pymysql和MySQLdb
MySQLdb创建mysql数据库表
其实mysqldb创建表是有限制的,要求是5.1-5.5版本
pymsql是Python中操作MySQL的模块,其使用方法和MySQLdb几乎相同。
1.下载
首先要下载下载:请到官方网站http://sourceforge.net/projects/mysql-python/或者点击链接下载http://downloads.sourceforge.net/project/mysql-python/mysql-python-test/1.2.3c1/MySQL-python-1.2.3c1.tar.gz?use_mirror=nchc
2.解压安装
解压:tar zxvf MySQL-python* 进入文件目录,运行以下命令:
python setup.py install
3. 用法
'''
# 打开数据库连接
db = MySQLdb.connect("192.168.72.131","root","","test" )
# 使用cursor()方法获取操作游标
cursor = db.cursor()
# 如果数据表已经存在使用 execute() 方法删除表。
cursor.execute("DROP TABLE IF EXISTS EMPLOYEE")
# 创建数据表SQL语句
sql = \"\"\"CREATE TABLE EMPLOYEE (
FIRST_NAME CHAR() NOT NULL,
LAST_NAME CHAR(),
AGE INT,
SEX CHAR(),
INCOME FLOAT )\"\"\"
cursor.execute(sql)
# 关闭数据库连接
db.close()
'''
pymsql
一、下载安装:
pip3 install pymysql
二、使用
1、执行SQL
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf- -*-
import pymysql # 创建连接
conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=, user='root', passwd='', db='t1')
# 创建游标
cursor = conn.cursor() # 执行SQL,并返回收影响行数
effect_row = cursor.execute("update hosts set host = '1.1.1.2'") # 执行SQL,并返回受影响行数
#effect_row = cursor.execute("update hosts set host = '1.1.1.2' where nid > %s", (,)) # 执行SQL,并返回受影响行数
#effect_row = cursor.executemany("insert into hosts(host,color_id)values(%s,%s)", [("1.1.1.11",),("1.1.1.11",)]) # 提交,不然无法保存新建或者修改的数据
conn.commit() # 关闭游标
cursor.close()
# 关闭连接
conn.close()
2、获取新创建数据自增ID
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf- -*-
import pymysql conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=, user='root', passwd='', db='t1')
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.executemany("insert into hosts(host,color_id)values(%s,%s)", [("1.1.1.11",),("1.1.1.11",)])
conn.commit()
cursor.close()
conn.close() # 获取最新自增ID
new_id = cursor.lastrowid
3、获取查询数据
cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)---》 这么写可以让返回的值为字典
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf- -*-
import pymysql conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=, user='root', passwd='', db='t1')
cursor = conn.cursor()
cursor.execute("select * from hosts") # 获取第一行数据
row_1 = cursor.fetchone() # 获取前n行数据
# row_2 = cursor.fetchmany()
# 获取所有数据
# row_3 = cursor.fetchall() conn.commit()
cursor.close()
conn.close()
注:在fetch数据时按照顺序进行,可以使用cursor.scroll(num,mode)来移动游标位置,如:
- cursor.scroll(1,mode='relative') # 相对当前位置移动
- cursor.scroll(2,mode='absolute') # 相对绝对位置移动
4、fetch数据类型
关于默认获取的数据是元祖类型,如果想要或者字典类型的数据,即:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf- -*-
import pymysql conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=, user='root', passwd='', db='t1') # 游标设置为字典类型
cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
r = cursor.execute("call p1()") result = cursor.fetchone() conn.commit()
cursor.close()
conn.close()
5、插入数据注意的地方
li = tuple(['hrYjT71474436254', '2016-09-21 13:37:34']) #这句是重点
print li
sql = "insert INTO `222` VALUES {}".format(li)
print sql
cursor.execute(sql)
conn.commit()
自己造轮子, 二次封装pymysql
class base_pymysql(object):
def __init__(self, host, port, user, password, db_name=None):
self.db_host = host
self.db_port = int(port)
self.user = user
self.password = str(password)
self.db = db_name
self.conn = None
self.cursor = None def connect(self):
self.conn = pymysql.connect(host=self.db_host, port=self.db_port, user=self.user,
passwd=self.password, db=self.db, charset="utf8")
self.cursor = self.conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) class MyPymysql(base_pymysql):
"""
Basic Usage: ret = My_Pymysql('test1')
res = ret.selectone_sql("select * from aaa")
print(res)
ret.close()
--------------
class writer_information_tables():
def __init__(self, libname="metadata"):
self.libname = libname
self.res = MyPymysql('metadata') def insert_sql(self, data):
sql = '''insert INTO `meta_variable` SET DataTableID={}, VarValues="%s";'''.format(
data["DataTableID"])
value = (data["VarValues"])
# print(sql)
# self.res.idu_sql(sql)
self.res.insert_sql(sql, value=value)
def commit(self):
self.res.commit() def close(self):
self.res.close()
----------------
def CreateDataTableInfor(data):
sql = "insert into `meta_data_table` SET DataTableID='{}';".format(
data["DataTableID"])
ret = MyPymysql('metadata')
ret.idu_sql(sql)
ret.close()
--------------- Precautions:
Config.__init__(self, config_filename="my.cnf") """ def __init__(self, conf_name):
self.conf = Config().get_content(conf_name)
super(MyPymysql, self).__init__(**self.conf)
self.connect() def idu_sql(self, sql, value=None):
# adu: insert, delete, update的简写
# 考虑到多语句循环, try就不写在这里了
self.cursor.execute(sql, value)
self.conn.commit() def commit(self):
self.conn.commit() def rollback(self):
self.conn.rollback() def insert_sql(self, sql, value=None):
# adu: insert, delete, update的简写
# 防止sql注入
self.cursor.execute(sql, value)
def update_sql(self, sql, value=None):
# adu: insert, delete, update的简写
# 防止sql注入
self.cursor.execute(sql, value)
def delete_sql(self, sql, value=None):
# adu: insert, delete, update的简写
# 防止sql注入
self.cursor.execute(sql, value) def selectone_sql(self, sql):
self.cursor.execute(sql)
self.conn.commit()
return self.cursor.fetchone() def selectall_sql(self, sql):
self.cursor.execute(sql)
self.conn.commit()
return self.cursor.fetchall() def select_sql(self, sql, value=None):
# 防止sql注入
self.cursor.execute(sql, value)
self.conn.commit()
return self.cursor.fetchall() def close(self):
self.conn.close()
self.conn = None
self.cursor = None
自己造的轮子代码
class Config(object):
"""
# Config().get_content("user_information")
""" def __init__(self, config_filename="zk_css.cnf"):
file_path = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(__file__)), config_filename)
self.cf = configparser.ConfigParser()
self.cf.read(file_path) def get_sections(self):
return self.cf.sections() def get_options(self, section):
return self.cf.options(section) def get_content(self, section):
result = {}
for option in self.get_options(section):
value = self.cf.get(section, option)
result[option] = int(value) if value.isdigit() else value
return result
Config类
class base_pymysql(object):
def __init__(self, host, port, user, password, db_name=None, cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor):
self.db_host = host
self.db_port = int(port)
self.user = user
self.password = str(password)
self.db = db_name
self.conn = None
self.cursor = cursor def connect(self):
self.conn = pymysql.connect(host=self.db_host, port=self.db_port, user=self.user,
passwd=self.password, db=self.db, charset="utf8")
self.cursor = self.conn.cursor(cursor=self.cursor) class MyPymysql(base_pymysql):
"""
Basic Usage: ret = My_Pymysql('test1')
res = ret.selectone_sql("select * from aaa")
print(res)
ret.close()
--------------
class writer_information_tables():
def __init__(self, libname="metadata"):
self.libname = libname
self.res = MyPymysql('metadata') def insert_sql(self, data):
sql = '''insert INTO `meta_variable` SET DataTableID={}, VarValues="%s";'''.format(
data["DataTableID"])
value = (data["VarValues"])
# print(sql)
# self.res.idu_sql(sql)
self.res.insert_sql(sql, value=value)
def commit(self):
self.res.commit() def close(self):
self.res.close()
----------------
def CreateDataTableInfor(data):
sql = "insert into `meta_data_table` SET DataTableID='{}';".format(
data["DataTableID"])
ret = MyPymysql('metadata') 或者 MyPymysql('metadata', None), 返回结果将是两种不同的形态 {} 和 ()
ret.idu_sql(sql)
ret.close()
--------------- Precautions:
Config.__init__(self, config_filename="my.cnf") """ def __init__(self, conf_name, cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor):
self.conf = Config().get_content(conf_name)
super(MyPymysql, self).__init__(**self.conf, cursor=cursor)
self.connect() def idu_sql(self, sql, value=None):
# adu: insert, delete, update的简写
# 考虑到多语句循环, try就不写在这里了
self.cursor.execute(sql, value)
self.conn.commit() def commit(self):
self.conn.commit() def rollback(self):
self.conn.rollback() def insert_sql(self, sql, value=None):
# adu: insert, delete, update的简写
# 防止sql注入
self.cursor.execute(sql, value)
def update_sql(self, sql, value=None):
# adu: insert, delete, update的简写
# 防止sql注入
self.cursor.execute(sql, value)
def delete_sql(self, sql, value=None):
# adu: insert, delete, update的简写
# 防止sql注入
self.cursor.execute(sql, value) def selectone_sql(self, sql):
self.cursor.execute(sql)
self.conn.commit()
return self.cursor.fetchone() def selectall_sql(self, sql):
self.cursor.execute(sql)
self.conn.commit()
return self.cursor.fetchall() def select_sql(self, sql, value=None):
# 防止sql注入
self.cursor.execute(sql, value)
self.conn.commit()
return self.cursor.fetchall() def close(self):
self.conn.close()
self.conn = None
self.cursor = None
升级版, 改变返回值形态
注意:少写了一句: def close(self):里面需要增加一句: self.cursor.close() ------>忘了
class A():
def bb(self):
sql = \
"""
select * from db_metadata.meta_project limit ;
"""
data = self.pymysql.selectall_sql(sql)
return data
class DSF(A):
def __init__(self, libname="notdbMysql"):
self.libname = libname
self.pymysql = MyPymysql(self.libname)
def aa(self):
sql = \
"""
select * from db_metadata.meta_project limit ;
"""
data = self.pymysql.selectall_sql(sql)
return data
def close(self):
self.pymysql.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
ret = DSF()
print(ret.aa())
print(ret.bb())
ret.close()
model 类使用方法
class CreateProjectProduce(SelectInfo):
def __init__(self, libname="notdbMysql"):
self.libname = libname
self.pymysql = MyPymysql(self.libname) def __enter__(self):
return self def check_the_data(self, ProjectID):
'''
explain:
检查核对数据是否存在
:return:
'''
# 调用继承类方法
data = self.CatSimpleProjectProduceModel(ProjectID) return data def insert_sql(self, data):
sql = '''insert INTO `meta_variable` SET DataTableID={}, VarValues="%s";'''.format(
data["DataTableID"])
value = (data["VarValues"])
self.pymysql.insert_sql(sql, value=value) def close(self):
self.pymysql.close() def __exit__(self, exc_type, exc_val, exc_tb):
self.close()
Use Method
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*- import os, configparser, pymysql '''
1. Config 类的 my.cnf 需要指定路径
2. my.cnf 的文件详情
my.cnf: # -----<notdbMysql>----- #配置中没有写库的名字,这样更加灵活
[notdbMysql]
host = 192.168.2.137
port = 3306
user = root
password = python123
3. 返回值形态设置
class writer_information_tables():
def __init__(self, libname="notdbMysql"):
self.libname = libname
self.res = MyPymysql(self.libname) # --> 返回值形态是{'aid': 5, 'varlabel': 'adadsf', 'vid': 0}
# self.res = MyPymysql(self.libname, None) # --> 返回值形态是(0, 5, 'adadsf')
''' class Config(object):
"""
# Config().get_content("user_information")
""" def __init__(self, config_filename="my.cnf"):
file_path = "/opt/code/my_code/tornado_uedit/my.cnf"
self.cf = configparser.ConfigParser()
self.cf.read(file_path) def get_sections(self):
return self.cf.sections() def get_options(self, section):
return self.cf.options(section) def get_content(self, section):
result = {}
for option in self.get_options(section):
value = self.cf.get(section, option)
result[option] = int(value) if value.isdigit() else value
return result class base_pymysql(object):
def __init__(self, host, port, user, password, db_name=None, cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor):
self.db_host = host
self.db_port = int(port)
self.user = user
self.password = str(password)
self.db = db_name
self.conn = None
self.cursor = cursor def connect(self):
self.conn = pymysql.connect(host=self.db_host, port=self.db_port, user=self.user,
passwd=self.password, db=self.db, charset="utf8")
self.cursor = self.conn.cursor(cursor=self.cursor) class MyPymysql(base_pymysql):
"""
Basic Usage: ret = My_Pymysql('test1')
res = ret.selectone_sql("select * from aaa")
print(res)
ret.close()
--------------
class writer_information_tables():
def __init__(self, libname="metadata"):
self.libname = libname
self.res = MyPymysql('metadata') def insert_sql(self, data):
sql = '''insert INTO `meta_variable` SET DataTableID={}, VarValues="%s";'''.format(
data["DataTableID"])
value = (data["VarValues"])
# print(sql)
# self.res.idu_sql(sql)
self.res.insert_sql(sql, value=value)
def commit(self):
self.res.commit() def close(self):
self.res.close()
----------------
def CreateDataTableInfor(data):
sql = "insert into `meta_data_table` SET DataTableID='{}';".format(
data["DataTableID"])
ret = MyPymysql('metadata') 或者 MyPymysql('metadata', None), 返回结果将是两种不同的形态 {} 和 ()
ret.idu_sql(sql)
ret.close()
--------------- Precautions:
Config.__init__(self, config_filename="my.cnf") """ def __init__(self, conf_name, cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor):
self.conf = Config().get_content(conf_name)
super(MyPymysql, self).__init__(**self.conf, cursor=cursor)
self.connect() def idu_sql(self, sql, value=None):
# adu: insert, delete, update的简写
# 考虑到多语句循环, try就不写在这里了
self.cursor.execute(sql, value)
self.conn.commit() def commit(self):
self.conn.commit() def rollback(self):
self.conn.rollback() def insert_sql(self, sql, value=None):
# adu: insert, delete, update的简写
# 防止sql注入
self.cursor.execute(sql, value) def update_sql(self, sql, value=None):
# adu: insert, delete, update的简写
# 防止sql注入
self.cursor.execute(sql, value) def delete_sql(self, sql, value=None):
# adu: insert, delete, update的简写
# 防止sql注入
self.cursor.execute(sql, value) def selectone_sql(self, sql):
self.cursor.execute(sql)
self.conn.commit()
return self.cursor.fetchone() def selectall_sql(self, sql):
self.cursor.execute(sql)
self.conn.commit()
return self.cursor.fetchall() def select_sql(self, sql, value=None):
# 防止sql注入
self.cursor.execute(sql, value)
self.conn.commit()
return self.cursor.fetchall() def close(self):
self.conn.close()
self.conn = None
self.cursor = None class writer_information_tables():
def __init__(self, libname="notdbMysql"):
self.libname = libname
self.res = MyPymysql(self.libname) # --> 返回值形态是{'aid': 5, 'varlabel': 'adadsf', 'vid': 0}
# self.res = MyPymysql(self.libname, None) # --> 返回值形态是(0, 5, 'adadsf') def insert_sql(self):
sql = "select * from myTest.a1"
data = self.res.selectone_sql(sql)
return data def commit(self):
self.res.commit() def close(self):
self.res.close() if __name__ == '__main__':
pym_obj = writer_information_tables()
print(pym_obj.insert_sql())
pym_obj.close()
Use Method
Pymysql 进行事务回滚
#!/usr/bin/env python
import MySQLdb def connect_mysql():
db_config = {
'host': '127.0.0.1',
'port': ,
'user': 'root',
'passwd': 'pzk123'
}
c = MySQLdb.connect(**db_config)
return c if __name__ == '__main__':
c = connect_mysql() # 首先连接数据库
cus = c.cursor() # 生成游标对象
sql = 'drop database test;' # 定义要执行的SQL语句
try:
cus.execute(sql) # 执行SQL语句
c.commit() # 如果执行成功就提交事务
except Exception as e:
c.rollback() # 如果执行失败就回滚事务
raise e
finally:
c.close() # 最后记得关闭数据库连接
mysqldb的
PYMYSQL防止sql注入问题
1.寻找到SQL注入的位置
2.判断服务器类型和后台数据库类型
3.针对不通的服务器和数据库特点进行SQL注入攻击
案例:
1、字符串拼接查询,造成注入
import pymysql conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='', db='User')
cursor = conn.cursor()
username=input()
password =input()
# 正常构造语句的情况
sql = "select user,pwd from User where user='%s' and pwd='%s'" % (username,password) row_count = cursor.execute(sql)
row_1 = cursor.fetchone()
print(row_count, row_1)
conn.commit()
cursor.close()
conn.close()
案例
其实用户可以这样输入实现免帐号登录:
username: ‘or 1 = 1 –-
password:
如若没有做特殊处理,那么这个非法用户直接登陆进去了.
当输入了上面的用户名和密码,服务端的sql就变成:
sql = "select user,pwd from User where user=‘'or 1 = 1 –-' and pwd='%s'"
因为条件后面username=”or 1=1 用户名等于 ” 或1=1 那么这个条件一定会成功;然后后面加两个-,这意味着注释,它将后面的语句注释,让他们不起作用,这样语句永远都能正确执行,用户轻易骗过系统,获取合法身份。
解决方法:
注意:一定要用"%s" 而不是‘%s’
#! /usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import pymysql conn = pymysql.connect(host='127.0.0.1', port=3306, user='root', passwd='', db='User')
cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
username= input()
password =input() #执行参数化查询
row_count=cursor.execute("select user,pwd from User where user='%s' and pwd='%s'" ,(username,password))
#execute()函数本身就有接受SQL语句变量的参数位,只要正确的使用(直白一点就是:使用”逗号”,而不是”百分号”)就可以对传入的值进行correctly转义,从而避免SQL注入的发生。 #内部执行参数化生成的SQL语句,对特殊字符进行了加\转义,避免注入语句生成。
# sql=cursor.mogrify("select user,pwd from User where user='%s' and pwd='%s'" ,(username,password))
# print (sql) row_1 = cursor.fetchone()
print(row_count,row_1) conn.commit()
cursor.close()
conn.close()
防sql注入问题2
报错:TypeError: %d format: a number is required, not str"
cursor.execute("""
insert into tree (id,parent_id,level,description,code,start,end)
values (%d,%d,%d,%s,%s,%f,%f)
""", (1,1,1,'abc','def',1,1)
)
如果这么写报错
对应mysql表类型
id int(),
parent_id int(),
level int(),
description varchar(),
code varchar(),
start decimal(,),
end decimal(,)
" File "/usr/lib/pymodules/python2./MySQLdb/cursors.py", line 151, in execute query = query % db.literal(args) TypeError: %d format: a number is required, not str"
解决办法:
The format string is not really a normal Python format string. You must always use %s for all fields.
防sql注入问题3
pymysql防sql注入必须是"%s", 可以这种%s形式的
from collections import OrderedDict
from common.Base import MyPymysql d = {'is_top': '', 'input_data_text': 'adfadf', 'is_comment': '', 'title': 'adsf', 'tag': ';分离', 'input_data_html': , 'is_release': '', 'input_data_content': '<p>adfadf<br/></p>', 'is_homepage': '', 'Password': '', 'edit_category': '', 'is_password': ''} def AddArticleModel(info):
sql = """
INSERT INTO blog.text
SET
ArticleTitle="%s", Release=%s ----> 这样是错的, pymysql防sql注入必须是"%s", 不能用这种%s形式的,包括数据是int都不行《---可以%s,留着这句话,看看当时因为release关键字让自己写的傻逼笔记 """
ret = MyPymysql('notdbMysql')
value = (
info["title"], # ArticleTitle int(info["is_release"]), # Release )
ret.idu_sql(sql, value=value)
ret.close() if __name__ == '__main__':
AddArticleModel(d)
三、错误集锦
1.
查看mysql单个库大小容量的命令(单位为字节,得到多少M需要除以1048576)
SELECT sum(DATA_LENGTH)+sum(INDEX_LENGTH) FROM information_schema.TABLES where TABLE_SCHEMA='数据库名';
2.
变量名为关键字(尤其前朝余孽留下的坑,特别注意了需要加``)
update `test` set a='' where `index`=; 这个index耗费了我2个小时,下午5点头晕沉沉的
3.
那么转换一下,上次是测试的语句,下面就直接换正式的了, %s也加引号,视情况而定
sql2 = "update `%s` set a10b1j='%s' where `index`='%s'" % (table_name, li[j], j)
4.
2.7存入mysql以后unicode的转义解决办法
"""
import pymysql
conn = pymysql.connect(host='112.126.70.69', port=, user='datapl', passwd='Rome78Uj', db='data_index_test')
cursor = conn.cursor(cursor=pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
cursor.execute("select cid FROM data_bak")
row_3 = cursor.fetchall()
li = [i[] for i in row_3]
err_li = []
for i in range(len(li)):
try:
print i
a, json_sumdata = VSummary().do_(, li[i])
sql = "INSERT INTO data_cid_json SET cid='%s', json_sumdata='%s'" % (li[i], pymysql.escape_string(json_sumdata))
cursor.execute(sql)
conn.commit()
except Exception as e:
err_li.append(li[i])
continue
cursor.close() conn.close() """
5.
调用oracle的时候需要注意的问题
他说一直是编码的问题,其实是oracle的问题

6.

解决办法
在创建连接的时候设置一下编码,如: conn = MySQLdb.connect(host="localhost", user="root", passwd="root", db="db", charset="utf8")
7. 注意一定要用"%s", 而不能用'%s'
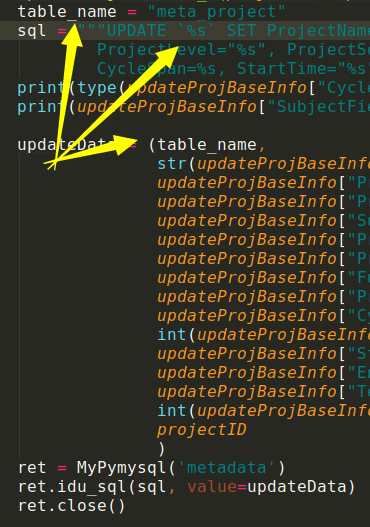
8. 在pymysql里面防sql要注意, 例如: update `%s` 这个时候会把表名也转义, 所以报错
会变成update `\'meta_project\' set ....这样就找不到表名
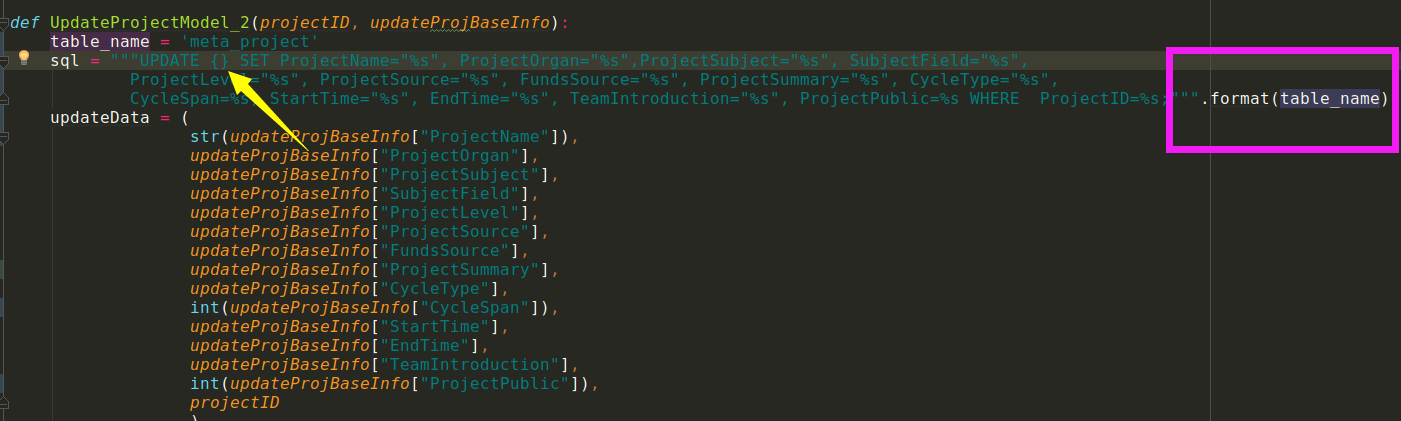
之前这么写的
pymysql和MySQLdb的更多相关文章
- MySQL、sqlalchemy、pymysql、mysqldb、DBAPI之间关系梳理(终于明白了)
MySQL.sqlalchemy.pymysql.mysqldb.DBAPI之间关系梳理(终于明白了) python3不再支持mysqldb 请用pymysql和mysql.connector 问题背 ...
- 用pymysql代替MySQLdb
在我刚开始学python的时候,用的是python2.7,那时候连接mysql用的库是MySQLdb(很诡异的大小写,初学者经常因为记不住大小写导致“No module named xxx”).燃鹅, ...
- PyMySQL和MySQLdb的区别
网上很多关于Scrapy存入MySQL的教程,都会发现又这么一个包的引入: import MySQLdb import MySQLdb.cursors 聪明的你或许已经算到,需要安装MySQLdb ...
- pyhton 自动化pymysql操作mysqldb数据库增删改查封装
# coding=utf-8 import pymysql import os import configparser """ /* @:param: python ve ...
- python peewee.ImproperlyConfigured: MySQLdb or PyMySQL must be installed.
最近在学习Python,打算先看两个在线教程,再在github上找几个开源的项目练习一下,在学到“被解放的姜戈”时遇到django同步数据库时无法执行的错误,记录一下. 错误现象: 执行python ...
- Python3出现"No module named 'MySQLdb'"问题-以及使用PyMySQL连接数据库
Python3 与 Django 连接数据库,出现了报错:Error loading MySQLdb module: No module named 'MySQLdb'.原因如下:在 python2 ...
- Python 3.x 连接数据库(pymysql 方式)
==================pymysql=================== 由于 MySQLdb 模块还不支持 Python3.x,所以 Python3.x 如果想连接MySQL需要安装 ...
- python pymysql和orm
pymsql是Python中操作MySQL的模块,其使用方法和MySQLdb几乎相同. 1. 安装 管理员打开cmd,切换到python的安装路径,进入到Scripts目录下(如:C:\Users\A ...
- Python 3.5 连接Mysql数据库(pymysql 方式)
由于 MySQLdb 模块还不支持 Python3.x,官方的Mysql连接包只支持到3.4,所以 Python3.5 如果想连接MySQL需要安装 pymysql 模块. pymysql 模块可以通 ...
随机推荐
- [na]ping提示&各系统默认的TTL值
1,Win7 ping 不存在的地址(请求超时) ip routing和no ip routing no ip routing----不查路由表 不配置网关---arp-catch中存在很多条目(相当 ...
- HTML5学习笔记(十三):JavaScript函数
函数定义 在JavaScript中,定义函数的方式如下: function abs(x) { if (x >= 0) { return x; } else { return -x; } } 上述 ...
- 行为类模式(十):模板方法(Template Method)
定义 定义一个操作中的算法的骨架,而将步骤延迟到子类中.模板方法使得子类可以不改变一个算法的结构即可重定义算法的某些特定步骤. UML 优点 模板方法模式通过把不变的行为搬移到超类,去除了子类中的重复 ...
- step-by-step-creating-a-sql-server-2012-alwayson-availability-group/
https://blogs.technet.microsoft.com/canitpro/2013/08/19/step-by-step-creating-a-sql-server-2012-alwa ...
- [Windows Azure] What is a Storage Account?
What is a Storage Account? A storage account gives your applications access to Windows Azure Blob, T ...
- java 多线程 23 : Timer
前言 定时/计划功能在Java应用的各个领域都使用得非常多,比方说Web层面,可能一个项目要定时采集话单.定时更新某些缓存.定时清理一批不活跃用户等等.定时计划任务功能在Java中主要使用的就是Tim ...
- Faiss教程:GPU
Fassi通过CUDA支持GPU,要求3.5以上算力,float16要求CUDA7.5+ 通过index_gpu_to_cpu可以将索引从GPU复制到CPU,index_cpu_to_gpu 和 in ...
- 基于jquery下拉列表树插件代码
分享一款基于jquery下拉列表树插件代码.这是一款实用的jquery 树形下拉框 下拉树代码下载.效果图如下: 在线预览 源码下载 实现的代码. html代码: <table width= ...
- MYSQL优化9大法!
通常网站的性能瓶颈在数据库查询,如果你希望你的网站在一定阶段之内保持稳定,优化你的SQL和数据库是非常必要的一个优化环节.优化数据库是一个很大的话题,这里只是摘要一些比较关键的优化参考建议,并且需要具 ...
- 【转】使用scipy进行层次聚类和k-means聚类
scipy cluster库简介 scipy.cluster是scipy下的一个做聚类的package, 共包含了两类聚类方法: 1. 矢量量化(scipy.cluster.vq):支持vector ...
