JDK源码那些事儿之ArrayBlockingQueue
线程在JDK中是非常重要的一块内容,所有的应用服务都离不开线程的相关操作,对于大量线程的使用都是推荐使用线程池来进行操作和管理,JDK本身提供的线程池在服务中经常被使用到,以往经常使用Executors来创建,但是阿里规范中也指出了其存在的隐患,从源码来看,内部大量使用了队列相关的类,所以在深入线程部分之前,我们需要了解队列相关的内容,本文就以ArrayBlockingQueue开始对JDK中的常用的队列进行说明
前言
首先我们需要明白其结构特点:ArrayBlockingQueue是数组实现的线程安全的有界的阻塞队列
- 内部是通过数组来实现的,从源码部分也能看出来
- 线程安全说明的是ArrayBlockingQueue内部通过ReentrantLock保护竞争资源,实现了多线程对竞争资源的互斥访问
- 有界,ArrayBlockingQueue对应的数组是有界限的
- 阻塞队列,是指多线程访问竞争资源时,当竞争资源已被某线程获取时,其它要获取该资源的线程需要阻塞等待;而且,ArrayBlockingQueue是按 FIFO(先进先出)原则对元素进行排序,元素都是从尾部插入到队列,从头部开始返回。
从上边的结构特点我们基本上能够理解了其主要的实现,下面来稍微具体描述下其内部实现:
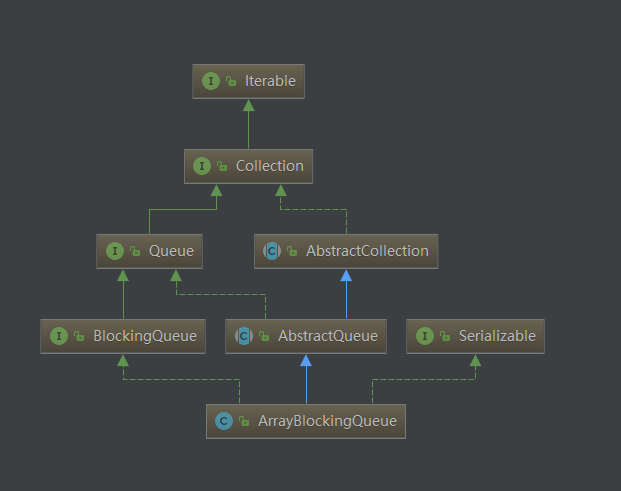
- ArrayBlockingQueue继承于AbstractQueue,并且它实现了BlockingQueue接口
- ArrayBlockingQueue内部是通过Object[]数组保存数据的,印证上边通过数组实现的特点。ArrayBlockingQueue的大小,即数组的容量是创建ArrayBlockingQueue时需要指定的
- ArrayBlockingQueue中包含一个ReentrantLock对象(lock)。ReentrantLock是可重入的互斥锁,ArrayBlockingQueue就是根据该互斥锁实现“多线程对竞争资源的互斥访问”。而且,ReentrantLock分为公平锁和非公平锁,关于具体使用公平锁还是非公平锁,在创建ArrayBlockingQueue时可以指定;而且,ArrayBlockingQueue默认会使用非公平锁。
- ArrayBlockingQueue中包含两个Condition对象(notEmpty和notFull)。Condition又依赖于ArrayBlockingQueue而存在,通过Condition可以实现对ArrayBlockingQueue的更精确的访问。例如,若线程A要取数据时,数组正好为空,则该线程会执行notEmpty.await()进行等待;当其它某个线程(线程B)向数组中插入了数据之后,会调用notEmpty.signal()唤醒“notEmpty上的等待线程”。此时,线程A会被唤醒从而得以继续运行。若线程C要插入数据时,数组已满,则该线程会它执行notFull.await()进行等待;当其它某个线程(线程D)取出数据之后,会调用notFull.signal()唤醒“notFull上的等待线程”。此时,线程C就会被唤醒从而得以继续运行。
ArrayBlockingQueue中入队出队操作如上例子相对比较简单也比较好理解,复杂部分在于迭代器部分,下面通过源码来一步一步说明
类定义
public class ArrayBlockingQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E>
implements BlockingQueue<E>, java.io.Serializable
常量/变量
/** The queued items */
// 队列内部实现使用数组
final Object[] items;
/** items index for next take, poll, peek or remove */
// 下一次从队列中获取的队列元素索引
int takeIndex;
/** items index for next put, offer, or add */
// 下一次插入队列的队列元素索引
int putIndex;
/** Number of elements in the queue */
// 队列长度
int count;
/*
* Concurrency control uses the classic two-condition algorithm
* found in any textbook.
*/
/** Main lock guarding all access */
// 互斥锁
final ReentrantLock lock;
/** Condition for waiting takes */
// 非空信号量
private final Condition notEmpty;
/** Condition for waiting puts */
// 非满信号量
private final Condition notFull;
/**
* Shared state for currently active iterators, or null if there
* are known not to be any. Allows queue operations to update
* iterator state.
*/
// 迭代器维护列表,每次队列更新操作需要更新迭代器保证正确性
// 第二部分迭代器部分单独说明,这里先简单理解就好
transient Itrs itrs = null;
构造方法
默认使用非公平锁,创建一个互斥锁和两个Condition来帮助完成整个队列的操作,从构造方法上也可以看到,队列容量是必须要传的
public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity) {
this(capacity, false);
}
public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair) {
if (capacity <= 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.items = new Object[capacity];
lock = new ReentrantLock(fair);
notEmpty = lock.newCondition();
notFull = lock.newCondition();
}
public ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity, boolean fair,
Collection<? extends E> c) {
this(capacity, fair);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
// 使用锁操作确保可见性,因为item这里本身并不保证可见性,防止并发操作下线程内存中数组不一致的情况出现
lock.lock(); // Lock only for visibility, not mutual exclusion
try {
int i = 0;
try {
for (E e : c) {
checkNotNull(e);
items[i++] = e;
}
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
count = i;
// 队列被占满 putIndex置0,从这里也能看出来这个数组是循环利用的,达到最大值,置成0,类似环状数组
putIndex = (i == capacity) ? 0 : i;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
重要方法
enqueue
入队操作,添加元素到队列中,当且仅当持有lock的时候。每次添加完毕后通过notEmpty.signal()唤醒之前通过notEmpty.await()进入等待状态的线程
/**
* Inserts element at current put position, advances, and signals.
* Call only when holding lock.
*/
private void enqueue(E x) {
// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1;
// assert items[putIndex] == null;
final Object[] items = this.items;
items[putIndex] = x;
// 达到数组最大索引时,putIndex指向数组为0的位置
if (++putIndex == items.length)
putIndex = 0;
// 队列长度加1
count++;
notEmpty.signal();
}
dequeue
出队操作,获取队列元素,当且仅当持有lock的时候。每次获取完毕后通过notFull.signal()唤醒之前通过notFull.await()进入等待状态的线程
/**
* Extracts element at current take position, advances, and signals.
* Call only when holding lock.
*/
private E dequeue() {
// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1;
// assert items[takeIndex] != null;
final Object[] items = this.items;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E x = (E) items[takeIndex];
// 指向置空,删除队列中的这个元素
items[takeIndex] = null;
// takeIndex同putIndex,达到数组最大索引时,指向数组为0的位置
if (++takeIndex == items.length)
takeIndex = 0;
// 队列长度减1
count--;
// 更新迭代器中的元素数据,保证在并发操作中迭代的正确性
// 后边迭代器说明时可以回来看下
if (itrs != null)
itrs.elementDequeued();
notFull.signal();
return x;
}
add/offer/put
入队操作有以下几个方法,同时各个方法有些许不同
public boolean add(E e) {
// 调用offer获取结果 不成功则抛错
return super.add(e);
}
public boolean add(E e) {
if (offer(e))
return true;
else
throw new IllegalStateException("Queue full");
}
public boolean offer(E e) {
// 检查元素是否为空
checkNotNull(e);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
// 队列已满则返回false
if (count == items.length)
return false;
else {
// 入队
enqueue(e);
return true;
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public boolean offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
checkNotNull(e);
// 阻塞等待时间 纳秒
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
// lockInterruptibly方法可被中断
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count == items.length) {
if (nanos <= 0)
// 超时返回
return false;
// 队列已满则阻塞等待nanos纳秒
nanos = notFull.awaitNanos(nanos);
}
// 入队
enqueue(e);
return true;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
checkNotNull(e);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count == items.length)
// 队列已满阻塞等待
notFull.await();
// 入队
enqueue(e);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
向队列中添加元素主要包含上述3个方法,不同之处如下:
| 方法名(含参数) | 说明 |
|---|---|
| add(E e) | 实际调用offer,元素入队操作,成功则返回true,失败则抛错IllegalStateException |
| offer(E e) | 元素入队操作,成功返回true,失败返回false |
| put(E e) | 可中断,元素入队操作,队列已满则阻塞等待直到被通知可入队 |
| offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) | 可中断,元素入队操作,设置阻塞等待超时时间,超时则返回false,成功入队则返回true |
以上操作其实已经在BlockingQueue接口中定义,需根据接口自行实现
poll/take/peek/remove
出队方法同入队方法,也稍有不同,如下
public E poll() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
// 队列无元素返回null,有元素则出队列操作
return (count == 0) ? null : dequeue();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public E take() throws InterruptedException {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
// 可中断
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count == 0)
// 队列为空则阻塞等待直到被唤醒
notEmpty.await();
return dequeue();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public E poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count == 0) {
if (nanos <= 0)
return null;
// 阻塞等待超时nanos纳秒
nanos = notEmpty.awaitNanos(nanos);
}
return dequeue();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public E peek() {
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
// 返回队列takeIndex索引处的值,不进行出队列操作,元素不会被删除
return itemAt(takeIndex); // null when queue is empty
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) return false;
final Object[] items = this.items;
final ReentrantLock lock = this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
if (count > 0) {
final int putIndex = this.putIndex;
int i = takeIndex;
do {
if (o.equals(items[i])) {
// 移除i处的元素,同时队列进行整理,移除元素后的元素依次向前移动进行填补空缺
removeAt(i);
return true;
}
// 循环到数组长度,从0继续
if (++i == items.length)
i = 0;
} while (i != putIndex);
}
return false;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
从队列中获取元素主要包含上述4个方法,除peek不执行出队操作外,remove是删除之外,其余均需执行出队操作,不同之处如下:
| 方法名(含参数) | 说明 |
|---|---|
| poll() | 出队操作,队列为空返回null,不为空则返回对应元素 |
| take() | 可中断,出队操作,队列为空则阻塞等待直到被通知获取值返回 |
| poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) | 可中断,出队操作,设置阻塞等待超时时间,超时则返回null,成功则返回对应元素 |
| peek() | 仅仅返回队列元素的值,但是不执行出队操作 |
| remove(Object o) | 删除队列中的对应元素(可处于队列任何位置),队列需进行整理 |
removeAt
移除指定位置的队列元素并调整队列
/**
* Deletes item at array index removeIndex.
* Utility for remove(Object) and iterator.remove.
* Call only when holding lock.
*/
void removeAt(final int removeIndex) {
// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1;
// assert items[removeIndex] != null;
// assert removeIndex >= 0 && removeIndex < items.length;
final Object[] items = this.items;
// 移除队列元素索引是队列出队索引时,参考出队操作即可
if (removeIndex == takeIndex) {
// removing front item; just advance
// 移除队列元素置空
items[takeIndex] = null;
// 调整队列出队索引
if (++takeIndex == items.length)
takeIndex = 0;
// 队列长度减1
count--;
// 如果有迭代器则需要更新,这部分后边说
if (itrs != null)
itrs.elementDequeued();
} else {
// 到这里表明删除的元素非队列出队索引,删除元素在队列中间
// an "interior" remove
// slide over all others up through putIndex.
final int putIndex = this.putIndex;
// 调整队列元素,队列删除元素后的所有元素向前移动一位
for (int i = removeIndex;;) {
int next = i + 1;
if (next == items.length)
next = 0;
if (next != putIndex) {
items[i] = items[next];
i = next;
} else {
// next = putIndex 说明是putIndex前一个元素,则置空更新putIndex即可结束
items[i] = null;
this.putIndex = i;
break;
}
}
count--;
// 同步迭代器操作,后面进行说明
if (itrs != null)
itrs.removedAt(removeIndex);
}
// 唤醒入队线程
notFull.signal();
}
源码在方法中多次将操作的类成员变量赋予方法内部的局部变量,例如这里的 ReentrantLock lock = this.lock,其实是为了加快程序运行效率,每次都直接引用类成员,比如this.lock这样的读取操作相对于在方法内部直接操作方法栈的局部变量效率相对要低一点,涉及到了JVM部分,不详细说明,有兴趣可以自行查找相关资料
迭代器说明
以上源码部分为队列操作部分,整体上来看算是很好理解了,下面说明最复杂的迭代器部分
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Itr();
}
对于外部调用方来说,需要先获取对应的迭代器,源码如上,从这个地方我们能明白一件事,迭代器是调用这个方法那个时间的队列的类似于快照的保存,保存了那个时刻的队列状态,在下面的内部类源码中我们也能看到保存了哪些属性,这里没有保存队列内部具体元素,所以会造成一个比较大的问题,就是在多线程频繁的入队出队操作如何保证迭代器取值的正确性?当然,如果我们把队列元素也保存一份,本身也是不正确的。迭代器的复杂部分就在于此,保证迭代器正确性导致了迭代器源码的复杂性
这里先给出结论:
- 创建的迭代器Itr会保存当时队列的状态(不保存队列元素值)
- 创建的迭代器会放入Itrs(迭代器维护列表)中进行统一的维护和管理
- 在每次next()操作时会更新迭代器状态查看是都用完或失效,通过Itrs的doSomeSweeping进行清理无效迭代器
- 出队操作时会通过itrs.elementDequeued()更新迭代器维护列表Itrs
- 首次创建迭代器时会保存下一次调用next方法的值,故在调用hasNext时为true,在next()调用前队列空了,再调用next()依旧会返回值,算是一种保护
- 在创建了迭代器之后,队列中的元素被两次循环替代后,则判定此迭代器无效
迭代器相关内部类
内部类主要在迭代时使用,从iterator方法可以看出,每次调用时都会重新创建一个Itr对象,那么如何保证增删改时迭代器的正确性?看下内部实现
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
/** Index to look for new nextItem; NONE at end */
// 指向下一个迭代元素的游标,结束时为NONE(-1)
private int cursor;
/** Element to be returned by next call to next(); null if none */
// 下次调用next()返回的元素,无则返回null,这里即对应结论上的5
private E nextItem;
/** Index of nextItem; NONE if none, REMOVED if removed elsewhere */
// 下一个元素nextItem的索引值,空的话返回NONE(-1),如果被移除了则返回REMOVED(-2)
private int nextIndex;
/** Last element returned; null if none or not detached. */
// 上一次调用next()返回的元素,无则返回null
private E lastItem;
/** Index of lastItem, NONE if none, REMOVED if removed elsewhere */
// 上一个元素的索引值,空的话返回NONE,如果被移除了则返回REMOVED
private int lastRet;
/** Previous value of takeIndex, or DETACHED when detached */
// 上一个takeIndex对应的值,当处于无效状态时为DETACHED(-3),以这个变量标识迭代器DETACHED状态
private int prevTakeIndex;
/** Previous value of iters.cycles */
// 上一个cycles的值
private int prevCycles;
/** Special index value indicating "not available" or "undefined" */
// 标识不可用值或未定义值
private static final int NONE = -1;
/**
* Special index value indicating "removed elsewhere", that is,
* removed by some operation other than a call to this.remove().
*/
// 标识元素被移除
private static final int REMOVED = -2;
/** Special value for prevTakeIndex indicating "detached mode" */
// 标识prevTakeIndex为无效状态
private static final int DETACHED = -3;
Itr() {
// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 0;
// 构造时上一个元素索引为空
lastRet = NONE;
// 使用互斥锁
final ReentrantLock lock = ArrayBlockingQueue.this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
// 队列为空,初始化变量
if (count == 0) {
// assert itrs == null;
cursor = NONE;
nextIndex = NONE;
// 无效状态的迭代器
prevTakeIndex = DETACHED;
} else {
// 此时队列不为空
// 记录出队的takeIndex
final int takeIndex = ArrayBlockingQueue.this.takeIndex;
prevTakeIndex = takeIndex;
// 下一次使用迭代返回的值,这里就已经保存好了调用next的返回值
nextItem = itemAt(nextIndex = takeIndex);
// 游标指向takeIndex+1
cursor = incCursor(takeIndex);
// 使用Itrs来维护所有的迭代器
if (itrs == null) {
// 空则创建
itrs = new Itrs(this);
} else {
// 非空将次迭代器注册
itrs.register(this); // in this order
// 清理迭代器,每次创建新迭代器时都会进行一次简单的清理操作
itrs.doSomeSweeping(false);
}
// 保存队列循环的次数,cycles在itrs进行解释
prevCycles = itrs.cycles;
// assert takeIndex >= 0;
// assert prevTakeIndex == takeIndex;
// assert nextIndex >= 0;
// assert nextItem != null;
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
// 判断迭代器是否已经无效,通过prevTakeIndex来判断
boolean isDetached() {
// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1;
return prevTakeIndex < 0;
}
// 游标值+1
private int incCursor(int index) {
// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1;
// 达到最大值从0开始
if (++index == items.length)
index = 0;
// 与下一个入队元素位置相同,则表示队列已无元素,置NONE
if (index == putIndex)
index = NONE;
return index;
}
/**
* Returns true if index is invalidated by the given number of
* dequeues, starting from prevTakeIndex.
*/
// 从prevTakeIndex开始,队列索引index无效则返回true
// 在incorporateDequeues中使用,比较index,prevTakeIndex的距离与实际距离
private boolean invalidated(int index, int prevTakeIndex,
long dequeues, int length) {
// 初始化时设置小于0
if (index < 0)
return false;
// 当前index与prevTakeIndex的距离
int distance = index - prevTakeIndex;
// 发生循环操作,很好理解,加上数组length,即为正确的距离
if (distance < 0)
distance += length;
// 如果distance小于实际距离,则无效返回true
return dequeues > distance;
}
/**
* Adjusts indices to incorporate all dequeues since the last
* operation on this iterator. Call only from iterating thread.
*/
// 迭代操作后元素出队调整索引
private void incorporateDequeues() {
// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1;
// assert itrs != null;
// assert !isDetached();
// assert count > 0;
// 获取当前变量
final int cycles = itrs.cycles;
final int takeIndex = ArrayBlockingQueue.this.takeIndex;
final int prevCycles = this.prevCycles;
final int prevTakeIndex = this.prevTakeIndex;
// cycles != prevCycles 表示队列已经被循环使用过,相当于循环到0重新入队出队
// takeIndex != prevTakeIndex 表示队列元素有出队,需重新排序
if (cycles != prevCycles || takeIndex != prevTakeIndex) {
final int len = items.length;
// how far takeIndex has advanced since the previous
// operation of this iterator
// 队列实际移动的长度
long dequeues = (cycles - prevCycles) * len
+ (takeIndex - prevTakeIndex);
// Check indices for invalidation
// lastRet处元素被移除了
if (invalidated(lastRet, prevTakeIndex, dequeues, len))
lastRet = REMOVED;
// nextIndex处元素被移除了
if (invalidated(nextIndex, prevTakeIndex, dequeues, len))
nextIndex = REMOVED;
// 游标索引无效置为当前队列takeIndex
if (invalidated(cursor, prevTakeIndex, dequeues, len))
cursor = takeIndex;
// 迭代器无效进行清理操作
if (cursor < 0 && nextIndex < 0 && lastRet < 0)
detach();
else {
// 更新索引
this.prevCycles = cycles;
this.prevTakeIndex = takeIndex;
}
}
}
/**
* Called when itrs should stop tracking this iterator, either
* because there are no more indices to update (cursor < 0 &&
* nextIndex < 0 && lastRet < 0) or as a special exception, when
* lastRet >= 0, because hasNext() is about to return false for the
* first time. Call only from iterating thread.
*/
//
private void detach() {
// Switch to detached mode
// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1;
// assert cursor == NONE;
// assert nextIndex < 0;
// assert lastRet < 0 || nextItem == null;
// assert lastRet < 0 ^ lastItem != null;
if (prevTakeIndex >= 0) {
// assert itrs != null;
// 设置迭代器DETACHED状态,无效状态
prevTakeIndex = DETACHED;
// try to unlink from itrs (but not too hard)
// 所有的迭代器进行一次清理
itrs.doSomeSweeping(true);
}
}
/**
* For performance reasons, we would like not to acquire a lock in
* hasNext in the common case. To allow for this, we only access
* fields (i.e. nextItem) that are not modified by update operations
* triggered by queue modifications.
*/
// 出于对性能的考虑,这里不会进行加锁
public boolean hasNext() {
// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 0;
// 直接判断nextItem,故首次初始化时后续清空队列这里nextItem不为空,会返回第一个队列值
if (nextItem != null)
return true;
// nextItem为空时才会进入noNext
noNext();
return false;
}
// 无元素,清理
private void noNext() {
final ReentrantLock lock = ArrayBlockingQueue.this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
// assert cursor == NONE;
// assert nextIndex == NONE;
// prevTakeIndex >= 0,需要进行处理
if (!isDetached()) {
// assert lastRet >= 0;
incorporateDequeues(); // might update lastRet
if (lastRet >= 0) {
// 保存lastItem值,remove方法中需要用到
lastItem = itemAt(lastRet);
// assert lastItem != null;
detach();
}
}
// assert isDetached();
// assert lastRet < 0 ^ lastItem != null;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public E next() {
// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 0;
// 迭代返回值,每次调用next前已经确定了nextItem值
final E x = nextItem;
if (x == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
final ReentrantLock lock = ArrayBlockingQueue.this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
if (!isDetached())
incorporateDequeues();
// assert nextIndex != NONE;
// assert lastItem == null;
// next调用之后调用remove删除元素的时候使用
lastRet = nextIndex;
final int cursor = this.cursor;
if (cursor >= 0) {
// 下一次迭代返回值
nextItem = itemAt(nextIndex = cursor);
// assert nextItem != null;
// 游标加1
this.cursor = incCursor(cursor);
} else {
// 无下一个迭代元素
nextIndex = NONE;
nextItem = null;
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
return x;
}
public void remove() {
// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 0;
final ReentrantLock lock = ArrayBlockingQueue.this.lock;
lock.lock();
try {
if (!isDetached())
incorporateDequeues(); // might update lastRet or detach
final int lastRet = this.lastRet;
this.lastRet = NONE;
// 删除时需要用到lastRet
if (lastRet >= 0) {
if (!isDetached())
removeAt(lastRet);
else {
// 处理在hasNext()返回false之后调用iterator .remove()的特殊情况
final E lastItem = this.lastItem;
// assert lastItem != null;
this.lastItem = null;
// 和预期元素一致才进行删除
if (itemAt(lastRet) == lastItem)
removeAt(lastRet);
}
} else if (lastRet == NONE)
// lastRet为NONE时会抛错
throw new IllegalStateException();
// else lastRet == REMOVED and the last returned element was
// previously asynchronously removed via an operation other
// than this.remove(), so nothing to do.
if (cursor < 0 && nextIndex < 0)
detach();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
// assert lastRet == NONE;
// assert lastItem == null;
}
}
/**
* Called to notify the iterator that the queue is empty, or that it
* has fallen hopelessly behind, so that it should abandon any
* further iteration, except possibly to return one more element
* from next(), as promised by returning true from hasNext().
*/
// 队列为空或者无效时应清理掉,更新内部变量值
void shutdown() {
// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1;
cursor = NONE;
if (nextIndex >= 0)
nextIndex = REMOVED;
if (lastRet >= 0) {
lastRet = REMOVED;
lastItem = null;
}
prevTakeIndex = DETACHED;
// nextItem不置空是因为有可能调用的next方法需要用到
// Don't set nextItem to null because we must continue to be
// able to return it on next().
//
// Caller will unlink from itrs when convenient.
}
// 计算index与prevTakeIndex的距离
private int distance(int index, int prevTakeIndex, int length) {
int distance = index - prevTakeIndex;
if (distance < 0)
distance += length;
return distance;
}
/**
* Called whenever an interior remove (not at takeIndex) occurred.
*
* @return true if this iterator should be unlinked from itrs
*/
// 队列内部元素被删除时调用,保证迭代器的正确性
boolean removedAt(int removedIndex) {
// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1;
// 当前迭代器无效时直接返回true
if (isDetached())
return true;
final int cycles = itrs.cycles;
final int takeIndex = ArrayBlockingQueue.this.takeIndex;
final int prevCycles = this.prevCycles;
final int prevTakeIndex = this.prevTakeIndex;
final int len = items.length;
int cycleDiff = cycles - prevCycles;
// 删除的索引位置小于takeIndex,循环次数+1
if (removedIndex < takeIndex)
cycleDiff++;
// 删除元素的实际距离
final int removedDistance =
(cycleDiff * len) + (removedIndex - prevTakeIndex);
// assert removedDistance >= 0;
int cursor = this.cursor;
if (cursor >= 0) {
int x = distance(cursor, prevTakeIndex, len);
// 游标指向被删除的元素位置
if (x == removedDistance) {
// 已经没有元素了,置NONE
if (cursor == putIndex)
this.cursor = cursor = NONE;
}
// 游标已经超过removedDistance,索引游标需-1,因为删除元素算在了游标内,
// 需减1才能保证队列删除元素之后整体元素位置调整之后迭代器这里的正确性
else if (x > removedDistance) {
// assert cursor != prevTakeIndex;
this.cursor = cursor = dec(cursor);
}
}
int lastRet = this.lastRet;
// lastRet同上
if (lastRet >= 0) {
int x = distance(lastRet, prevTakeIndex, len);
if (x == removedDistance)
this.lastRet = lastRet = REMOVED;
else if (x > removedDistance)
this.lastRet = lastRet = dec(lastRet);
}
// nextIndex同上
int nextIndex = this.nextIndex;
if (nextIndex >= 0) {
int x = distance(nextIndex, prevTakeIndex, len);
if (x == removedDistance)
this.nextIndex = nextIndex = REMOVED;
else if (x > removedDistance)
this.nextIndex = nextIndex = dec(nextIndex);
}
// 迭代器无效状态
else if (cursor < 0 && nextIndex < 0 && lastRet < 0) {
this.prevTakeIndex = DETACHED;
return true;
}
return false;
}
/**
* Called whenever takeIndex wraps around to zero.
*
* @return true if this iterator should be unlinked from itrs
*/
// 每当takeIndex循环到0时调用
boolean takeIndexWrapped() {
// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1;
if (isDetached())
return true;
if (itrs.cycles - prevCycles > 1) {
// All the elements that existed at the time of the last
// operation are gone, so abandon further iteration.
// 迭代器所有元素都已经在入队出队中不存在了,需置迭代器无效,这里也能看到相差2的时候已经无效了
shutdown();
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
提一句,下面的Itrs中的Node使用了弱引用,这可以在迭代器实例被使用完时(例如将其置为null)被GC及时的回收掉,同样涉及到JVM,自行查找相关资料吧
class Itrs {
/**
* Node in a linked list of weak iterator references.
*/
// 继承WeakReference实现Node的弱引用,这里也能看出来是链表
private class Node extends WeakReference<Itr> {
Node next;
Node(Itr iterator, Node next) {
super(iterator);
this.next = next;
}
}
/** Incremented whenever takeIndex wraps around to 0 */
// takeIndex循环到0时加1,记录循环次数
int cycles = 0;
/** Linked list of weak iterator references */
// 头节点
private Node head;
/** Used to expunge stale iterators */
// 记录上次清理到的节点,方便下次使用
private Node sweeper = null;
// 每次迭代器清理操作时有两种模式,一种查找次数少,一种查找次数多
private static final int SHORT_SWEEP_PROBES = 4;
private static final int LONG_SWEEP_PROBES = 16;
Itrs(Itr initial) {
register(initial);
}
/**
* Sweeps itrs, looking for and expunging stale iterators.
* If at least one was found, tries harder to find more.
* Called only from iterating thread.
*
* @param tryHarder whether to start in try-harder mode, because
* there is known to be at least one iterator to collect
*/
// 清理操作,通过tryHarder判断使用哪种清理模式
void doSomeSweeping(boolean tryHarder) {
// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1;
// assert head != null;
int probes = tryHarder ? LONG_SWEEP_PROBES : SHORT_SWEEP_PROBES;
Node o, p;
final Node sweeper = this.sweeper;
boolean passedGo; // to limit search to one full sweep
if (sweeper == null) {
// 无上次记录,则从头开始
o = null;
p = head;
passedGo = true;
} else {
// 上次记录继续清理
o = sweeper;
p = o.next;
passedGo = false;
}
for (; probes > 0; probes--) {
if (p == null) {
if (passedGo)
break;
o = null;
p = head;
passedGo = true;
}
final Itr it = p.get();
final Node next = p.next;
// 迭代器无效处理
if (it == null || it.isDetached()) {
// found a discarded/exhausted iterator
// 发现一个迭代器无效则转换成try harder模式
probes = LONG_SWEEP_PROBES; // "try harder"
// unlink p
p.clear();
p.next = null;
if (o == null) {
head = next;
if (next == null) {
// We've run out of iterators to track; retire
itrs = null;
return;
}
}
else
o.next = next;
} else {
o = p;
}
p = next;
}
// 记录下次清理需要使用的节点数据
this.sweeper = (p == null) ? null : o;
}
/**
* Adds a new iterator to the linked list of tracked iterators.
*/
// 将迭代器添加到迭代管理列表中,从头部添加
void register(Itr itr) {
// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1;
head = new Node(itr, head);
}
/**
* Called whenever takeIndex wraps around to 0.
*
* Notifies all iterators, and expunges any that are now stale.
*/
// 队列takeIndex循环到0时调用
void takeIndexWrapped() {
// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1;
// cycles加1记录循环次数
cycles++;
// 调用每个迭代器的takeIndexWrapped更新,同时清理无效迭代器
for (Node o = null, p = head; p != null;) {
final Itr it = p.get();
final Node next = p.next;
if (it == null || it.takeIndexWrapped()) {
// unlink p
// assert it == null || it.isDetached();
p.clear();
p.next = null;
if (o == null)
head = next;
else
o.next = next;
} else {
o = p;
}
p = next;
}
// 迭代管理列表空,无迭代器了
if (head == null) // no more iterators to track
itrs = null;
}
/**
* Called whenever an interior remove (not at takeIndex) occurred.
*
* Notifies all iterators, and expunges any that are now stale.
*/
// 队列删除元素时调用迭代管理列表的removedAt
void removedAt(int removedIndex) {
for (Node o = null, p = head; p != null;) {
final Itr it = p.get();
final Node next = p.next;
// 迭代管理列表itrs调用每个迭代器的removedAt完成更新
// 同时进行无效迭代器的清理
if (it == null || it.removedAt(removedIndex)) {
// unlink p
// assert it == null || it.isDetached();
p.clear();
p.next = null;
if (o == null)
head = next;
else
o.next = next;
} else {
o = p;
}
p = next;
}
if (head == null) // no more iterators to track
itrs = null;
}
/**
* Called whenever the queue becomes empty.
*
* Notifies all active iterators that the queue is empty,
* clears all weak refs, and unlinks the itrs datastructure.
*/
// 队列为空时调用,迭代管理器将清理所有迭代器
void queueIsEmpty() {
// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1;
for (Node p = head; p != null; p = p.next) {
Itr it = p.get();
if (it != null) {
p.clear();
it.shutdown();
}
}
head = null;
itrs = null;
}
/**
* Called whenever an element has been dequeued (at takeIndex).
*/
// 队列出队时调用判断队列是否为空和队列循环次数
void elementDequeued() {
// assert lock.getHoldCount() == 1;
if (count == 0)
queueIsEmpty();
else if (takeIndex == 0)
takeIndexWrapped();
}
}
上边两个内部类实现了迭代器的相关操作,还是比较复杂的,通过一个中间类Itrs来完成对所有的迭代器的管理和更新操作,在队列操作时也要对迭代器的相关变量进行更新来保证迭代的正确性
总结
整体来说,ArrayBlockingQueue本身在队列操作这块并不是很复杂,基本的阻塞队列操作能理解就已经ok了。其中涉及到锁的部分先简单理解为好,毕竟涉及到了AQS,后续再进行介绍,在迭代器部分还是比较复杂的,不过最终都是为了保证迭代时数据的正确性,这个方面还是比较好理解的
以上的源码分析中,我们也能看出一些问题,ArrayBlockingQueue内部的大部分操作方法都需要先获取同一个ReentrantLock独占锁才能继续执行,这极大的降低了吞吐量,几乎每个操作都会阻塞其它操作,最主要是入队操作和出队操作之间互斥。所以ArrayBlockingQueue不适用于需要高吞吐量的高效率数据生成与消费场景。在常用的线程池中也没有用到ArrayBlockingQueue
以上内容如有问题欢迎指出,笔者验证后将及时修正,谢谢
JDK源码那些事儿之ArrayBlockingQueue的更多相关文章
- JDK源码那些事儿之并发ConcurrentHashMap上篇
前面已经说明了HashMap以及红黑树的一些基本知识,对JDK8的HashMap也有了一定的了解,本篇就开始看看并发包下的ConcurrentHashMap,说实话,还是比较复杂的,笔者在这里也不会过 ...
- JDK源码那些事儿之红黑树基础下篇
说到HashMap,就一定要说到红黑树,红黑树作为一种自平衡二叉查找树,是一种用途较广的数据结构,在jdk1.8中使用红黑树提升HashMap的性能,今天就来说一说红黑树,上一讲已经给出插入平衡的调整 ...
- JDK源码那些事儿之浅析Thread上篇
JAVA中多线程的操作对于初学者而言是比较难理解的,其实联想到底层操作系统时我们可能会稍微明白些,对于程序而言最终都是硬件上运行二进制指令,然而,这些又太过底层,今天来看一下JAVA中的线程,浅析JD ...
- JDK源码那些事儿之LinkedBlockingQueue
今天继续讲解阻塞队列,涉及到了常用线程池的其中一个队列LinkedBlockingQueue,从类命名部分我们就可以看出其用意,队列中很多方法名是通用的,只是每个队列内部实现不同,毕竟实现的都是同一个 ...
- JDK源码那些事儿之ConcurrentLinkedDeque
非阻塞队列ConcurrentLinkedQueue我们已经了解过了,既然是Queue,那么是否有其双端队列实现呢?答案是肯定的,今天就继续说一说非阻塞双端队列实现ConcurrentLinkedDe ...
- JDK源码那些事儿之ConcurrentLinkedQueue
阻塞队列的实现前面已经讲解完毕,今天我们继续了解源码中非阻塞队列的实现,接下来就看一看ConcurrentLinkedQueue非阻塞队列是怎么完成操作的 前言 JDK版本号:1.8.0_171 Co ...
- JDK源码那些事儿之LinkedBlockingDeque
阻塞队列中目前还剩下一个比较特殊的队列实现,相比较前面讲解过的队列,本文中要讲的LinkedBlockingDeque比较容易理解了,但是与之前讲解过的阻塞队列又有些不同,从命名上你应该能看出一些端倪 ...
- JDK源码那些事儿之LinkedTransferQueue
在JDK8的阻塞队列实现中还有两个未进行说明,今天继续对其中的一个阻塞队列LinkedTransferQueue进行源码分析,如果之前的队列分析已经让你对阻塞队列有了一定的了解,相信本文要讲解的Lin ...
- JDK源码那些事儿之DelayQueue
作为阻塞队列的一员,DelayQueue(延迟队列)由于其特殊含义而使用在特定的场景之中,主要在于Delay这个词上,那么其内部是如何实现的呢?今天一起通过DelayQueue的源码来看一看其是如何完 ...
随机推荐
- poj3348(求凸包面积)
题目链接:https://vjudge.net/problem/POJ-3348 题意:转换题意后即是求凸包的面积. 思路: 套模板,求凸包面积即转换为多个三角形面积之和,用叉积求,然后除2,因为本题 ...
- lnmp二级域名配置相关
阿里云那域名解析那有误读 我在偏远的电信网选择中国联通解析死活解析不出来 以上这么配置就对了....选择默认.瞬间解析出来.... 出于对nginx 配置不够熟悉 后来一点点理出来. 不带www 也正 ...
- PAT(A) 1144 The Missing Number(C)统计
题目链接:1144 The Missing Number (20 point(s)) Description Given N integers, you are supposed to find th ...
- WUSTOJ 1326: Graph(Java)费马数
题目链接:1326: Graph 参考博客:HNUSTOJ-1617 Graph(费马数)--G2MI Description Your task is to judge whether a regu ...
- sequence(线段树+单调栈) (2019牛客暑期多校训练营(第四场))
示例: 输入: 31 -1 11 2 3 输出: 3 题意:求最大的(a区间最小值*b区间和) 线段树做法:用单调栈求出每个数两边比b数组大的左右边界,然后用线段树求出每段区间的和sum.最小前缀ls ...
- 5-24 c++语言之【基础知识】
最近一段时间继续开始了c++的学习,作为c plus plus 难免会与c语言做一个对比,很明显的感受到c++语言注重代码的复用性和拓展性,而c语言更加注重其算法的高效性,这也是今后需要注意的地方,避 ...
- ALV报表——选择屏幕变量赋值
ABAP选择屏幕变量赋值 运行效果: 代码: *&---------------------------------------------------------------------* ...
- Java版Kafka使用及配置解释
Java版Kafka使用及配置解释 一.Java示例 kafka是吞吐量巨大的一个消息系统,它是用scala写的,和普通的消息的生产消费还有所不同,写了个demo程序供大家参考.kafka的安装请参考 ...
- 为Visual Studio安装其他控件(cognex 康耐视)时报错:未能加载文件或程序集 EnvDTE, Version=8.0.0.0
解决办法: 在VS的路径下(一般为:C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio\2017\Enterprise\Common7\IDE\Private ...
- 1.MVC基础-初识MVC,与WebForm比较
1.Net WebForm的开发模式
