YBT 1.1 贪心算法
本人因为过于懒所以以后就将题解放进原文件中,存入百度网盘,自行下载,里面包含题目网站,源文件,与相应题解(这次没有写)
链接: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1eSoQ_LFWMxFHPpiXkmy4UA 密码: cgsk
--------------------------------以后就没有后边了-------------------------------------------
活动安排 https://loj.ac/problem/10000
问题描述:设有n个活动的集合E = {1,2,…,n},其中每个活动都要求使用同一资源,如演讲会场等,而在同一时间内只有一个活动能使用这一资源。每个活i都有一个要求使用该资源的起始时间si和一个结束时间fi,且si < fi 。如果选择了活动i,则它在半开时间区间[si, fi)内占用资源。若区间[si, fi)与区间[sj, fj)不相交,则称活动i与活动j是相容的。也就是说,当si >= fj或sj >= fi时,活动i与活动j相容。选择出由互相兼容的活动组成的最大集合。
输入格式
第一行一个整数 n;
接下来的 n行,每行两个整数 si和 fi。
输出格式
输出互相兼容的最大活动个数。
样例
样例输入
4
1 3
4 6
2 5
1 7样例输出
2数据范围与提示
1≤n≤1000
其实这种题只要将末尾时间从小到大排序即可,证法请读者自己思考
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
inline int read()
{
int f=,ans=;char c;
while(c<''||c>''){if(c=='-')f=-;c=getchar();}
while(c>=''&&c<=''){ans=ans*+c-'';c=getchar();}
return ans*f;
}
struct node{
int f,e;
}a[];
bool cmp(node a,node b)
{
return a.e<b.e;
}
int n;
int main()
{
n=read();
for(int i=;i<=n;i++) a[i].f=read(),a[i].e=read();
sort(a+,a+n+,cmp);
int ans=,t=a[].e;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
if(a[i].f>=t) ans++,t=a[i].e;
cout<<ans;
}
种树 https://loj.ac/problem/10001
题目描述
一条街的一边有几座房子。因为环保原因居民想要在路边种些树。路边的地区被分割成块,并被编号成1..N。每个部分为一个单位尺寸大小并最多可种一棵树。每个居民想在门前种些树并指定了三个号码B,E,T。这三个数表示该居民想在B和E之间最少种T棵树。当然,B≤E,居民必须记住在指定区不能种多于区域地块数的树,所以T≤E-B+l。居民们想种树的各自区域可以交叉。你的任务是求出能满足所有要求的最少的树的数量。
写一个程序完成以下工作:
输入输出格式
输入格式:
第一行包含数据N,区域的个数(0<N≤30000);
第二行包含H,房子的数目(0<H≤5000);
下面的H行描述居民们的需要:B E T,0<B≤E≤30000,T≤E-B+1。
输出格式:
输出文件只有一行写有树的数目
输入输出样例
9
4
1 4 2
4 6 2
8 9 2
3 5 2
5
从最后从小到大排序,使用used数组记录当前位置有没有树即可
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
inline int read()
{
int f=,ans=;char c;
while(c<''||c>''){if(c=='-')f=-;c=getchar();}
while(c>=''&&c<=''){ans=ans*+c-'';c=getchar();}
return ans*f;
}
struct node{
int f;int e;int x;
}a[];
bool used[];
bool cmp(node a,node b)
{
return a.e<b.e;
}
int n,h;
int main()
{
n=read(),h=read();
for(int i=;i<=h;i++) a[i].f=read(),a[i].e=read(),a[i].x=read();
sort(a+,a+h+,cmp);
for(int i=;i<=h;i++)
{
int ans=;
for(int j=a[i].e;j>=a[i].f;j--)
if(used[j]) ans++;
if(ans>=a[i].x) continue;
for(int j=a[i].e;j>=a[i].f;j--)
{
if(!used[j]) used[j]=,ans++;
if(ans==a[i].x) break;
}
}
int sum=;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
if(used[i]) sum++;
cout<<sum;
return ;
}
/*
9
4
1 4 2
4 6 2
8 9 2
3 5 2
*/
喷水装置 https://loj.ac/problem/10002
题目描述
长 L米,宽 W 米的草坪里装有 n 个浇灌喷头。每个喷头都装在草坪中心线上(离两边各各 W/2 米)。我们知道每个喷头的位置(离草坪中心线左端的距离),以及它能覆盖到的浇灌范围。
请问:如果要同时浇灌整块草坪,最少需要打开多少个喷头?

输入格式
输入包含若干组测试数据。
第一行一个整数 T 表示数据组数;
每组数据的第一行是整数 n、L 和 W;
接下来的 n 行,每行包含两个整数,给出一个喷头的位置和浇灌半径(上面的示意图是样例输入第一组数据所描述的情况)。
输出格式
对每组测试数据输出一个数字,表示要浇灌整块草坪所需喷头数目的最小值。如果所有喷头都打开也不能浇灌整块草坪,则输出 −1 。
样例
样例输入
3
8 20 2
5 3
4 1
1 2
7 2
10 2
13 3
16 2
19 4
3 10 1
3 5
9 3
6 1
3 10 1
5 3
1 1
9 1样例输出
6
2
-1数据范围与提示
对于 100% 的数据,n≤15000
这题是线段覆盖题目,首先先用勾股定理求出线段左右端点的距离,并从当前没有被覆盖的t中找到a[i].x<=s并且a[i].y大于当前可以覆盖的值,并将s=a[i].y,表示使用当前木棍
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
inline double read()
{
double f=,ans=;char c;
while(c<''||c>''){if(c=='-')f=-;c=getchar();}
while(c>=''&&c<=''){ans=ans*+c-'';c=getchar();}
return ans*f;
}
struct node{
double x,y;
}a[];
bool cmp(node aa,node bb)
{
if(aa.x!=bb.x)return aa.x<bb.x;
return aa.y<bb.y; }
double t,l,w;
int n;
int main()
{
t=read();
while(t--)
{
int cnt;
n=;
cnt=read(),l=read(),w=read();
for(int i=;i<=cnt;i++)
{
double xx=read(),yy=read();
if(yy<=w/) continue;
a[++n].x=xx-sqrt(yy*yy-(w/)*(w/));
a[n].y=xx+sqrt(yy*yy-(w/)*(w/));
}
// cout<<cnt<<" "<<n;
// system("pause");
sort(a+,a+n+,cmp);
// cout<<endl;
// for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cout<<a[i].x<<" "<<a[i].y<<endl;
// system("pause");
double t=,maxn=;
int ans=;
bool f=false;
while(t<l)
{
ans++;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
if(a[i].x<=t)
{
if(a[i].y>=maxn) maxn=a[i].y;
}
else break;
}
if(t==maxn&&t<l)
{
cout<<-<<endl;
f=true;
break;
}
t=maxn;
}
if(!f) cout<<ans<<endl;
}
}
加工生产调度 https://loj.ac/problem/10003
题目描述
某工厂收到了n个产品的订单,这n个产品分别在A、B两个车间加工,并且必须先在A车间加工后才可以到B车间加工。求怎样安排这n个产品的加工顺序,才能使总的加工时间最短。这里所说的加工时间是指,从开始加工第一个产品到最后所有的产品都已在A、B两车间加工完毕的时间。
输入格式
第一行仅—个数据 n,表示产品的数量;
接下来 n 个数据是表示这 n个产品在 A 车间加工各自所要的时间;
最后的 n 个数据是表示这 n 个产品在 B 车间加工各自所要的时间。
输出格式
第一行一个数据,表示最少的加工时间;
第二行是一种最小加工时间的加工顺序。
样例
样例输入
5
3 5 8 7 10
6 2 1 4 9样例输出
34
1 5 4 2 3数据范围与提示
对于 100%的数据, 0<n<1000,所有数值皆为整数。
这题就比较神奇,先将m[i]=min(a[i],b[i]) 在从小到大排序(比较严格的证明:https://wenku.baidu.com/view/9c31776727d3240c8447ef42.html###),详细思路见代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
inline int read()
{
int f=,ans=;char c;
while(c<''||c>''){if(c=='-')f=-;c=getchar();}
while(c>=''&&c<=''){ans=ans*+c-'';c=getchar();}
return ans*f;
}
int n,a[],b[],m[],s[],ans[];
int main()
{
n=read();
for(int i=;i<=n;i++) a[i]=read();
for(int i=;i<=n;i++) b[i]=read();
for(int i=;i<=n;i++) m[i]=min(a[i],b[i]),s[i]=i;
for(int i=;i<=n-;i++)
for(int j=i+;j<=n;j++)
if(m[i]>m[j]) swap(m[i],m[j]),swap(s[i],s[j]);
// for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cout<<m[i]<<" ";
// cout<<endl;
// for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cout<<s[i]<<" ";
// cout<<endl;
// system("pause");
int ans1=,ans2=n+;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
// cout<<m[i]<<" "<<s[i]<<" "<<a[s[i]]<<" "<<b[s[i]]<<" "<<i<<" ";
if(m[i]==a[s[i]])ans[++ans1]=s[i];
else if(m[i]==b[s[i]])ans[--ans2]=s[i];
}
int s1=,s2=;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
s1+=a[ans[i]];
if(s1>s2) s2=s1;
s2+=b[ans[i]];
}
cout<<s2<<endl;
for(int i=;i<n;i++) cout<<ans[i]<<" ";cout<<ans[n];
return ;
}
智力大冲浪 https://loj.ac/problem/10004
题目描述
小伟报名参加中央电视台的智力大冲浪节目。本次挑战赛吸引了众多参赛者,主持人为了表彰大家的勇气,先奖励每个参赛者 m 元。先不要太高兴!因为这些钱还不一定都是你的?!接下来主持人宣布了比赛规则:
首先,比赛时间分为 n个时段,它又给出了很多小游戏,每个小游戏都必须在规定期限 ti 前完成。如果一个游戏没能在规定期限前完成,则要从奖励费 m 元中扣去一部分钱 wi,wi为自然数,不同的游戏扣去的钱是不一样的。当然,每个游戏本身都很简单,保证每个参赛者都能在一个时段内完成,而且都必须从整时段开始。主持人只是想考考每个参赛者如何安排组织自己做游戏的顺序。作为参赛者,小伟很想赢得冠军,当然更想赢取最多的钱!注意:比赛绝对不会让参赛者赔钱!
输入格式
输入共四行。
第一行为 m,表示一开始奖励给每位参赛者的钱;
第二行为 n,表示有 n 个小游戏;
第三行有 n 个数,分别表示游戏 1 到 n 的规定完成期限;
第四行有 n 个数,分别表示游戏 1 到 n 不能在规定期限前完成的扣款数。
输出格式
输出仅一行,表示小伟能赢取最多的钱。
样例
样例输入
10000
7
4 2 4 3 1 4 6
70 60 50 40 30 20 10样例输出
9950数据范围与提示
对于 100%的数据,有 n≤500,1≤ti≤n。
将罚款从大到小排序,将大的先安排,若不能安排则就拉的越远越好
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
inline int read()
{
int f=,ans=;char c;
while(c<''||c>''){if(c=='-')f=-;c=getchar();}
while(c>=''&&c<=''){ans=ans*+c-'';c=getchar();}
return ans*f;
}
struct node{
int t;
int x;
}a[];
int money,n;
bool book[];
bool cmp(node x1,node x2)
{
return x1.x>x2.x;
}
int main()
{
money=read(),n=read();
for(int i=;i<=n;i++) a[i].t=read();
for(int i=;i<=n;i++) a[i].x=read();
sort(a+,a+n+,cmp);
int ans=,sum=;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
bool f=false;
for(int j=a[i].t;j>=;j--)
if(!book[j]){book[j]=;f=true;break;}
if(!f)
{
for(int j=n;j>=;j--)
if(!book[j]){book[j]=;break;}
sum+=a[i].x;
}
}
cout<<money-sum;
return ;
}
数列极差 https://loj.ac/problem/10005
题目描述
佳佳的老师在黑板上写了一个由 n 个正整数组成的数列,要求佳佳进行如下操作:每次擦去其中的两个数 a 和 b,然后在数列中加入一个数 a×b+1,如此下去直至黑板上剩下一个数为止,在所有按这种操作方式最后得到的数中,最大的为 max\maxmax,最小的为 min\minmin, 则该数列的极差定义为 M=max−min。
由于佳佳忙于准备期末考试,现请你帮助他,对于给定的数列,计算出相应的极差 d。
输入格式
第一行为一个正整数 n 表示正整数序列的长度;
在接下来的 n行中,每行输入一个正整数。
接下来的一行有一个 0,表示数据结束。
输出格式
输出只有一行,为相应的极差 d。
样例
样例输入
3
1
2
3
0样例输出
2数据范围与提示
0≤n≤50000。
自己写了一个证明,
a<b<maxn
a,b,maxn
1)a*b+1 maxn (a*b+1)*maxn+1=a*b*maxn+maxn+1
2)a*maxn+1 b (a*maxn+1)*b+1=a*b*maxn+b+1
3)b*maxn+1 a (b*maxn+1)*a+1=a*b*maxn+a+1
则1)>2)>3)
后可推倒小于情况,
详情看代码,用优先队列维护:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
inline int read()
{
int f=,ans=;char c;
while(c<''||c>''){if(c=='-')f=-;c=getchar();}
while(c>=''&&c<=''){ans=ans*+c-'';c=getchar();}
return ans*f;
}
int n;
int x;
int main()
{
priority_queue<int> qmin;
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int> > qmax;
n=read();
for(int i=;i<=n;i++) x=read(),qmin.push(x),qmax.push(x);
while(qmin.size()>)
{
int a1=qmin.top();qmin.pop();
int a2=qmin.top();qmin.pop();
qmin.push(a1*a2+);
}
while(qmax.size()>)
{
int a1=qmax.top();qmax.pop();
int a2=qmax.top();qmax.pop();
qmax.push(a1*a2+);
}
cout<<qmax.top()-qmin.top();
}
数列分段 https://loj.ac/problem/10006
题目描述
对于给定的一个长度为 N的正整数数列 Ai,现要将其分成连续的若干段,并且每段和不超过 M(可以等于 M),问最少能将其分成多少段使得满足要求。
输入格式
第一行包含两个正整数 N,M,表示了数列 Ai的长度与每段和的最大值;
第二行包含 N 个空格隔开的非负整数 Ai。
输出格式
输出文件仅包含一个正整数,输出最少划分的段数。
样例
样例输入
5 6
4 2 4 5 1样例输出
3数据范围与提示
对于 100%的数据,有 N≤10^5,M≤10^9,M 大于所有数的最大值,Ai 之和不超过 10^9。
这种水题不想解释
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
inline int read()
{
int f=,ans=;char c;
while(c<''||c>''){if(c=='-')f=-;c=getchar();}
while(c>=''&&c<=''){ans=ans*+c-'';c=getchar();}
return ans*f;
}
int n,x,sum,ans=,m;
int main()
{
n=read(),m=read();
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
x=read();
if(sum+x<=m) sum+=x;
else ans++,sum=x;
//cout<<sum<<" "<<ans<<endl;
}
cout<<ans;
}
线段 https://loj.ac/problem/10007
题目描述
数轴上有 n 条线段,选取其中 k条线段使得这 k 条线段两两没有重合部分,问 k 最大为多少。
输入格式
第一行为一个正整数 n;
在接下来的 n 行中,每行有 2个数 ai,bi,描述每条线段。
输出格式
输出一个整数,为 k 的最大值。
样例
样例输入
3
0 2
2 4
1 3样例输出
2数据范围与提示
对于 100%的数据,n≤10^6, 0≤ai<bi≤10^6 。
这道题与活动安排类似
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
inline int read()
{
int f=,ans=;char c;
while(c<''||c>''){if(c=='-')f=-;c=getchar();}
while(c>=''&&c<=''){ans=ans*+c-'';c=getchar();}
return ans*f;
}
struct node{
int x;
int y;
}a[];
bool cmp(node x1,node x2)
{
return x1.y<x2.y;
}
int n;
int main()
{
n=read();
for(int i=;i<=n;i++) a[i].x=read(),a[i].y=read();
sort(a+,a+n+,cmp);
int ans=,t=a[].y;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
if(a[i].x>=t) ans++,t=a[i].y;
cout<<ans;
}
家庭作业 https://loj.ac/problem/10008
题目描述
老师在开学第一天就把所有作业都布置了,每个作业如果在规定的时间内交上来的话才有学分。每个作业的截止日期和学分可能是不同的。例如如果一个作业学分为 10,要求在 6天内交,那么要想拿到这 10 学分,就必须在第 6 天结束前交。
每个作业的完成时间都是只有一天。
你的任务就是找到一个完成作业的顺序获得最大学分。
输入格式
第一行一个整数 N,表示作业的数量;
接下来 N 行,每行包括两个整数,第一个整数表示作业的完成期限,第二个数表示该作业的学分。
输出格式
输出一个整数表示可以获得的最大学分。保证答案不超过 C/C++ 的 int 范围。
样例
样例输入
7
1 6
1 7
3 2
3 1
2 4
2 5
6 1样例输出
15数据范围与提示
对于 100% 的数据,N≤10^6,作业的完成期限均小于 7*10^5。
这题与智力大冲浪类似
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
inline int read()
{
int f=,ans=;char c;
while(c<''||c>''){if(c=='-')f=-;c=getchar();}
while(c>=''&&c<=''){ans=ans*+c-'';c=getchar();}
return ans*f;
}
struct node{
int t;
int w;
}a[];
bool cmp(node x1,node x2)
{
return x1.w>x2.w;
}
int n,sum;
bool book[];
int f[];
int find(int x)
{
if(f[x]==x) return x;
return f[x]=find(f[x]);
}
void merge(int x,int y)
{
f[find(x)]=f[find(y)];
return;
}
int main()
{
n=read();
for(int i=;i<=n;i++) a[i].t=read(),a[i].w=read();
sort(a+,a+n+,cmp);
for(int i=;i<=n;i++) f[i]=i;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
int ff=find(a[i].t);
// cout<<a[i].t<<" "<<ff<<" "<<a[i].w<<" "<<sum<<endl;
if(ff!=)
{
sum+=a[i].w;
merge(ff,ff-);
}
}
printf("%d",sum);
return ;
}
钓鱼 https://loj.ac/problem/10009
题目描述
话说发源于小朋友精心设计的游戏被电脑组的童鞋们藐杀之后非常不爽,为了表示安慰和鼓励,VIP999决定请他吃一次“年年大丰收”,为了表示诚意,他还决定亲自去钓鱼,但是,因为还要准备2013NOIP,z老师只给了他H(1<=H<=16)个小时的空余时间,假设有N(2<=n<=25)个鱼塘都在一条水平路边,从左边到右编号为1、2、3、。。。、n)。VIP是个很讲究效率的孩子,他希望用这些时间钓到尽量多的鱼。他从湖1出发,向右走,有选择的在一些湖边停留一定的时间钓鱼,最后在某一个湖边结束钓鱼。他测出从第I个湖到I+1个湖需要走5*ti分钟的路,还测出在第I个湖边停留,第一个5分钟可以钓到鱼fi,以后再每钓5分钟鱼,鱼量减少di。为了简化问题,他假定没有其他人钓鱼,也不会有其他因素影响他钓到期望数量的鱼。请编程求出能钓最多鱼的数量。
输入输出格式
输入格式:
第一行:湖的数量n。
第二行:时间h(小时)。
第三行:n个数,f1,f2,…fn。
第四行:n个数,d1,d2,….dn。
第五行:n-1个数,t1,t2,….tn-1
输出格式:
一个数,所能钓鱼的最大数量。
输入输出样例
输入样例#1:
2
1
10 1
2 5
2
输出样例#1:
31
将时间先算出来,在通过优先队列进行维护
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
inline int read()
{
int f=,ans=;char c;
while(c<''||c>''){if(c=='-')f=-;c=getchar();}
while(c>=''&&c<=''){ans=ans*+c-'';c=getchar();}
return ans*f;
}
struct node{
int cost;
int d;
}a[];
bool operator<( node a, node b ){
return a.cost<b.cost;
}
priority_queue<node> que;
int n,t,h[],sum,sry,maxn;
int main()
{
n=read();t=read();t*=;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++) a[i].cost=read();
for(int i=;i<=n;i++) a[i].d=read();
for(int i=;i<n;i++) h[i]=read();
// cout<<t;system("pause");
// int sry=0;
int tt=t;
for(int i=;i<=n;i++)
{
sry=;
sum=;
for(int j=;j<=i;j++) que.push(a[j]);
for(int j=;j<i;j++) sum+=h[j];
// cout<<sum<<endl;
t=tt-sum*;
while(t>)
{
node s=que.top(); que.pop();
if(s.cost<) break;
sry+=s.cost;
// cout<<s.cost<<" "<<t<<endl;
s.cost=s.cost-s.d;
que.push(s);
t-=;
}
// cout<<sry<<endl;
maxn=max(maxn,sry);
while(!que.empty()) que.pop();
}
cout<<maxn;
return ;
}
糖果传递 https://loj.ac/problem/10010
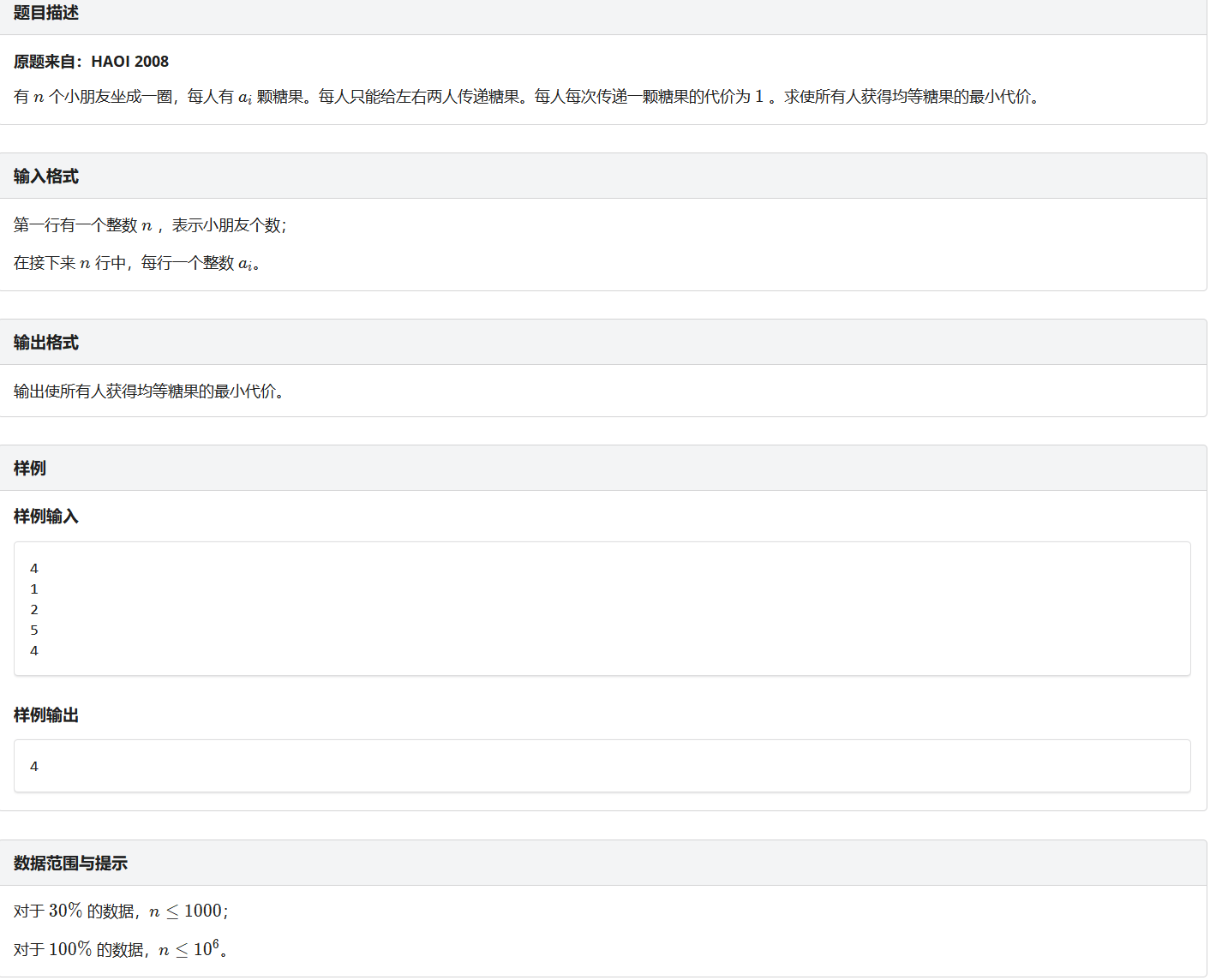
这就有一个比较神奇的证明,不是我写的,但是非常聪明,

详情见代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
long long a[],c[];
inline long long read()
{
long long f=,ans=;char c;
while(c<''||c>''){if(c=='-')f=-;c=getchar();}
while(c>=''&&c<=''){ans=ans*+c-'';c=getchar();}
return ans*f;
}
long long tot,n;
int main()
{
n=read();
for(long long i=;i<=n;i++) a[i]=read(),tot+=a[i];
tot/=n;
for(long long i=;i<=n;i++) c[i]=c[i-]+a[i]-tot;
sort(c+,c+n+);
long long bz=c[n/];
long long sum=;
for(long long i=;i<=n;i++) sum+=abs(c[i]-bz);
cout<<sum;
}
YBT 1.1 贪心算法的更多相关文章
- 贪心算法(Greedy Algorithm)
参考: 五大常用算法之三:贪心算法 算法系列:贪心算法 贪心算法详解 从零开始学贪心算法 一.基本概念: 所谓贪心算法是指,在对问题求解时,总是做出在当前看来是最好的选择.也就是说,不从整体最优上加以 ...
- 算法导论----贪心算法,删除k个数,使剩下的数字最小
先贴问题: 1个n位正整数a,删去其中的k位,得到一个新的正整数b,设计一个贪心算法,对给定的a和k得到最小的b: 一.我的想法:先看例子:a=5476579228:去掉4位,则位数n=10,k=4, ...
- LEETCODE —— Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II [贪心算法]
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II Say you have an array for which the ith element is the price of a ...
- ACM_ICPC hdu-2111(简单贪心算法)
一道非常简单的贪心算法,但是要注意输入的价值是单位体积的价值,并不是这个物品的总价值!#include <iostream> #include <stdio.h> #inclu ...
- 基于贪心算法的几类区间覆盖问题 nyoj 12喷水装置(二) nyoj 14会场安排问题
1)区间完全覆盖问题 问题描述:给定一个长度为m的区间,再给出n条线段的起点和终点(注意这里是闭区间),求最少使用多少条线段可以将整个区间完全覆盖 样例: 区间长度8,可选的覆盖线段[2,6],[1, ...
- 增强学习贪心算法与Softmax算法
(一) 这个算法是基于一个概率来对探索和利用进行折中:每次尝试时,以概率进行探索,即以均匀概率随机选取一个摇臂,以的概率进行利用,即以这个概率选择当前平均奖赏最高的摇臂(如有多个,则随机选取). 其中 ...
- 【九度OJ】题目1434贪心算法
题目 本题的贪心算法策略需要深入思考一下 看到题目,最初没有理解题目的要求:看尽量多的完整的节目.尽量多是指数量多,自己理解成观看的时间最长.这样想其实简化了这道题. 正确理解题意后,首先想到的想法是 ...
- 题目1437:To Fill or Not to Fill:贪心算法解决加油站选择问题(未解决)
//贪心算法解决加油站选择问题 //# include<iostream> # include<stdio.h> using namespace std; # include& ...
- 贪心算法(Greedy Algorithm)之最小生成树 克鲁斯卡尔算法(Kruskal's algorithm)
克鲁斯卡尔算法(Kruskal's algorithm)是两个经典的最小生成树算法的较为简单理解的一个.这里面充分体现了贪心算法的精髓.大致的流程能够用一个图来表示.这里的图的选择借用了Wikiped ...
随机推荐
- hdu1422重温世界杯(动态规划,最长子序列)
重温世界杯 Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submi ...
- Linux命令应用大词典-第13章 用户和组群管理
13.1 useradd:创建用户账户 13.2 adduser:创建用户账户 13.3 lnewusers:创建用户账户 13.4 usermod:修改用户账户 13.5 userdel:删除用户账 ...
- angular-使用iframe做独立页(iframe传值到angular和iframe里请求后台数据)
这个方法使用过两次.一次是在项目中嵌入一个表达式生成器.因为用别人做好的网页变成组件很难,而且里面用了jq,与angular思想相反不能用.另一次是因为想要单独引用样式.而innerHTML使用的样式 ...
- 【转】MMO即时战斗:技能实现
转自 http://blog.csdn.net/cyblueboy83/article/details/41628743 一.前言 基本所有MMO游戏无论是回合制.策略类.即时战斗等等类型都需要有相应 ...
- c字符指针与字符数组的区别
1.定义 char *pchar; //定义了指针,没赋值之前不能使用.如果:printf("*pchar:%c\n",*pchar); 出现段错误Segmentation fa ...
- asp.net mvc5 模式的现象思考
.net mv5简化了一些应用逻辑,与其说是mvc架构模式,不如说应用.net Entity更好. 现在你只需要去随便创建一个类 相关数据 然后用一个类去继承 DbContext 定义一个 DbSet ...
- nordic mesh 任务调度实现
nordic mesh 任务调度实现 nordic mesh的任务调度室基于定时器实现的,有两个链表结构维护任务. 需要注意的是,任务调度的部分接口只能在"bearer event" ...
- js如何使浏览器允许脚本异步加载
js如何使浏览器允许脚本异步加载 如果脚本体积很大,下载和执行的时间就会很长,因此造成浏览器堵塞,用户会感觉到浏览器“卡死”了,没有任何响应.这显然是很不好的体验,所以浏览器允许脚本异步加载,下面就是 ...
- Android 开发 之 JNI入门 - NDK从入门到精通
NDK项目源码地址 : -- 第一个JNI示例程序下载 : GitHub - https://github.com/han1202012/NDKHelloworld.git -- Java传递参数给C ...
- Coursera-Note: Internet History, Technology and Secure (1st week to 9th week)
目录 Coursera-Note: Internet History, Technology and Secure 第一周 第二周 数据交换: Packet switching技术: 第三周 创造ht ...
