关联容器:unordered_map详细介绍
版权声明:博主辛辛苦苦码的字哦~转载注明一下啦~ <a class="copy-right-url" href=" https://blog.csdn.net/hk2291976/article/details/51037095"> https://blog.csdn.net/hk2291976/article/details/51037095</a>
</div>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://csdnimg.cn/release/phoenix/template/css/ck_htmledit_views-3019150162.css">
<div id="content_views" class="markdown_views">
<!-- flowchart 箭头图标 勿删 -->
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" style="display: none;">
<path stroke-linecap="round" d="M5,0 0,2.5 5,5z" id="raphael-marker-block" style="-webkit-tap-highlight-color: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0);"></path>
</svg>
<p></p><div class="toc"><div class="toc">
1.介绍
最近使用到一个c++的容器——unordered_map,它是一个关联容器,内部采用的是hash表结构,拥有快速检索的功能。
1.1 特性
- 关联性:通过key去检索value,而不是通过绝对地址(和顺序容器不同)
- 无序性:使用hash表存储,内部无序
- Map : 每个值对应一个键值
- 键唯一性:不存在两个元素的键一样
- 动态内存管理:使用内存管理模型来动态管理所需要的内存空间
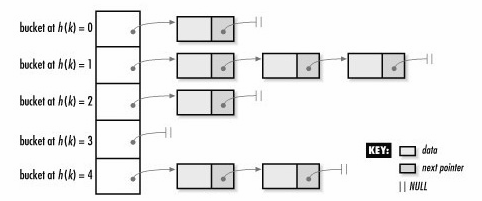
1.2 Hashtable和bucket
由于unordered_map内部采用的hashtable的数据结构存储,所以,每个特定的key会通过一些特定的哈希运算映射到一个特定的位置,我们知道,hashtable是可能存在冲突的(多个key通过计算映射到同一个位置),在同一个位置的元素会按顺序链在后面。所以把这个位置称为一个bucket是十分形象的(像桶子一样,可以装多个元素)。可以参考这篇介绍哈希表的文章
所以unordered_map内部其实是由很多哈希桶组成的,每个哈希桶中可能没有元素,也可能有多个元素。
2. 模版
template < class Key, // unordered_map::key_type
class T, // unordered_map::mapped_type
class Hash = hash<Key>, // unordered_map::hasher
class Pred = equal_to<Key>, // unordered_map::key_equal
class Alloc = allocator< pair<const Key,T> > // unordered_map::allocator_type
> class unordered_map;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
主要使用的也是模板的前2个参数<键,值>(需要更多的介绍可以点击这里)
unordered_map<const Key, T> map;
- 1
2.1 迭代器
unordered_map的迭代器是一个指针,指向这个元素,通过迭代器来取得它的值。
unordered_map<Key,T>::iterator it;
(*it).first; // the key value (of type Key)
(*it).second; // the mapped value (of type T)
(*it); // the "element value" (of type pair<const Key,T>)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
它的键值分别是迭代器的first和second属性。
it->first; // same as (*it).first (the key value)
it->second; // same as (*it).second (the mapped value)
- 1
- 2
3. 功能函数
3.1 构造函数
unordered_map的构造方式有几种:
- 构造空的容器
- 复制构造
- 范围构造
- 用数组构造
3.1.2示例代码
// constructing unordered_maps
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
typedef unordered_map<string,string> stringmap;
stringmap merge (stringmap a,stringmap b) {
stringmap temp(a); temp.insert(b.begin(),b.end()); return temp;
}
int main ()
{
stringmap first; // 空
stringmap second ( {{"apple","red"},{"lemon","yellow"}} ); // 用数组初始
stringmap third ( {{"orange","orange"},{"strawberry","red"}} ); // 用数组初始
stringmap fourth (second); // 复制初始化
stringmap fifth (merge(third,fourth)); // 移动初始化
stringmap sixth (fifth.begin(),fifth.end()); // 范围初始化
cout << "sixth contains:";
for (auto& x: sixth) cout << " " << x.first << ":" << x.second;
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
输出结果:
sixth contains: apple:red lemon:yellow orange:orange strawberry:red
- 1
3.2 容量操作
3.2.1 size
size_type size() const noexcept;
- 1
返回unordered_map的大小
3.2.2 empty
bool empty() const noexcept;
- 1
- 为空返回true
- 不为空返回false,和用size() == 0判断一样。
3.3 元素操作
3.3.1 find
iterator find ( const key_type& k );
- 1
查找key所在的元素。
- 找到:返回元素的迭代器。通过迭代器的second属性获取值
- 没找到:返回unordered_map::end
3.3.2 insert
插入有几种方式:
- 复制插入(复制一个已有的pair的内容)
- 数组插入(直接插入一个二维数组)
- 范围插入(复制一个起始迭代器和终止迭代器中间的内容)
- 数组访问模式插入(和数组的[]操作很相似)
具体的例子可以看后面示例代码。
3.3.3 at
mapped_type& at ( const key_type& k );
- 1
查找key所对应的值
- 如果存在:返回key对应的值,可以直接修改,和[]操作一样。
- 如果不存在:抛出 out_of_range 异常.
mymap.at(“Mars”) = 3396; //mymap[“Mars”] = 3396
3.3.4 erase
擦除元素也有几种方式:
通过位置(迭代器)
iterator erase ( const_iterator position );- 1
通过key
size_type erase ( const key_type& k );- 1
通过范围(两个迭代器)
iterator erase ( const_iterator first, const_iterator last );- 1
3.3.5 clear
void clear() noexcept
- 1
清空unordered_map
3.3.6 swap
void swap ( unordered_map& ump );
- 1
交换两个unordered_map(注意,不是交换特定元素,是整个交换两个map中的所有元素)
3.3.7 示例代码
// unordered_map::insert
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
void display(unordered_map<string,double> myrecipe,string str)
{
cout << str << endl;
for (auto& x: myrecipe)
cout << x.first << ": " << x.second << endl;
cout << endl;
}
int main ()
{
unordered_map<string,double>
myrecipe,
mypantry = {{"milk",2.0},{"flour",1.5}};
/****************插入*****************/
pair<string,double> myshopping ("baking powder",0.3);
myrecipe.insert (myshopping); // 复制插入
myrecipe.insert (make_pair<string,double>("eggs",6.0)); // 移动插入
myrecipe.insert (mypantry.begin(), mypantry.end()); // 范围插入
myrecipe.insert ({{"sugar",0.8},{"salt",0.1}}); // 初始化数组插入(可以用二维一次插入多个元素,也可以用一维插入一个元素)
myrecipe["coffee"] = 10.0; //数组形式插入
display(myrecipe,"myrecipe contains:");
/****************查找*****************/
unordered_map<string,double>::const_iterator got = myrecipe.find ("coffee");
if ( got == myrecipe.end() )
cout << "not found";
else
cout << "found "<<got->first << " is " << got->second<<"\n\n";
/****************修改*****************/
myrecipe.at("coffee") = 9.0;
myrecipe["milk"] = 3.0;
display(myrecipe,"After modify myrecipe contains:");
/****************擦除*****************/
myrecipe.erase(myrecipe.begin()); //通过位置
myrecipe.erase("milk"); //通过key
display(myrecipe,"After erase myrecipe contains:");
/****************交换*****************/
myrecipe.swap(mypantry);
display(myrecipe,"After swap with mypantry, myrecipe contains:");
/****************清空*****************/
myrecipe.clear();
display(myrecipe,"After clear, myrecipe contains:");
return 0;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
输出结果:
myrecipe contains:
salt: 0.1
milk: 2
flour: 1.5
coffee: 10
eggs: 6
sugar: 0.8
baking powder: 0.3
found coffee is 10
After modify myrecipe contains:
salt: 0.1
milk: 3
flour: 1.5
coffee: 9
eggs: 6
sugar: 0.8
baking powder: 0.3
After erase myrecipe contains:
flour: 1.5
coffee: 9
eggs: 6
sugar: 0.8
baking powder: 0.3
After swap with mypantry, myrecipe contains:
flour: 1.5
milk: 2
After clear, myrecipe contains:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
3.4 迭代器和bucket操作
3.4.1 begin
iterator begin() noexcept;
local_iterator begin ( size_type n );
- 1
- 2
- begin() : 返回开始的迭代器(和你的输入顺序没关系,因为它的无序的)
- begin(int n) : 返回n号bucket的第一个迭代器
3.4.2 end
iterator end() noexcept;
local_iterator end( size_type n );
- 1
- 2
- end(): 返回结束位置的迭代器
- end(int n) : 返回n号bucket的最后一个迭代器
3.4.3 bucket
size_type bucket ( const key_type& k ) const;
- 1
返回通过哈希计算key所在的bucket(注意:这里仅仅做哈希计算确定bucket,并不保证key一定存在bucket中!)
3.4.4 bucket_count
size_type bucket_count() const noexcept;
- 1
返回bucket的总数
3.4.5 bucket_size
size_type bucket_size ( size_type n ) const;
- 1
返回第i个bucket的大小(这个位置的桶子里有几个元素,注意:函数不会判断n是否在count范围内)
3.4.6 示例代码
// unordered_map::bucket_count
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
unordered_map<string,string> mymap =
{
{"house","maison"},
{"apple","pomme"},
{"tree","arbre"},
{"book","livre"},
{"door","porte"},
{"grapefruit","pamplemousse"}
};
/************begin和end迭代器***************/
cout << "mymap contains:";
for ( auto it = mymap.begin(); it != mymap.end(); ++it )
cout << " " << it->first << ":" << it->second;
cout << endl;
/************bucket操作***************/
unsigned n = mymap.bucket_count();
cout << "mymap has " << n << " buckets.\n";
for (unsigned i=0; i<n; ++i)
{
cout << "bucket #" << i << "'s size:"<<mymap.bucket_size(i)<<" contains: ";
for (auto it = mymap.begin(i); it!=mymap.end(i); ++it)
cout << "[" << it->first << ":" << it->second << "] ";
cout << "\n";
}
cout <<"\nkey:'apple' is in bucket #" << mymap.bucket("apple") <<endl;
cout <<"\nkey:'computer' is in bucket #" << mymap.bucket("computer") <<endl;
return 0;
}
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
输出结果:
mymap contains: door:porte grapefruit:pamplemousse tree:arbre apple:pomme book:livre house:maison
mymap has 7 buckets.
bucket #0's size:2 contains: [book:livre] [house:maison]
bucket #1's size:0 contains:
bucket #2's size:0 contains:
bucket #3's size:2 contains: [grapefruit:pamplemousse] [tree:arbre]
bucket #4's size:0 contains:
bucket #5's size:1 contains: [apple:pomme]
bucket #6's size:1 contains: [door:porte]
key:'apple' is in bucket #5
key:'computer' is in bucket #6
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
最后
unordered_map常用的功能函数介绍就这么多了,还有一些比较不常用的功能的介绍,可以参考这里
关联容器:unordered_map详细介绍的更多相关文章
- 关联容器:unordered_map详细介绍(附可运行代码)
介绍 1 特性 2 Hashtable和bucket 模版 1 迭代器 功能函数 1 构造函数 12示例代码 2 容量操作 21 size 22 empty 3 元素操作 31 find 32 ins ...
- web.xml 详细介绍(转)
web.xml 详细介绍 1.启动一个WEB项目的时候,WEB容器会去读取它的配置文件web.xml,读取<listener>和<context-param>两个结点. 2.紧 ...
- Java 集合系列 10 Hashtable详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例
java 集合系列目录: Java 集合系列 01 总体框架 Java 集合系列 02 Collection架构 Java 集合系列 03 ArrayList详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例 Java ...
- web.xml 详细介绍(zz)
web.xml 详细介绍 博客分类: CoreJava WebXMLServletJSPTomcat http://mianhuaman.iteye.com/blog/1105522 1.启动一个W ...
- Tkinter 控件详细介绍
Tkinter 控件详细介绍 1.Button 按钮.类似标签,但提供额外的功能,例如鼠标掠过.按下.释放以及键盘操作/事件 2.Canvas 画布.提供绘图功能(直线.椭圆.多边形.矩形) ;可以包 ...
- 《STL源码剖析》——第五、六:关联容器与算法
第五章.关联容器 5.0.关联容器 标准的STL关联式容器分为set(集合)和map(映射表)两大类,以及这两大类的衍生体multiset(多键集合)和multimap(多键映射表).这些容器的底层 ...
- Oracle Merge into 详细介绍
Oracle Merge into 详细介绍 /*Merge into 详细介绍MERGE语句是Oracle9i新增的语法,用来合并UPDATE和INSERT语句.通过MERGE语句,根据一张表或子查 ...
- Java 集合系列12之 TreeMap详细介绍(源码解析)和使用示例
概要 这一章,我们对TreeMap进行学习.我们先对TreeMap有个整体认识,然后再学习它的源码,最后再通过实例来学会使用TreeMap.内容包括:第1部分 TreeMap介绍第2部分 TreeMa ...
- C++中引用与指针的区别(详细介绍)
C++中引用与指针的区别(详细介绍) C++中的引用与指针的区别 指向不同类型的指针的区别在于指针类型可以知道编译器解释某个特定地址(指针指向的地址)中的内存内容及大小,而void*指针则只表示一 ...
随机推荐
- laravel Excel导入导出
1.简介 Laravel Excel 在 Laravel 5 中集成 PHPOffice 套件中的 PHPExcel,从而方便我们以优雅的.富有表现力的代码实现Excel/CSV文件的导入和导出. 该 ...
- blog主题——黑夜
blog主题,存储一下 /* Author: Io_oTI*/ /*Public*/ * { margin: 0; padding: 0; box-sizing: border-box; trans ...
- 【C语言】计算N名同学的某门功课的平均成绩
分析: 循环输入number只童鞋的成绩,累加为sum,最后输出sum/number即可! 代码: #include<stdio.h> int main() { , score;//sco ...
- 【Python 多进程】
" 一.模块介绍 multiprocess模快 仔细说来,multiprocess不是一个模块,而是python中的一个操作.管理进程的包,之所以叫multi是取自multiple的多功能的 ...
- X86汇编指令集大全【转】
[原文地址]https://blog.csdn.net/bjbz_cxy/article/details/79467688[原文地址] ---------- 一.数据传输指令 ------------ ...
- FYF的煎饼果子
利用等差数列公式就行了,可以考虑特判一下m >= n($ m, n \neq 1 $),这时一定输出“AIYAMAYA”. #include <iostream> using nam ...
- 【实战】Springboot +jjwt+注解实现需登录才能操作
springboot +jjwt+注解实现需登录才能调用接口 1.开发需要登录才能进行操作的自定义注解NeedLogin,后面可以写在需要登陆后操作的接口上 package com.songzhen. ...
- SQL 层级数据查询出树形状态
WITH TEST AS (SELECT DEPTID,PARENTDEPT,SORTORDER,1 SPAC,CONVERT(CHAR(200),RTRIM(DEPTID)+CONVERT(CHA ...
- combobox实现模糊搜索匹配
如图,输入关键字,进行匹配检索: 这里使用的是combobox组合框,对于combobox的创建可以使用<input>输入框,也可以使用<select>下拉选 HTML代码: ...
- C:C语言中表示进制数
#include <stdio.h> int main() { int a = 123; //十进制方式赋值 int b = 0123; //八进制方式赋值, 以数字0开头 int c = ...