VGG16内置于Keras,可以通过keras.applications模块中导入。
--------------------------------------------------------将VGG16 卷积实例化:-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
from keras.applications import VGG16
conv_base = VGG16(weights = 'imagenet',#指定模型初始化的权重检查点
include_top = False,
input_shape = (150,150,30))
weights:指定模型初始化的权重检查点、
include_top: 指定模型最后是否包含密集连接分类器。默认情况下,这个密集连接分类器对应于ImageNet的100个类别。如果打算使用自己的密集连接分类器,可以不适用它,置为False。
input_shape: 是输入到网络中的图像张量的形状。这个参数完全是可选的,如果不传入这个参数,那么网络能够处理任意形状的输入。
--------------------------------------------------------查看VGG详细架构:conv_base.summary()----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
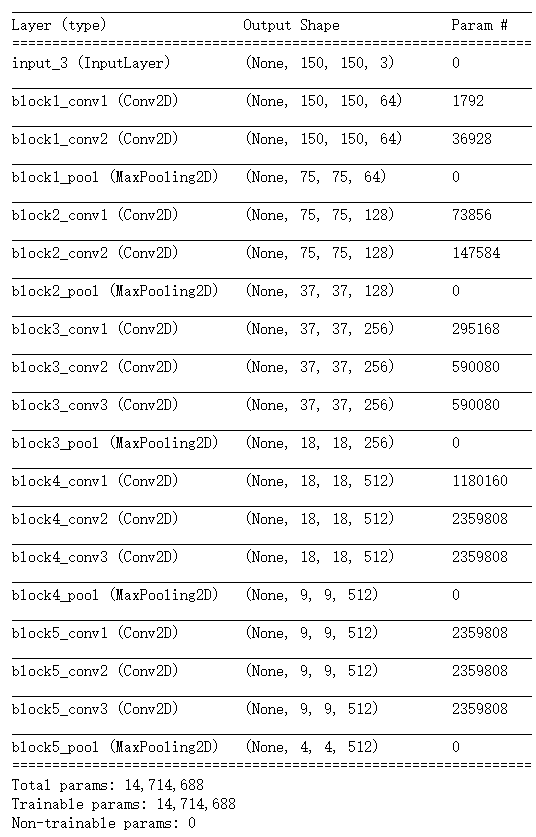
最后一特征图形状为(4,4,512),我们将在这个特征上添加一个密集连接分类器,有两种方式:
|
方法一:在你的数据集上运行卷积基,将输出保存为numpy数组,然后用这个数据做输入,输入到独立的密集连接分类器中。这种方法速度快,计算代价低,因为对于每个输入图像只需运行一次卷积基,而卷积基是日前流程中计算代价最高的。但这种方法不允许使用数据增强。
|
方法二:在顶部添加Dense层来扩展已有模型,并在输入数据上端到端地运行整个模型。这样你可以使用数据增强,因为每个输入图像进入模型时都会经过卷积基。但这种方法的计算代价比第一种要高很多。
|
#方法一:不使用数据增强的快速特征提取
import os
import numpy as np
from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
base_dir = 'cats_dogs_images'
train_dir = os.path.join(base_dir,'train')
validation_dir = os.path.join(base_dir,'validation')
test_dir = os.path.join(base_dir,'test')
datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale = 1./255)#将所有图像乘以1/255缩放
batch_size = 20
def extract_features(directory,sample_count):
features = np.zeros(shape=(sample_count,4,4,512))
labels = np.zeros(shape=(sample_count))
# 通过.flow或.flow_from_directory(directory)方法实例化一个针对图像batch的生成器,这些生成器
# 可以被用作keras模型相关方法的输入,如fit_generator,evaluate_generator和predict_generator
generator = datagen.flow_from_directory(
directory,
target_size = (150,150),
batch_size = batch_size,
class_mode = 'binary')
i = 0
for inputs_batch,labels_batch in generator:
features_batch = conv_base.predict(inputs_batch)
features[i * batch_size:(i+1) * batch_size] = features_batch
labels[i * batch_size:(i+1)*batch_size] = labels_batch
i += 1
if i * batch_size >= sample_count:
break
return features,labels
train_features,train_labels = extract_features(train_dir,2000)
validation_features,validation_labels = extract_features(validataion_dir,1000)
test_features,test_labels = extract_features(test_dir,1000)
#要将特征(samples,4,4,512)输入密集连接分类器中,首先必须将其形状展平为(samples,8192)
train_features = np.reshape(train_features,(2000,4*4*512))
validation_features = np.reshape(validation_features,(2000,4*4*512))
test_features = np.reshape(test_features,(2000,4*4*512))
#定义并训练密集连接分类器
from keras import models
from keras import layers
from keras import optimizers
model = models.Sequential()
model.add(layers.Dense(256,activation='relu',input_dim=4*4*512))
model.add(layers.Dropout(0.5))
model.add(layers.Dense(1,activation='sigmoid'))
model.compile(optimizer=optimizers.RMSprop(lr=2e-5),
loss='binary_crossentropy',
metrics = ['acc'])
history = model.fit(train_features,train_labels,
epochs=30,batch_size=20,
validation_data = (validation_features,validation_labels) )
|
#在卷积基上添加一个密集连接分类器
from keras import models
from keras import layers
model = models.Sequential()
model.add(conv_base)
model.add(layers.Flatten())
model.add(layers.Dense(256,activation='relu'))
model.add(layers.Dense(1,activation='sigmoid'))
model.summary()
 如上图,VGG16的卷积基有14714688个参数,非常多。在其上添加的分类器有200万个参数。 如上图,VGG16的卷积基有14714688个参数,非常多。在其上添加的分类器有200万个参数。
在编译和训练模型之前,一定要“冻结”卷积基。
冻结☞ 指一个或多个层在训练过程中保持其权重不变
如果不这么做,那么卷积基之前学到的表示将会在训练过程中被修改。因为其上添加的Dense层是随机初始化的,所以非常大的权重更新将会在网络中传播,对之前学到的表示造成很大破坏。
在keras中,冻结网络的方法是将其trainable属性设置为False
eg. conv_base.trainable = False
#使用冻结的卷积基端到端地训练模型
conv_base.trainable = False
from keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
from keras import optimizers
train_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(
rescale = 1./255,
rotation_range = 40,
width_shift_range = 0.2,
height_shift_range = 0.2,
shear_range = 0.2,
zoom_range = 0.2,
horizontal_flip = True,
fill_mode = 'nearest'
)
test_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(rescale=1./255)
train_generator = train_datagen.flow_from_directory(
train_dir,
target_size = (150,150),
batch_size = 20,
class_mode = 'binary'
)
validation_generator = test_datagen.flow_from_directory(
validation_dir,
target_size = (150,150),
batch_size = 20,
class_mode = 'binary'
)
model.compile(optimizer=optimizers.RMSprop(lr=2e-5),
loss='binary_crossentropy',
metrics = ['acc'])
history = model.fit_generator(
train_generator,
steps_per_epoch = 100,
epochs = 30,
validation_data = validation_generator,
validation_steps=50
)
|
#绘制损失曲线和精度曲线
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
acc = history.history['acc']
val_acc = history.history['val_acc']
loss = history.history['loss']
val_loss = history.history['val_loss']
epochs = range(1,len(acc)+1)
plt.plot(epochs,acc,'bo',label='Training_acc')
plt.plot(epochs,val_acc,'b',label='Validation_acc')
plt.title('Traing and validation accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.figure()
plt.plot(epochs,loss,'bo',label='Training loss')
plt.plot(epochs,val_loss,'b',label='Validation_loss')
plt.title('Traing and validation loss')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
|
|
|
|
电脑带不起来,慢死,这边就不截图了。
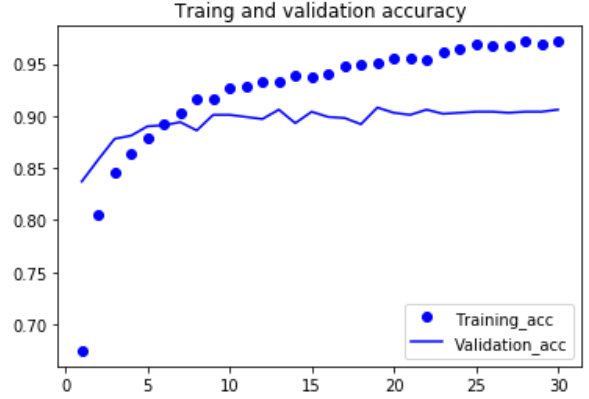
验证精度约为96%
|
--------------------------------------------------------微调模型--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
另外一种广泛使用的模型复用方法是模型微调,与特征提取互为补充。
对于用于特征提取的冻结的模型基,微调是指将其顶部的几层“解冻”,并将这解冻的几层和新增加的部分联合训练。之所以叫作微调,是因为他只是略微调整了所复用模型中更加抽象的表示,
以便让这些表示与手头的问题更加相关。
冻结VGG16的卷积基是为了能够在上面训练一个随机初始化的分类器。同理,只有上面的分类器训练好了,才能微调卷积基的顶部几层。如果分类器没有训练好,那么训练期间通过网络传播的
误差信号会特别大,微调的几层之前学到的表示都会被破坏。因此,微调网络的步骤如下:
(1)在已经训练好的基网络上添加自定义网络
(2)冻结基网络
(3)训练所添加的部分
(4)解冻基网络的一些层
(5)联合训练解冻的这些层和添加的部分
# 冻结直到某一层的所有层
#仅微调卷积基的最后的两三层
conv_base.trainable = True
set_trainable = False
for layer in conv_base.layers[:-1]:
if layer.name == 'block5_conv1':
set_trainable = True
if set_trainable:
print(layer)
set_trainable = True
else:
set_trainable = False
|

|
#微调模型
model.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy',
optimizer = optimizers.RMSprop(lr=1e-5),
metrics = ['acc'])
history = model.fit_generator(
train_generator,
steps_per_epoch=10,
epochs = 5,
validation_data = validation_generator,
validation_steps = 50
)
|
|
test_generator = test_datagen.flow_from_directory(
test_dir,
target_size = (150,150),
batch_size = 20,
class_mode = 'binary'
)
test_loss,test_acc = model.evaluate_generator(test_generator,steps=50)
|
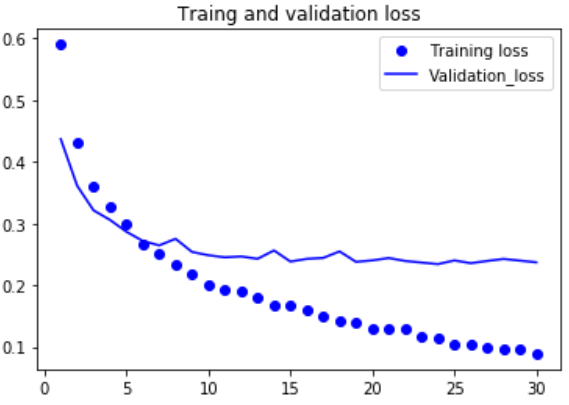
得到了97%的测试精度
|
#使曲线变得平滑
def smooth_curve(points,factor = 0.2):
smoothed_points = []
for point in points:
if smoothed_points:
previous = smoothed_points[-1]
smoothed_points.append(previous*factor+point*(1-factor))
else:
smoothed_points.append(point)
return smoothed_points
|
|
为什么不微调更多层?为什么不微调整个卷积基?当然可以这么做,但需要先考虑以下几点:
(1)卷积基中更靠底部的层编码的是更加通用的可复用特征,而更靠顶部的层编码的是更专业化的特征。微调这些更专业化的特征更加有用,因为它们需要在你的新问题上改变用途。
微调更靠底部的层,得到的汇报会更少
(2)训练的参数越多,过拟合的风险越大。卷积基有1500万个参数,所以在你的小型数据集上训练这么多参数是有风险的。
--------------------------------------------------------卷积神经网络的可视化------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
三种最容易理解也最有用的方法:
(1)可视化卷积神经网络的中间输出(中间激活):有助于理解卷积神经网络连续的层如何对输入进行变换,也有助于初步了解神经网络每个过滤器的含义
(2)可视化卷积神经网络的过滤器:有助于精确理解卷积神经网络中每个过滤器容易接受的视觉模式或视觉概念
(3)可视化图像中类激活的热力图:有助于理解图像的哪个部分被识别为属于哪个类别,从而可以定位图像中的物体
| 可视化卷积神经网络的中间输出(中间激活) |
可视化卷积神经网络的过滤器 |
|
from keras.models import load_model
model = load_model('cats_and_dogs_small_2.h5')
model.summary()
|
#为过滤器的可视化定义损失张量
from keras.applications import VGG16
from keras import backend as K
model = VGG16(weights = 'imagenet',include_top = False)
def generate_pattern(layer_name,filter_index,size=150):
layer_output = model.get_layer(layer_name).output
loss = K.mean(layer_output[:,:,:,filter_index])
#获取损失相对于输入的梯度
grads = K.gradients(loss,model.input)[0]
#梯度标准化
grads /= (K.sqrt(K.mean(K.square(grads))) + 1e-5)#1e-5防止不小心除以0
#给定numpy输入值,得到numpy输出值
iterate = K.function([model.input],[loss,grads])
#通过随机梯度下降让损失最大化
input_img_data = np.random.random((1,size,size,3))*20+128.
step = 1.
for i in range(40):
loss_value,grads_value = iterate([input_img_data])
input_img_data += grads_value * step
img = input_img_data[0]
return deprocess_image(img)
|
#预处理单张图像
img_path = 'cats_and_dogs_small/test/cats/cat.1501.jpg'
from keras.preprocessing import image
import numpy as np
img = image.load_img(img_path,target_size=(150,150))
img_tensor = image.img_to_array(img)
# img_tensor = np.expand_dims(img_tensor,axis=0)
img_tensor = img_tensor.reshape((1,)+img_tensor.shape)
img_tensor /= 255.
print(img_tensor.shape)

|
#将张量转化为有效图像的实用函数
def deprocess_image(x):
x -= x.mean()
x /= (x.std() + 1e-5)
x *= 0.1
x += 0.5
x = np.clip(x,0,1)
x *= 255
x = np.clip(x,0,255).astype('uint8')
return x
|
#显示测试图像
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.imshow(img_tensor[0])
plt.show()
|
plt.imshow(generate_pattern('block3_conv1',0))
|
|
|
#用一个输入张量和一个输出张量列表将模型实例化
from keras import models
layer_outputs = [layer.output for layer in model.layers[:8]]
activation_model = models.Model(inputs=model.input,outputs=layer_outputs)#创建一个模型,给定模型输入,可以返回这些输出
#这个模型有一个输入和8个输出,即每层激活对于一个输出

|
#生成某一层中所有过滤器响应模式组成的网络
def create_vision(layer_name):
size = 64
margin = 5
results = np.zeros((8 * size + 7 * margin , 8 * size + 7*margin ,3))
for i in range(8):
for j in range(8):
filter_img = generate_pattern(layer_name, i + (j * 8), size = size)
horizontal_start = i * size + i * margin
horizontal_end = horizontal_start + size
vertical_start = j*size + j * margin
vertical_end = vertical_start + size
results[horizontal_start:horizontal_end, vertical_start:vertical_end, :] = filter_img
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 20))
plt.imshow(results.astype('uint8'))
#不知为何deprocess_image无效,使得results矩阵并不是uint8格式,故需要转换否则不显示
|
#以预测模式运行模型
activations = activation_model.predict(img_tensor) #返回8个numpy数组组成的列表,每个层激活对应一个numpy数组
first_layer_activation = activations[3] #first_layer_activation.shape--> 32个通道 (1, 148, 148, 32)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
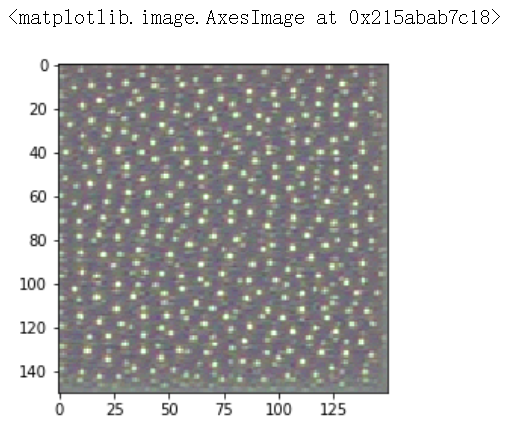
plt.matshow(first_layer_activation[0,:,:,15],cmap='viridis')
|
layer_name = 'block1_conv1'
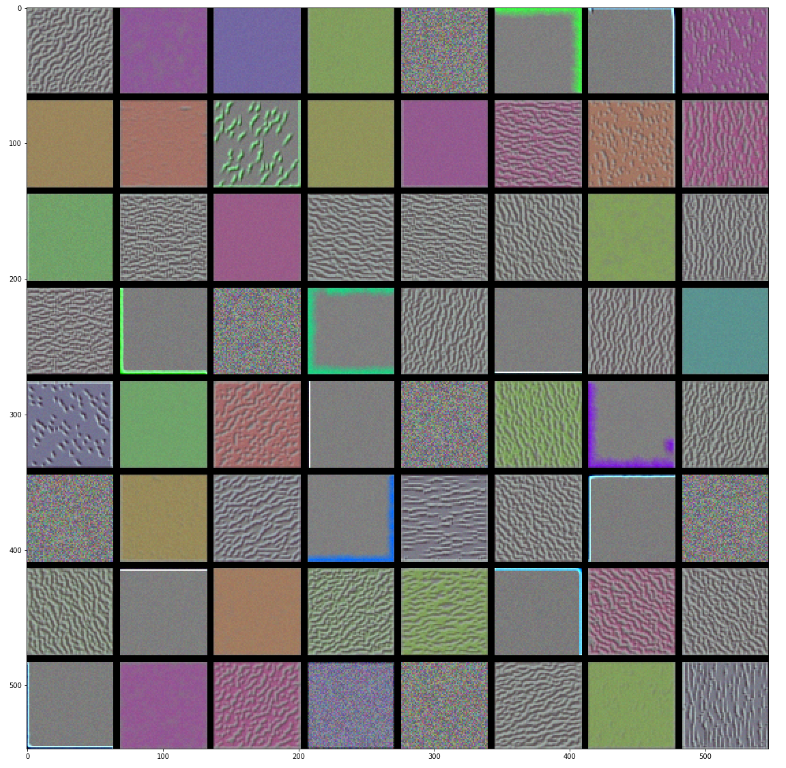
|

|
layer_name = 'block4_conv1'
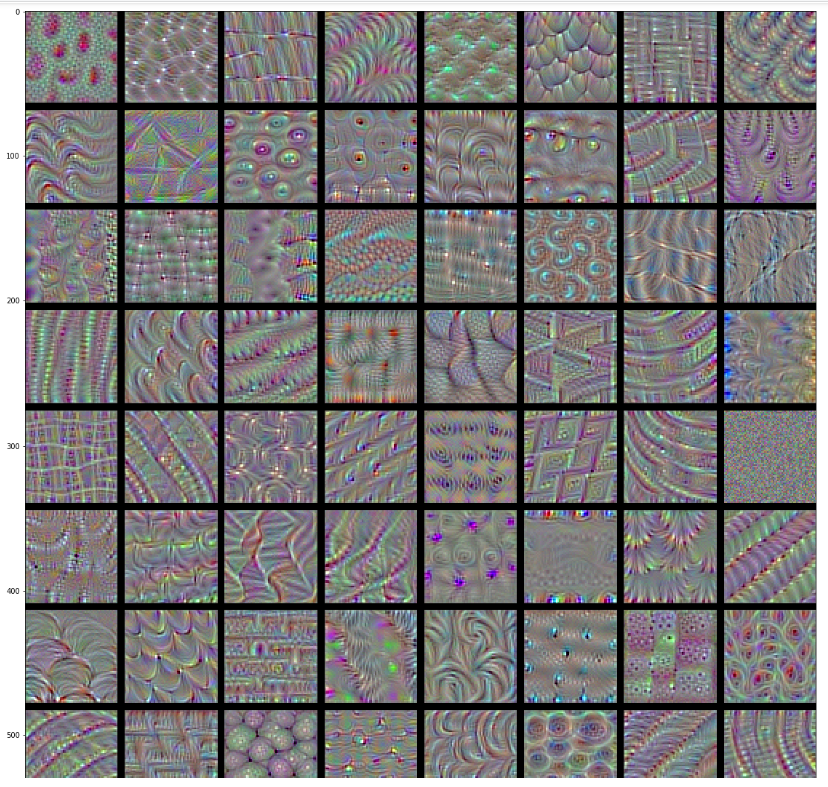
|
#将每个中间激活的所有通道可视化
layer_names = []
for layer in model.layers[:8]:
layer_names.append(layer.name)#层的名字
images_per_row = 16
for layer_name,layer_activation in zip(layer_names,activations):
n_features = layer_activation.shape[-1] #[32, 32, 64, 64, 128, 128, 128, 128] 特征个数
size = layer_activation.shape[1] #特征图的形状为(1,size,size,n_features)
n_cols = n_features // images_per_row
display_grid = np.zeros((size*n_cols,images_per_row*size))
for col in range(n_cols):
for row in range(images_per_row):
channel_image = layer_activation[0,:,:,col*images_per_row + row]
channel_image -= channel_image.mean()
channel_image /= channel_image.std()
channel_image *= 64
channel_image += 128
channel_image = np.clip(channel_image,0,255).astype('uint8')
display_grid[col*size:(col+1)*size,row*size:(row+1)*size]=channel_image
scale = 1./size
plt.figure(figsize=(scale*display_grid.shape[1],
scale*display_grid.shape[0]))
plt.title(layer_name)
plt.grid(False)
plt.imshow(display_grid,aspect='auto',cmap='viridis')
|
|
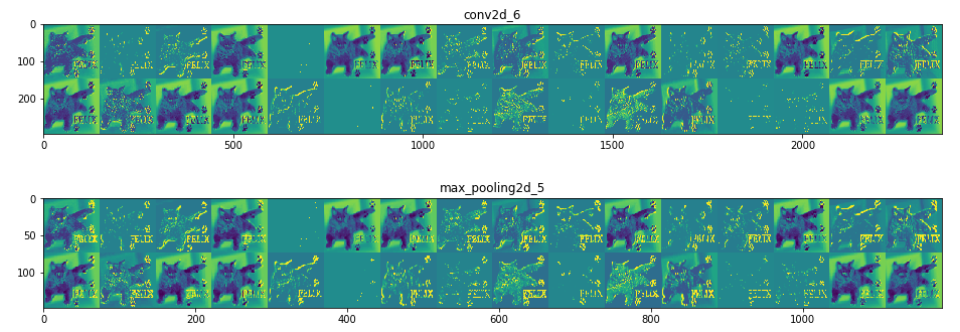
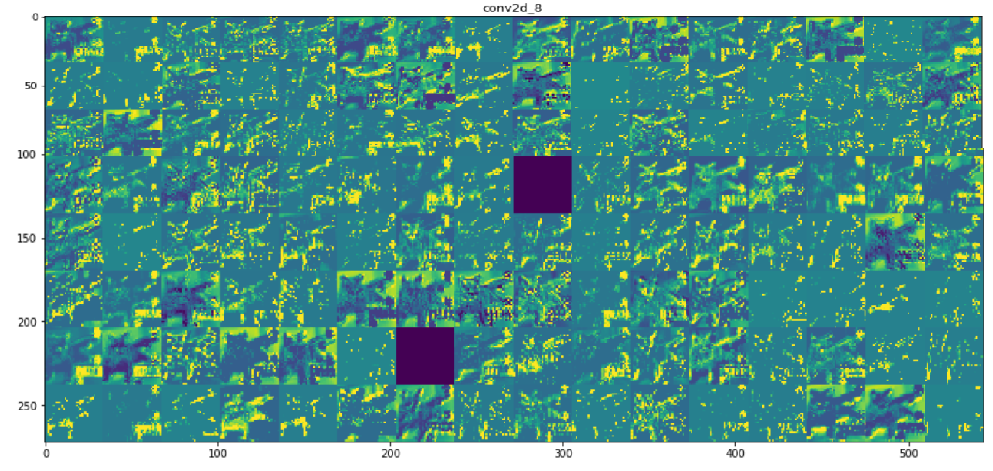
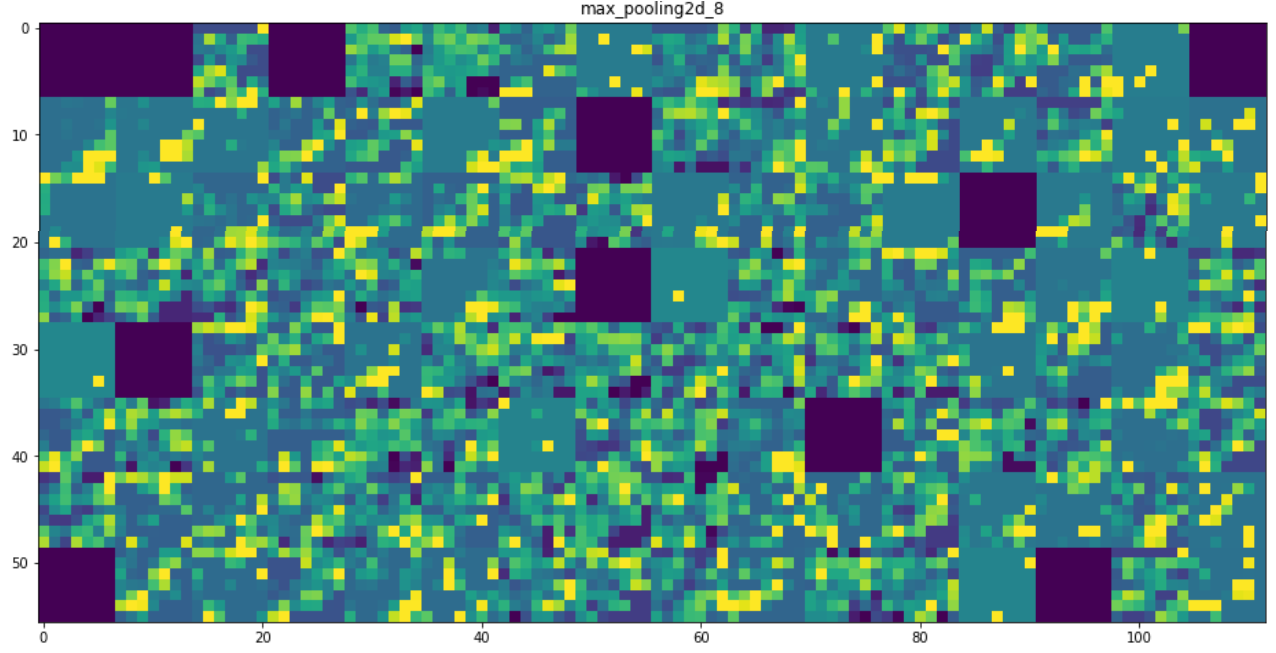
|
|
可视化图像中类激活的热力图
- 有助于了解一张图像的哪一步分让卷积神经网络做出了最终的分类决策。
- 这有助于对CNN进行调试,特别是在分类错误的情况下。
- 这种方法还能定位图像中的特定目标
|
|
from keras.applications import VGG16
model = VGG16(weights = 'imagenet',include_top = True)
|
|
#为VGG16模型预处理一张输入图像
from keras.preprocessing import image
from keras.applications.vgg16 import preprocess_input,decode_predictions
import numpy as np
img_path = 'E:/软件/nxf_software/pythonht/nxf_practice/keras/大象.jpg'
img = image.load_img(img_path,target_size=(224,224))#读取图像并调整大小
x = image.img_to_array(img) # ==> array(150,150,3)
plt.figure()
implot = plt.imshow(image.array_to_img(x))
plt.show()
|
|
x = x.reshape((1,)+x.shape) # ==> array(1,150,150,3)
x = preprocess_input(x)#对批量进行预处理(按通道进行颜色标准化)
preds = model.predict(x)
np.argmax(preds[0])
decode_predictions(preds,top=3)[0]
|
|
#为了展示图像中哪些部分最像非洲象,我们使用Grad-CAM算法
african_elephant_output = model.output[:386] #预测向量中的'非洲象'元素
last_conv_layer = model.get_layer('block5_conv3')#VGG16的最后一个卷积层
grads = K.gradients(african_elephant_output,last_conv_layer)[0]
iterate = K.function([model.input],[pooled_grads,last_conv_layer.output[0]])
pooled_grads_value,conv_layer_output_value = iterate([x])
for i in range(512):
conv_layer_output_value[:,:,i] *= pooled_grads_value[i]
headmap = np.mean(conv_layer_output_value,axis = -1)
|
|
|
heatmap = np.maximum(heatmap,0)
headmap /= np.max(heatmap)
plt.matshow(heatmap)
|
|
#将热力图与原始图像叠加
import cv2
img = cv2.imread(img_path) #用cv2加载原始图像
heatmap = cv2.resize(heatmap,(img.shape[1],img.shape[0]))#将热力图的大小调整为与原始图像相同
heatmap = np.uint8(255 * heatmap)#将热力图转换为RGB格式
heatmap = cv2.applyColorMap(heatmap,cv2.COLORMAP_JET)#将热力图应用于原始图像
superimposed_img = heatmap * 0.4 + img #0.4是热力图强度因子
cv2.imwrite('E:/软件/nxf_software/pythonht/nxf_practice/keras/大象1.jpg',superimposed_img) #将图像保存到硬盘
|
|
这种可视化方法回答了两个重要问题
- 网络为什么会认为这张图像中包含一头非洲象
- 非洲象在图像中的什么位置
|
|
| |
|
- keras中VGG19预训练模型的使用
keras提供了VGG19在ImageNet上的预训练权重模型文件,其他可用的模型还有VGG16.Xception.ResNet50.InceptionV3 4个. VGG19在keras中的定义: ...
- 卷积神经网络(CNN)的训练过程
卷积神经网络的训练过程 卷积神经网络的训练过程分为两个阶段.第一个阶段是数据由低层次向高层次传播的阶段,即前向传播阶段.另外一个阶段是,当前向传播得出的结果与预期不相符时,将误差从高层次向底层次进行传 ...
- LeNet - Python中的卷积神经网络
本教程将 主要面向代码, 旨在帮助您 深入学习和卷积神经网络.由于这个意图,我 不会花很多时间讨论激活功能,池层或密集/完全连接的层 - 将来会有 很多教程在PyImageSearch博客上将 ...
- 卷积神经网络CNN在自然语言处理中的应用
卷积神经网络(Convolution Neural Network, CNN)在数字图像处理领域取得了巨大的成功,从而掀起了深度学习在自然语言处理领域(Natural Language Process ...
- TensorFlow实战之实现AlexNet经典卷积神经网络
本文根据最近学习TensorFlow书籍网络文章的情况,特将一些学习心得做了总结,详情如下.如有不当之处,请各位大拿多多指点,在此谢过. 一.AlexNet模型及其基本原理阐述 1.关于AlexNet ...
- TensorFlow实现卷积神经网络
1 卷积神经网络简介 在介绍卷积神经网络(CNN)之前,我们需要了解全连接神经网络与卷积神经网络的区别,下面先看一下两者的结构,如下所示: 图1 全连接神经网络与卷积神经网络结构 虽然上图中显示的全连 ...
- 直白介绍卷积神经网络(CNN)【转】
英文地址:https://ujjwalkarn.me/2016/08/11/intuitive-explanation-convnets/ 中文译文:http://mp.weixin.qq.com/s ...
- 论文解读丨基于局部特征保留的图卷积神经网络架构(LPD-GCN)
摘要:本文提出一种基于局部特征保留的图卷积网络架构,与最新的对比算法相比,该方法在多个数据集上的图分类性能得到大幅度提升,泛化性能也得到了改善. 本文分享自华为云社区<论文解读:基于局部特征保留 ...
- 在Keras模型中one-hot编码,Embedding层,使用预训练的词向量/处理图片
最近看了吴恩达老师的深度学习课程,又看了python深度学习这本书,对深度学习有了大概的了解,但是在实战的时候, 还是会有一些细枝末节没有完全弄懂,这篇文章就用来总结一下用keras实现深度学习算法的 ...
随机推荐
- QT开发之旅二TCP调试工具
TCP调试工具顾名思义用来调试TCP通信的,网上这样的工具N多,之前用.NET写过一个,无奈在XP下还要安装个.NET框架才能运行,索性这次用QT重写,发现QT写TCP通信比.NET还要便捷一些,运行 ...
- 【大数据系列】apache hive 官方文档翻译
GettingStarted 开始 Created by Confluence Administrator, last modified by Lefty Leverenz on Jun 15, 20 ...
- iPhone X 上删除白条
方案一:纯色背景的情况下,解决方案就是background-color在您的body代码上设置属性: 方案二:视口入,viewport-fit=cover: <meta name="v ...
- BZOJ3163&Codevs1886: [Heoi2013]Eden的新背包问题[分治优化dp]
3163: [Heoi2013]Eden的新背包问题 Time Limit: 10 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MBSubmit: 428 Solved: 277[Submit][ ...
- rpmdb: unable to join the environment的问题解决
今天笔者在Centos 6.3上使用yum安装lsof软件时,报如下错误: [root@ ~]# yum install lsof -y rpmdb: unable to join the envir ...
- 【LOJ6077】「2017 山东一轮集训 Day7」逆序对 生成函数+组合数+DP
[LOJ6077]「2017 山东一轮集训 Day7」逆序对 题目描述 给定 n,k ,请求出长度为 n的逆序对数恰好为 k 的排列的个数.答案对 109+7 取模. 对于一个长度为 n 的排列 p ...
- Android 国内集成使用谷歌地图
extends:http://blog.csdn.net/qduningning/article/details/44778751 由于众做周知的原因在国内使用谷歌地图不太方便,在开发中如果直接使用会 ...
- java如何把文件转化成oracle的blob
import java.io.File;import java.io.FileInputStream;import java.io.FileOutputStream;import java.io.IO ...
- 关于IP地址子网的划分
- Linux查看磁盘目录内存空间使用情况
du 显示每个文件和目录的磁盘使用空间 命令参数 -c或--total 除了显示个别目录或文件的大小外,同时也显示所有目录或文件的总和. -s或--summarize 仅显示总计,只列出最后加总的 ...







 如上图,VGG16的卷积基有14714688个参数,非常多。在其上添加的分类器有200万个参数。
如上图,VGG16的卷积基有14714688个参数,非常多。在其上添加的分类器有200万个参数。






