[SPDK/NVMe存储技术分析]002 - SPDK官方介绍
Introduction to the Storage Performance Development Kit (SPDK) | SPDK概述
By Jonathan S. (Intel), Updated December 5, 2016
Solid-state storage media is in the process of taking over the data center. Current-generation flash storage enjoys significant advantages in performance, power consumption, and rack density over rotational media. These advantages will continue to grow as next-generation media enter the marketplace.
固态存储设备正在逐步接管数据中心。目前这一代的闪存存储,相对于传统的磁盘设备来说,在性能(performance)、功耗(power consumption)和机架密度(rack density)上都具有显著的优势。这些优势将会进一步增大,使闪存存储作为下一代存储设备进入到存储市场。

Introduction to the Storage Performance Development Kit (SPDK) Customers integrating current solid-state media, such as the Intel SSD DC P3700 Series Non-Volatile Memory Express* (NVMe*) drive, face a major challenge: because the throughput and latency performance are so much better than that of a spinning disk, the storage software now consumes a larger percentage of the total transaction time. In other words, the performance and efficiency of the storage software stack is increasingly critical to the overall storage system. As storage media continues to evolve, it risks outstripping the software architectures that use it, and in coming years the storage media landscape will continue evolving at an incredible pace.
用户使用现在的固态设备,比如Intel SSD DC P3700 Series Non-Volatile Memory Express(NVMe)驱动,面临着一个主要的挑战:因为吞吐量和时延性能比传统的磁盘好太多,现在的存储软件在总的处理时间中占用了较大的比例。换句话说,存储软件栈的性能和效率在整个存储系统中显得越来越重要了。随着存储设备继续向前发展,它将面临远远超过正在使用的软件体系结构的风险(即存储设备受制于相关软件的不足而不能发挥其全部性能),在接下来的几年中,存储设备将会继续发展到一个令人难以置信的高度。
To help storage OEMs and ISVs integrate this hardware, Intel has created a set of drivers and a complete, end-to-end reference storage architecture called the Storage Performance Development Kit (SPDK). The goal of SPDK is to highlight the outstanding efficiency and performance enabled by using Intel’s networking, processing, and storage technologies together. By running software designed from the silicon up, SPDK has demonstrated that millions of I/Os per second are easily attainable by using a few processor cores and a few NVMe drives for storage with no additional offload hardware. Intel provides the entire Linux* reference architecture source code under the broad and permissive BSD license and is distributed to the community through GitHub*. A blog, mailing list, and additional documentation can be found at spdk.io.
为了帮助存储OEM(设备代工厂)和ISV(独立软件开发商)整合硬件,Inte构造了一系列驱动,以及一个完备的、端对端的参考存储体系结构,被命名为Storage Performance Development Kit(SPDK)。SPDK的目标是通过同时使用Intel的网络技术,处理技术和存储技术来显著地提高效率和性能。通过运行为硬件定制的软件,通过使用多个core和几个NVMe存储(没有额外的offlload硬件),SPDK已经证明很容易达到每秒钟数百万次I/O读取。Intel使用BSD license通过Github分发提供其全部的基于Linux架构的源码。博客、邮件列表和其他文档可在spdk.io中找到。
Software Architectural Overview | 软件体系结构概览
How does SPDK work? The extremely high performance is achieved by combining two key techniques: running at user level and using Poll Mode Drivers (PMDs). Let’s take a closer look at these two software engineering terms.
SPDK是如何工作的?达到这样的超高性能运用了两项关键技术:运行于用户态和轮询模式。让我们对这两个软件工程术语做进一步的了解。
First, running our device driver code at user level means that, by definition, driver code does not run in the kernel. Avoiding the kernel context switches and interrupts saves a significant amount of processing overhead, allowing more cycles to be spent doing the actual storing of the data. Regardless of the complexity of the storage algorithms (deduplication, encryption, compression, or plain block storage), fewer wasted cycles means better performance and latency. This is not to say that the kernel is adding unnecessary overhead; rather, the kernel adds overhead relevant to general-purpose computing use cases that may not be applicable to a dedicated storage stack. The guiding principle of SPDK is to provide the lowest latency and highest efficiency by eliminating every source of additional software overhead.
首先,我们的设备驱动代码运行在用户态,这意味着(在定义上)驱动代码不会运行在内核态。避免内核上下文切换和中断将会节省大量的处理开销,允许更多的时钟周期被用来做实际的数据存储。无论存储算法(去冗,加密,压缩,空白块存储)多么复杂,浪费更少的时钟周期总是意味着更好的性能和时延。这并不是说内核增加了不必要的开销;相反,内核增加了一些与通用计算用例相关的开销,因而可能不适合专用的存储栈。SPDK的指导原则是通过消除每一处额外的软件开销来提供最少的时延和最高的效率。
Second, PMDs change the basic model for an I/O. In the traditional I/O model, the application submits a request for a read or a write, and then sleeps while awaiting an interrupt to wake it up once the I/O has been completed. PMDs work differently; an application submits the request for a read or write, and then goes off to do other work, checking back at some interval to see if the I/O has yet been completed. This avoids the latency and overhead of using interrupts and allows the application to improve I/O efficiency. In the era of spinning media (tape and HDDs), the overhead of an interrupt was a small percentage of the overall I/O time, thus was a tremendous efficiency boost to the system. However, as the age of solid-state media continues to introduce lower-latency persistent media, interrupt overhead has become a non-trivial portion of the overall I/O time. This challenge will only become more glaring with lower latency media. Systems are already able to process many millions of I/Os per second, so the elimination of this overhead for millions of transactions compounds quickly into multiple cores being saved. Packets and blocks are dispatched immediately and time spent waiting is minimized, resulting in lower latency, more consistent latency (less jitter), and improved throughput.
其次,轮询模式驱动(Polled Mode Drivers, PMDs)改变了I/O的基本模型。在传统的I/O模型中,应用程序提交读写请求后进入睡眠状态,一旦I/O完成,中断就会将其唤醒。PMDs的工作方式则不同,应用程序提交读写请求后继续执行其他工作,以一定的时间间隔回头检查I/O是否已经完成。这种方式避免了中断带来的延迟和开销,并使得应用程序提高了I/O效率。在旋转设备时代(磁带和机械硬盘),中断开销只占整个I/O时间的很小的百分比,因此给系统带来了巨大的效率提升。然而,在固态设备时代,持续引入更低时延的持久化设备,中断开销成为了整个I/O时间中不可忽视的部分。这个问题在更低时延的设备上只会越来越严重。系统已经能够每秒处理数百万个I/O,所以消除数百万个事务的这种开销,能够快速地复制到多个core中。数据包和数据块被立即分发,因为等待花费的时间变小,使得时延更低,一致性时延更多(抖动更少),吞吐量也得到了提高。
SPDK is composed of numerous subcomponents, interlinked and sharing the common elements of user-level and poll-mode operation. Each of these components was created to overcome a specific performance bottleneck encountered while creating the end-to-end SPDK architecture. However, each of these components can also be integrated into non-SPDK architectures, allowing customers to leverage the experience and techniques used within SPDK to accelerate their own software.
SPDK由多个子组件构成,相互连接并共享用户态操作和轮询模式操作的共有部分。当构造端对端SPDK体系结构时,每个组件被构造来克服遭遇到的特定的性能瓶颈。然而,每个组件也可以被整合进非SPDK体系结构,允许用户利用SPDK中使用的经验和技术来加速自己的软件。
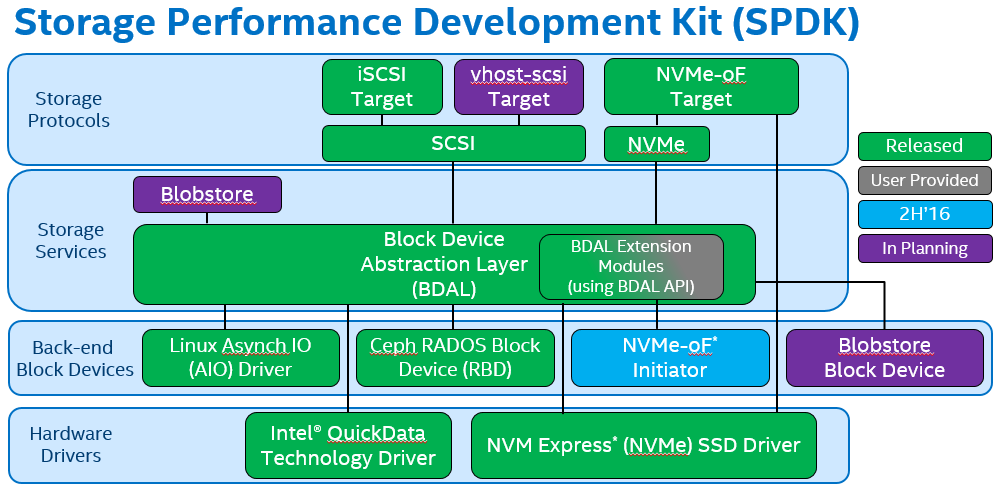
Starting at the bottom and building up:
让我们就上图自底向上开始讲述:
Hardware Drivers | 硬件驱动
NVMe driver: The foundational component for SPDK, this highly optimized, lockless driver provides unparalleled scalability, efficiency, and performance.
NVMe driver:SPDK的基础组件,高度优化且无锁的驱动提供了前所未有的高扩展性,高效性和高性能。
Intel QuickData Technology: Also known as Intel I/O Acceleration Technology (Intel IOAT), this is a copy offload engine built into the Intel Xeon processor-based platform. By providing user space access, the threshold for DMA data movement is reduced, allowing greater utilization for small-size I/Os or NTB.
Inter QuickData Technology:也称为Intel I/O Acceleration Technology(Inter IOAT,Intel I/O加速技术),这是一种基于Xeon处理器平台上的copy offload引擎。通过提供用户空间访问,减少了DMA数据移动的阈值,允许对小尺寸I/O或NTB(非透明桥)做更好地利用。
Back-End Block Devices | 后端块设备
NVMe over Fabrics (NVMe-oF) initiator: From a programmer’s perspective, the local SPDK NVMe driver and the NVMe-oF initiator share a common set of API commands. This means that local/remote replication, for example, is extraordinarily easy to enable.
NVMe over Fabrics(NVMe-oF)initiator:从程序员的角度来看,本地SPDK NVMe驱动和NVMe-oF initiator共享一套公共的API命令。这意味着本地/远程复制非常容易实现。
Ceph* RADOS Block Device (RBD): Enables Ceph as a back-end device for SPDK. This might allow Ceph to be used as another storage tier, for example.
Ceph RADOS Block Device(RBD):使Ceph成为SPDK的后端设备,这可能允许Ceph用作另一个存储层。
Blobstore Block Device: A block device allocated by the SPDK Blobstore, this is a virtual device that VMs or databases could interact with. These devices enjoy the benefits of the SPDK infrastructure, meaning zero locks and incredibly scalable performance.
Blobstore Block Device:由SPDK Blobstore分配的块设备,是虚拟机或数据库可与之交互的虚拟设备。这些设备享有SPDK基础架构带来的优势,意味着无锁和令人难以置信的可扩展性。
Linux* Asynchronous I/O (AIO): Allows SPDK to interact with kernel devices like HDDs.
Linux Asynchrounous I/O(AIO):允许SPDK与内核设备(如机械硬盘)发生交互。
Storage Services | 存储服务
Block device abstraction layer (bdev): This generic block device abstraction is the glue that connects the storage protocols to the various device drivers and block devices. Also provides flexible APIs for additional customer functionality (RAID, compression, dedup, and so on) in the block layer.
Block device abstration layer(bdev):这种通用的块设备抽象是连接到各种不同设备驱动和块设备的存储协议的粘合剂。在块层中还提供了灵活的API用于额外的用户功能(磁盘阵列,压缩,去冗等)。
Blobstore: Implements a highly streamlined file-like semantic (non-POSIX*) for SPDK. This can provide high-performance underpinnings for databases, containers, virtual machines (VMs), or other workloads that do not depend on much of a POSIX file system’s feature set, such as user access control.
Blobstore:为SPDK实现一个高精简的类文件的语义(非POSIX)。这可为数据库,容器,虚拟机或其他不依赖于大部分POSIX文件系统功能集(比如用户访问控制)的工作负载提供高性能支撑。
Storage Protocols | 存储协议
iSCSI target: Implementation of the established specification for block traffic over Ethernet; about twice as efficient as kernel LIO. Current version uses the kernel TCP/IP stack by default.
iSCSI target:建立了通过以太网的块流量规范,大约是内核LIO效率的两倍。现在的版本默认使用内核TCP/IP协议栈。
NVMe-oF target: Implements the new NVMe-oF specification. Though it depends on RDMA hardware, the NVMe-oF target can serve up to 40 Gbps of traffic per CPU core.
NVMe-oF target:实现了新的NVMe-oF规范。虽然这取决于RDMA硬件,NVMe-oF target可以为每个CPU核提供高达40Gbps的流量。
vhost-scsi target: A feature for KVM/QEMU that utilizes the SPDK NVMe driver, giving guest VMs lower latency access to the storage media and reducing the overall CPU load for I/O intensive workloads.
vhost-scsi target:KVM/QEMU的功能利用了SPDK NVMe驱动,使得访客虚拟机访问存储设备时延更低,使得I/O密集型工作负载的整体CPU负载有所下降。
SPDK does not fit every storage architecture. Here are a few questions that might help you determine whether SPDK components are a good fit for your architecture.
SPDK不适用于所有的存储架构。这里有一些问题可能会帮助用户决定SPDK组件是否适合他们的架构。
》 Is the storage system based on Linux or or FreeBSD*?
这个存储系统是否基于Linux或FreeBSD?
SPDK is primarily tested and supported on Linux. The hardware drivers are supported on both FreeBSD and Linux.
是的。 SPDK主要在Linux上测试和支持。硬件驱动被FreeBSD和Linux所支持。
》Is the hardware platform for the storage system Intel architecture?
存储系统的硬件平台是否要求是Intel体系结构?
SPDK is designed to take full advantage of Intel platform characteristics and is tested and tuned for Intel chips and systems.
是的。SPDK被设计来充分地利用Intel平台的特性,并针对Intel芯片和系统做测试和调优。
》Does the performance path of the storage system currently run in user mode?
这个存储系统的高性能路径是否运行在用户态?
SPDK is able to improve performance and efficiency by running more of the performance path in user space. By combining applications with SPDK features like the NVMe-oF target, initiator, or Blobstore, the entire data path may be able to run in user space, offering substantial efficiencies.
是的。SPDK通过更多地在用户态下运行从网卡到磁盘的高性能通路从而提高性能和效率。通过将具有SPDK功能(比如NVMe-oF target,NVMe-oFinitator,Blobstore)的应用程序结合起来,整个数据通路能够在用户态运行,从而显著地提供高效率。
》Can the system architecture incorporate lockless PMDs into its threading model?
该系统架构可以将无锁的PMDs合并到它的线程模型中去吗?
Since PMDs continually run on their threads (instead of sleeping or ceding the processor when unused), they have specific thread model requirements.
不能。 因为PMDs持续运行在它们的线程中(而不是睡眠或者不用时让出处理器),所以它们有特殊的线程模型需求。
》Does the system currently use the Data Plane Development Kit (DPDK) to handle network packet workloads?
系统现在是否用DPDK处理网络数据包的工作负载?
SPDK shares primitives and programming models with DPDK, so customers currently using DPDK will likely find the close integration with SPDK useful. Similarly, if customers are using SPDK, adding DPDK features for network processing may present a significant opportunity.
是的。 SPDK和DPDK共享早期的编程模型,所以现在使用DPDK的用户可能会发现与SPDK紧密整合非常有用。同样地,如果正在使用SPDK的用户为网络处理添加DPDK功能可能是个重要的机遇。
》Does the development team have the expertise to understand and troubleshoot problems themselves?
开发团队自己是否必须具有理解和解决问题的专业技能?
Intel shall have no support obligations for this reference software. While Intel and the open source community around SPDK will use commercially reasonable efforts to investigate potential errata of unmodified released software, under no circumstances will Intel have any obligation to customers with respect to providing any maintenance or support of the software.
是的。Intel没有义务为相关软件提供支持。Intel和围绕SPDK的开源社区会付出合理的商业努力去调查未修改的发布版本的软件中的潜在的错误,其他任何情况下,Intel都没有义务为用户提供针对该软件任何形式的维护和支持。
If you’d like to find out more about SPDK, please fill out the contact request form or check out SPDK.io for access to the mailing list, documentation, and blogs.
关于SPDK, 如果您想了解更多,请填写联系请求表,或者访问SPDK.io的邮件列表、文档和博客。
Intel technologies’ features and benefits depend on system configuration and may require enabled hardware, software or service activation. Performance varies depending on system configuration. Check with your system manufacturer or retailer or learn more at intel.com.
英特尔技术的特性及优势依赖于具体的系统配置,并且可能需要启用硬件、 软件或激活某些服务。性能因系统配置不同而有所不同。请咨询您的系统制造商或零售商,或访问intel.com了解更多信息.
Software and workloads used in performance tests may have been optimized for performance only on Intel microprocessors. Performance tests, such as SYSmark* and MobileMark*, are measured using specific computer systems, components, software, operations and functions. Any change to any of those factors may cause the results to vary. You should consult other information and performance tests to assist you in fully evaluating your contemplated purchases, including the performance of that product when combined with other products.
软件和性能测试中使用的工作负载可能仅在英特尔微处理器上针对性能做了优化。SYSmark* 和 MobileMark* 等性能测试使用了特定的计算机系统、 组件、 软件、 操作和功能。对这些因素作任何修改都可能导致不同的结果。为了帮助您完整地评估您的采购决策,请查询其他信息和做其他性能测试,包括该产品与其它产品一同使用时的性能。
Performance testing configuration:
性能测试配置:
2S Intel Xeon processor E5-2699 v3: 18 C, 2.3 GHz (hyper-threading off)
Note: Single socket was used while performance testing
32 GB DDR4 2133 MT/s
4 Memory Channel per CPU
1x 4GB 2R DIMM per channel
Ubuntu* (Linux) Server 14.10
3.16.0-30-generic kernel
Intel Ethernet Controller XL710 for 40GbE
8x P3700 NVMe drive for storage NVMe configuration
Total 8 PCIe* Gen 3 x 4 NVMes
4 NVMes coming from first x16 slot
(bifurcated to 4 x4s in the BIOS)
Another 4 NVMes coming from second x16 slot (bifurcated to 4 x4s in the BIOS)
Intel SSD DC P3700 Series 800 GB
Firmware: 8DV10102 FIO BenchMark Configuration
Direct: Yes
Queue depth
4KB Random I/O: 32 outstanding I/O
64KB Seq. I/O: 8 outstanding I/O
Ramp Time: 30 seconds
Run Time:180 seconds
Norandommap: 1
I/O Engine: Libaio
Numjobs: 1 BIOS Configuration
Speed Step: Disabled
Turbo Boost: Disabled
CPU Power and Performance Policy: Performance
For more information go to http://www.intel.com/performance.
更多信息,请访问http://www.intel.com/performance.
In the confrontation between the stream and the rock, the stream always wins, not through strength but by perseverance. | 在溪流与与岩石的对峙里,溪流永远都是胜利者,它靠的不是力量而是毅力。
[SPDK/NVMe存储技术分析]002 - SPDK官方介绍的更多相关文章
- [SPDK/NVMe存储技术分析]001 - SPDK/NVMe概述
1. NVMe概述 NVMe是一个针对基于PCIe的固态硬盘的高性能的.可扩展的主机控制器接口. NVMe的显著特征是提供多个队列来处理I/O命令.单个NVMe设备支持多达64K个I/O 队列,每个I ...
- [SPDK/NVMe存储技术分析]004 - SSD设备的发现
源代码及NVMe协议版本 SPDK : spdk-17.07.1 DPDK : dpdk-17.08 NVMe Spec: 1.2.1 基本分析方法 01 - 到官网http://www.spdk.i ...
- [SPDK/NVMe存储技术分析]003 - NVMeDirect论文
说明: 之所以要翻译这篇论文,是因为参考此论文可以很好地理解SPDK/NVMe的设计思想. NVMeDirect: A User-space I/O Framework for Application ...
- [SPDK/NVMe存储技术分析]008 - RDMA概述
毫无疑问地,用来取代iSCSI/iSER(iSCSI Extensions for RDMA)技术的NVMe over Fabrics着实让RDMA又火了一把.在介绍NVMe over Fabrics ...
- [SPDK/NVMe存储技术分析]005 - DPDK概述
注: 之所以要中英文对照翻译下面的文章,是因为SPDK严重依赖于DPDK的实现. Introduction to DPDK: Architecture and PrinciplesDPDK概论:体系结 ...
- [SPDK/NVMe存储技术分析]006 - 内存屏障(MB)
在多核(SMP)多线程的情况下,如果不知道CPU乱序执行的话,将会是一场噩梦,因为无论怎么进行代码Review也不可能发现跟内存屏障(MB)相关的Bug.内存屏障分为两类: 跟编译有关的内存屏障: 告 ...
- [SPDK/NVMe存储技术分析]012 - 用户态ibv_post_send()源码分析
OFA定义了一组标准的Verbs,并提供了一个标准库libibvers.在用户态实现NVMe over RDMA的Host(i.e. Initiator)和Target, 少不了要跟OFA定义的Ver ...
- [SPDK/NVMe存储技术分析]015 - 理解内存注册(Memory Registration)
使用RDMA, 必然关系到内存区域(Memory Region)的注册问题.在本文中,我们将以mlx5 HCA卡为例回答如下几个问题: 为什么需要注册内存区域? 注册内存区域有嘛好处? 注册内存区域的 ...
- [SPDK/NVMe存储技术分析]014 - (NVMe over PCIe)Host端的命令处理流程
NVMe over PCIe最新的NVMe协议是1.3. 在7.2.1讲了Command Processing流程.有图有真相. This section describes command subm ...
随机推荐
- python基础语法_7运算符
http://www.runoob.com/python3/python3-basic-operators.html#ysf7 目录 Python语言支持以下8类型的运算符: 算术运算符(-,+,*, ...
- Java面向对象之各种变量详解
在Java中一定有很多变量让大家头疼,成员变量.类变量.局部变量等等,今天就来分别认识认识他们吧! Java面向对象之各种变量详解 前言 在 Java语言中, 根据定义变量位置的不同,可以将变量分成两 ...
- Spring Boot-开启第一步
Spring Boot开发的目的是为了简化Spring应用的开发,使用Spring Boot可以零配置开启一个Spring应用.这得益于Spring Boot中的自动配置组件,如果开发者觉得默认的配置 ...
- Solution -「ARC 110E」Shorten ABC
\(\mathcal{Description}\) Link. 给定长度为 \(n\),包含 A, B, C 三种字符的字符串 \(S\),定义一次操作为将其中相邻两个不相同的字符替换为字符集 ...
- suse 12 二进制部署 Kubernetets 1.19.7 - 第04章 - 部署docker服务
文章目录 1.4.部署docker 1.4.0.下载docker二进制文件 1.4.1.配置docker镜像加速 1.4.2.配置docker为systemctl管理 1.4.3.启动docker服务 ...
- 【故障公告】k8s 开船记:增加控制舱(control-plane)造成的翻船
春节期间我们更换了 kubernetes 生产集群,旧集群的 kubernetes 版本是 1.17.0,新集群版本是 1.23.3,新集群上部署了 dapr,最近准备将更多独立部署的服务器部署到 k ...
- ICLR 2018 | Deep Gradient Compression: Reducing the Communication Bandwidth for Distributed Training
为了降低大规模分布式训练时的通信开销,作者提出了一种名为深度梯度压缩(Deep Gradient Compression, DGC)的方法.DGC通过稀疏化技术,在每次迭代时只选择发送一部分比较&qu ...
- RSA公私钥生成与使用
参考 KeyStore 简述 Keytool 简述 Certificate Chain (证书链) 简述 详解RSA加密算法
- Python中编码encode()与解码decode()
1 print('这是编码'.encode('utf-8')) # 结果 b'\xe8\xbf\x99\xe6\x98\xaf\xe7\xbc\x96\xe7\xa0\x81' 2 print('这是 ...
- k8s之pod讲解
什么是Pod? Pod 是一组紧密关联的容器集合,它由一组.一个或多个容器组成,每个Pod还包含了一个Pause容器,Pause容器是Pod的父容器,主要负责僵尸进程的回收管理,通过Pause容 ...
