SRS之RTMP的TCP线程(即监听线程)
本文分析的是 SRS 针对 rtmp 的端口建立的 tcp 线程。具体建立过程: SRS之监听端口的管理:RTMP
RTMP 的 TCP 线程中各个类之间 handler 的关系图
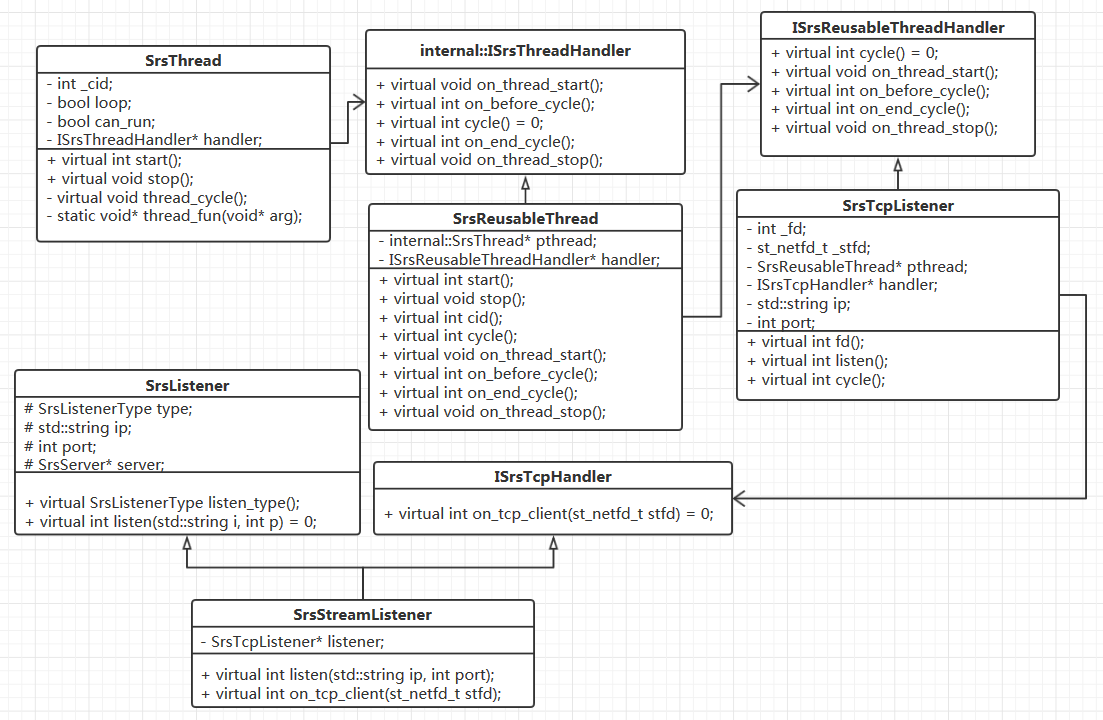
1. RTMP之TCP线程:SrsThread::thread_fun
void* SrsThread::thread_fun(void* arg)
{
SrsThread* obj = (SrsThread*)arg;
srs_assert(obj);
/* 进入线程主循环 */
obj->thread_cycle();
// for valgrind to detect.
SrsThreadContext* ctx = dynamic_cast<SrsThreadContext*>(_srs_context);
if (ctx) {
ctx->clear_cid();
}
st_thread_exit(NULL);
return NULL;
}
1.1 SrsThread::thread_cycle()
void SrsThread::thread_cycle()
{
int ret = ERROR_SUCCESS;
_srs_context->generate_id();
srs_info("thread %s cycle start", _name);
_cid = _srs_context->get_id();
srs_assert(handler);
/* 父类 ISrsThreadHandler 指针 handler 调用子类对象
* SrsReusableThread 的成员函数 on_thread_start */
handler->on_thread_start();
// thread is running now.
really_terminated = false;
// wait for cid to ready, for parent thread to get the cid.
while (!can_run && loop) {
st_usleep(10 * 1000);
}
while (loop) {
/* 调用子类SrsReusableThread的成员函数on_before_cycle */
if ((ret = handler->on_before_cycle()) != ERROR_SUCCESS) {
srs_warn("thread %s on before cycle failed, ignored and retry, ret=%d",
_name, ret);
goto failed;
}
srs_info("thread %s on before cycle success", _name);
/* 调用子类 SrsReusableThread 的成员函数 cycle */
if ((ret = handler->cycle()) != ERROR_SUCCESS) {
if (!srs_is_client_gracefully_close(ret) && !srs_is_system_control_error(ret))
{
srs_warn("thread %s cycle failed, ignored and retry, ret=%d", _name, ret);
}
goto failed;
}
srs_info("thread %s cycle success", _name);
/* 调用子类 SrsReusableThread 的成员函数 on_end_cycle */
if ((ret = handler->on_end_cycle()) != ERROR_SUCCESS) {
srs_warn("thread %s on end cycle failed, ignored and retry, ret=%d",
_name, ret);
goto failed;
}
srs_info("thread %s on end cycle success", _name);
failed:
/* 检测是否仍然继续循环 */
if (!loop) {
break;
}
/* 每次循环完成一次后,就休眠 cycle_interval_us(>0) 微妙 */
// to improve performance, donot sleep when interval is zero.
// @see: https://github.com/ossrs/srs/issues/237
if (cycle_interval_us != 0) {
st_usleep(cycle_interval_us);
}
}
// readly terminated now.
really_terminated = true;
handler->on_thread_stop();
srs_info("thread %s cycle finished", _name);
}
1.2 SrsReusableThread::on_thread_start
void SrsReusableThread::on_thread_start()
{
/* 由于子类 SrsTcpListener 没有实现 on_thread_start,
* 因此调用的是父类 ISrsReusableThreadHandler 的 on_thread_start,
* 但是,该父类实现的函数为空 */
handler->on_thread_start();
}
void ISrsReusableThreadHandler::on_thread_start()
{
}
1.3 SrsReusableThread::on_before_cycle
int SrsReusableThread::on_before_cycle()
{
/* 由于子类 SrsTcpListener 没有实现 on_before_cycle,
* 因此调用的是父类 ISrsReusableThreadHandler 的 on_before_cycle */
return handler->on_before_cycle();
}
int ISrsReusableThreadHandler::on_before_cycle()
{
return ERROR_SUCCESS;
}
1.4 SrsReusableThread::cycle
int SrsReusableThread::cycle()
{
/* 调用子类 SrsTcpListener 实现的 cycle 函数 */
return handler->cycle();
}
1.5 SrsTcpListener::cycle
位于 srs_app_listener.cpp:
int SrsTcpListener::cycle()
{
int ret = ERROR_SUCCESS;
/* 调用ST的库函数st_accept监听接收客户端的连接请求 */
st_netfd_t client_stfd = st_accept(_stfd, NULL, NULL, ST_UTIME_NO_TIMEOUT);
if (client_stfd == NULL) {
// ignore error.
if (errno != EINTR) {
srs_error("ignore accept thread stoppped for accept client error");
}
return ret;
}
srs_verbose("get a client. fd=%d", st_netfd_fileno(client_stfd));
/* 调用子类SrsStreamListener的on_tcp_client函数 */
if ((ret = handler->on_tcp_client(client_stfd)) != ERROR_SUCCESS) {
srs_warn("accept client error. ret=%d", ret);
return ret;
}
return ret;
}
1.5.1 st_accept
#ifdef MD_ALWAYS_UNSERIALIZED_ACCEPT
_st_netfd_t *st_accept(_st_netfd_t *fd, struct sockaddr *addr, int *addrlen,
st_utime_t timeout)
{
int osfd, err;
_st_netfd_t *newfd;
/* 调用accept接受客户端的连接请求,若当前没有客户端请求连接,即accept返回失败,
* 则会调用st_netfd_poll函数向epoll添加fd的POLLIN事件,即监听该fd是否可读,
* 然后当前线程让出控制权,调度其他线程运行,直到有客户端连接请求到来时,
* 才会再次调度该线程,accept 该连接请求 */
while ((osfd = accept(fd->osfd, addr, (socklen_t *)addrlen)) < 0) {
if (errno == EINTR)
continue;
if (!_IO_NOT_READY_ERROR)
return NULL;
/* Wait until the socket becomes readable */
if (st_netfd_poll(fd, POLLIN, timeout) < 0)
return NULL;
}
/* On some platforms the new socket created by accept() inherits */
/* the nonblocking attribute of the listening socket */
#if defined(MD_ACCEPT_NB_INHERITED)
newfd = _st_netfd_new(osfd, 0, 1);
#elif defined(MD_ACCEPT_NB_NOT_INHERITED)
newfd = _st_netfd_new(osfd, 1, 1);
#else
#error Unknown OS
#endif
if (!newfd) {
err = errno;
close(osfd);
errno = err;
}
return newfd;
}
#else
#endif
1.6 SrsStreamListener::on_tcp_client
/**
* @stfd: 保存的是accept客户端连接后生成的已连接套接字信息
*/
int SrsStreamListener::on_tcp_client(st_netfd_t stfd)
{
int ret = ERROR_SUCCESS;
if ((ret = server->accept_client(type, stfd)) != ERROR_SUCCESS) {
srs_warn("accept client error. ret=%d", ret);
return ret;
}
return ret;
}
1.7 SrsServer::accept_client
位于 srs_app_server.cpp 中:
int SrsServer::accept_client(SrsListenerType type, st_netfd_t client_stfd)
{
int ret = ERROR_SUCCESS;
int fd = st_netfd_fileno(client_stfd);
/* 获取配置文件中限定的最大连接数 */
int max_connections = _srs_config->get_max_connections();
/* 若当前连接数已经达到最大限制值,则关闭该连接 */
if ((int)conns.size() >= max_connections) {
srs_error("exceed the max connections, drop client: "
"clients=%d, max=%d, fd=%d", (int)conns.size(), max_connections, fd);
srs_close_stfd(client_stfd);
return ret;
}
// avoid fd leak when fork.
// @see https://github.com/ossrs/srs/issues/518
if (true) {
int val;
if ((val = fcntl(fd, F_GETFD, 0)) < 0) {
ret = ERROR_SYSTEM_PID_GET_FILE_INFO;
srs_error("fnctl F_GETFD error! fd=%d. ret=%#x", fd, ret);
srs_close_stfd(client_stfd);
return ret;
}
/* 给该已连接套接字 fd 设置执行时关闭标志 */
val |= FD_CLOEXEC;
if (fcntl(fd, F_SETFD, val) < 0) {
ret = ERROR_SYSTEM_PID_SET_FILE_INFO;
srs_error("fcntl F_SETFD error! fd=%d ret=%#x", fd, ret);
srs_close_stfd(client_stfd);
return ret;
}
}
SrsConnection *conn = NULL;
if (type == SrsListenerRtmpStream) {
/* 当为 RTMP 连接时,构造一个 RTMP 连接 */
conn = new SrsRtmpConn(this, client_stfd);
} else if (type == SrsListenerHttpApi) {
#ifdef SRS_AUTO_HTTP_API
conn = new SrsHttpApi(this, client_stfd, http_api_mux);
#else
srs_warn("close http client for server not support http-server");
srs_close_stfd(client_stfd);
return ret;
#endif
} else {
// TODO: FIXME: handler others
}
srs_assert(conn);
/* 将新构造的 conn 放到 SrsServer 类中的成员 conns 容器中,该容器保存着当前
* SRS 所有的连接 */
// directly enqueue, the cycle thread will remove the client.
conns.push_back(conn);
srs_verbose("add conn to vector.");
// cycle will start process thread and when finished remove the client.
// @remark never use the conn, for it maybe destroyed.
/* 调用子类 SrsRtmpConn 实现有 start 虚函数,则调用子类的start,这里子类没有实现,
* 因此调用的是父类的 start 函数,该函数最终会调用 st_thread_create 函数创建一个
* 线程 */
if ((ret = conn->start()) != ERROR_SUCCESS) {
return ret;
}
srs_verbose("conn started success.");
srs_verbose("accept client finished. conns=%d, ret=%d", (int)conns.size(), ret);
return ret;
}
1.8 构造 SrsRtmpConn
1.8.1 SrsRtmpConn 类定义
/**
* the client provides the main logic control for RTMP clients.
*/
class SrsRtmpConn : public virtual SrsConnection, public virtual ISrsReloadHandler
{
// for the thread to directly access any field of connection.
friend class SrsPublishRecvThread;
private:
SrsServer* server;
SrsRequest* req;
SrsResponse* res;
SrsStSocket* skt;
SrsRtmpServer* rtmp;
SrsRefer* refer;
SrsBandwidth* bandwidth;
SrsSecurity* security;
// the wakable handler, maybe NULL.
ISrsWakable* wakable;
// elapse duration in ms
// for live play duration, for instance, rtmpdump to record.
// @see https://github.com/ossrs/srs/issues/47
int64_t duration;
SrsKbps* kbps;
// the MR(merged-write) sleep time in ms.
int mw_sleep;
// the MR(merged-write) only enabled for play.
int mw_enabled;
// for realtime;
// @see https://github.com/ossrs/srs/issues/257
bool realtime;
// the minimal interval in ms for delivery stream.
double send_min_interval;
// publish 1st packet timeout in ms
int publish_1stpkt_timeout;
// publish normal packet timeout in ms
int publish_normal_timeout;
// whether enable the tcp_nodelay.
bool tcp_nodelay;
// The type of client, play or publish.
SrsRtmpConnType client_type;
public:
SrsRtmpConn(SrsServer* svr, st_netfd_t c);
virtual ~SrsRtmpConn();
public:
virtual void dispose();
protected:
virtual int do_cycle();
// interface ISrsReloadHandler
public:
virtual int on_reload_vhost_removed(std::string vhost);
virtual int on_reload_vhost_mw(std::string vhost);
virtual int on_reload_vhost_smi(std::string vhost);
virtual int on_reload_vhost_tcp_nodelay(std::string vhost);
virtual int on_reload_vhost_realtime(std::string vhost);
virtual int on_reload_vhost_p1stpt(std::string vhost);
virtual int on_reload_vhost_pnt(std::string vhost);
// interface IKbpsDelta
public:
virtual void resample();
virtual int64_t get_send_bytes_delta();
virtual int64_t get_recv_bytes_delta();
virtual void cleanup();
private:
// when valid and connected to vhost/app, service the client.
virtual int service_cycle();
// stream(play/publish) service cycle, identify client first.
virtual int stream_service_cycle();
virtual int check_vhost();
virtual int playing(SrsSource* source);
virtual int do_playing(SrsSource* source, SrsConsumer* consumer,
SrsQueueRecvThread* trd);
virtual int publishing(SrsSource* source);
virtual int do_publishing(SrsSource* source, SrsPublishRecvThread* trd);
virtual int acquire_publish(SrsSource* source, bool is_edge);
virtual void release_publish(SrsSource* source, bool is_edge);
virtual int handle_publish_message(SrsSource* source, SrsCommonMessage* msg,
bool is_fmle, bool vhost_is_edge);
virtual int process_publish_message(SrsSource* source, SrsCommonMessage* msg,
bool vhost_is_edge);
virtual int process_play_control_msg(SrsConsumer* consumer, SrsCommonMessage* msg);
virtual void change_mw_sleep(int sleep_ms);
virtual void set_sock_options();
private:
virtual int check_edge_token_traverse_auth();
virtual int connect_server(int origin_index, st_netfd_t* pstsock);
virtual int do_token_traverse_auth(SrsRtmpClient* client);
private:
virtual int http_hooks_on_connect();
virtual void http_hooks_on_close();
virtual int http_hooks_on_publish();
virtual void http_hooks_on_unpublish();
virtual int http_hooks_on_play();
virtual void http_hooks_on_stop();
};
1.8.2 SrsConnection 类定义
/**
* the basic connection of SRS,
* all connections accept from listener must extends from this base class,
* server will add the connectin to manager, and delete it when remove.
*/
class SrsConnection : public virtual ISrsOneCycleThreadHandler, public virtual IKbpsDelta
{
private:
/**
* each connection start a green thread,
* when thread stop, the connection will be delete by server.
*/
SrsOneCycleThread* pthread;
/**
* the id of connection.
*/
int id;
protected:
/**
* the manager object to manager the connection.
*/
IConnectionManager* manager;
/**
* the underlayer st fd handler.
*/
st_netfd_t stfd;
/**
* the ip of client.
*/
std::string ip;
/**
* whether the connection is disposed,
* when disposed, connection should stop cycle and cleanup itself.
*/
bool disposed;
/**
* whether connection is expired, application definetion.
* when expired, the connection must never be served and quit ASAP.
*/
bool expired;
public:
SrsConnection(IConnectionManager* cm, st_netfd_t c);
virtual ~SrsConnection();
public:
/**
* to dipose the connection.
*/
virtual void dispose();
/**
* start the client green thread.
* when server get a client from listener,
* 1. server will create an concrete connection(for instance, RTMP connection),
* 2. then add connection to its connection manager
* 3. start the client thread by invoke this start()
* when client cycle thread stop, invoke the on_thread_stop(), which will use server
* to remove the client by server->remove(this);
*/
virtual int start();
// interface ISrsOneCycleThreadHandler
public:
/**
* the thread cycle function,
* when serve connection completed, terminater the loop which will terminater the
* thread, thread will invoke the on_thread_stop() when it terminated.
*/
virtual int cycle();
/**
* when then thread cycle finished, thread will invoke the on_thread_stop(),
* which will remove self from server, server will remove the connection from manager
* then delete the connection.
*/
virtual void on_thread_stop();
public:
/**
* get the srs id which identify the client.
*/
virtual int srs_id();
/**
* set connection to expired.
*/
virtual void expire();
protected:
/**
* for concrete connection to do the cycle.
*/
virtual int do_cycle() = 0;
};
1.8.3 ISrsOneCycleThreadHandler 类定义
/**
* the one cycle thread is a thread do the cycle only one time,
* that is, the thread will quit when return from the cycle.
* user can create thread which stop itself,
* generally only need to provides a start method,
* the object will destroy itself then terminate the thread, @see SrsConnection
* 1. create SrsThread field
* 2. the thread quit when return from cycle.
* for example:
* class SrsConnection : public ISrsOneCycleThreadHandler {
* public: SrsConnection() { pthread = new SrsOneCycleThread("conn", this); }
* public: virtual int start() { return pthread->start(); }
* public: virtual int cycle() {
* // serve client.
* // set loop to stop to quit, stop thread itself.
* pthread->stop_loog();
* }
* public: virtual void on_thread_stop() {
* // remove the connection in thread itself.
* server->remove(this);
* }
}
* };
*/
class ISrsOneCycleThreadHandler
{
public:
ISrsOneCycleThreadHandler();
virtual ~ISrsOneCycleThreadHandler();
public:
/**
* the cycle method for the one cycle thread.
*/
virtual int cycle() = 0;
public:
/**
* other callback for handler.
* @remark all callback is optional, handler can ignore it.
*/
virtual void on_thread_start();
virtual int on_before_cycle();
virtual int on_end_cycle();
virtual void on_thread_stop();
};
1.8.4 IKbpsDelta 类定义
/**
* the interface which provices delta of bytes.
* for a delta, for example, a live stream connection, we can got the delta by:
* IKbpsDelta* delta = ...;
* delta->resample();
* kbps->add_delta(delta);
* delta->cleanup();
*/
class IKbpsDelta
{
public:
IKbpsDelta();
virtual ~IKbpsDelta();
public:
/**
* resample to generate the value of delta bytes.
*/
virtual void resample() = 0;
/**
* get the send or recv bytes delta.
*/
virtual int64_t get_send_bytes_delta() = 0;
virtual int64_t get_recv_bytes_delta() = 0;
/**
* cleanup the value of delta bytes.
*/
virtual void cleanup() = 0;
};
上面几个类之间的关系图
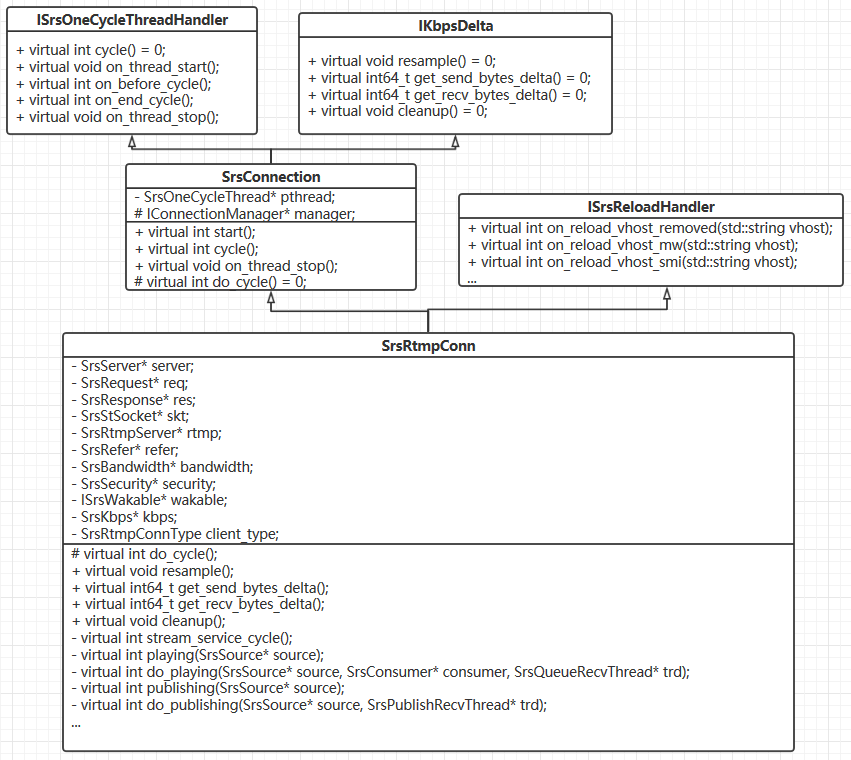
构造 SrsRtmpConn 类,首先调用的是其父类 SrsConnection 的构造函数.
1.8.3 SrsConnection 构造函数
位于 srs_app_conn.cpp:
SrsConnection::SrsConnection(IConnectionManager* cm, st_netfd_t c)
{
id = 0;
/* manager 是 IConnectionManager 类的指针,该指针管理着当前连接.
* cm 是 由构造 SrsRtmpConn 传入的表示当前 SrsServer 类的 this 指针,
* 而 IConnectionManager 类是 SrsServer 的父类,因此,
* 这里是父类 IConnectionManager 指针 manager 指向子类 SrsServer 指针 this */
manager = cm;
stfd = c;
disposed = false;
expired = false;
// the client thread should reap itself,
// so we never use joinable.
// TODO: FIXME maybe other thread need to stop it.
// @see: https://github.com/ossrs/srs/issues/78
/* pthread 是 SrsOneCycleThread 类的指针,该指针指向新构造的
* SrsOneCycleThread 类结构体对象 */
pthread = new SrsOneCycleThread("conn", this);
}
在该函数中接着构造 SrsOneCycleThread 类。
1.8.4 构造 SrsOneCycleThread
1.8.4.1 SrsOneCycleThread 类定义
class SrsOneCycleThread : public internal::ISrsThreadHandler
{
private:
internal::SrsThread* pthread;
ISrsOneCycleThreadHandler* handler;
public:
SrsOneCycleThread(const char* n, ISrsOneCycleThreadHandler* h);
virtual ~SrsOneCycleThread();
public:
/**
* for the cycle thread, quit when cycle return.
*/
virtual int start();
// interface internal::ISrsThreadHandler
public:
virtual int cycle();
virtual void on_thread_start();
virtual int on_before_cycle();
virtual int on_end_cycle();
virtual void on_thread_stop();
};
1.8.4.2 SrsOneCycleThread 构造函数
SrsOneCycleThread::SrsOneCycleThread(const char* n, ISrsOneCycleThreadHandler* h)
{
/* handler 是 ISrsOneCycleThreadHandler 类的指针,h 是传入的 SrsConnection 类的
* this 指针,ISrsOneCycleThreadHandler 类是 SrsConnection 类的父类 */
handler = h;
/* pthread 是指向 internal::SrsThread 类的指针,pthread 指向新构造的
* internal::SrsThread 类对象. */
pthread = new internal::SrsThread(n, this, 0, false);
}
1.8.4.3 internal::SrsThread 构造函数
位于 srs_app_thread.cpp:
SrsThread::SrsThread(const char* name, ISrsThreadHandler* thread_handler, int64_t interval_us, bool joinable)
{
/* 该线程的名称,由前面可知为 "conn" */
_name = name;
/* handler 是 ISrsThreadHandler 类的指针,thread_handler 是传入的 SrsOneCycleThread 类的
* this 指针,ISrsThreadHandler 是 SrsOneCycleThread 的父类 */
handler = thread_handler;
cycle_interval_us = interval_us;
tid = NULL;
loop = false;
really_terminated = true;
_cid = -1;
_joinable = joinable;
disposed = false;
// in start(), the thread cycle method maybe stop and remove the thread itself,
// and the thread start() is waiting for the _cid, and segment fault then.
// @see https://github.com/ossrs/srs/issues/110
// thread will set _cid, callback on_thread_start(), then wait for the can_run signal.
can_run = false;
}
1.8.5 SrsRtmpConn 构造函数
位于 srs_app_rtmp_conn.cpp 中:
SrsRtmpConn::SrsRtmpConn(SrsServer* svr, st_netfd_t c)
: SrsConnection(svr, c)
{
server = svr;
req = new SrsRequest();
res = new SrsResponse();
skt = new SrsStSocket(c);
rtmp = new SrsRtmpServer(skt);
refer = new SrsRefer();
bandwidth = new SrsBandwidth();
security = new SrsSecurity();
duration = 0;
kbps = new SrsKbps();
kbps->set_io(skt, skt);
wakable = NULL;
mw_sleep = SRS_PERF_MW_SLEEP;
mw_enabled = false;
realtime = SRS_PERF_MIN_LATENCY_ENABLED;
send_min_interval = 0;
tcp_nodelay = false;
client_type = SrsRtmpConnUnknown;
_srs_config->subscribe(this);
}
1.8.5.1 SrsRequest
SrsRequest 类定义,位于 srs_rtmp_stack.hpp:
/**
* the original request from client.
*/
class SrsRequest
{
public:
// client ip.
std::string ip;
public:
/**
* tcUrl: rtmp://request_vhost:port/app/stream
* support pass vhost in query string, such as:
* rtmp://ip:port/app?vhost=request_vhost/stream
* rtmp://ip:port/app...vhost...request_vhost/stream
*/
std::string tcUrl;
std::string pageUrl;
std::string swfUrl;
double objectEncoding;
// data discovery from request.
public:
// discovery from tcUrl and play/publish.
std::string schema;
// the vhost in tcUrl.
std::string vhost;
// the host in tcUrl.
std::string host;
// the port in tcUrl.
std::string port;
// the app in tcUrl, without param.
std::string app;
// the param in tcUrl(app).
std::string param;
// the stream in play/publish
std::string stream;
// for play live stream,
// used to specified the stop when exceed the duration.
// @see https://github.com/ossrs/srs/issues/45
// in ms.
double duration;
// the token in the connect request,
// used for edge traverse to origin authentication,
// @see https://github.com/ossrs/srs/issues/104
SrsAmf0Object* args;
public:
SrsRequest();
virtual ~SrsRequest();
public:
/**
* deep copy the request, for source to use it to support reload,
* for when initialize the source, the request is valid,
* when reload it, the request maybe invalid, so need to copy it.
*/
virtual SrsRequest* copy();
/**
* update the auth info of request,
* to keep the current request ptr is ok,
* for many components use the ptr of request.
*/
virtual void update_auth(SrsRequest* req);
/**
* get the stream identify, vhost/app/stream.
*/
virtual std::string get_stream_url();
/**
* strip url, user must strip when update the url.
*/
virtual void strip();
};
SrsRequest 的构造函数:
#define RTMP_SIG_AMF0_VER 0
SrsRequest::SrsRequest()
{
/* 初始化编码对象为 AMF0 */
objectEncoding = RTMP_SIG_AMF0_VER;
duration = -1;
args = NULL;
}
1.8.5.2 SrsResponse
SrsResponse 类定义,位于 srs_rtmp_stack.hpp:
/**
* the response to client.
*/
class SrsResponse
SrsResponse 类定义,位于 srs_rtmp_stack.hpp:
{
public:
/**
* the stream id to response client createStream.
*/
int stream_id;
public:
SrsResponse();
virtual ~SrsResponse();
};
SrsResponse 类构造函数,位于 srs_rtmp_stack.cpp:
// default stream id for response the createStream request.
#define SRS_DEFAULT_SID 1
SrsResponse::SrsResponse()
{
/* 该 stream_id 用于响应客户端的 createStream 命令时使用的流 id */
stream_id = SRS_DEFAULT_SID;
}
1.8.5.3 SrsStSocket
SrsStSocket 类定义,位于 srs_app_st.hpp:
/**
* the socket provides TCP socket over st,
* that is, the sync socket mechanism.
*/
class SrsStSocket : public ISrsProtocolReaderWriter
{
private:
int64_t recv_timeout;
int64_t send_timeout;
int64_t recv_bytes;
int64_t send_bytes;
st_netfd_t stfd;
public:
SrsStSocket(st_netfd_t client_stfd);
virtual ~SrsStSocket();
public:
virtual bool is_never_timeout(int64_t timeout_us);
virtual void set_recv_timeout(int64_t timeout_us);
virtual int64_t get_recv_timeout();
virtual void set_send_timeout(int64_t timeout_us);
virtual int64_t get_send_timeout();
virtual int64_t get_recv_bytes();
virtual int64_t get_send_bytes();
public:
/**
* @param nread, the actual read bytes, ignore if NULL.
*/
virtual int read(void* buf, size_t size, ssize_t* nread);
virtual int read_fully(void* buf, size_t size, ssize_t* nread);
/**
* @param nwrite, the actual write bytes, ignore if NULL.
*/
virtual int write(void* buf, size_t size, ssize_t* nwrite);
virtual int writev(const iovec *iov, int iov_size, ssize_t* nwrite);
};
SrsStSocket 构造函数,位于 srs_app_st.cpp:
#define ST_UTIME_NO_TIMEOUT ((st_utime_t) -1LL)
SrsStSocket::SrsStSocket(st_netfd_t client_stfd)
{
/* client_stfd 保存已连接套接字描述符的信息 */
stfd = client_stfd;
/* 设置发送 rtmp 包时的超时时间,这里初始值为 -1,即一直等待,直到发送或接受成功 */
send_timeout = recv_timeout = ST_UTIME_NO_TIMEOUT;
/* 这两个分别是接受或发送字节数的统计值 */
recv_bytes = send_bytes = 0;
}
1.8.5.4 SrsRtmpServer
SrsRtmpServer 类定义,位于 srs_rtmp_stack.hpp:
/**
* the rtmp provices rtmp-command-protocol services,
* a high level protocol, media stream oriented services,
* such as connect to vhost/app, play stream, get audio/video data.
*/
class SrsRtmpServer
{
private:
SrsHandshakeBytes* hs_bytes;
SrsProtocol* protocol;
ISrsProtocolReaderWriter* io;
public:
SrsRtmpServer(ISrsProtocolReaderWriter* skt);
virtual ~SrsRtmpServer();
// protocol methods proxy
public:
/**
* set the auto response message when rece for protocol stack.
* @param v, whether auto response message when rece message.
* @see: https://github.com/ossrs/srs/issues/217
*/
virtual void set_auto_response(bool v);
#ifdef SRS_PERF_MERGED_READ
/**
* to improve read performance, merge some packets then read,
* when it on and read small bytes, we sleep to wait more data,
* that is, we merge some data to read together.
* @param v true to enable merged read.
* @param handler the handler when merge read is enabled.
* @see https://github.com/ossrs/srs/issues/241
*/
virtual void set_merge_read(bool v, IMergeReadHandler* handlers);
/**
* create buffer with specified size.
* @param buffer the size of buffer.
* @remark when MR(SRS_PERF_MERGED_READ) disabled, always set to 8K.
* @remark when buffer changed, the previous ptr maybe invalid.
* @see https://github.com/ossrs/srs/issues/241
*/
virtual void set_recv_buffer(int buffer_size);
#endif
/**
* set/get the recv timeout in us.
* if timeout, recv/send message return ERROR_SOCKET_TIMEOUT.
*/
virtual void set_recv_timeout(int64_t timeout_us);
virtual int64_t get_recv_timeout();
/**
* set/get the send timeout in us.
* if timeout, recv/send message return ERROR_SOCKET_TIMEOUT.
*/
virtual void set_send_timeout(int64_t timeout_us);
virtual int64_t get_send_timeout();
/**
* get recv/send bytes.
*/
virtual int64_t get_recv_bytes();
virtual int64_t get_send_bytes();
/**
* recv a RTMP message, which is bytes oriented.
* user can use decode_message to get the decoded RTMP packet.
* @param pmsg, set the received message
* always NULL if error,
* NULL for unknown packet but return success.
* never NULL if decode seccess.
* @remark, drop message when msg is empty or payload length is empty.
*/
virtual int recv_message(SrsCommonMessage** pmsg);
/**
* decode bytes oriented RTMP message to RTMP packet,
* @param ppacket, output decoded packet,
* always NULL if error, never NULL if success.
* @return error when unknown packet, error when decode failed.
*/
virtual int decode_message(SrsCommonMessage* msg, SrsPacket** ppacket);
/**
* send the RTMP message and always free it.
* user must never free or use the msg after this method,
* for it will always free the msg.
* @param msg, the msg to send out, never be NULL.
* @param stream_id, the stream id of packet to send over, 0 for control message.
*/
virtual int send_and_free_message(SrsSharedPtrMessage* msg, int stream_id);
/**
* send the RTMP message and always free it.
* user must never free or use the msg after this method,
* for it will always free the msg.
* @param msgs, the msgs to send out, never be NULL.
* @param nb_msgs, the size of msgs to send out.
* @param stream_id, the stream id of packet to send over, 0 for control message.
*
* @remark performance issue, to support 6k+ 250kbps client,
* @see https://github.com/ossrs/srs/issues/194
*/
virtual int send_and_free_messages(SrsSharedPtrMessage** msgs, int nb_msgs,
int stream_id);
/**
* send the RTMP packet and always free it.
* user must never free or use the packet after this method,
* for it will always free the packet.
* @param packet, the packet to send out, never be NULL.
* @param stream_id, the stream id of packet to send over, 0 for control message.
*/
virtual int send_and_free_packet(SrsPacket* packet, int stream_id);
public:
/**
* handshake with client, try complex then simple.
*/
virtual int handshake();
/**
* do connect app with client, to discovery tcUrl.
*/
virtual int connect_app(SrsRequest* req);
/**
* set ack size to client, client will send ack-size for each ack window
*/
virtual int set_window_ack_size(int ack_size);
/**
* @type: The sender can mark this message hard (0), soft (1), or dynamic (2)
* using the Limit type field.
*/
virtual int set_peer_bandwidth(int bandwidth, int type);
/**
* @param server_ip the ip of server.
*/
virtual int response_connect_app(SrsRequest* req, const char* server_ip = NULL);
/**
* reject the connect app request.
*/
virtual void response_connect_reject(SrsRequest* req, const char* desc);
/**
* response client the onBWDone message.
*/
virtual int on_bw_done();
/**
* recv some message to identify the client.
* @stream_id, client will createStream to play or publish by flash,
* the stream_id used to response the createStream request.
* @type, output the client type.
* @stream_name, output the client publish/play stream name. @see: SrsRequest.stream
* @duration, output the play client duration. @see: SrsRequest.duration
*/
virtual int identify_client(int stream_id, SrsRtmpConnType& type,
std::string& stream_name, double& duration);
/**
* set the chunk size when client type identified.
*/
virtual int set_chunk_size(int chunk_size);
/**
* when client type is play, response with packets:
* StreamBegin,
* onStatus(NetStream.Play.Reset), onStatus(NetStream.Play.Start).,
* |RtmpSampleAccess(false, false),
* onStatus(NetStream.Data.Start).
*/
virtual int start_play(int stream_id);
/**
* when client(type is play) send pause message,
* if is_pause, response the following packets:
* onStatus(NetStream.Pause.Notify)
* StreamEOF
* if not is_pause, response the following packets:
* onStatus(NetStream.Unpause.Notify)
* StreamBegin
*/
virtual int on_play_client_pause(int stream_id, bool is_pause);
/**
* when client type is publish, response with packets:
* releaseStream response
* FCPublish
* FCPublish response
* createStream response
* onFCPublish(NetStream.Publish.Start)
* onStatus(NetStream.Publish.Start)
*/
virtual int start_fmle_publish(int stream_id);
/**
* For encoder of Haivision, response the startup request.
* @see https://github.com/ossrs/srs/issues/844
*/
virtual int start_haivision_publish(int stream_id);
/**
* process the FMLE unpublish event.
* @unpublish_tid the unpublish request transaction id.
*/
virtual int fmle_unpublish(int stream_id, double unpublish_tid);
/**
* when client type is publish, response with packets:
* onStatus(NetStream.Publish.Start)
*/
virtual int start_flash_publish(int stream_id);
public:
/**
* expect a specified message, drop others util got specified one.
* @pmsg, user must free it. NULL if not success.
* @ppacket, user must free it, which decode from payload of message.
* NULL if not success.
* @remark, only when success, user can use and must free the pmsg and ppacket.
* for example:
* SrsCommonMessage* msg = NULL;
* SrsConnectAppResPacket* pkt = NULL;
* if ((ret = server->expect_message<SrsConnectAppResPacket>(protocol,
* &msg, &pkt))
* != ERROR_SUCCESS) {
* return ret;
* }
* // use then free msg and pkt
* srs_freep(msg);
* srs_freep(pkt);
* user should never recv message and convert it, use this method instead.
* if need to set timeout, use set timeout of SrsProtocol.
*/
template<class T>
int expect_message(SrsCommonMessage** pmsg, T** ppacket)
{
return protocol->expect_message<T>(pmsg, ppacket);
}
private:
virtual int identify_create_stream_client(SrsCreateStreamPacket* req, int stream_id,
SrsRtmpConnType& type, std::string& stream_name, double& duration);
virtual int identify_fmle_publish_client(SrsFMLEStartPacket* req,
SrsRtmpConnType& type, std::string& stream_name);
virtual int identify_haivision_publish_client(SrsFMLEStartPacket* req,
SrsRtmpConnType& type, std::string& stream_name);
virtual int identify_flash_publish_client(SrsPublishPacket* req,
SrsRtmpConnType& type, std::string& stream_name);
private:
virtual int identify_play_client(SrsPlayPacket* req, SrsRtmpConnType& type,
std::string& stream_name, double& duration);
};
SrsRtmpServer 构造函数,位于 srs_rtmp_stack.cpp:
SrsRtmpServer::SrsRtmpServer(ISrsProtocolReaderWriter* skt)
{
/* io 是指向 ISrsProtocolReaderWriter 类对象的指针,skt 是传入的
* 指向刚构造的 SrsStSocket 类对象的指针, ISrsProtocolReaderWriter 是
* SrsStSocket 的父类 */
io = skt;
/* 构造 SrsProtocol 类, 该类用于提供 rtmp 消息协议的服务,
* 如从 rtmp 块流中接收 rtmp 消息,或者通过 rtmp 块流发送
* rtmp 消息*/
protocol = new SrsProtocol(skt);
/* 构造 SrsHandshakeBytes 类,该类用于读取或构建 handshake 过程的
* 数据,并保存 */
hs_bytes = new SrsHandshakeBytes();
}
1.8.6 SrsRtmpConn 构造总结
- 首先调用 SrsRtmpConn 的父类 SrsConnection 的构造函数,在该构造函数中,为其 SrsOneCycleThread 类的成员指针 pthread 构造了 SrsOneCycleThread 对象,在 SrsOneCycleThread 构造函数中,又接着为其 internal::SrsThread 类的成员 pthread 构造了 internal::SrsThread 对象。SrsOneCycleThread 是一个只循环一次的线程,当从循环中返回时便终止该线程。具体创建步骤可参考 ISrsOneCycleThreadHandler 类的说明。
- 接着调用 SrsRtmpConn 的构造函数,在该构造函数中,为其成员 req、res、skt、rtmp、refer、bandwidth、security 等类对象的指针构造了新的类对象,分别对应 SrsRequest、SrsResponse、SrsStSocket、SrsRtmpServer、SrsRefer、SrsBandwidth、SrsSecurity。
1.9 启动 conn 线程:SrsConnection::start
位于 srs_app_conn.cpp 中:
int SrsConnection::start()
{
/* pthread 是指向 SrsOneCycleThread 类的指针,因此调用该类的成员函数
* start 函数 */
return pthread->start();
}
int SrsOneCycleThread::start()
{
/* pthread 是 internal::SrsThread 类的指针,因此接着调用该类的成员函数 start */
return pthread->start();
}
int SrsThread::start()
{
int ret = ERROR_SUCCESS;
if(tid) {
srs_info("thread %s already running.", _name);
return ret;
}
if((tid = st_thread_create(thread_fun, this, (_joinable? 1:0), 0)) == NULL){
ret = ERROR_ST_CREATE_CYCLE_THREAD;
srs_error("st_thread_create failed. ret=%d", ret);
return ret;
}
disposed = false;
// we set to loop to true for thread to run.
loop = true;
// wait for cid to ready, for parent thread to get the cid.
while (_cid < 0) {
st_usleep(10 * 1000);
}
// now, cycle thread can run.
can_run = true;
return ret;
}
从 SrsConnection::start 开始,一路层层调用下来,最终调用 SrsThread::start() 函数,在该函数中会调用 st_thread_create 创建一个线程,然后进入休眠等待 _cid 大于 0,才会再次继续往下运行。
致此,该 RTMP的TCP线程的 cycle 循环完成一次,一路返回到 SrsThread::thread_cycle() 函数中调用 handler->cycle() 的地方继续往下执行。
1.10 SrsReusableThread::on_end_cycle
int SrsReusableThread::on_end_cycle()
{
/* handler 是 ISrsReusableThreadHandler 类的指针,由开篇的 handler 关系图知,
* 这里调用的是 ISrsReusableThreadHandler 的 on_end_cycle 函数 */
return handler->on_end_cycle();
}
int ISrsReusableThreadHandler::on_end_cycle()
{
return ERROR_SUCCESS;
}
3. 总结
整个 RTMP 的 TCP 线程的大致流程是:
- 在线程循环中调用 ST 的库函数 st_accept 接受客户端的连接请求,若当前没有连接请求则将当前线程添加到 IO 队列中,然后将控制权让出去,调度其他线程运行。直到有客户端的连接请求到来后才再次调度;
- 接受客户端的连接请求后,根据客户端连接的类型:RTMP 或 HTTP api 等构建相应的 connection 类,然后添加到 SrsServe 类下的 conns 容器中,该容器保存着所有的连接;
- 接着为该连接创建一个线程,如对于 RTMP,创建的线程是 SrsOneCycleThread 类的,该类型的线程是只循环一次就结束该线程;
- 同时在 SrsRtmpConn 的构造函数中也构建了多个类对象,这些对象用于为服务器与客户端之间的 RTMP 通信提供服务,如 SrsRtmpServer 类对象。
- 该 RTMP 的 TCP 线程循环一次后即代表建立了一个连接,接着休眠后再次循环接受下一个连接请求。
SRS之RTMP的TCP线程(即监听线程)的更多相关文章
- 【MINA】OrderedThreadPoolExecutor和UnorderedThreadPoolExecutor的事件监听线程池的选择
mina中有两个线程池概念 1.处理监听建立连接的线程池 2.处理读写事件的线程池 本文中主要探讨读写事件的线程池的选择 这两种都经过实际项目的使用和检测,说说优缺点 早期的项目是用Unordere ...
- 一个类,有新增元素(add)和获取元素数量(size)方法。 启动两个线程。线程1向容器中新增数据。线程2监听容器元素数量,当容器元素数量为5时,线程2输出信息并终止
方式一: /** * 两个线程要是可见的所以要加上votalile */public class Test_01 { public static void main(String[] args) { ...
- SRS之RTMP连接处理线程conn:接收客户端推流
由 SRS之RTMP的TCP线程 分析可知,SRS 接受客户端的连接后创建了一个线程:conn,用于处理与客户端的 RTMP 连接. 本文的分析是基于该配置文件的: listen 1935; max_ ...
- Java线程监听,意外退出线程后自动重启
Java线程监听,意外退出线程后自动重启 某日,天朗气清,回公司,未到9点,刷微博,顿觉问题泛滥,惊恐万分! 前一天写了一个微博爬行程序,主要工作原理就是每隔2分钟爬行一次微博,获取某N个关注朋友微博 ...
- eventloop & actor模式 & Java线程模型演进 & Netty线程模型 总结
eventloop的基本概念可以参考:http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2013/10/event_loop.html Eventloop指的是独立于主线程的一条线程,专门 ...
- C# Socket基础(一)之启动异步服务监听
本文主要是以代码为主..NET技术交流群 199281001 .欢迎加入. //通知一个或多个正在等待的线程已发生事件. ManualResetEvent manager = new ManualRe ...
- Netty事件监听和处理(上)
陪产假结束了,今天又开始正常上班了,正好赶上米粉节活动,又要忙上一阵了,米粉节活动时间为4.03 - 4.10,有不少优惠,感兴趣的可以关注mi.com或小米商城app. 今天给大家送了福利:小爱音箱 ...
- Scoket 服务器监听多个客户端发来的图片
这是服务器 直接上代码 都有详细注释 注意线程需要自己手动关闭 不然程序会卡死 /* ######### ############ ############# ## ########### ### # ...
- Netty源码解析一——线程池模型之线程池NioEventLoopGroup
本文基础是需要有Netty的使用经验,如果没有编码经验,可以参考官网给的例子:https://netty.io/wiki/user-guide-for-4.x.html.另外本文也是针对的是Netty ...
随机推荐
- js实现浅拷贝和深拷贝
实现浅拷贝和深拷贝 1. 浅拷贝和深拷贝的区别 简单点说,浅拷贝拷贝完后,修改拷贝的内容可能会对源内容产生影响.而深拷贝就是拷贝前后的内容相互不影响. 那为什么拷贝前后的内容会相互影响呢? ...
- java面试4
1.两个对象a和b,请问a==b和a.equals(b)有什么区别? a==b; 比较对象地址 a.equals(b);如果a对象没有重写equals方法,效果和==相同,如果重写了就按照重写的规则比 ...
- 微信小程序常用事件
bind bind事件绑定不会阻止冒泡事件向上冒泡,catch事件绑定可以阻止冒泡事件向上冒泡. bindtap 跳转页面 bindchange .value 改变时触发 change 事件 bi ...
- odoo字段属性
以下为可用的非关联字段类型以及其对应的位置参数: Char(string)是一个单行文本,唯一位置参数是string字段标签. Text(string)是一个多行文本,唯一位置参数是string字段标 ...
- centos 7 Apache-Tomcat-8.5.46 安装 Web 应用服务器
tomcat 官网版本地址:https://tomcat.apache.org/whichversion.html Servlet规格 JSP规范 EL规格 WebSocket规范 JASPIC规格 ...
- C#微信公众平台账号开发真正给初学者的文章
微信越来越受到大众人群的喜爱,但是对于开发人员来说刚接触肯能还是一头雾水的,比如像我,看了三四天文档感觉要吐,但是程序还是要写知识还是要学.发现了一个比较适合初学者的文章送给大家,废话到此:(转贴吧) ...
- Access数据库LIKE问题
access里like的通配符用法是这样:“?”表示任何单一字符: “*”表示零个或多个字符: “#”表示任何一个数字 有时候用%作为通配符不行,需要用*号作为通配符select * from tab ...
- 需要以管理员的身份运行程序(winform)
1.添加应用程序清单文件(app.manifest) 2.打开app.manifest,将<requestedExecutionLevel level="asInvoker" ...
- MFC总结
1.首先是ListControl 简介: 列表视图控件List Control同样比较常见,它能够把任何字符串内容以列表的方式显示出来,这种显示方式的特点是整洁.直观,在实际应用中能为用户带来方便. ...
- linux weblogic的sh文件
setDomainEnv.sh JAVA_HOME和各种jvm参数,CLASSPATH都在这里配置 #!/bin/sh # WARNING: This file is created by ...
