MyBatis详解(二)
前言
本篇幅是继 MyBatis详解(一)的下半部分。
MyBatis执行Sql的流程分析
【1】基于前面已经将XML文件进行build解析了并且返回了SqlSessionFactory
【1.1】那么分析SqlSessionFactory.openSession()方法是怎么返回SqlSession的,且SqlSession又是什么东西:
@Override
public SqlSession openSession() {
return openSessionFromDataSource(configuration.getDefaultExecutorType(), null, false);
} /**
* 方法实现说明:从session中开启一个数据源
* @param execType:执行器类型
* @param level:隔离级别
*/
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
// 获取环境变量
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
// 获取事务工厂
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
// 创建一个sql执行器对象
// 一般情况下 若我们的mybaits的全局配置文件的cacheEnabled默认为ture就返回一个cacheExecutor,若关闭的话返回的就是一个SimpleExecutor
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
// 创建返回一个DeaultSqlSessoin对象返回
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
【1.1.1】分析newExecutor方法中执行器的产生:
/**
* 方法实现说明:创建一个sql语句执行器对象
* @param transaction:事务
* @param executorType:执行器类型
* @return:Executor执行器对象
*/
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction, ExecutorType executorType) {
executorType = executorType == null ? defaultExecutorType : executorType;
executorType = executorType == null ? ExecutorType.SIMPLE : executorType;
Executor executor;
//判断执行器的类型
// 批量的执行器
if (ExecutorType.BATCH == executorType) {
executor = new BatchExecutor(this, transaction);
} else if (ExecutorType.REUSE == executorType) {
//可重复使用的执行器
executor = new ReuseExecutor(this, transaction);
} else {
//简单的sql执行器对象
executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
}
//判断mybatis的全局配置文件是否开启缓存
if (cacheEnabled) {
//把当前的简单的执行器包装成一个CachingExecutor
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
//调用所有的拦截器对象plugin方法,也就是生成代理对象
executor = (Executor) interceptorChain.pluginAll(executor);
return executor;
}
【1.1.1.1】图示:
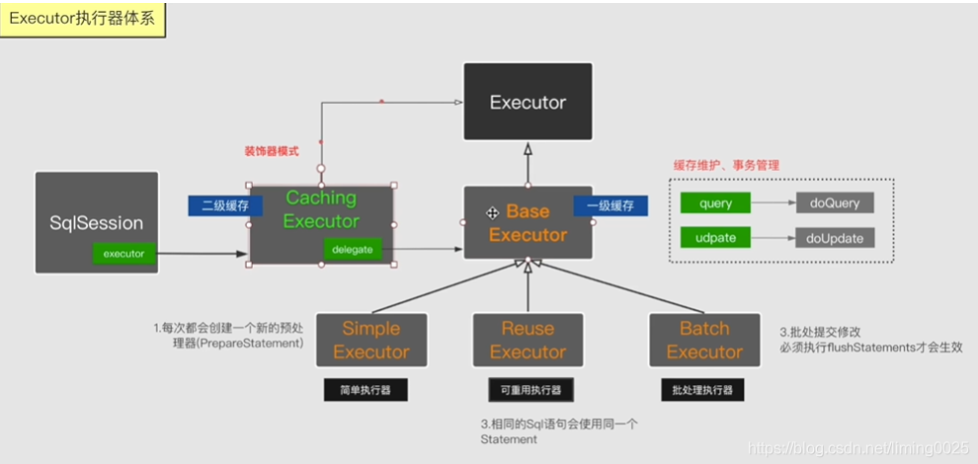
【1.1.2】分析底层如何执行JDBC【User user = (User)session.selectOne("com.mapper.UserMapper.selectById", 1);】
/**
* 方法实现说明:查询我们当个对象
* @param statement:SQL语句
* @param parameter:调用时候的参数
* @return: T 返回结果
*/
@Override
public <T> T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) {
// 这里selectOne调用也是调用selectList方法
List<T> list = this.selectList(statement, parameter);
//若查询出来有且有一个一个对象,直接返回要给
if (list.size() == 1) {
return list.get(0);
} else if (list.size() > 1) {
//查询的有多个,那么就抛出异常
throw new TooManyResultsException("Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: " + list.size());
} else {
return null;
}
} @Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter) {
return this.selectList(statement, parameter, RowBounds.DEFAULT);
} /**
* @param statement: statementId
* @param parameter:参数对象
* @param rowBounds :mybiats的逻辑分页对象
*/
@Override
public <E> List<E> selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
//第一步:通过我们的statement去我们的全局配置类中获取MappedStatement
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
//通过执行器去执行我们的sql对象
//第一步:包装我们的集合类参数
//第二步:一般情况下是executor为cacheExetory对象
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
【1.1.2.0】分析两种方法的本质:
方法一:User user = (User)session.selectOne("com.mapper.UserMapper.selectById", 1);
源码流程:
//通过statement去我们的全局配置类中获取MappedStatement
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
public MappedStatement getMappedStatement(String id) {
return this.getMappedStatement(id, true);
}
public MappedStatement getMappedStatement(String id, boolean validateIncompleteStatements) {
if (validateIncompleteStatements) {
buildAllStatements();
}
// 这个mappedStatements便是在SqlSessionFactory进行build过程中parse解析出来的
return mappedStatements.get(id);
}
方法二:UserMapper mapper = session.getMapper(UserMapper.class); 与 User user = mapper.selectById(1L);
源码流程:
@Override
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) {
return configuration.getMapper(type, this);
}
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession);
}
/**
* 方法实现说明:通过class类型和sqlSessionTemplate获取Mapper(代理对象)
* @param type:Mapper的接口类型
* @param sqlSession:接口类型实际上是我们的sqlSessionTemplate类型
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
// 直接去缓存knownMappers中通过Mapper的class类型去找mapperProxyFactory
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
// 缓存中没有获取到 直接抛出异常
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
// 通过MapperProxyFactory来创建我们的实例
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
【1.1.2.1】如果是定义了二级缓存,那么会走CachingExecutor逻辑:
/**
* 方法实现说明:通过我们的sql执行器对象执行sql
* @param ms 用于封装我们一个个的insert|delete|update|select 对象
* @param parameterObject:参数对象
* @param rowBounds :mybaits的逻辑分页对象
* @param resultHandler:结果处理器对象
*/
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
// 通过参数对象解析sql详细信息1339025938:1570540512:com.project.mapper.selectById:0:2147483647:select id,user_name,create_time from t_user where id=?:1:development
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
} @Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
//判断mapper中是否开启了二级缓存<cache></cache>
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
// 判断是否配置了cache
if (cache != null) {
//判断是否需要刷新缓存
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
ensureNoOutParams(ms, boundSql);
// 先去二级缓存中获取
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key); //也就是去PerpetualCache里面寻找
// 二级缓存中没有获取到
if (list == null) {
//通过查询数据库去查询
list = delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
//加入到二级缓存中
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list); // issue #578 and #116
}
return list;
}
}
//没有整合二级缓存,直接去查询
return delegate.query(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
【1.1.2.1.1】事务的TransactionalCacheManager:
【1.1.2.1.1.1】它存在的意义在于:避免事务不成功的sql语句填充到了Cache里面,淘汰掉一些已经执行过的语句,相当于包装了一层。
【1.1.2.1.1.2】存储的地方:本质上会先存在自身类的属性值private final Map<Cache, TransactionalCache> transactionalCaches = new HashMap<>();
【1.1.2.1.1.3】当成功后才会提交到PerpetualCache里面。
【1.1.2.1.2】分析语句的解析【ms.getBoundSql(parameterObject)】:
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
if (parameterMappings == null || parameterMappings.isEmpty()) {
boundSql = new BoundSql(configuration, boundSql.getSql(), parameterMap.getParameterMappings(), parameterObject);
}
// check for nested result maps in parameter mappings (issue #30)
for (ParameterMapping pm : boundSql.getParameterMappings()) {
String rmId = pm.getResultMapId();
if (rmId != null) {
ResultMap rm = configuration.getResultMap(rmId);
if (rm != null) {
hasNestedResultMaps |= rm.hasNestedResultMaps();
}
}
}
return boundSql;
}
//DynamicSqlSource类#getBoundSql方法
@Override
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
DynamicContext context = new DynamicContext(configuration, parameterObject);
//责任链处理SqlNode,编译出完整的sql
rootSqlNode.apply(context);
SqlSourceBuilder sqlSourceParser = new SqlSourceBuilder(configuration);
//处理sql中的#{..}
Class<?> parameterType = parameterObject == null ? Object.class : parameterObject.getClass();
//将#{..}中的内容封装为parameterMapping,替换为?
SqlSource sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(context.getSql(), parameterType, context.getBindings());
BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
context.getBindings().forEach(boundSql::setAdditionalParameter);
return boundSql;
}
//BoundSql类的结构
public class BoundSql {
private final String sql; //语句
private final List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings;
private final Object parameterObject; //参数处理
private final Map<String, Object> additionalParameters; //结果集处理
private final MetaObject metaParameters;
}
【1.1.2.2】如果没有定义的话,则会选择BaseExecutor的三个子类中的一个【但其实还是会走BaseExecutor的逻辑】:
//BaseExecutor类#query方法,子类重写的是doQuery,如果是使用query方法本质上还是走BaseExecutor类的
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
//已经关闭,则抛出 ExecutorException 异常
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
// 清空本地缓存,如果 queryStack 为零,并且要求清空本地缓存。
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
// 从一级缓存中,获取查询结果
queryStack++; //BaseExecutor类的属性值:protected PerpetualCache localCache;
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null; // 获取到,则进行处理
if (list != null) {
//处理存过的
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
// 获得不到,则从数据库中查询
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
// issue #601
deferredLoads.clear();
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
// issue #482
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
} //至于为什么会说一级缓存是session级别的,因为一旦提交或者回滚之后都会被清空
@Override
public void commit(boolean required) throws SQLException {
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Cannot commit, transaction is already closed");
}
clearLocalCache();
flushStatements();
if (required) {
transaction.commit();
}
} @Override
public void rollback(boolean required) throws SQLException {
if (!closed) {
try {
clearLocalCache();
flushStatements(true);
} finally {
if (required) {
transaction.rollback();
}
}
}
} // 清楚本地一级缓存
@Override
public void clearLocalCache() {
if (!closed) {
localCache.clear();
localOutputParameterCache.clear();
}
}
【1.1.2.3】分析queryFromDatabase方法:
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
List<E> list;
//一级缓存中先占位
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
//调用子类的查询方法
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
localCache.putObject(key, list);
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
return list;
}
//以默认的SimpleExecutor为例查看doQuery方法
@Override
public <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
//创建StatementHandler,主要职责是拿到链接,拿到执行者
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
//分析如何创建StatementHandler
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
return statementHandler;
}
//存在三种StatementHandler
public RoutingStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
switch (ms.getStatementType()) {
case STATEMENT:
delegate = new SimpleStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
case PREPARED:
delegate = new PreparedStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
case CALLABLE:
delegate = new CallableStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
default:
throw new ExecutorException("Unknown statement type: " + ms.getStatementType());
}
}
//但是这三种都是继承BaseStatementHandler,因为BaseStatementHandler里面才会有resultSetHandler和parameterHandler
protected BaseStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
this.configuration = mappedStatement.getConfiguration();
this.executor = executor;
this.mappedStatement = mappedStatement;
this.rowBounds = rowBounds;
this.typeHandlerRegistry = configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry();
this.objectFactory = configuration.getObjectFactory();
if (boundSql == null) { // issue #435, get the key before calculating the statement
generateKeys(parameterObject);
boundSql = mappedStatement.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
}
this.boundSql = boundSql;
this.parameterHandler = configuration.newParameterHandler(mappedStatement, parameterObject, boundSql);
this.resultSetHandler = configuration.newResultSetHandler(executor, mappedStatement, rowBounds, parameterHandler, resultHandler, boundSql);
}
【2.2】对于执行器Executor的分析,先分析接口的定义:
/**
* 类的描述:sql执行器接口,主要用于维护一级缓存和二级缓存,并且提供事务管理功能
* Executor
* --BaseExecutor(一级缓存)
* --batchExecutor(批量执行器)
* --ReUseExecutor(可重用的)
* --SimpleExecutor简单的
* --CacheExecutor(加入了二级缓存)
*/
public interface Executor { //ResultHandler 对象的枚举
ResultHandler NO_RESULT_HANDLER = null; /**
* 更新 or 插入 or 删除,由传入的 MappedStatement 的 SQL 所决定
* @param ms 我们的执行sql包装对象(MappedStatement)
* @param parameter 执行的参数
*/
int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException; /**
* 查询带缓存key查询
* @param ms 我们的执行sql包装对象(MappedStatement)
* @param parameter:参数
* @param rowBounds 逻辑分页参数
* @param resultHandler:返回结果处理器
* @param cacheKey:缓存key
* @param boundSql:我们的sql对象
* @return 查询结果集list
* @throws SQLException
*/
<E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey cacheKey, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException; /**
* 不走缓存查询
* @param ms 我们的执行sql包装对象(MappedStatement)
* @param parameter:参数
* @param rowBounds 逻辑分页参数
* @param resultHandler:返回结果处理器
* @return 结果集list
* @throws SQLException
*/
<E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException; /**
* 调用存过查询返回游标对象
* @param ms 我们的执行sql包装对象(MappedStatement)
* @param parameter:参数
* @param rowBounds 逻辑分页参数
* @return Cursor数据库游标
* @throws SQLException
*/
<E> Cursor<E> queryCursor(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) throws SQLException; // 刷入批处理语句
List<BatchResult> flushStatements() throws SQLException; //提交事务
void commit(boolean required) throws SQLException; //回滚事务
void rollback(boolean required) throws SQLException; //创建缓存key
CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql); // 判断是否缓存
boolean isCached(MappedStatement ms, CacheKey key);
// 清除本地缓存
void clearLocalCache(); // 延迟加载
void deferLoad(MappedStatement ms, MetaObject resultObject, String property, CacheKey key, Class<?> targetType); //获取一个事务
Transaction getTransaction();
// 关闭事务
void close(boolean forceRollback); //判断是否关闭
boolean isClosed(); // 设置包装的 Executor 对象
void setExecutorWrapper(Executor executor);
}
MyBatis详解(二)的更多相关文章
- Mybatis详解(二) sqlsession的创建过程
我们处于的位置 我们要清楚现在的情况. 现在我们已经调用了SqlSessionFactoryBuilder的build方法生成了SqlSessionFactory 对象. 但是如标题所说,要想生成sq ...
- mybatis 详解(三)------入门实例(基于注解)
1.创建MySQL数据库:mybatisDemo和表:user 详情参考:mybatis 详解(二)------入门实例(基于XML) 一致 2.建立一个Java工程,并导入相应的jar包,具体目录如 ...
- [原创]mybatis详解说明
mybatis详解 2017-01-05MyBatis之代理开发模式1 mybatis-Dao的代理开发模式 Dao:数据访问对象 原来:定义dao接口,在定义dao的实现类 dao的代理开发模式 只 ...
- .NET DLL 保护措施详解(二)关于性能的测试
先说结果: 加了缓存的结果与C#原生代码差异不大了 我对三种方式进行了测试: 第一种,每次调用均动态编译 第二种,缓存编译好的对象 第三种,直接调用原生C#代码 .net dll保护系列 ------ ...
- mybatis 详解------动态SQL
mybatis 详解------动态SQL 目录 1.动态SQL:if 语句 2.动态SQL:if+where 语句 3.动态SQL:if+set 语句 4.动态SQL:choose(when,o ...
- PopUpWindow使用详解(二)——进阶及答疑
相关文章:1.<PopUpWindow使用详解(一)——基本使用>2.<PopUpWindow使用详解(二)——进阶及答疑> 上篇为大家基本讲述了有关PopupWindow ...
- Android 布局学习之——Layout(布局)详解二(常见布局和布局参数)
[Android布局学习系列] 1.Android 布局学习之——Layout(布局)详解一 2.Android 布局学习之——Layout(布局)详解二(常见布局和布局参数) 3.And ...
- logback -- 配置详解 -- 二 -- <appender>
附: logback.xml实例 logback -- 配置详解 -- 一 -- <configuration>及子节点 logback -- 配置详解 -- 二 -- <appen ...
- 爬虫入门之urllib库详解(二)
爬虫入门之urllib库详解(二) 1 urllib模块 urllib模块是一个运用于URL的包 urllib.request用于访问和读取URLS urllib.error包括了所有urllib.r ...
- [转]文件IO详解(二)---文件描述符(fd)和inode号的关系
原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/frank-yxs/p/5925563.html 文件IO详解(二)---文件描述符(fd)和inode号的关系 ---------------- ...
随机推荐
- 1.nexus的安装
1,Nexus 介绍 Nexus是什么 Nexus 是一个强大的maven仓库管理器,它极大地简化了本地内部仓库的维护和外部仓库的访问. 不仅如此,他还可以用来创建yum.pypi.npm.docke ...
- Gitlab备份以及恢复
1.迁移准备工作和思路 从a服务器迁移到b服务器,由于Gitlab自身的兼容性问题,高版本的Gitlab无法恢复低版本备份的数据,需要注意在b服务器部署和a服务器一样版本的gitlab,部署好环境后开 ...
- 官方文档采用Docker方式安装
官方文档地址:https://github.com/grafana/loki/tree/master/production The Docker images for Loki and Promtai ...
- Docker MySql 查看版本的三种方法
目录 Docker MySql 查看版本的三种方法 1.mysql -V命令查看版本 2.status命令查看版本 3.version命令查看版本 Docker MySql 查看版本的三种方法 1.m ...
- 谣言检测(ClaHi-GAT)《Rumor Detection on Twitter with Claim-Guided Hierarchical Graph Attention Networks》
论文信息 论文标题:Rumor Detection on Twitter with Claim-Guided Hierarchical Graph Attention Networks论文作者:Erx ...
- P2216 [HAOI2007]理想的正方形 方法记录
[HAOI2007]理想的正方形 题目描述 有一个 \(a \times b\) 的整数组成的矩阵,现请你从中找出一个 \(n \times n\) 的正方形区域,使得该区域所有数中的最大值和最小值的 ...
- Python编程之定时任务(crontab)详解
引言 python-crontab是python模块,提供了对cron任务的访问,并使得我们可以通过python对crontab文件进行修改. 安装 pip install python-cronta ...
- BigDecimal的运算——加减乘除
BigDecimal的运算--加减乘除 1.初始化(尽量用字符串的形式初始化) BigDecimal num12 = new BigDecimal("0.005"); BigDec ...
- 2022年整理最详细的java面试题、掌握这一套八股文、面试基础不成问题[吐血整理、纯手撸]
这里是参考B站上的大佬做的面试题笔记.大家也可以去看视频讲解!!! 文章目录 1.面向对象 2.JDK.JRE.JVM区别和联系 3.==和equals 4.final 5.String .Strin ...
- Educational Codeforces Round 122 (Rated for Div. 2)/codeforces1633
CodeForces1633 Div. 7 解析: 题目大意 给定 \(t\) 组数据.每组数据给定一个数 \(n\)(\(10\le n\le 999\)). 每次操作可以修改 \(n\) 任意一位 ...
