PRM路径规划算法
路径规划作为机器人完成各种任务的基础,一直是研究的热点。研究人员提出了许多规划方法:如人工势场法、单元分解法、随机路标图(PRM)法、快速搜索树(RRT)法等。传统的人工势场、单元分解法需要对空间中的障碍物进行精确建模,当环境中的障碍物较为复杂时,将导致规划算法计算量较大。基于随机采样技术的PRM法可以有效解决高维空间和复杂约束中的路径规划问题。
PRM是一种基于图搜索的方法,它将连续空间转换成离散空间,再利用A*等搜索算法在路线图上寻找路径,以提高搜索效率。这种方法能用相对少的随机采样点来找到一个解,对多数问题而言,相对少的样本足以覆盖大部分可行的空间,并且找到路径的概率为1(随着采样数增加,P(找到一条路径)指数的趋向于1)。显然,当采样点太少,或者分布不合理时,PRM算法是不完备的,但是随着采用点的增加,也可以达到完备。所以PRM是概率完备且不最优的。

The PRM path planner constructs a roadmap in the free space of a given map using randomly sampled nodes in the free space and connecting them with each other. Once the roadmap has been constructed, you can query for a path from a given start location to a given end location on the map.
The probabilistic roadmap planner consists of two phases: a construction and a query phase. 学习阶段:在给定图的自由空间里随机撒点(自定义个数),构建一个路径网络图。查询阶段:查询从一个起点到一个终点的路径。
• Roadmap is a graph G(V, E) (无向网络图G,其中V代表随机点集,E代表所有可能的两点之间的路径集)
• Robot configuration q→Q_free is a vertex (每个点都要确保机器人与障碍物无碰撞)
• Edge (q1, q2) implies collision-free path between these robot configurations
• A metric is needed for d(q1,q2) (e.g. Euclidean distance) (Dist function计算Configuration Space中点与点之间的距离,判断是否是同一个点)
• Uses coarse sampling of the nodes, and fine sampling of the edges
• Result: a roadmap in Q_free
Step 1, Learning the Map
• Initially empty Graph G
• A configuration q is randomly chosen
• If q →Q_free then added to G (collision detection needed here)
• Repeat until N vertices chosen
• For each q, select k closest neighbors,
• Local planner connects q to neighbor q’
• If connect successful (i.e. collision free local path), add edge (q, q’)

参考这里的MATLAB代码,输入一幅500×500的地图,根据Roadmap Construction Algorithm建立网络图,然后使用A*算法搜索出一条最短路径。
PRM.m文件如下,注意下面代码中并没有选取k个最近点进行连接(或是限定连接距离),而是连接了全部的节点。
%% PRM parameters
map=im2bw(imread('map1.bmp')); % input map read from a bmp file. for new maps write the file name here
source=[10 10]; % source position in Y, X format
goal=[490 490]; % goal position in Y, X format
k=50; % number of points in the PRM
display=true; % display processing of nodes if ~feasiblePoint(source,map), error('source lies on an obstacle or outside map'); end
if ~feasiblePoint(goal,map), error('goal lies on an obstacle or outside map'); end imshow(map);
rectangle('position',[1 1 size(map)-1],'edgecolor','k')
vertex=[source;goal]; % source and goal taken as additional vertices in the path planning to ease planning of the robot
if display, rectangle('Position',[vertex(1,2)-5,vertex(1,1)-5,10,10],'Curvature',[1,1],'FaceColor','r'); end % draw circle
if display, rectangle('Position',[vertex(2,2)-5,vertex(2,1)-5,10,10],'Curvature',[1,1],'FaceColor','r'); end tic; % tic-toc: Functions for Elapsed Time %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% Step 1, Constructs the Map %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
%% iteratively add vertices
while length(vertex)<k+2
x = double(int32(rand(1,2) .* size(map))); % using randomly sampled nodes(convert to pixel unit)
if feasiblePoint(x,map),
vertex=[vertex;x];
if display, rectangle('Position',[x(2)-5,x(1)-5,10,10],'Curvature',[1,1],'FaceColor','r'); end
end
end if display
disp('click/press any key');
% blocks the caller's execution stream until the function detects that the user has pressed a mouse button or a key while the Figure window is active
waitforbuttonpress;
end %% attempts to connect all pairs of randomly selected vertices
edges = cell(k+2,1); % edges to be stored as an adjacency list
for i=1:k+2
for j=i+1:k+2
if checkPath(vertex(i,:),vertex(j,:),map);
edges{i}=[edges{i};j];
edges{j}=[edges{j};i];
if display, line([vertex(i,2);vertex(j,2)],[vertex(i,1);vertex(j,1)]); end
end
end
end if display
disp('click/press any key');
waitforbuttonpress;
end %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% Step 2, Finding a Path using A* %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%% % structure of a node is taken as: [index of node in vertex, historic cost, heuristic cost, total cost, parent index in closed list (-1 for source)]
Q=[1 0 heuristic(vertex(1,:),goal) 0+heuristic(vertex(1,:),goal) -1]; % the processing queue of A* algorihtm, open list
closed=[]; % the closed list taken as a list
pathFound=false;
while size(Q,1) > 0 % while open-list is not empty
[A, I] = min(Q,[],1);% find the minimum value of each column
current = Q(I(4),:); % select smallest total cost element to process
Q=[Q(1:I(4)-1,:);Q(I(4)+1:end,:)]; % delete element under processing if current(1)==2 % index of node in vertex==2(goal)
pathFound=true;break;
end for mv = 1:length(edges{current(1)}) % iterate through all edges from the node
newVertex=edges{current(1)}(mv); % move to neighbor node
if length(closed)==0 || length(find(closed(:,1)==newVertex))==0 % not in closed(Ignore the neighbor which is already evaluated)
historicCost = current(2) + historic(vertex(current(1),:),vertex(newVertex,:)); % The distance from start to a neighbor
heuristicCost = heuristic(vertex(newVertex,:),goal);
totalCost = historicCost + heuristicCost; add = true; % not already in queue with better cost
if length(find(Q(:,1)==newVertex))>=1
I = find(Q(:,1)==newVertex);
if totalCost > Q(I,4), add=false; % not a better path
else Q=[Q(1:I-1,:);Q(I+1:end,:);];add=true;
end
end if add
Q=[Q;newVertex historicCost heuristicCost totalCost size(closed,1)+1]; % add new nodes in queue
end
end
end
closed=[closed;current]; % update closed lists
end if ~pathFound
error('no path found')
end fprintf('processing time=%d \nPath Length=%d \n\n', toc, current(4)); path=[vertex(current(1),:)]; % retrieve path from parent information
prev = current(5);
while prev > 0
path = [vertex(closed(prev,1),:);path];
prev = closed(prev, 5);
end imshow(map);
rectangle('position',[1 1 size(map)-1],'edgecolor','k')
line(path(:,2),path(:,1),'color','r');
其它M文件:
%% checkPath.m
function feasible=checkPath(n,newPos,map)
feasible = true;
dir=atan2(newPos(1)-n(1),newPos(2)-n(2));
for r=0:0.5:sqrt(sum((n-newPos).^2))
posCheck = n + r.*[sin(dir) cos(dir)];
if ~(feasiblePoint(ceil(posCheck),map) && feasiblePoint(floor(posCheck),map) && ...
feasiblePoint([ceil(posCheck(1)) floor(posCheck(2))],map) && feasiblePoint([floor(posCheck(1)) ceil(posCheck(2))],map))
feasible = false;break;
end
if ~feasiblePoint(newPos,map), feasible = false; end
end
end %% feasiblePoint.m
function feasible=feasiblePoint(point,map)
feasible=true;
% check if collission-free spot and inside maps
% 0: obstacle 1: free space
if ~(point(1)>=1 && point(1)<=size(map,1) && point(2)>=1 && point(2)<=size(map,2) && map(point(1),point(2))==1)
feasible=false;
end
end %% heuristic.m
function h=heuristic(X,goal)
h = sqrt(sum((X-goal).^2));
end %% historic.m
function h=historic(a,b)
h = sqrt(sum((a-b).^2));
end

MATLAB Robotics System Toolbox
MATLAB的robotics system toolbox中提供了PRM路径规划方法,可以很方便的创建一个probabilistic roadmap path planner来进行路径规划。使用时有下面几点需要注意:
- Tune the Number of Nodes(调整节点数目)
Increasing the number of nodes can increase the efficiency of the path by giving more feasible paths. However, the increased complexity increases computation time. To get good coverage of the map, you might need a large number of nodes. Due to the random placement of nodes, some areas of the map may not have enough nodes to connect to the rest of the map. In this example, you create a large and small number of nodes in a roadmap.
% Create an occupancy grid
map = robotics.OccupancyGrid(simpleMap, ); % Create a simple roadmap with 50 nodes.
prmSimple = robotics.PRM(map, );
show(prmSimple)

% Create a dense roadmap with 250 nodes.
prmComplex = robotics.PRM(map,);
show(prmComplex)
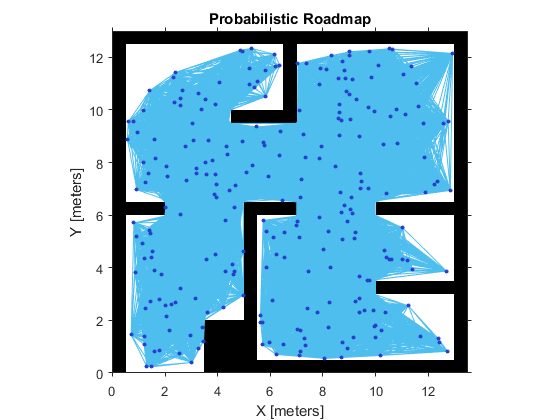
- Tune the Connection Distance(调整连接距离)
Use the ConnectionDistance property on the PRM object to tune the algorithm. ConnectionDistance is an upper threshold for points that are connected in the roadmap. Each node is connected to all nodes within this connection distance that do not have obstacles between them. By lowering the connection distance, you can limit the number of connections to reduce the computation time and simplify the map. However, a lowered distance limits the number of available paths from which to find a complete obstacle-free path. When working with simple maps, you can use a higher connection distance with a small number of nodes to increase efficiency. For complex maps with lots of obstacles, a higher number of nodes with a lowered connection distance increases the chance of finding a solution.
% Save the random number generation settings using the rng function. The saved settings enable you to reproduce the same points and see the effect of changingConnectionDistance.
rngState = rng;
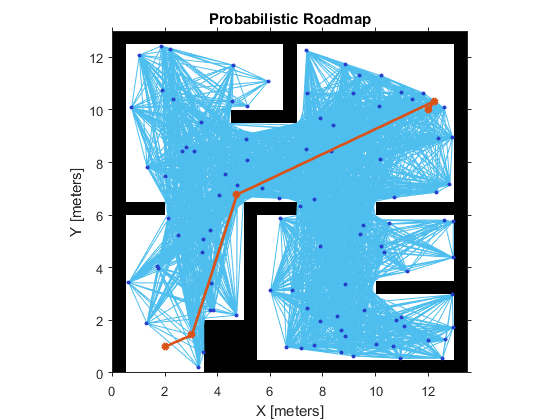
% Create a roadmap with 100 nodes and calculate the path. The default ConnectionDistance is set to inf.
prm = robotics.PRM(map, );
startLocation = [ ];
endLocation = [ ];
path = findpath(prm,startLocation,endLocation);
show(prm)
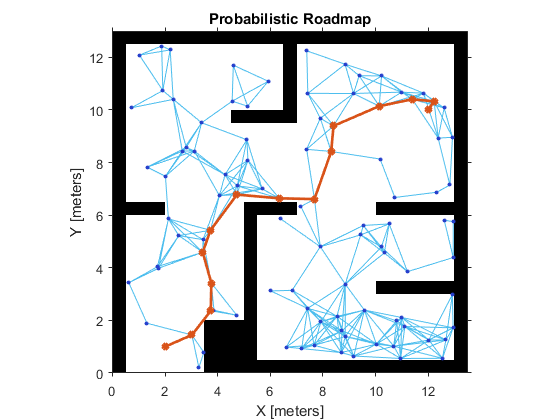
% Reload the random number generation settings to have PRM use the same nodes
rng(rngState);
% Lower ConnectionDistance to 2 m
prm.ConnectionDistance = ;
path = findpath(prm, startLocation, endLocation);
show(prm)
Create or Update PRM
This roadmap changes only if you call update or change the properties in the PRM object. When properties change, any method (update, findpath, or show) called on the object triggers the roadmap points and connections to be recalculated. Because recalculating the map can be computationally intensive, you can reuse the same roadmap by calling findpath with different starting and ending locations. 即当使用update函数进行更新或者改变PRM对象属性后,调用findpath、show等方法会引发重新计算。
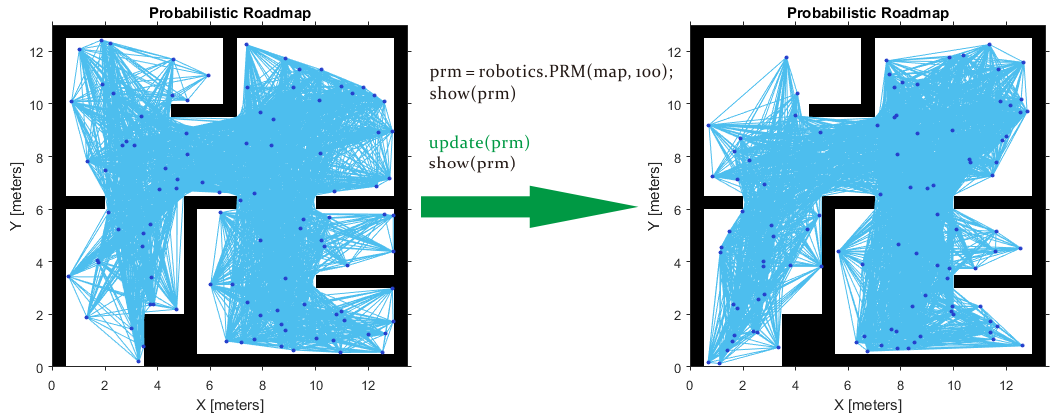
The PRM algorithm recalculates the node placement and generates a new network of nodes
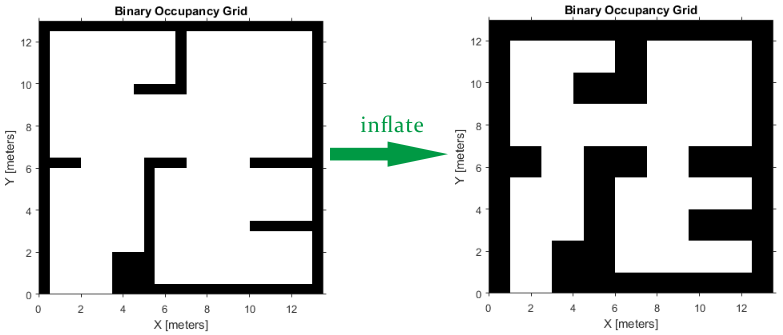
- Inflate the Map Based on Robot Dimension
PRM does not take into account the robot dimension while computing an obstacle free path on a map. Hence, you should inflate the map by the dimension of the robot, in order to allow computation of an obstacle free path that accounts for the robot's size and ensures collision avoidance for the actual robot. This inflation is used to add a factor of safety on obstacles and create buffer zones between the robot and obstacle in the environment. The inflate method of an occupancy grid object converts the specified radius to the number of cells rounded up from the resolution*radius value.
robotRadius = 0.2; mapInflated = copy(map);
inflate(mapInflated,robotRadius);
show(mapInflated)
- Find a Feasible Path on the Constructed PRM
Since you are planning a path on a large and complicated map, larger number of nodes may be required. However, often it is not clear how many nodes will be sufficient. Tune the number of nodes to make sure there is a feasible path between the start and end location.
path = findpath(prm, startLocation, endLocation)
while isempty(path)
% No feasible path found yet, increase the number of nodes
prm.NumNodes = prm.NumNodes + ; % Use the |update| function to re-create the PRM roadmap with the changed attribute
update(prm); % Search for a feasible path with the updated PRM
path = findpath(prm, startLocation, endLocation);
end
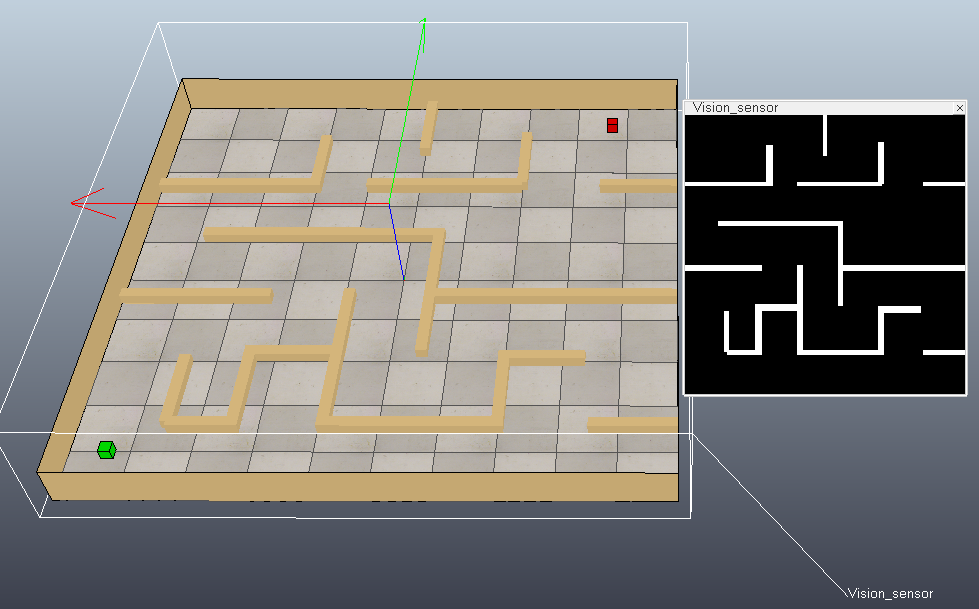
下面在VREP仿真软件中搭建一个简单的场景(修改practicalPathPlanningDemo.ttt):在地图正上方放置一个视觉传感器采集地图黑白图像,绿色方块代表起始位置,红色方块代表目标位置。然后使用MATLAB中的PRM进行路径规划。
MATLAB代码如下:
function simpleTest()
disp('Program started');
vrep=remApi('remoteApi'); % using the prototype file (remoteApiProto.m)
vrep.simxFinish(-1); % just in case, close all opened connections
clientID=vrep.simxStart('127.0.0.1',19999,true,true,5000,5); if (clientID>-1)
disp('Connected to remote API server'); [returnCode,sensorHandle] = vrep.simxGetObjectHandle(clientID,'Vision_sensor',vrep.simx_opmode_blocking);
[returnCode,objectHandle] = vrep.simxGetObjectHandle(clientID,'start',vrep.simx_opmode_blocking);
[returnCode,goalHandle] = vrep.simxGetObjectHandle(clientID,'goal',vrep.simx_opmode_blocking); % Retrieves the image of a vision sensor as an image array(each image pixel is a byte (greyscale image))
[returnCode,resolution,image] = vrep.simxGetVisionSensorImage2(clientID, sensorHandle, 1, vrep.simx_opmode_blocking); % Creates a BinaryOccupancyGrid object with resolution specified in cells per meter.
width = 5; height = 5; % Map width / height, specified as a double in meters.
grid = robotics.BinaryOccupancyGrid(image, resolution(1) / width);
grid.GridLocationInWorld = [-width/2, -height/2]; % world coordinates of the bottom-left corner of the grid % Inflate the Map Based on Robot Dimension
inflate(grid, 0.1); % Create a roadmap with 200 nodes and calculate the path
prm = robotics.PRM(grid, 200);
prm.ConnectionDistance = 1; [returnCode,startLocation] = vrep.simxGetObjectPosition(clientID,objectHandle,-1,vrep.simx_opmode_blocking);
[returnCode,endLocation] = vrep.simxGetObjectPosition(clientID,goalHandle, -1,vrep.simx_opmode_blocking); path = findpath(prm, double(startLocation(1:2)), double(endLocation(1:2)));
show(prm) % Simply jump through the path points, no interpolation here:
for i=1 : size(path,1)
pos = [path(i,:), 0.05];
vrep.simxSetObjectPosition(clientID, objectHandle, -1, pos, vrep.simx_opmode_blocking);
pause(0.5);
end % Now close the connection to V-REP:
vrep.simxFinish(clientID);
else
disp('Failed connecting to remote API server');
end
vrep.delete(); % call the destructor! disp('Program ended');
end
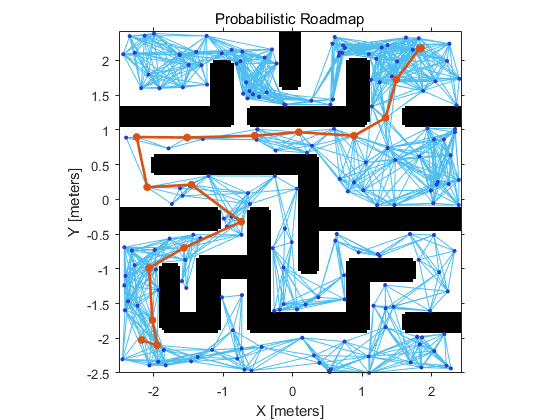
下图是MATLAB根据获取到的黑白图像创建的栅格图,并进行路径规划的结果:
下图可以看出方块沿着生成的路径移动到目标位置,只是路径还需要进一步优化。
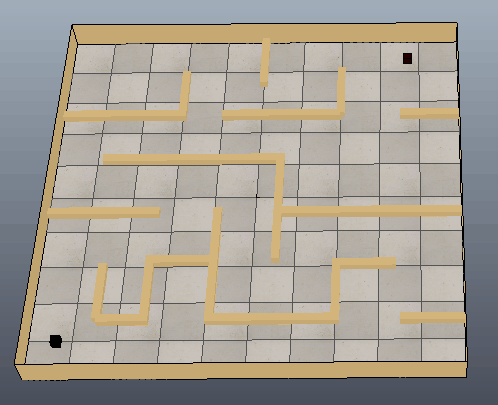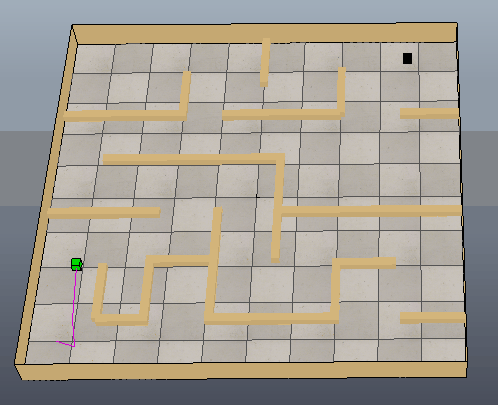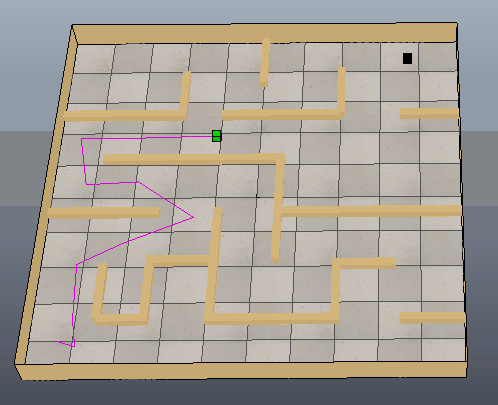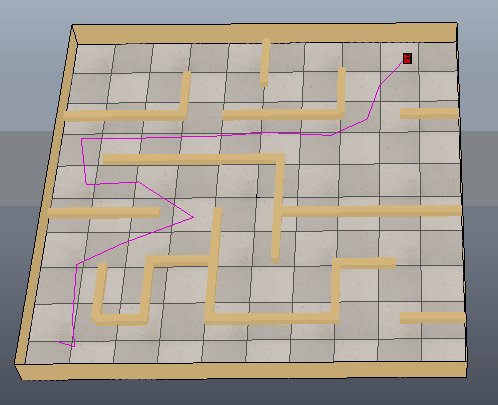
参考:
Path Planning in Environments of Different Complexity
Code for Robot Path Planning using Probabilistic Roadmap
Roadmap Methods for Multiple Queries
Probabilistic Roadmap Path Planning
Motion Planning-UC Berkeley EECS
PRM路径规划算法的更多相关文章
- 路径规划: PRM 路径规划算法 (Probabilistic Roadmaps 随机路标图)
随机路标图-Probabilistic Roadmaps (路径规划算法) 路径规划作为机器人完成各种任务的基础,一直是研究的热点.研究人员提出了许多规划方法如: 1. A* 2. Djstar 3. ...
- RRT路径规划算法
传统的路径规划算法有人工势场法.模糊规则法.遗传算法.神经网络.模拟退火算法.蚁群优化算法等.但这些方法都需要在一个确定的空间内对障碍物进行建模,计算复杂度与机器人自由度呈指数关系,不适合解决多自由度 ...
- RRT路径规划算法(matlab实现)
基于快速扩展随机树(RRT / rapidly exploring random tree)的路径规划算法,通过对状态空间中的采样点进行碰撞检测,避免了对空间的建模,能够有效地解决高维空间和复杂约束的 ...
- 全局路径规划算法Dijkstra(迪杰斯特拉算法)- matlab
参考博客链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/kex1n/p/4178782.html Dijkstra是常用的全局路径规划算法,其本质上是一个最短路径寻优算法.算法的详细介绍参考上述 ...
- DWA局部路径规划算法论文阅读:The Dynamic Window Approach to Collision Avoidance。
DWA(动态窗口)算法是用于局部路径规划的算法,已经在ROS中实现,在move_base堆栈中:http://wiki.ros.org/dwa_local_planner DWA算法第一次提出应该是1 ...
- 基础路径规划算法(Dijikstra、A*、D*)总结
引言 在一张固定地图上选择一条路径,当存在多条可选的路径之时,需要选择代价最小的那条路径.我们称这类问题为最短路径的选择问题.解决这个问题最经典的算法为Dijikstra算法,其通过贪心选择的步骤从源 ...
- 路径规划算法之Bellman-Ford算法
最近由于工作需要一直在研究Bellman-Ford算法,这也是我第一次用C++编写代码. 1.Bellman-Ford算法总结 (1)Bellman-Ford算法计算从源点(起始点)到任意一点的最短路 ...
- 机器人路径规划其一 Dijkstra Algorithm【附动态图源码】
首先要说明的是,机器人路径规划与轨迹规划属于两个不同的概念,一般而言,轨迹规划针对的对象为机器人末端坐标系或者某个关节的位置速度加速度在时域的规划,常用的方法为多项式样条插值,梯形轨迹等等,而路径规划 ...
- 机器人路径规划其二 A-Star Algorithm【附动态图源码】
首先要说明的是,机器人路径规划与轨迹规划属于两个不同的概念,一般而言,轨迹规划针对的对象为机器人末端坐标系或者某个关节的位置速度加速度在时域的规划,常用的方法为多项式样条插值,梯形轨迹等等,而路径规划 ...
随机推荐
- vanilla
In information technology, vanilla (pronounced vah-NIHL-uh ) is an adjective meaning plain or basic. ...
- [转]vi 常用命令行
From : http://www.cnblogs.com/sunormoon/archive/2012/02/10/2345326.html vi 常用命令行 1.vi 模式 a) 一般模式: v ...
- 对于DQN的三大改进 - 这篇讲的好些
可以看这篇文章: https://blog.csdn.net/u013236946/article/details/73161586 这篇也讲的不错: https://www.cnblogs.com/ ...
- Shell bc命令进行数学运算
通常情况做简单的运算,很多命令里面都是支持的.比如for, awk等. #!/bin/bash num= #for循环这里的数字也是运算 #也可以使用 #也可以使用数组 ;i<=;++i)) d ...
- 【Error】centos7 minimal connect: Network is unreachable
参考链接:http://www.centoscn.com/CentosBug/osbug/2015/1208/6500.html 由于centos7 和之前的版本差异比较大,之前的一些命令不能完全使用 ...
- Python爬虫实例(三)代理的使用
一些网站会有相应的反爬虫措施,例如很多网站会检测某一段时间某个IP的访问次数,如果访问频率太快以至于看起来不像正常访客,它可能就会会禁止这个IP的访问.所以我们需要设置一些代理服务器,每隔一段时间换一 ...
- [干货]Kaggle热门 | 用一个框架解决所有机器学习难题
新智元推荐 来源:LinkedIn 作者:Abhishek Thakur 译者:弗格森 [新智元导读]本文是数据科学家Abhishek Thakur发表的Kaggle热门文章.作者总结了自己参加100 ...
- dubbo Framework pic
dubbo Framework pic
- 在Android Studio中打开Android Device Monitor时报错的解决方法
在Android Studio中打开Android Device Monitor时报以下错误时(Android-SDK\tools\lib\monitor-x86_64\configuration\1 ...
- 【树形DP】 HDU 2412 Party at Hali-Bula
给出根节点(BOSS) 然后还有N-1个边 A B 由B指向A (B为A 的上司) 每次仅仅能选择这个关系中的当中一个 求最多选几个点 而且输出是不是唯一的 重点推断是否唯一: 1.若下属不去和去都 ...
