Java IO流学习总结二:File
Java File类的功能非常强大,利用java基本上可以对文件进行所有操作。
首先来看File类的构造函数的源码
/**
* Internal constructor for already-normalized pathname strings.
*/
private File(String pathname, int prefixLength) {
this.path = pathname;
this.prefixLength = prefixLength;
} /**
* Internal constructor for already-normalized pathname strings.
* The parameter order is used to disambiguate this method from the
* public(File, String) constructor.
*/
private File(String child, File parent) {
assert parent.path != null;
assert (!parent.path.equals(""));
this.path = fs.resolve(parent.path, child);
this.prefixLength = parent.prefixLength;
} /**
* Creates a new <code>File</code> instance by converting the given
* pathname string into an abstract pathname. If the given string is
* the empty string, then the result is the empty abstract pathname.
*
* @param pathname A pathname string
* @throws NullPointerException
* If the <code>pathname</code> argument is <code>null</code>
*/
public File(String pathname) {
if (pathname == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
this.path = fs.normalize(pathname);
this.prefixLength = fs.prefixLength(this.path);
} /**
* @param parent The parent pathname string
* @param child The child pathname string
* @throws NullPointerException
* If <code>child</code> is <code>null</code>
*/
public File(String parent, String child) {
if (child == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
if (parent != null && !parent.isEmpty()) {
this.path = fs.resolve(fs.normalize(parent),
fs.normalize(child));
} else {
this.path = fs.normalize(child);
}
this.prefixLength = fs.prefixLength(this.path);
} /**
* @param parent The parent abstract pathname
* @param child The child pathname string
* @throws NullPointerException
* If <code>child</code> is <code>null</code>
*/
public File(File parent, String child) {
if (child == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
if (parent != null) {
if (parent.path.equals("")) {
this.path = fs.resolve(fs.getDefaultParent(),
fs.normalize(child));
} else {
this.path = fs.resolve(parent.path,
fs.normalize(child));
}
} else {
this.path = fs.normalize(child);
}
this.prefixLength = fs.prefixLength(this.path);
} /**
* @param uri
* An absolute, hierarchical URI with a scheme equal to
* <tt>"file"</tt>, a non-empty path component, and undefined
* authority, query, and fragment components
*
* @throws NullPointerException
* If <tt>uri</tt> is <tt>null</tt>
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException
* If the preconditions on the parameter do not hold
*/
public File(URI uri) { // Check our many preconditions
if (!uri.isAbsolute())
throw new IllegalArgumentException("URI is not absolute");
if (uri.isOpaque())
throw new IllegalArgumentException("URI is not hierarchical");
String scheme = uri.getScheme();
if ((scheme == null) || !scheme.equalsIgnoreCase("file"))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("URI scheme is not \"file\"");
if (uri.getAuthority() != null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("URI has an authority component");
if (uri.getFragment() != null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("URI has a fragment component");
if (uri.getQuery() != null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("URI has a query component");
String p = uri.getPath();
if (p.equals(""))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("URI path component is empty"); // Okay, now initialize
p = fs.fromURIPath(p);
if (File.separatorChar != '/')
p = p.replace('/', File.separatorChar);
this.path = fs.normalize(p);
this.prefixLength = fs.prefixLength(this.path);
}
从源码可以看出File类的构造函数有6个,精简如下
public File(String pathname) //文件的绝对路径
public File(URI uri) //文件的URI地址 public File(String parent, String child) //指定父文件绝对路径、子文件绝对路径
public File(File parent, String child) //指定父文件、子文件相对路径 //下面这两个是File类中私有的构造函数,外面不能调用
private File(String child, File parent)
private File(String pathname, int prefixLength)
现在就看的比较清楚了,6个构造函数,可以分为2类。4个公共构造函数,2个私有构造函数。
构造函数1:
//电脑d盘中的cat.png 图片的路径
String filePath1 = "D:/cat.png" ;
File file = new File( filePath1 ) ;
构造函数2:
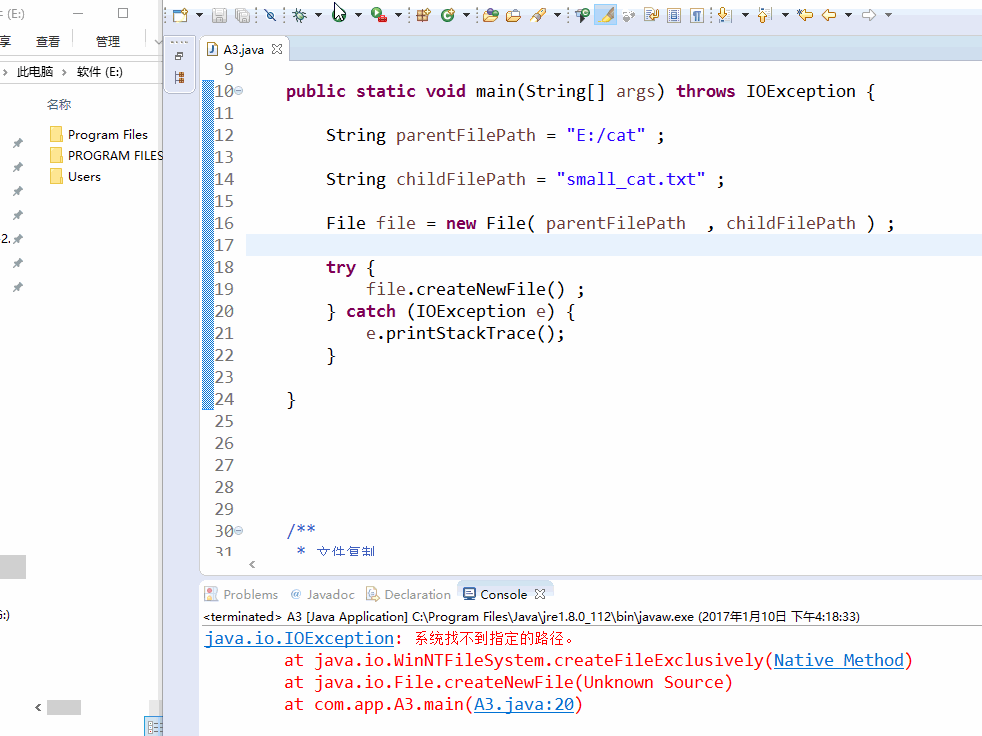
String parentFilePath = "E:/cat" ; String childFilePath = "small_cat.txt" ; //创建parentFile文件
File parentFile = new File( parentFilePath ) ;
parentFile.mkdir() ; //如果parentFile不存在,就会报异常
File file = new File( parentFilePath , childFilePath ) ; try {
file.createNewFile() ;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
效果图:
构造函数3:
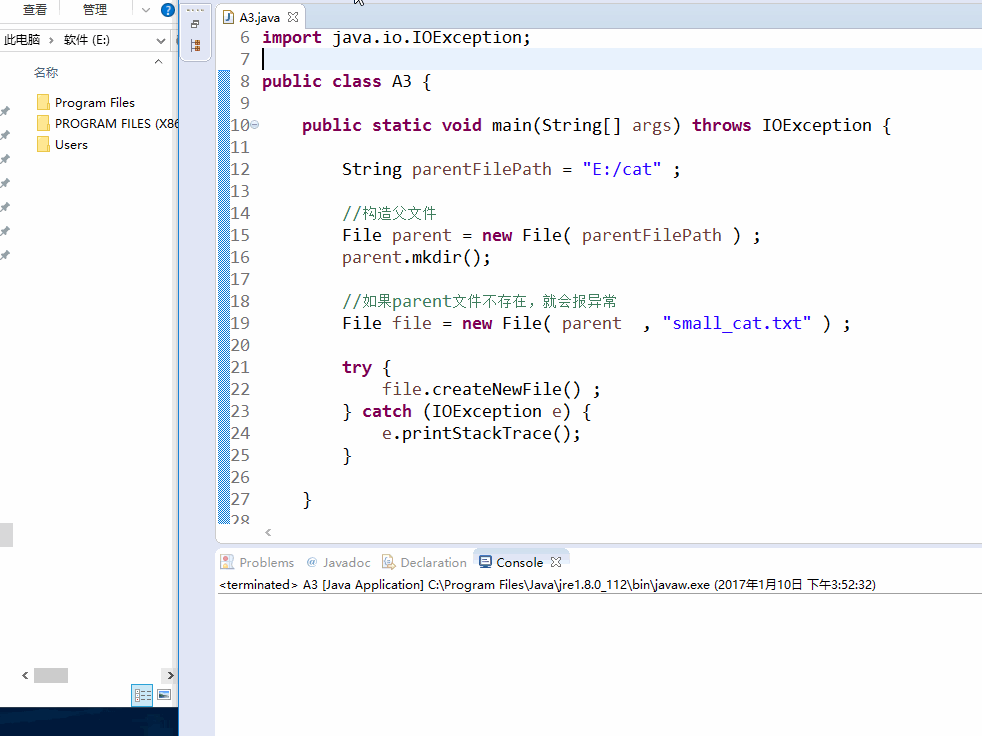
String parentFilePath = "E:/cat" ; //构造父文件
File parent = new File( parentFilePath ) ;
parent.mkdir(); //如果parent文件不存在,就会报异常
File file = new File( parent , "small_cat.txt" ) ; try {
file.createNewFile() ;
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
效果图:
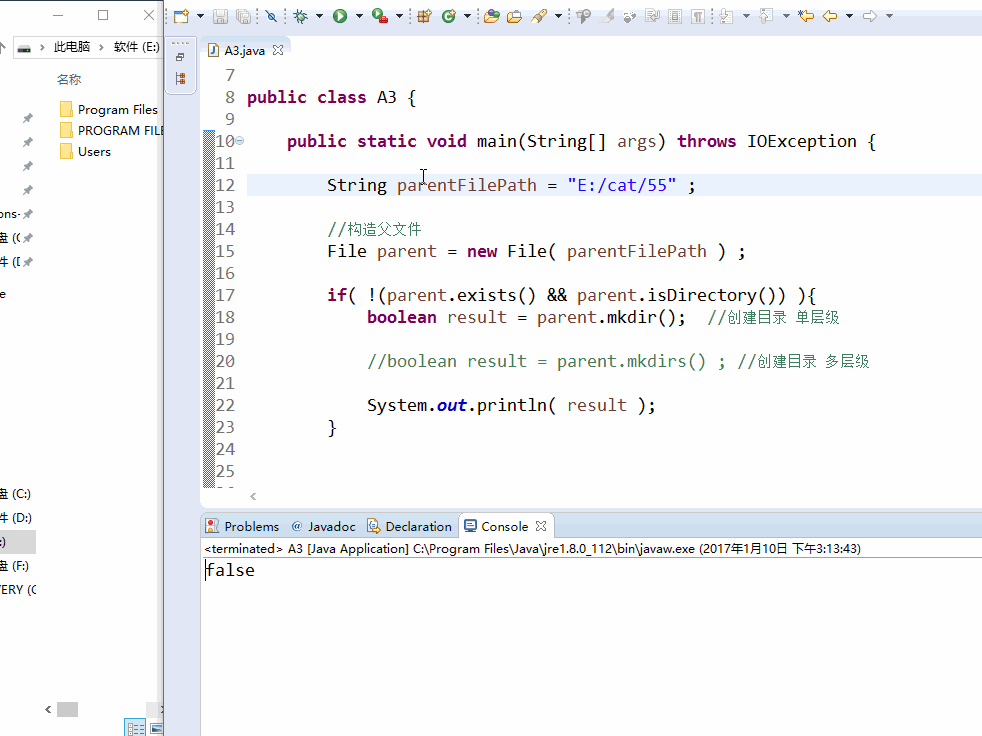
- 创建目录
boolean file.mkdir()
如果创建成功,返回 true , 创建失败,返回false。如果这个文件夹已经存在,则返回false.
只能创建一级目录,如果父目录不存在,返回false.
- 创建多级目录
boolean file.mkdirs()
创建多级目录,创建成功,返回true,创建失败,返回false。如果父目录不存在,就创建,并且返回true.
- 创建一个新的文件
boolean file.createNewFile() ;
如果文件不存在就创建该文件,创建成功,返回 true ;创建失败,返回false。如果这个文件已经存在,则返回false.
- 判断方法
boolean file.exists() //文件是否存在 boolean file.isFile() //是否是文件 boolean file.isDirectory() //是否是目录 boolean file.isHidden() //是否隐藏(windows上可以设置某个文件是否隐藏) boolean file.isAbsolute() //是否为绝对路径 boolean file.canRead() //是否可读 boolean file.canWrite() //是否可写 boolean file.canExecute() //是否可执行
获取文件的信息
String file.getName() //获取文件的名字,只是名字,没有路径 String file.getParent() //获取父目录的绝对路径,返回值是一个字符串。如果文件有父目录,那么返回父目录的绝对路径,(比如:`E:\cat`) , 如果文件本身就在磁盘的根目录,那么返回磁盘的路径,(比如:`E:\`)。 File file.getParentFile() //获取父文件,返回值是一个File对象。 long time = file.lastModified() ; //返回文件最后一次修改的时间
Date dt = new Date(time); boolean renameTo(File file) //文件命名 long file.length() //返回文件的大小,单位字节 boolean file.delete() //删除文件 String[] file.list() //获取该目录下的所有的文件的名字。如果`file`为文件,返回值为`null`,在使用时记得判空;但是如果`file`为目录,那么返回这个目录下所有文件的名字,只是名字,不含路径;如果`file`是一个空目录,返回一个长度为0的数组;从上面的结果可以看出,`list()` 方法,只是对`file`为目录时有效,当`file`为一个文件的时候,该方法毫无意义。 File[] file.listFiles() //获取该目录下的所有的文件。如果`file`为文件,返回值为`null`,在使用时记得判空;但是如果`file`为目录,那么返回这个目录下所有的文件 ;如果`file`是一个空目录,返回一个长度为0的数组;从上面的结果可以看出,`listFiles()` 方法,只是对`file`为目录时有效,当`file`为一个文件的时候,该方法毫无意义。
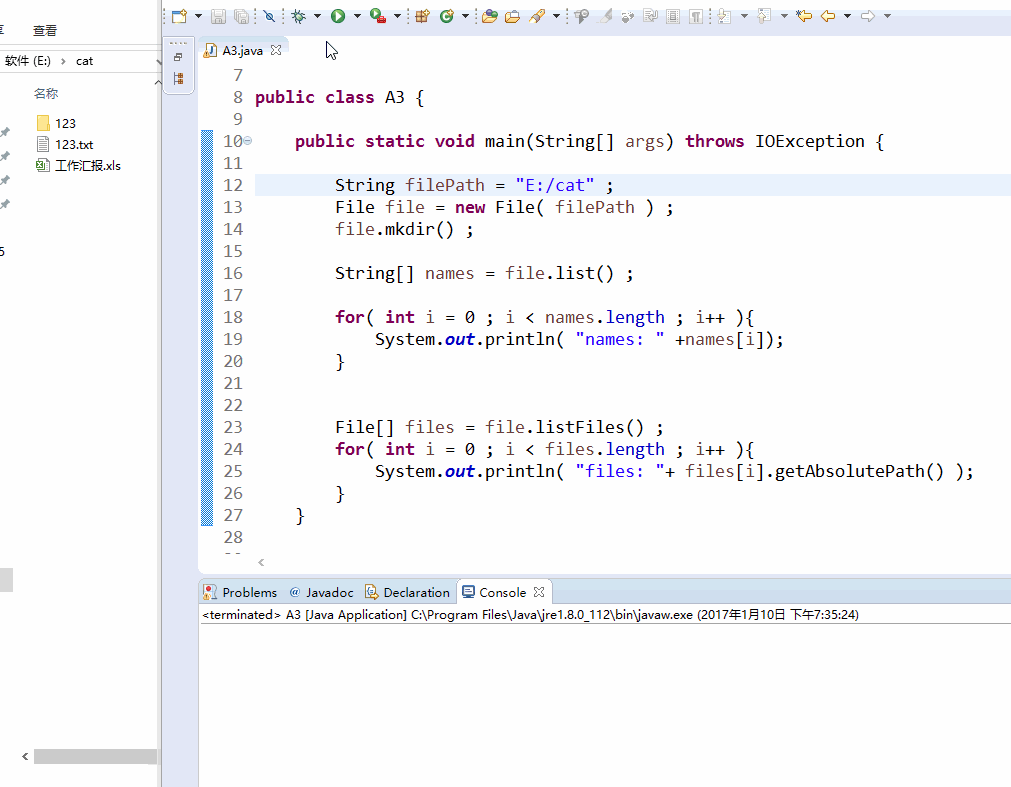
实战经验1: file.list() , file.listFiles()
String filePath = "E:/cat" ;
File file = new File( filePath ) ;
file.mkdir() ; String[] names = file.list() ; for( int i = 0 ; i < names.length ; i++ ){
System.out.println( "names: " +names[i]);
} File[] files = file.listFiles() ;
for( int i = 0 ; i < files.length ; i++ ){
System.out.println( "files: "+ files[i].getAbsolutePath() );
}
效果图:
实战经验2:扫描F盘所有的文件
public class A3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String filePath = "F:/" ;
File file = new File( filePath ) ;
getFile(file);
}
private static void getFile( File file ){
File[] files = file.listFiles() ;
for( File f : files ){
if ( f.isHidden() ) continue ;
if(f.isDirectory() ){
getFile( f );
}else{
System.out.println( f.getAbsolutePath() + " " + f.getName() );
}
}
}
}
效果图:
在上面的实战演练中用到了,file.list() , file.listFiles() 。这是两个无参的方法,实际上还有两个有参的方法,分别是
file.list(FilenameFilter filter) ; file.listFiles( FilenameFilter filter) ; file.listFiles(FileFilter filter)
FileFilter
FileFilter是io包里面的一个接口,从名字上可以看出,这个类是文件过滤功能的。
需要重写accept方法
比如:
static class MyFileFilter implements FileFilter {
MyFileFilter(){
}
//pathname:文件的绝对路径+ 文件名 , 比如:F:\安来宁 - 难得.mp3 , 或者: F:\文件夹1
@Override
public boolean accept(File pathname) {
return false;
}
}
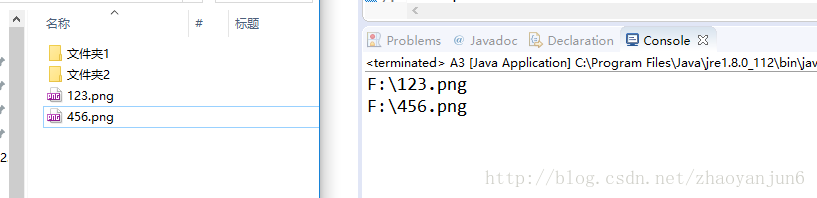
实战:获取指定目录的所有文件夹
package com.app;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileFilter;
import java.io.IOException; public class A3 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String filePath = "F:/" ;
File file = new File( filePath ) ;
getFile(file); } /**
* 获取指定目录的所有文件夹
* @param file
*/
private static void getFile( File file ){
MyFileFilter myFileFilter = new MyFileFilter() ; File[] files = file.listFiles( myFileFilter ) ;
for( File f : files ){
if ( f.isHidden() ) continue ; System.out.println( f.getAbsolutePath() );
}
} static class MyFileFilter implements FileFilter { MyFileFilter(){ } //pathname:文件的绝对路径+ 文件名 , 比如:F:\安来宁 - 难得.mp3 , 或者: F:\文件夹1
@Override
public boolean accept(File pathname) {
if( pathname.isDirectory() ){
return true ;
}
return false;
} } }
FilenameFilter
FileFilter是io包里面的一个接口,从名字上可以看出,这个类是文件名字过滤功能的。
需要重写里面的accept方法。
比如:
package com.app; import java.io.File;
import java.io.FilenameFilter; public class MyFilenameFilter implements FilenameFilter {
//type为需要过滤的条件,比如如果type=".jpg",则只能返回后缀为jpg的文件
private String type;
MyFilenameFilter( String type){
this.type = type ;
} @Override
public boolean accept(File dir, String name) {
//dir表示文件的当前目录,name表示文件名;
return name.endsWith( type ) ;
} }
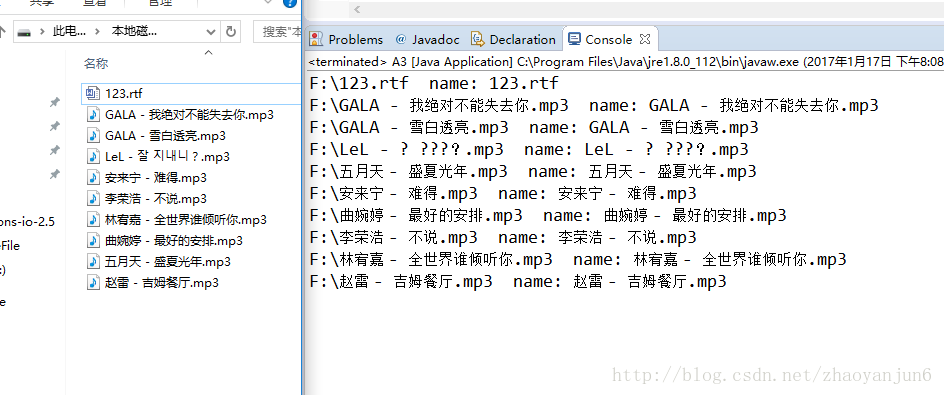
实战:扫描出指定路径的所有图片
package com.app;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FilenameFilter;
import java.io.IOException; public class A3 { public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException { String filePath = "F:/" ;
File file = new File( filePath ) ;
getFile(file); } /**
* 扫描出指定路径的所有图片
* @param file
*/
private static void getFile( File file ){
MyFilenameFilter myFileFilter = new MyFilenameFilter( ".png") ; File[] files = file.listFiles( myFileFilter ) ;
for( File f : files ){
if ( f.isHidden() ) continue ; System.out.println( f.getAbsolutePath() );
}
} static class MyFilenameFilter implements FilenameFilter {
//type为需要过滤的条件,比如如果type=".jpg",则只能返回后缀为jpg的文件
private String type;
MyFilenameFilter( String type){
this.type = type ;
} @Override
public boolean accept(File dir, String name) {
//dir表示文件的当前目录,name表示文件名;
return name.endsWith( type ) ;
} } }
运行结果:
转载 https://blog.csdn.net/zhaoyanjun6/article/details/54581478
Java IO流学习总结二:File的更多相关文章
- Java IO流学习
Java IO流学习 Java流操作有关的类或接口: Java流类图结构: 流的概念和作用 流是一组有顺序的,有起点和终点的字节集合,是对数据传输的总称或抽象.即数据在两设备间的传输称为流,流的本质是 ...
- Java IO流学习总结三:缓冲流-BufferedInputStream、BufferedOutputStream
Java IO流学习总结三:缓冲流-BufferedInputStream.BufferedOutputStream 转载请标明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/zhaoyanjun6/ ...
- Java IO流学习总结(1)
Java IO流学习总结 Java流操作有关的类或接口: Java流类图结构: 流的概念和作用 流是一组有顺序的,有起点和终点的字节集合,是对数据传输的总称或抽象.即数据在两设备间的传输称为流,流的本 ...
- Java IO流学习总结四:缓冲流-BufferedReader、BufferedWriter
在上一篇文章中Java IO流学习总结三:缓冲流-BufferedInputStream.BufferedOutputStream介绍了缓冲流中的字节流,而这一篇着重介绍缓冲流中字符流Buffered ...
- Java IO流学习总结八:Commons IO 2.5-IOUtils
Java IO流学习总结八:Commons IO 2.5-IOUtils 转载请标明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/zhaoyanjun6/article/details/550519 ...
- Java IO流学习总结一:输入输出流
Java IO流学习总结一:输入输出流 转载请标明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/zhaoyanjun6/article/details/54292148 本文出自[赵彦军的博客] J ...
- JAVA.IO流学习笔记
一.java.io 的描述 通过数据流.序列化和文件系统提供系统输入和输出.IO流用来处理设备之间的数据传输 二.流 流是一个很形象的概念,当程序需要读取数据的时候,就会开启一个通向数据源的流,这个数 ...
- Java IO流学习总结
Java流操作有关的类或接口: Java流类图结构: 流的概念和作用 流是一组有顺序的,有起点和终点的字节集合,是对数据传输的总称或抽象.即数据在两设备间的传输称为流,流的本质是数据传输,根据数据传输 ...
- Java IO流学习总结(转)
Java流操作有关的类或接口: Java流类图结构: 流的概念和作用 流是一组有顺序的,有起点和终点的字节集合,是对数据传输的总称或抽象.即数据在两设备间的传输称为流,流的本质是数据传输,根据数据传输 ...
随机推荐
- [UE4]Authority,网络控制权
复制的条件 1.是否可复制开关打开 2.而且是服务器创建,或者放在关卡中. Authority,网络控制权 1.在网络游戏中,由当前进程创建的Actor,对其拥有网络控制权 2.Has Authori ...
- 高可用hadoop的hdfs启动的时候namenode启动不了
启动的时候,一直要求输入namenode密码: 查看namenode的日志如下: 2019-03-28 18:38:08,961 INFO org.apache.hadoop.ipc.Client: ...
- Centos 7: 改变docker的image存放目录
1.创建新的数据目录 mkdir /data/docker 2.关闭docker进程 systemctl stop docker 3.修改配置文件/usr/lib/systemd/system/doc ...
- 小众Python库介绍
Python 是世界上发展最快的编程语言之一.它一次又一次地证明了自己在开发人员和跨行业的数据科学中的实用性.Python 及其机器学习库的整个生态系统使全世界的用户(无论新手或老手)都愿意选择它.P ...
- 使用原子类或synchronized(没用Lock)解决阐述多线程所遇到线程安全问题和解决方案
例子题目: 创建10个线程,每个线程执行10000次加1,输出总和 正常结果100000 但是如果出现线程不安全会低于100000 import java.util.concurrent.Count ...
- replace实现替换全部
方法: string.replace(new RegExp(oldString,"gm"),newString)) gm g=global, m=multiLine , 大致上方法 ...
- error while obtaining ui hierarchy xml file...用 uiautomatorviewer 获取安卓手机软件页面时报错
Error while obtaining UI hierarchy XML file: com.android.ddmlib.SyncException: Remote object doesn't ...
- thinkphp 验证的使用
TP5验证可分为独立验证和验证器: 独立验证是可直接写在控制器里直接验证如下: //独立验证 $data = [ 'name'=>'vendor33333', 'email'=>'vaen ...
- 理解 with递归调用 Sqlserver 树查询
--with用法 --可以这么理解 with SQL语句变量或者叫临时表名 as( SQL语句 ) select * from SQL语句变量或者叫临时表名 --递归调用 with CTE as( s ...
- OpenGL Hello World
▶ OpenGL 的环境配置与第一个程序 ● CUDA 中自带 OpenGL 需要的头文件和库,直接拉进项目里边去就行 ● VS项目属性右键,属性,C/C++ 目录,包含目录,添加 CUDA 的头文件 ...
