Codeforces Round #301 (Div. 2) C. Ice Cave BFS
C. Ice Cave
Time Limit: 1 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB
题目连接
http://codeforces.com/contest/540/problem/C
Description
You play a computer game. Your character stands on some level of a multilevel ice cave. In order to move on forward, you need to descend one level lower and the only way to do this is to fall through the ice.
The level of the cave where you are is a rectangular square grid of n rows and m columns. Each cell consists either from intact or from cracked ice. From each cell you can move to cells that are side-adjacent with yours (due to some limitations of the game engine you cannot make jumps on the same place, i.e. jump from a cell to itself). If you move to the cell with cracked ice, then your character falls down through it and if you move to the cell with intact ice, then the ice on this cell becomes cracked.
Let's number the rows with integers from 1 to n from top to bottom and the columns with integers from 1 to m from left to right. Let's denote a cell on the intersection of the r-th row and the c-th column as (r, c).
You are staying in the cell (r1, c1) and this cell is cracked because you've just fallen here from a higher level. You need to fall down through the cell (r2, c2) since the exit to the next level is there. Can you do this?
Input
The first line contains two integers, n and m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 500) — the number of rows and columns in the cave description.
Each of the next n lines describes the initial state of the level of the cave, each line consists of m characters "." (that is, intact ice) and "X" (cracked ice).
The next line contains two integers, r1 and c1 (1 ≤ r1 ≤ n, 1 ≤ c1 ≤ m) — your initial coordinates. It is guaranteed that the description of the cave contains character 'X' in cell (r1, c1), that is, the ice on the starting cell is initially cracked.
The next line contains two integers r2 and c2 (1 ≤ r2 ≤ n, 1 ≤ c2 ≤ m) — the coordinates of the cell through which you need to fall. The final cell may coincide with the starting one.
Output
If you can reach the destination, print 'YES', otherwise print 'NO'.
Sample Input
4 6
X...XX
...XX.
.X..X.
......
1 6
2 2
Sample Output
YES
HINT
In the first sample test one possible path is:
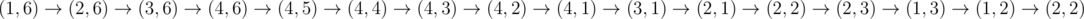
After the first visit of cell (2, 2) the ice on it cracks and when you step there for the second time, your character falls through the ice as intended.
题意
有一个矩形区域,一开始你在一个地方,你只能走.的位置,走了之后.就会变成X,然后你必须让终点变成x,然后再走上去
问你可不可行
题解:
BFS搞一搞就好了,裸题= =
代码:
//qscqesze
#include <cstdio>
#include <cmath>
#include <cstring>
#include <ctime>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
#include <sstream>
#include <queue>
#include <typeinfo>
#include <fstream>
#include <map>
#include <stack>
typedef long long ll;
using namespace std;
//freopen("D.in","r",stdin);
//freopen("D.out","w",stdout);
#define sspeed ios_base::sync_with_stdio(0);cin.tie(0)
#define maxn 200001
#define mod 10007
#define eps 1e-9
int Num;
char CH[];
//const int inf=0x7fffffff; //§ß§é§à§é¨f§³
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
/* inline void P(int x)
{
Num=0;if(!x){putchar('0');puts("");return;}
while(x>0)CH[++Num]=x%10,x/=10;
while(Num)putchar(CH[Num--]+48);
puts("");
}
*/
inline ll read()
{
int x=,f=;char ch=getchar();
while(ch<''||ch>''){if(ch=='-')f=-;ch=getchar();}
while(ch>=''&&ch<=''){x=x*+ch-'';ch=getchar();}
return x*f;
}
inline void P(int x)
{
Num=;if(!x){putchar('');puts("");return;}
while(x>)CH[++Num]=x%,x/=;
while(Num)putchar(CH[Num--]+);
puts("");
}
//************************************************************************************** string s[];
int dx[]={,-,,};
int dy[]={,,,-};
struct node
{
int x,y;
int t;
};
int vis[][];
int main()
{
int n=read(),m=read();
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
cin>>s[i];
node st,ed;
cin>>st.x>>st.y;
st.x--,st.y--;
st.t=;
cin>>ed.x>>ed.y;
ed.x--,ed.y--;
queue<node> q;
q.push(st);
while(!q.empty())
{
node now=q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i=;i<;i++)
{
node next=now;
next.x+=dx[i];
next.y+=dy[i];
next.t++;
if(next.x<||next.x>=n||next.y<||next.y>=m)
continue;
if(next.x==ed.x&&next.y==ed.y&&s[next.x][next.y]=='X')
{
printf("YES\n");
return ;
}
if(s[next.x][next.y]=='X')
continue;
q.push(next);
s[next.x][next.y]='X';
}
}
printf("NO\n");
}
Codeforces Round #301 (Div. 2) C. Ice Cave BFS的更多相关文章
- DFS/BFS Codeforces Round #301 (Div. 2) C. Ice Cave
题目传送门 /* 题意:告诉起点终点,踩一次, '.'变成'X',再踩一次,冰块破碎,问是否能使终点冰破碎 DFS:如题解所说,分三种情况:1. 如果两点重合,只要往外走一步再走回来就行了:2. 若两 ...
- 贪心 Codeforces Round #301 (Div. 2) B. School Marks
题目传送门 /* 贪心:首先要注意,y是中位数的要求:先把其他的都设置为1,那么最多有(n-1)/2个比y小的,cnt记录比y小的个数 num1是输出的1的个数,numy是除此之外的数都为y,此时的n ...
- 贪心 Codeforces Round #301 (Div. 2) A. Combination Lock
题目传送门 /* 贪心水题:累加到目标数字的距离,两头找取最小值 */ #include <cstdio> #include <iostream> #include <a ...
- CodeForces Round #301 Div.2
今天唯一的成果就是把上次几个人一起开房打的那场cf补一下. A. Combination Lock 此等水题看一眼样例加上那个配图我就明白题意了,可是手抽没有注释掉freopen,WA了一发. #in ...
- Codeforces Round #599 (Div. 2) D. 0-1 MST(bfs+set)
Codeforces Round #599 (Div. 2) D. 0-1 MST Description Ujan has a lot of useless stuff in his drawers ...
- Codeforces Round #301 (Div. 2)(A,【模拟】B,【贪心构造】C,【DFS】)
A. Combination Lock time limit per test:2 seconds memory limit per test:256 megabytes input:standard ...
- Codeforces Round #301 (Div. 2)A B C D 水 模拟 bfs 概率dp
A. Combination Lock time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard ...
- 【解题报告】Codeforces Round #301 (Div. 2) 之ABCD
A. Combination Lock 拨密码..最少次数..密码最多有1000位. 用字符串存起来,然后每位大的减小的和小的+10减大的,再取较小值加起来就可以了... #include<st ...
- 「日常训练」Ice Cave(Codeforces Round 301 Div.2 C)
题意与分析(CodeForces 540C) 这题坑惨了我....我和一道经典的bfs题混淆了,这题比那题简单. 那题大概是这样的,一个冰塔,第一次踩某块会碎,第二次踩碎的会掉落.然后求可行解. 但是 ...
随机推荐
- linux 进程优先级 之设置实时进程 (另一种方式是设置nice值)【转】
转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/jkred369/p/6731353.html Linux内核的三种调度策略: 1,SCHED_OTHER 分时调度策略, 2,SCHED_FIF ...
- makefile里PHONY的相关介绍
Phony Targets PHONY 目标并非实际的文件名:只是在显式请求时执行命令的名字.有两种理由需要使用PHONY 目标:避免和同名文件冲突,改善性能. 如果编写一个规则,并不产生目标文件 ...
- The algorithm of entropy realization
近似熵的一种快速实用算法 Pincus提出的近似熵算法中有很多冗余的计算,效率低,速度慢,不利于实际应用,洪波等人在定义的基础上引入二值距离矩阵的概率,提出了一种实用快速的算法. function A ...
- [转载]锁无关的数据结构与Hazard指针——操纵有限的资源
Lock-Free Data Structures with Hazard Pointers 锁无关的数据结构与Hazard指针----操纵有限的资源 By Andrei Alexandrescu a ...
- C++——map注意事项
1. C++标准模块库STL中提供了两种基本的关联容器:set和map.其内部实现是都是采用红黑树,但不同的是,set中结点存储的是键值,map中结点存储的是<key,value>的键值对 ...
- Nginx - 限制并发、限制访问速率、限制流量
1. 前言 本文针对 Nginx 的三个模块进行配置,并证实各自的功能特点: (1)limit_conn_zone 模块 - 限制同一 IP 地址并发连接数: (2)limit_request 模块 ...
- 根据名字杀死进程Killall
Killall命令可以用来给一个特定的进程发送一个信号.这个信号默认情况下是SIGTERM,但也可以由killall命令使用参数来指定其它信号.现在让我们通过一些实际的例子来看看这个命令的实际用法. ...
- TCP可靠传输和拥塞控制
1.TCP的可靠传输 tcp的可靠传输主要靠 来自接收方的确认报文 和 超时重传. 发出报文,计时器开始计时,在规定超时时间内未收到确认报文则重新发送. 注意:发送报文都留一个副本,如果收到确认报文就 ...
- javscript练习(三)
编写一个函数,计算两个数字的和差积商 function calculator(num1,num2,sign){ switch(sign){ cas ...
- css 字符图标浏览器自带
项目中用到的一些特殊字符和图标 html代码 <div class="cross"></div> css代码 .cross{ width: 20px; he ...
