authentication please see http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=532715 app.UseMvc(routes => { routes.MapRoute( name: "default", template: "{controller=Home}/{action=Index}/{id?}"); });} |
ConfigureServices() does dependency injection for EntityFramework based on the connection string and the Identity based on the Application User and IdentityRole. This method also adds the MVC service. The Configure() method defines the use of Identity, using UseIdentity() method and defines the routing for MVC using UseMvc() method. UseStaticFiles() method will be used to read the CSS and jQuery files in application.
Run the application. The home page will be displayed as shown in the following image

Click on the Person link, this will redirect to the Login page as shown in the following image

Click on Register as a new user link to show the register page as shown in the following image

Create a new user, once the registration is successful the Person view will be displayed as shown in the following image

Conclusion:
ASP.NET MVC 6 provides an easy approach for implementing Authentication. Using Microsoft.AspNet.Identity, we can create users and roles for the application and integrate them with controllers.
Download the entire source code of this article (Github)
Share on Facebook
Share on Twitter
Share on Google+
-->
Custom Model Binder in ASP.NET MVC
Using MongoDB with Web API and ASP.NET Core
Action Method Selector in ASP.NET MVC
Access same Action Method by Multiple Roles in ASP.NET MVC using Configuration File
Creating Tag Helpers in ASP.NET MVC 6 / ASP.NET Core 1.0

[转]Implementing User Authentication in ASP.NET MVC 6的更多相关文章
- Forms Authentication in ASP.NET MVC 4
原文:Forms Authentication in ASP.NET MVC 4 Contents: Introduction Implement a custom membership provid ...
- Implementing HTTPS Everywhere in ASP.Net MVC application.
Implementing HTTPS Everywhere in ASP.Net MVC application. HTTPS everywhere is a common theme of the ...
- Active Directory Authentication in ASP.NET MVC 5 with Forms Authentication and Group-Based Authorization
I know that blog post title is sure a mouth-full, but it describes the whole problem I was trying to ...
- Demystifying ASP.NET MVC 5 Error Pages and Error Logging
出处:http://dusted.codes/demystifying-aspnet-mvc-5-error-pages-and-error-logging Error pages and error ...
- 【记录】ASP.NET MVC 4/5 Authentication 身份验证无效
在 ASP.NET MVC 4/5 应用程序发布的时候,遇到一个问题,在本应用程序中进行身份验证是可以,但不能和其他"二级域名"共享,在其他应用程序身份验证,不能和本应用程序共享, ...
- ASP.NET MVC 5 Authentication Breakdown
In my previous post, "ASP.NET MVC 5 Authentication Breakdown", I broke down all the parts ...
- ASP.NET MVC:Form Authentication 相关的学习资源
看完此图就懂了 看完下面文章必须精通 Form authentication and authorization in ASP.NET Explained: Forms Authentication ...
- 【ASP.NET MVC 5】第27章 Web API与单页应用程序
注:<精通ASP.NET MVC 3框架>受到了出版社和广大读者的充分肯定,这让本人深感欣慰.目前该书的第4版不日即将出版,现在又已开始第5版的翻译,这里先贴出该书的最后一章译稿,仅供大家 ...
- 【转】ASP.NET MVC 的最佳实践
[This post is based on a document authored by Ben Grover (a senior developer at Microsoft). It is ou ...
随机推荐
- Nginx conf基本配置
#定义Nginx运行的用户和用户组 user www www; #nginx进程数,建议设置为等于CPU总核心数. worker_processes 8; #全局错误日志定义类型,[ debu ...
- NSKeyedArchiver数据归档
前言 在 OC 语言中,归档是一个过程,即用某种格式来保存一个或多个对象,以便以后还原这些对象. 通常,这个过程包括将(多个)对象写入文件中,以便以后读取该对象.可以使用归档的方法进行对象的深复制. ...
- 洛谷P4011 孤岛营救问题(状压+BFS)
传送门 和网络流有半毛钱关系么…… 可以发现$n,m,p$都特别小,那么考虑状压,每一个状态表示位置以及钥匙的拥有情况,然后每次因为只能走一步,所以可以用bfs求出最优解 然后是某大佬说的注意点:每个 ...
- xtrabackup使用
转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/waynechou/p/xtrabackup_backup.html 阅读目录 xtrabackup 选项 xtrabackup 全量备份恢复 x ...
- ARKit的使用
//创建场景 let scene = SCNScene() /* //1.几何 let box = SCNBox.init(width: 0.1, height: 0.1, length: 0.1, ...
- javascrip 词法分析详解
JavaScript的高级知识---词法分析 词法分析 词法分析方法: js运行前有一个类似编译的过程即词法分析,词法分析主要有三个步骤: 分析参数 再分析变量的声明 分析函数说明 函数在运行的瞬 ...
- python学习之路---day09
函数案例: return 可以终止函数后面的调用 def abc() print("1") print("2") print("3") pr ...
- JavaScript 调用 Windows 的打印 代码
JavaScript 调用 Windows 的打印 代码 2009-02-24 10:36 <%@ Page Language="C#" AutoEventWireup=&q ...
- codeforces 1072D Minimum path bfs+剪枝 好题
题目传送门 题目大意: 给出一幅n*n的字符,从1,1位置走到n,n,会得到一个字符串,你有k次机会改变某一个字符(变成a),求字典序最小的路径. 题解: (先吐槽一句,cf 标签是dfs题????) ...
- SPOJ - FREQ2 莫队 / n^1.5logn爆炸
题意:给定\(a[1...n]\)和\(Q\)次询问,每次统计\([L,R]\)范围内出现频率最高的数的次数 想法没啥好说的,分别统计该数出现的次数和次数出现的次数,然后莫队暴力 注意本题时间卡的很紧 ...
