Codeforces Round #283 (Div. 2) A. Minimum Difficulty【一个数组定义困难值是两个相邻元素之间差的最大值。 给一个数组,可以去掉任意一个元素,问剩余数列的困难值的最小值是多少】
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Mike is trying rock climbing but he is awful at it.
There are n holds on the wall, i-th hold is at height ai off the ground. Besides, let the sequence aiincrease, that is, ai < ai + 1 for all i from 1 to n - 1; we will call such sequence a track. Mike thinks that the track a1, ..., an has difficulty 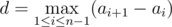 . In other words, difficulty equals the maximum distance between two holds that are adjacent in height.
. In other words, difficulty equals the maximum distance between two holds that are adjacent in height.
Today Mike decided to cover the track with holds hanging on heights a1, ..., an. To make the problem harder, Mike decided to remove one hold, that is, remove one element of the sequence (for example, if we take the sequence (1, 2, 3, 4, 5) and remove the third element from it, we obtain the sequence(1, 2, 4, 5)). However, as Mike is awful at climbing, he wants the final difficulty (i.e. the maximum difference of heights between adjacent holds after removing the hold) to be as small as possible among all possible options of removing a hold. The first and last holds must stay at their positions.
Help Mike determine the minimum difficulty of the track after removing one hold.
The first line contains a single integer n (3 ≤ n ≤ 100) — the number of holds.
The next line contains n space-separated integers ai (1 ≤ ai ≤ 1000), where ai is the height where the hold number i hangs. The sequence ai is increasing (i.e. each element except for the first one is strictly larger than the previous one).
Print a single number — the minimum difficulty of the track after removing a single hold.
3
1 4 6
5
5
1 2 3 4 5
2
5
1 2 3 7 8
4
In the first sample you can remove only the second hold, then the sequence looks like (1, 6), the maximum difference of the neighboring elements equals 5.
In the second test after removing every hold the difficulty equals 2.
In the third test you can obtain sequences (1, 3, 7, 8), (1, 2, 7, 8), (1, 2, 3, 8), for which the difficulty is 4, 5 and 5, respectively. Thus, after removing the second element we obtain the optimal answer — 4.
【题意】:对一个数组,定义困难值是两个相邻元素之间差的最大值。
现在又一个数组,可以去掉任意一个元素,问剩余数列的困难值的最小值是多少。
【分析】:由于数据小,可以枚举去掉的元素然后暴力更新,复杂度是 O(nn)。如果数据比较大的话,可以利用动态规划O(n)过。
【代码】:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define N 100010
using namespace std;
#define oo 99999
int a[110];
int b[110]; int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
cin>>a[i];
} int ans=oo;
for(int i=2;i<n;i++){
int k=0;
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++){
if(j==i)continue;
b[k++]=a[j];
}
int MAX=0;
for(int j=0;j<n-1;j++){
MAX=max(MAX,b[j+1]-b[j]);
}
ans=min(ans,MAX);
}
cout<<ans<<endl;
return 0;
}
Codeforces Round #283 (Div. 2) A. Minimum Difficulty【一个数组定义困难值是两个相邻元素之间差的最大值。 给一个数组,可以去掉任意一个元素,问剩余数列的困难值的最小值是多少】的更多相关文章
- Codeforces Round #283 (Div. 2) A. Minimum Difficulty 暴力水题
A. Minimum Difficulty time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standa ...
- 暴力+构造 Codeforces Round #283 (Div. 2) C. Removing Columns
题目传送门 /* 题意:删除若干行,使得n行字符串成递增排序 暴力+构造:从前往后枚举列,当之前的顺序已经正确时,之后就不用考虑了,这样删列最小 */ /*********************** ...
- 构造+暴力 Codeforces Round #283 (Div. 2) B. Secret Combination
题目传送门 /* 构造+暴力:按照题目意思,只要10次加1就变回原来的数字,暴力枚举所有数字,string大法好! */ /************************************** ...
- Codeforces Round #283 (Div. 2) A
解题思路:给出一个递增数列,a1,a2,a3,-----,an.问任意去掉a2到a3之间任意一个数之后, 因为注意到该数列是单调递增的,所以可以先求出原数列相邻两项的差值的最大值max, 得到新的一个 ...
- Codeforces Round #283 (Div. 2) A ,B ,C 暴力,暴力,暴力
A. Minimum Difficulty time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standa ...
- Codeforces Round #283 (Div. 2)
A:暴力弄就好,怎么方便怎么来. B:我们知道最多加10次, 然后每次加1后我们求能移动的最小值,大概O(N)的效率. #include<bits/stdc++.h> using name ...
- Codeforces Round #411 div 2 D. Minimum number of steps
D. Minimum number of steps time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input st ...
- Codeforces Round #283 (Div. 2) C. Removing Columns 暴力
C. Removing Columns time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard ...
- Codeforces Round #555 (Div. 3) E. Minimum Array 【数据结构 + 贪心】
一 题面 E. Minimum Array 二 分析 注意前提条件:$0 \le a_{i} \lt n$ 并且 $0 \le b_{i} \lt n$.那么,我们可以在$a_{i}$中任取一个数 ...
随机推荐
- elasticsearch 中文API facets(⑩)
facets Elasticsearch提供完整的java API用来支持facets.在查询的过程中,将需要计数的facets添加到FacetBuilders中.然后将该FacetBuilders条 ...
- 解决使用mybatis模糊查询为空的问题
解决方法: 在数据库配置的url后添加?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8 参考: https://blog.csdn.net/IT_private ...
- 从github下载项目出现yes/no的选项,无法下载项目
解决办法: # 本地执行: ssh-keygen # 将id_rsa_pub文件中公钥拷贝到github上的ssh认证 oodful@:~/Volumes/Term2 :::$cat ~/.ssh/i ...
- resin乱码
一.jsp乱码 为何jsp 在resin下乱码,但在tomcat下却工作良好的问题 关于JSP页面中的pageEncoding和contentType两种属性的区别: pageEncodi ...
- Ceisum官方教程3 -- 空间数据可视化
原文地址:https://cesiumjs.org/tutorials/Visualizing-Spatial-Data/ 这篇教程教你如何使用Cesium的Entity API去绘制空间数据,如点, ...
- JS基础之EL表达式
一.EL表达式简介 EL 全名为Expression Language.EL主要作用: 1.获取数据 EL表达式主要用于替换JSP页面中的脚本表达式,以从各种类型的web域 中检索java对象.获取数 ...
- [Day4] Nginx Http模块二
一. POST_READ阶段 1. 用户ip在http请求中的传递? 前提:Tcp连接四元组(src ip,src port,dst ip,dst port) HTTP头部 X-Formard ...
- Python学习之for循环--输出1-100中的偶数和登录身份认证
输出1-100中的偶数 效果图: 实现代码: for i in range(2,101,2): print(i,end = '\t') if(i == 34): print('\n') if (i = ...
- 责任链模式(Chain of Responsibility、Handler)(请求处理建立链)
(使多个对象都有机会处理请求,从而避免了请求的发送者和接受者之间的耦合关系.将这些对象连成一条链,并沿着这条链传递该请求,直到有对象处理它为止.) 从名字中看出 ,系统中将会存在多个有类似处理能力的对 ...
- spring-注解配置-junit整合测试-aop
1 使用注解配置spring 1.1 步骤 导包4+2+spring-aop 1.为主配置文件引入新的命名空间(约束) 2.开启使用注解代理配置文件 3.在类中使用注解完成配置 1.2 将对象注册到容 ...
