PAT甲级——A1131 Subway Map【30】
In the big cities, the subway systems always look so complex to the visitors. To give you some sense, the following figure shows the map of Beijing subway. Now you are supposed to help people with your computer skills! Given the starting position of your user, your task is to find the quickest way to his/her destination.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤ 100), the number of subway lines. Then N lines follow, with the i-th (,) line describes the i-th subway line in the format:
M S[1] S[2] ... S[M]
where M (≤ 100) is the number of stops, and S[i]'s (,) are the indices of the stations (the indices are 4-digit numbers from 0000 to 9999) along the line. It is guaranteed that the stations are given in the correct order -- that is, the train travels between S[i] and S[i+1] (,) without any stop.
Note: It is possible to have loops, but not self-loop (no train starts from S and stops at S without passing through another station). Each station interval belongs to a unique subway line. Although the lines may cross each other at some stations (so called "transfer stations"), no station can be the conjunction of more than 5 lines.
After the description of the subway, another positive integer K (≤ 10) is given. Then K lines follow, each gives a query from your user: the two indices as the starting station and the destination, respectively.
The following figure shows the sample map.
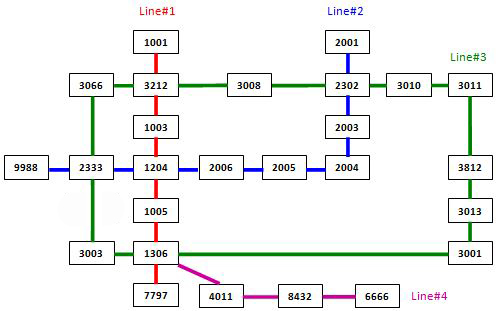
Note: It is guaranteed that all the stations are reachable, and all the queries consist of legal station numbers.
Output Specification:
For each query, first print in a line the minimum number of stops. Then you are supposed to show the optimal path in a friendly format as the following:
Take Line#X1 from S1 to S2.
Take Line#X2 from S2 to S3.
......
where Xi's are the line numbers and Si's are the station indices. Note: Besides the starting and ending stations, only the transfer stations shall be printed.
If the quickest path is not unique, output the one with the minimum number of transfers, which is guaranteed to be unique.
Sample Input:
4
7 1001 3212 1003 1204 1005 1306 7797
9 9988 2333 1204 2006 2005 2004 2003 2302 2001
13 3011 3812 3013 3001 1306 3003 2333 3066 3212 3008 2302 3010 3011
4 6666 8432 4011 1306
3
3011 3013
6666 2001
2004 3001
Sample Output:
2
Take Line#3 from 3011 to 3013.
10
Take Line#4 from 6666 to 1306.
Take Line#3 from 1306 to 2302.
Take Line#2 from 2302 to 2001.
6
Take Line#2 from 2004 to 1204.
Take Line#1 from 1204 to 1306.
Take Line#3 from 1306 to 3001.#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
vector<int> route[];
int visit[], minCnt, minTra, n, m, k, start, end1;
unordered_map<int, int>line;
vector<int>path, tempPath;
int transferCnt(vector<int>a)
{
int cnt = -, preLine = ;
for (int i = ; i < a.size(); ++i)
{
if (line[a[i - ] * + a[i]] != preLine)
{
cnt++;//换乘了
preLine = line[a[i - ] * + a[i]];
}
}
return cnt;
}
void DFS(int node, int cnt)
{
if (node == end1 && (cnt < minCnt || (cnt == minCnt && transferCnt(tempPath) < minTra)))
{
minCnt = cnt;
minTra = transferCnt(tempPath);
path = tempPath;
}
if (node == end1)return;
for (int i = ; i < route[node].size(); ++i)
{
if (visit[route[node][i]] == )//未遍历过
{
visit[route[node][i]] = ;
tempPath.push_back(route[node][i]);//保存可行路径
DFS(route[node][i], cnt + );//经过一站
visit[route[node][i]] = ;
tempPath.pop_back();//使用回溯法
}
}
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = ; i <= n; ++i)
{
cin >> m >> start;
for (int j = ; j < m; ++j)
{
cin >> end1;
route[start].push_back(end1);
route[end1].push_back(start);
line[start * + end1] = line[end1 * + start] = i;//用pot1*10000+pot来表示这两个站是可行的
start = end1;
}
}
cin >> k;
while (k--)
{
cin >> start >> end1;
minCnt = minTra = INT32_MAX-;
tempPath.clear();
tempPath.push_back(start);
visit[start] = ;
DFS(start, );
visit[start] = ;
cout << minCnt << endl;
int preLine = , preTra = start;
for (int i = ; i < path.size(); ++i)
{
if (line[path[i - ] * + path[i]] != preLine)//换乘了
{
if (preLine != )
printf("Take Line#%d from %04d to %04d.\n", preLine, preTra, path[i - ]);
preLine = line[path[i - ] * + path[i]];
preTra = path[i - ];
}
}
printf("Take Line#%d from %04d to %04d.\n", preLine, preTra, end1);
}
return ;
}
PAT甲级——A1131 Subway Map【30】的更多相关文章
- PAT甲级1131. Subway Map
PAT甲级1131. Subway Map 题意: 在大城市,地铁系统对访客总是看起来很复杂.给你一些感觉,下图显示了北京地铁的地图.现在你应该帮助人们掌握你的电脑技能!鉴于您的用户的起始位置,您的任 ...
- PAT甲级——1131 Subway Map (30 分)
可以转到我的CSDN查看同样的文章https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44385565/article/details/89003683 1131 Subway Map (30 ...
- A1131. Subway Map (30)
In the big cities, the subway systems always look so complex to the visitors. To give you some sense ...
- PAT甲级1131 Subway Map【dfs】【输出方案】
题目:https://pintia.cn/problem-sets/994805342720868352/problems/994805347523346432 题意: 告诉你一个地铁线路图,站点都是 ...
- PAT甲级1111. Online Map
PAT甲级1111. Online Map 题意: 输入我们当前的位置和目的地,一个在线地图可以推荐几条路径.现在你的工作是向你的用户推荐两条路径:一条是最短的,另一条是最快的.确保任何请求存在路径. ...
- PAT甲级——1111 Online Map (单源最短路经的Dijkstra算法、priority_queue的使用)
本文章同步发布在CSDN:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44385565/article/details/90041078 1111 Online Map (30 分) ...
- PAT 1131. Subway Map (30)
最短路. 记录一下到某个点,最后是哪辆车乘到的最短距离.换乘次数以及从哪个位置推过来的,可以开$map$记录一下. #include<map> #include<set> #i ...
- PAT甲级——A1111 Online Map【30】
Input our current position and a destination, an online map can recommend several paths. Now your jo ...
- PAT A1131 Subway Map
dfs,选择最优路径并输出~ 这道题难度非常炸裂,要求完完整整自己推一遍,DFS才算过关!思路:一遍dfs,过程中要维护两个变量,minCnt 中途停靠最少的站.minTransfer需要换成的最少次 ...
随机推荐
- Jenkins忘记 admin 密码
进入 jenkins home(我的是/var/jenkins_home)路径下的users 文件夹 cd /var/jenkins_home/users sudo vim admin/config. ...
- 1.MySQL基础架构
好久没发博客了,终于又学完了一点知识并且进行了整理.就从这个MySQL系列开始继续坚持每个月产出几篇. 声明一下,这次的MySQL系列是针对已有一定基础的小伙伴的,关于SQL的使用,一些概念的介绍就不 ...
- 【SQL】ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE
在实际应用中,经常碰到导入数据的功能,当导入的数据不存在时则进行添加,有修改时则进行更新, 在刚碰到的时候,第一反应是将其实现分为两块,分别是判断增加,判断更新,后来发现在mysql中有 ON DUP ...
- 好久没写题解了= =这次是bzoj 1051
唉= =这道题我都想到了tarjan缩点,但是没有想到最后一步啊= =我们很容易想到反向建边然后缩点,这时候我们看由多少个联通块的入度为0,如果为1个,那就输出这个块的大小,否则输出0: #inclu ...
- 43 编译原理及cmake使用手册学习
0 引言 大量开源库需要通过cmake编译后使用,了解cmake的基本指令以及CMakeLists.txt的写法非常重要,其基础是了解编译原理.另外,为了对cmake编译的代码进行调试,需要了解CMa ...
- NX二次开发-UFUN打开选择文件夹对话框UF_UI_create_filebox
#include <uf.h> #include <uf_ui.h> #include <string> using namespace std; string O ...
- (转) mysql的分区技术 .
转:http://blog.csdn.net/feihong247/article/details/8100960 一.概述 当 MySQL的总记录数超过了100万后,会出现性能的大幅度下降吗?答案是 ...
- Java-Class-C:org.springframework.http.converter.StringHttpMessageConverter
ylbtech-Java-Class-C:org.springframework.http.converter.StringHttpMessageConverter 1.返回顶部 1.1. impor ...
- pip安装时ReadTimeoutError解决办法
主要是被阻断了,所以可以延长等待时间完美解决问题. 在下载终端先输入如下命令: pip --default-timeout=100 install -U pip 然后输入下载命令:pip insta ...
- spark2.+ sql 性能调优
1.在内存中缓存数据 性能调优主要是将数据放入内存中操作,spark缓存注册表的方法 版本 缓存 释放缓存 spark2.+ spark.catalog.cacheTable("tableN ...
