Mybatis源码解读-配置加载和Mapper的生成
问题
- Mybatis四大对象的创建顺序?
- Mybatis插件的执行顺序?
工程创建
环境:Mybatis(3.5.9)
简单示例
这里只放出main方法的示例,其余类请看demo工程。
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 配置文件路径
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
// 1.读取配置,创建SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
// 2.通过工厂获取SqlSession
SqlSession session = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
try {
// 3.获取mapper代理对象
StudentMapper mapper = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
// 4.执行查询,此处才真正连接数据库
System.out.println(mapper.selectByName("张三"));
} finally {
// 5.关闭连接
session.close();
}
}
Mapper的创建
我们使用Mybatis操作数据库,主要是通过mapper对象(在hibernate中叫dao对象)。
那么,我们不按顺序从读取配置初始化开始讲,直接看看mapper对象是如何获取与执行的。
获取mapper
// StudentMapper mapper = session.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
DefaultSqlSession.getMapper(Class<T> type) -->
Configuration.getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) -->
MapperRegistry.getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) -->
MapperProxyFactory.newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) -->
MapperProxyFactory.newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy)
咱们来看看MapperProxyFactory.newInstance(MapperProxy mapperProxy)的实现
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
// 可以转换成这样,返回的是StudentMapper的代理对象
// final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, StudentMapper.class, methodCache);
// Proxy.newProxyInstance(StudentMapper.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { StudentMapper.class }, mapperProxy);
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
也就是说,实际返回的是
MapperProxy对象,StudentMapper被代理了。执行mapper的方法
已知mapper对象被代理了,那么执行mapper的所有方法,都会先经过
MapperProxy的invoke方法public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
// 如果执行的是Object的方法,则直接执行,不继续处理mybatis的逻辑
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
// 举例,如果执行的是mapper.toString(),则进入此判断
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else {
// cachedInvoker(method):创建MapperMethodInvoker并缓存起来
return cachedInvoker(method).invoke(proxy, method, args, sqlSession);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
cachedInvoker(method)返回的是
PlainMethodInvoker,继续进去看看// PlainMethodInvoker的方法
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, SqlSession sqlSession) throws Throwable {
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
} // MapperMethod#execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args)
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
......
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
......
break;
}
case DELETE: {
......
break;
}
case SELECT:
......
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
......
return result;
}
终于,看到了熟悉insert、update关键字,这里就是具体解析执行sql,并返回结果的逻辑。咱们先略过。回去看看是如何加载配置以及生成SqlSession的。
SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory的生成过程如下
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream) {
return build(inputStream, null, null);
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, String environment, Properties properties) {
try {
// xml配置解析类
XMLConfigBuilder parser = new XMLConfigBuilder(inputStream, environment, properties);
// build方法返回DefaultSqlSessionFactory
// 主要看parser.parse()
return build(parser.parse());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error building SqlSession.", e);
} finally {
// 异常上下文对象,线程内共享
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
// Intentionally ignore. Prefer previous error.
}
}
}
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}
下面来看看parser.parse()方法
// XMLConfigBuilder#parse()
public Configuration parse() {
if (parsed) {
throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
}
parsed = true;
// parser.evalNode("/configuration"):获取configuration节点
// 例如:<configuration> xxx </configuration>
// parseConfiguration才是重点
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
return configuration;
}
// 这是重点
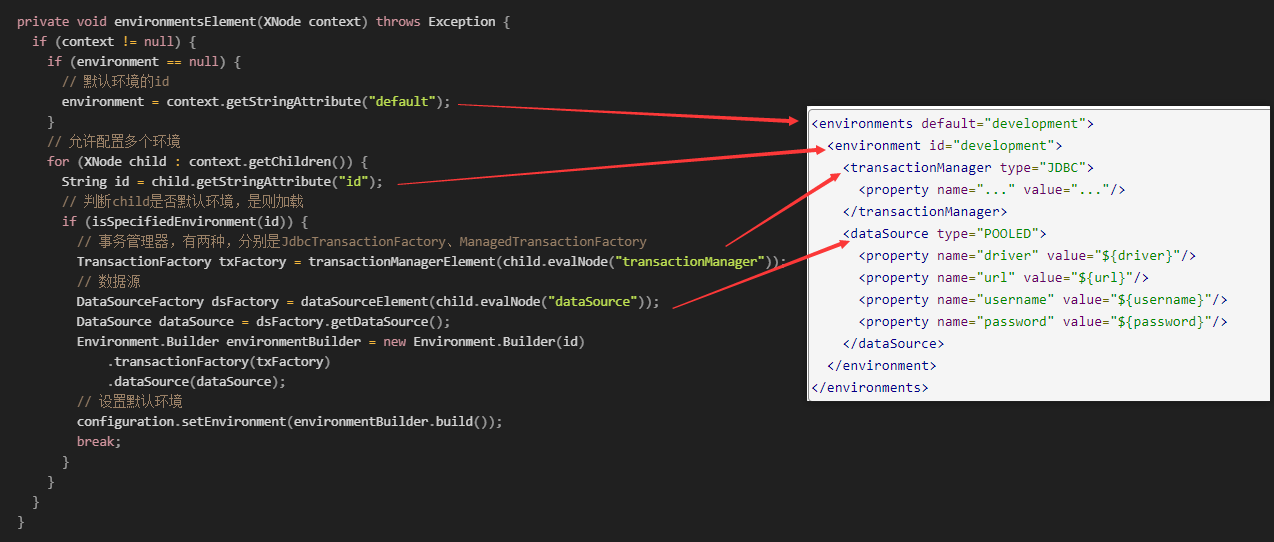
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings"));
loadCustomVfs(settings);
loadCustomLogImpl(settings);
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory"));
settingsElement(settings);
// 环境配置
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
// 映射器配置
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
详细XML的配置请参考官网:mybatis – MyBatis 3 | 配置
这里,咱们只讲环境配置,其他的篇幅有限,请自行查看源码。
SqlSession
接下来看看SqlSession的创建
// DefaultSqlSessionFactory#openSession() -->
// DefaultSqlSessionFactory#openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false)
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
// 默认环境
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
// 事务工厂
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
// 上面那两个对象,在创建SqlSessionFactory时,就已经创建好了
// 通过事务工厂创建事务
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
// 创建mybatis四大对象之一的Executor
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
看看四大对象之一Executor的创建
// Configuration#newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType)
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
// 判断需要创建的执行器的类型
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
// 批处理执行器
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
// 重用执行器
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
// 简单处理器(默认)
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
// 是否启用二级缓存(二级缓存默认启用)
if (cacheEnabled) {
// 此处使用的是装饰器模式,对executor进行二次包装
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
// 这块是mybatis的插件处理,用代理的方式,以后再开文章讲
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
Mapper的执行
Mapper的创建一节,讲到mapper执行会被代理。
下面就以StudentMapper为例,讲讲mapper的执行。
public interface StudentMapper {
List<Student> selectByName(@Param("name") String name);
}
当执行selectByName时候,进入到MapperMethod#execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args)方法。
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) {
......
// 忽略insert、update、delete的逻辑,直接看select
case SELECT:
// 如果返回null或者设置了自定义的结果处理器
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
// 如果返回集合或者数组,我们的查询会进到这里,因为selectByName返回值是List
// 这是入口
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
// 如果返回map
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
// 这个没用过,不会
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
// 默认返回单个对象
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
if (method.returnsOptional()
&& (result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {
result = Optional.ofNullable(result);
}
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
继续看executeForMany方法
private <E> Object executeForMany(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
List<E> result;
// 参数转换,如果参数有注解,则会转成map,且可使用param1, param2
// 例如:@Param("name")会转成 {"name":xxx, "param1": xxx}
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
// 是否分页
if (method.hasRowBounds()) {
RowBounds rowBounds = method.extractRowBounds(args);
result = sqlSession.selectList(command.getName(), param, rowBounds);
} else {
// 这是入口
result = sqlSession.selectList(command.getName(), param);
}
// 如果result不能强转成方法的返回值(在此例子中getReturnType就是List<Studet>)
if (!method.getReturnType().isAssignableFrom(result.getClass())) {
if (method.getReturnType().isArray()) {
return convertToArray(result);
} else {
return convertToDeclaredCollection(sqlSession.getConfiguration(), result);
}
}
return result;
}
继续看,因为案例中没用到分页,所以执行的是sqlSession.selectList(command.getName(), param);
// DefaultSqlSession#selectList(String statement, Object parameter) -->
// DefaultSqlSession#selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) -->
// DefaultSqlSession#selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler handler) -->
private <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler handler) {
try {
// MapperStatement在前面解析xml时,就已经创建了
// 忘了就看看创建SqlSessionFactory时是如何解析xml文件的mappers节点的
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
// 执行器执行查询方法
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, handler);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
继续看,executor.query方法,Mybatis-PageHelper插件就是通过拦截query方法,插入分页参数的。
// CachingExecutor
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
// 对sql进行预处理
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
// 创建一级缓存的key
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
// 这是入口
return query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql)
throws SQLException {
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
// 有缓存的逻辑
if (cache != null) {
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql);
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
list = delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
// delegate是SimpleExecutor
// 这是入口
return delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
// BaseExecutor
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
// 是否要清除缓存,默认设置是如果非select方法,都会清除缓存。
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
queryStack++;
// 从一级缓存提取数据
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
// 从数据库查询数据
// 这是入口
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
// 懒加载相关
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
// issue #601
deferredLoads.clear();
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
// issue #482
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
List<E> list;
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
// 这是入口
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
// 结果放入一级缓存
localCache.putObject(key, list);
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
return list;
}
下面,重点来了,准备了这么久,终于要查询数据库了
// SimpleExecutor
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
// 重点又来了,mybatis四大对象的3个,在这里创建
// 按顺序是:ParameterHandler、ParameterHandler、StatementHandler
// 又一个装饰器模式,实际创建的是PreparedStatementHandler(默认),但是使用RoutingStatementHandler又包了一层
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
// 创建jdbc的statement对象,直到这里,才会真正获取数据库连接
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
// 执行查询,并使用resultHandler处理结果
return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
答案
- 创建顺序为:Executor、ParameterHandler、ParameterHandler、StatementHandler
- 插件的执行顺序,如果都命中同一个方法,那么顺序为,越晚注册的插件,越先执行(因为代理)
Mybatis源码解读-配置加载和Mapper的生成的更多相关文章
- Mybatis源码解读-SpringBoot中配置加载和Mapper的生成
本文mybatis-spring-boot探讨在springboot工程中mybatis相关对象的注册与加载. 建议先了解mybatis在spring中的使用和springboot自动装载机制,再看此 ...
- Mybatis源码解析(二) —— 加载 Configuration
Mybatis源码解析(二) -- 加载 Configuration 正如上文所看到的 Configuration 对象保存了所有Mybatis的配置信息,也就是说mybatis-config. ...
- MyBatis 源码篇-资源加载
本章主要描述 MyBatis 资源加载模块中的 ClassLoaderWrapper 类和 Java 加载配置文件的三种方式. ClassLoaderWrapper 上一章的案例,使用 org.apa ...
- mybatis源码分析--如何加载配置及初始化
简介 Mybatis 是一个持久层框架,它对 JDBC 进行了高级封装,使我们的代码中不会出现任何的 JDBC 代码,另外,它还通过 xml 或注解的方式将 sql 从 DAO/Repository ...
- 精尽Spring Boot源码分析 - 配置加载
该系列文章是笔者在学习 Spring Boot 过程中总结下来的,里面涉及到相关源码,可能对读者不太友好,请结合我的源码注释 Spring Boot 源码分析 GitHub 地址 进行阅读 Sprin ...
- springboot集成mybatis源码分析-启动加载mybatis过程(二)
1.springboot项目最核心的就是自动加载配置,该功能则依赖的是一个注解@SpringBootApplication中的@EnableAutoConfiguration 2.EnableAuto ...
- Prism 源码解读3-Modules加载
介绍 在软件开发过程中,总想组件式的开发方式,各个组件之间最好互不影响,独立测试.Prism的Modules很好的满足了这一点. 这个架构图很好了讲解了Prism的Modules的概念 Prism支持 ...
- Mybatis源码解读-插件
插件允许对Mybatis的四大对象(Executor.ParameterHandler.ResultSetHandler.StatementHandler)进行拦截 问题 Mybatis插件的注册顺序 ...
- MyBatis源码解读之延迟加载
1. 目的 本文主要解读MyBatis 延迟加载实现原理 2. 延迟加载如何使用 Setting 参数配置 设置参数 描述 有效值 默认值 lazyLoadingEnabled 延迟加载的全局开关.当 ...
随机推荐
- JuiceFS v1.0 beta3 发布,支持 etcd、Amazon MemoryDB、Redis Cluster
JuiceFS v1.0 beta3 在元数据引擎方面继续增强,新增 etcd 支持小于 200 万文件的使用场景,相比 Redis 可以提供更好的可用性和安全性.同时支持了 Amazon Memor ...
- springcloud + nacos实现共用基础服务(灰度版本)
背景: 当我们使用微服务时,若想在本地联调就需要启动多个服务,为了避免本地启动过多服务,现将注册中心等基础服务共用.当我们在服务A开发时,都是注册到同一个nacos,这样本地和开发环境的服务A就会同时 ...
- python之贪婪算法
贪婪算法 贪婪算法也称为最优算法,这种算法并不是最准确的答案,但确认最接近答案的近似算法. 这时候有人会问,不是最准确的答案我要她干嘛?但是在日常中,我们有时候会遇到一些我们无法处理的问题,甚至是要花 ...
- 用c语言调用Easy X实现图像的输出,附带音乐的读取
要实现此功能需要用EasyX 一.下载VS编译环境和EasyX. ①Vs2019https://iwx.mail.qq.com/ftn/download?func=3&key=9e9b6c33 ...
- Jwt隐藏大坑,通过源码帮你揭秘
前言 JWT是目前最为流行的接口认证方案之一,有关JWT协议的详细内容,请参考:https://jwt.io/introduction 今天分享一下在使用JWT在项目中遇到的一个问题,主要是一个协议的 ...
- CA周记 - Build 2022 上开发者最应关注的七大方向主要技术更新
一年一度的 Microsoft Build 终于来了,带来了非常非常多的新技术和功能更新.不知道各位小伙伴有没有和我一样熬夜看了开幕式和五个核心主题的全过程呢?接下来我和大家来谈一下作为开发者最应关注 ...
- SpirngBoot 错误(1)
对于出现该错: Error starting ApplicationContext. To display the conditions report re-run your application ...
- Spring Cloud OpenFeign 的 5 个优化小技巧!
OpenFeign 是 Spring 官方推出的一种声明式服务调用和负载均衡组件.它的出现就是为了替代已经进入停更维护状态的 Feign(Netflix Feign),同时它也是 Spring 官方的 ...
- 04C++核心编程(二-泛型编程)
Day08 笔记 1 函数模板 1.1 泛型编程 – 模板技术 特点:类型参数化 1.2 template< typename T > 告诉编译器后面紧跟着的函数或者类中出现T,不要报错, ...
- 附001.Python多版本环境管理
一 环境背景 由于Python的版本过多,且不同版本之间差异性较大.同时又因系统底层需要调用当前版本Python,所以不能随意变更当前系统Python版本.因此,在多版本共存的情况下,Python多环 ...
