王之泰201771010131《面向对象程序设计(java)》第十三周学习总结
第一部分:理论知识学习部分
第11章 事件处理
11.1 事件处理基础
a)事件源(event source):能够产生事件的对象都可 以成为事件源,如文本框、按钮等。一个事件源是一个 能够注册监听器并向监听器发送事件对象的对象。
b) 事件监听器(event listener):事件监听器对象接 收事件源发送的通告(事件对象),并对发生的事件作 出响应。一个监听器对象就是一个实现了专门监听器接 口的类实例,该类必须实现接口中的方法,这些方法当 事件发生时,被自动执行。
c) 事件对象(event object):Java将事件的相关信息 封装在一个事件对象中,所有的事件对象都最终派生于 java.util.EventObject类。不同的事件源可以产生不 同类别的事件。
11.2 动作
a) 激活一个命令可以有多种方式,如用户可以通过 菜单、击键或工具栏上的按钮选择特定的功能。
b) 在AWT事件模型中,无论是通过哪种方式下达命 令(如:点击按钮、菜单选项、按下键盘),其 操作动作都是一样的。
11.3 鼠标事件
a)鼠标事件 – MouseEvent
b)鼠标监听器接口 – MouseListener – MouseMotionListener
c) 鼠标监听器适配器 – MouseAdapter – MouseMotionAdapter
11.4 AWT事件继承层次
a) 所有的事件都是由java.util包中的EventObject 类扩展而来。
b) AWTEevent 是所有AWT 事件类的父类, 也是 EventObject的直接子类。
c) 有些Swing组件生成其他类型的事件对象,一般直 接 扩 展 于 EventObject, 而不是AWTEvent,位于 javax.swing.event.*。
d) 事件对象封装了事件源与监听器彼此通信的事件 信息。在必要的时候,可以对传递给监听器对象的 事件对象进行分析。
第二部分:实验部分——图形界面事件处理技术
实验时间 2018-11-22
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 掌握事件处理的基本原理,理解其用途;
(2) 掌握AWT事件模型的工作机制;
(3) 掌握事件处理的基本编程模型;
(4) 了解GUI界面组件观感设置方法;
(5) 掌握WindowAdapter类、AbstractAction类的用法;
(6) 掌握GUI程序中鼠标事件处理技术。
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1: 导入第11章示例程序,测试程序并进行代码注释。
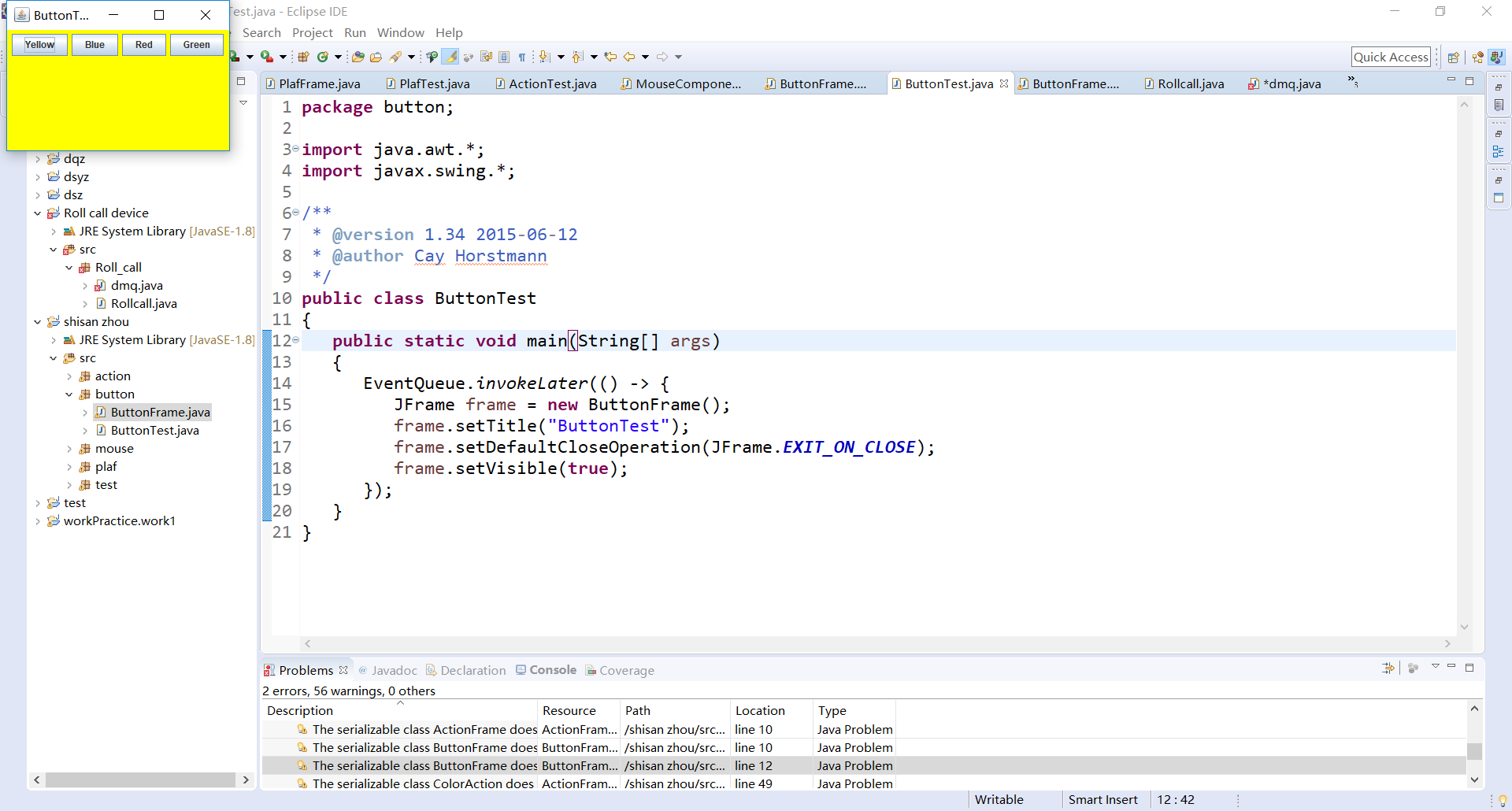
测试程序1:
1.在elipse IDE中调试运行教材443页-444页程序11-1,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
2.在事件处理相关代码处添加注释;
3.用lambda表达式简化程序;
4.掌握JButton组件的基本API;
5.掌握Java中事件处理的基本编程模型。
package test; import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*; /**
* 带按钮面板的框架
*/ public class ButtonFrame extends JFrame
{
private JPanel buttonPanel;
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 500;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 600; public ButtonFrame()
{
setSize(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); // 创建三个按钮
// JButton yellowButton = new JButton("Yellow");
// JButton blueButton = new JButton("Blue");
// JButton redButton = new JButton("Red"); buttonPanel = new JPanel(); // 向面板添加按钮
// buttonPanel.add(yellowButton);
// buttonPanel.add(blueButton);
// buttonPanel.add(redButton); // 将面板添加到帧
add(buttonPanel); // 创建按钮动作
// ColorAction yellowAction = new ColorAction(Color.YELLOW);
// ColorAction blueAction = new ColorAction(Color.BLUE);
// ColorAction redAction = new ColorAction(Color.RED);
//
// 用按钮关联动作
// yellowButton.addActionListener(yellowAction);
// blueButton.addActionListener(blueAction);
// redButton.addActionListener(redAction); MakeButton("黄色",Color.yellow);
MakeButton("蓝色",Color.blue);
MakeButton("红色",Color.red);
}
public void MakeButton(String name , Color backgroundColor)
{
JButton button=new JButton(name);
buttonPanel.add(button);
// ColorAction action=new ColorAction(backgroundColor);
// button.addActionListener(action);
button.addActionListener(new ActionListener()
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event)
{
buttonPanel.setBackground(backgroundColor);
}
}); } /**
* 设置面板背景颜色的动作侦听器
*/
private class ColorAction implements ActionListener
{
private Color backgroundColor; public ColorAction(Color c)
{
backgroundColor = c;
} public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event)
{
buttonPanel.setBackground(backgroundColor);
}
}
}
package button; import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*; /**
* @version 1.34 2015-06-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class ButtonTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new ButtonFrame();
frame.setTitle("ButtonTest");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
测试程序2:
1.在elipse IDE中调试运行教材449页程序11-2,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
2.在组件观感设置代码处添加注释;
3.了解GUI程序中观感的设置方法。
package plaf; import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JPanel;
import javax.swing.SwingUtilities;
import javax.swing.UIManager; /**
* 带有按钮面板的框架,用于改变外观和感觉
*/
public class PlafFrame extends JFrame
{
private JPanel buttonPanel; public PlafFrame()
{
buttonPanel = new JPanel(); UIManager.LookAndFeelInfo[] infos = UIManager.getInstalledLookAndFeels();
for (UIManager.LookAndFeelInfo info : infos)
makeButton(info.getName(), info.getClassName()); add(buttonPanel);
pack();
} /**
* 制作一个按钮来改变可插拔的外观和感觉.
* @param 命名按钮名称
* @param 类名:外观类的名称
*/
private void makeButton(String name, String className)
{
// 向面板添加按钮 JButton button = new JButton(name);
buttonPanel.add(button); // 设置按钮动作 button.addActionListener(event -> {
//按钮动作:切换到新的外观和感觉
try
{
UIManager.setLookAndFeel(className);
SwingUtilities.updateComponentTreeUI(this);
pack();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
}
package plaf; import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*; /**
* @version 1.32 2015-06-1222222222222222222222222222
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class PlafTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new PlafFrame();
frame.setTitle("PlafTest");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}

测试程序3:
1.在elipse IDE中调试运行教材457页-458页程序11-3,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
2.掌握AbstractAction类及其动作对象;
3.掌握GUI程序中按钮、键盘动作映射到动作对象的方法。
package action; import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*; /**
* @version 1.34 2015-06-1233333333333333333333333333
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class ActionTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new ActionFrame();
frame.setTitle("ActionTest");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
package action; import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*; /**
* 具有显示颜色变化动作的面板的框架
*/
public class ActionFrame extends JFrame
{
private JPanel buttonPanel;
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 200; public ActionFrame()
{
setSize(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); buttonPanel = new JPanel(); // 定义动作
Action yellowAction = new ColorAction("Yellow", new ImageIcon("yellow-ball.gif"),
Color.YELLOW);
Action blueAction = new ColorAction("Blue", new ImageIcon("blue-ball.gif"), Color.BLUE);
Action redAction = new ColorAction("Red", new ImageIcon("red-ball.gif"), Color.RED); // 为这些操作添加按钮
buttonPanel.add(new JButton(yellowAction));
buttonPanel.add(new JButton(blueAction));
buttonPanel.add(new JButton(redAction)); // 将面板添加到帧
add(buttonPanel); // 将Y、B和R键与名称关联
InputMap imap = buttonPanel.getInputMap(JComponent.WHEN_ANCESTOR_OF_FOCUSED_COMPONENT);
imap.put(KeyStroke.getKeyStroke("ctrl Y"), "panel.yellow");
imap.put(KeyStroke.getKeyStroke("ctrl B"), "panel.blue");
imap.put(KeyStroke.getKeyStroke("ctrl R"), "panel.red"); // 把名字和动作联系起来
ActionMap amap = buttonPanel.getActionMap();
amap.put("panel.yellow", yellowAction);
amap.put("panel.blue", blueAction);
amap.put("panel.red", redAction);
} public class ColorAction extends AbstractAction
{
/**
* 构造颜色动作。
* @param 在按钮上显示要显示的名称
* @param 图标按钮上显示的图标
* @param 背景颜色
*/
public ColorAction(String name, Icon icon, Color c)
{
putValue(Action.NAME, name);
putValue(Action.SMALL_ICON, icon);
putValue(Action.SHORT_DESCRIPTION, "Set panel color to " + name.toLowerCase());
putValue("color", c);
} public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event)
{
Color c = (Color) getValue("color");
buttonPanel.setBackground(c);
}
}
}
测试程序4:
1.在elipse IDE中调试运行教材462页程序11-4、11-5,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
2.掌握GUI程序中鼠标事件处理技术。
package mouse; import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*; /**
* @version 1.34 2015-06-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class MouseTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new MouseFrame();
frame.setTitle("MouseTest");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
package mouse; import javax.swing.*; /**
* 包含用于测试鼠标操作的面板的框架
*/
public class MouseFrame extends JFrame
{
public MouseFrame()
{
add(new MouseComponent());
pack();
}
}
package mouse; import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.awt.geom.*;
import java.util.*;
import javax.swing.*; /**
*一个带有鼠标操作的用于添加和删除正方形的组件。
*/
public class MouseComponent extends JComponent
{
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 200; private static final int SIDELENGTH = 10;
private ArrayList<Rectangle2D> squares;
private Rectangle2D current; // 包含鼠标光标的正方形 public MouseComponent()
{
squares = new ArrayList<>();
current = null; addMouseListener(new MouseHandler());
addMouseMotionListener(new MouseMotionHandler());
} public Dimension getPreferredSize() { return new Dimension(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT); } public void paintComponent(Graphics g)
{
Graphics2D g2 = (Graphics2D) g; // 绘制所有正方形
for (Rectangle2D r : squares)
g2.draw(r);
} /**
* 找到包含一个点的第一个方块。
* @param P—A点
* @return 包含P的第一个正方形
*/
public Rectangle2D find(Point2D p)
{
for (Rectangle2D r : squares)
{
if (r.contains(p)) return r;
}
return null;
} /**
* 向集合中添加正方形。
* @param 新闻中心
*/
public void add(Point2D p)
{
double x = p.getX();
double y = p.getY(); current = new Rectangle2D.Double(x - SIDELENGTH / 2, y - SIDELENGTH / 2, SIDELENGTH,
SIDELENGTH);
squares.add(current);
repaint();
} /**
* 从集合中移除正方形。
* @param S方移除
*/
public void remove(Rectangle2D s)
{
if (s == null) return;
if (s == current) current = null;
squares.remove(s);
repaint();
} private class MouseHandler extends MouseAdapter
{
public void mousePressed(MouseEvent event)
{
// 如果光标不在正方形中,则添加一个新的正方形
current = find(event.getPoint());
if (current == null) add(event.getPoint());
} public void mouseClicked(MouseEvent event)
{
// 如果双击,则移除当前正方形
current = find(event.getPoint());
if (current != null && event.getClickCount() >= 2) remove(current);
}
} private class MouseMotionHandler implements MouseMotionListener
{
public void mouseMoved(MouseEvent event)
{
// 设置鼠标光标,如果里面是交叉头发
// 矩形 if (find(event.getPoint()) == null) setCursor(Cursor.getDefaultCursor());
else setCursor(Cursor.getPredefinedCursor(Cursor.CROSSHAIR_CURSOR));
} public void mouseDragged(MouseEvent event)
{
if (current != null)
{
int x = event.getX();
int y = event.getY(); // 拖动当前矩形将其置于(x,y)中心
current.setFrame(x - SIDELENGTH / 2, y - SIDELENGTH / 2, SIDELENGTH, SIDELENGTH);
repaint();
}
}
}
}

实验2:结对编程练习
利用班级名单文件、文本框和按钮组件,设计一个有界面的点名器,要求用户点击开始按钮后在文本输入框随机显示2017级网络与信息安全班同学姓名,点击停止按钮后,文本输入框不再变换同学姓名,此同学则是被点到的同学姓名。
package Roll_call_device; import java.awt.Color;
import java.awt.FlowLayout;
import java.awt.Label;
import java.awt.event.ActionEvent;
import java.awt.event.ActionListener;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList; import javax.swing.JButton;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.Timer; public class Rollcall
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
try {
Dmq dmq = new Dmq();
dmq.lab.setText("随机点名器");
dmq.setTitle("点名器");
} catch (IOException e)
{
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} class Dmq extends JFrame
{
final Label lab = new Label();
ArrayList<String> namelist = new ArrayList<String>(); public Dmq() throws IOException
{
File file = new File("src/studentnamelist.txt");
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
InputStreamReader isr = new InputStreamReader(fis, "GBK");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
String line = "";
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null)
{
if (line.lastIndexOf("---") < 0)
{
namelist.add(line);
}
}
setBounds(550, 270, 200, 150);
final Timer timer = new Timer(50, new ActionListener()
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
{
lab.setText(namelist.get((int) (Math.random() * namelist.size())));
}
}); JButton jbutton = new JButton("开始");
jbutton.addActionListener(new ActionListener()
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e)
{
JButton jbutton = (JButton) e.getSource();
if (jbutton.getText().equals("开始"))
{
jbutton.setText("停止");
timer.start();
} else if (jbutton.getText().equals("停止"))
{
jbutton.setText("开始");
timer.stop();
} }
});
jbutton.setBounds(30, 30, 30, 30);
lab.setBackground(new Color(255, 255, 255));
this.setLayout(new FlowLayout());
this.add(lab);
this.add(jbutton);
this.setSize(300, 200);
this.setVisible(true);
this.setDefaultCloseOperation(EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
br.close();
} }

第三部分:总结
通过本周的学习,我掌握了事件处理的基本原理,理解了用途;并了解学习了以下几点。AWT事件模型的工作机制;事件处理的基本编程模型;了解了GUI界面组件观感设置方法;WindowAdapter类、AbstractAction类的用法;GUI程序中鼠标事件处理技术。并且在看了助教学长的教学视频和同学的帮助下,学会了如何设计一个小型界面,受益颇多!
王之泰201771010131《面向对象程序设计(java)》第十三周学习总结的更多相关文章
- 201871010124 王生涛《面向对象程序设计JAVA》第一周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/xbsf/ ...
- 201771010134杨其菊《面向对象程序设计java》第九周学习总结
第九周学习总结 第一部分:理论知识 异常.断言和调试.日志 1.捕获 ...
- 201871010132-张潇潇《面向对象程序设计(java)》第一周学习总结
面向对象程序设计(Java) 博文正文开头 项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cn ...
- 扎西平措 201571030332《面向对象程序设计 Java 》第一周学习总结
<面向对象程序设计(java)>第一周学习总结 正文开头: 项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 ...
- 杨其菊201771010134《面向对象程序设计Java》第二周学习总结
第三章 Java基本程序设计结构 第一部分:(理论知识部分) 本章主要学习:基本内容:数据类型:变量:运算符:类型转换,字符串,输入输出,控制流程,大数值以及数组. 1.基本概念: 1)标识符:由字母 ...
- 201871010115——马北《面向对象程序设计JAVA》第二周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p ...
- 201777010217-金云馨《面向对象程序设计(Java)》第二周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p ...
- 201871010132——张潇潇《面向对象程序设计JAVA》第二周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p ...
- 201771010123汪慧和《面向对象程序设计Java》第二周学习总结
一.理论知识部分 1.标识符由字母.下划线.美元符号和数字组成, 且第一个符号不能为数字.标识符可用作: 类名.变量名.方法名.数组名.文件名等.第二部分:理论知识学习部分 2.关键字就是Java语言 ...
- 201521123061 《Java程序设计》第十三周学习总结
201521123061 <Java程序设计>第十三周学习总结 1. 本周学习总结 2. 书面作业 1. 网络基础 1.1 比较ping www.baidu.com与ping cec.jm ...
随机推荐
- iconfont在线链接使用方法(转)
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/jinkingliao/article/details/51353937 基础流程就不多赘述,直接到http://www.iconfont.cn/官网 ...
- uboot - the bootloader of linux
[转载]https://blog.csdn.net/kernel_yx/article/details/53045424 最近一段时间一直在做uboot移植相关的工作,需要将uboot-2016-7移 ...
- 解决No converter found for return value of type: class java.util.ArrayList
十一月 02, 2018 7:37:44 下午 org.apache.catalina.core.StandardWrapperValve invoke 严重: Servlet.service() f ...
- oracle 主键,非空,检查,唯一,默认,外键约束
--首先添加主键约束alter table studentadd constraint PK_student_sno primary key(sno) --删除约束alter table studen ...
- tesseract库
1.简介 # -*-coding:utf8 -*- #图形验证码识别技术 ''' 阻碍我们爬虫的,有时候是在登录或者请求一些数据时候的图形验证码.因此这里我们讲解 一种能将图片翻译成文字的技术.将图片 ...
- gitbook build/serve 失败,Error: ENOENT: no such file or directory, stat ...
我使用的 gitbook 版本 CLI version: 2.3.2 GitBook version: 3.2.3 在使用 gitbook 生成文档时,发现编译偶尔不规律性地出现错误 d:\Mine\ ...
- 做一个有产品思维的研发:部署(Tomcat配置,Nginx配置,JDK配置)
每天10分钟,解决一个研发问题. 如果你想了解我在做什么,请看<做一个有产品思维的研发:课程大纲>传送门:https://www.cnblogs.com/hunttown/p/104909 ...
- Scala简介、安装、函数、面向对象
Scala是一门以java虚拟机(JVM)为目标运行环境并将面向对象和函数式编程的最佳特性结合在一起的静态类型编程语言. scala命令行窗口,我们称之为REPL,是指:Read->Evalua ...
- laravel中get()与 first()区别、collection与stdClass的区别
简单的,laravel里get()得到的是一组数据,first()得到的是一个model数据. 从形式上,laravel里每一个model数据(record),在取出的时候都是用的PHP的stdCla ...
- Python练习:爬虫练习,从一个提供免费代理的网站中爬取IP地址信息
西刺代理,http://www.xicidaili.com/,提供免费代理的IP,是爬虫程序的目标网站. 开始写程序 import urllib.requestimport re def open_u ...
