最简 Spring IOC 容器源码分析

前言
许多文章都是分析的 xml 配置,但是现在 Spring Boot 开发多基于注解。本文从注解的角度分析 Spring IOC 容器源码。
版本:
- Spring Boot:2.1.6.RELEASE
- Spring FrameWork:5.1.8.RELEASE
- Java 8
文章部分内容参考自:https://www.javadoop.com/post/spring-ioc
BeanDefinition
BeanDefinition 接口定义了一个包含属性、构造器参数、其他具体信息的 bean 实例。
public interface BeanDefinition extends AttributeAccessor, BeanMetadataElement {
// ConfigurableBeanFactory 中只有 2 种:singleton 和 prototype。
// request, session 等是基于 Web 的扩展
String SCOPE_SINGLETON = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_SINGLETON;
String SCOPE_PROTOTYPE = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE;
// 不重要
int ROLE_APPLICATION = 0;
int ROLE_SUPPORT = 1;
int ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE = 2;
// 设置父 Bean 的信息(继承父 Bean 的配置信息)
void setParentName(@Nullable String parentName);
@Nullable
String getParentName();
// 设置 Bean 的类名称,要通过反射来生成实例
void setBeanClassName(@Nullable String beanClassName);
// 返回当前 Bean 的 class name
String getBeanClassName();
void setScope(@Nullable String scope);
@Nullable
String getScope();
// 是否延迟初始化
void setLazyInit(boolean lazyInit);
boolean isLazyInit();
// 设置该 Bean 依赖的所有的 Bean,并非 @Autowire 标记的
void setDependsOn(@Nullable String... dependsOn);
@Nullable
String[] getDependsOn();
// 设置该 Bean 是否可以注入到其他 Bean 中,只对根据类型注入有效,
// 如果根据名称注入,即使这边设置了 false,也是可以的
void setAutowireCandidate(boolean autowireCandidate);
boolean isAutowireCandidate();
// 同一接口的多个实现,如果不指定名字,Spring 会优先选择设置 primary 为 true 的 bean
void setPrimary(boolean primary);
boolean isPrimary();
// 如果该 Bean 采用工厂方法生成,指定工厂名称;否则用反射生成
void setFactoryBeanName(@Nullable String factoryBeanName);
@Nullable
String getFactoryBeanName();
// 指定工厂类中的 工厂方法名称
void setFactoryMethodName(@Nullable String factoryMethodName);
@Nullable
String getFactoryMethodName();
// 返回该 bean 的构造器参数
ConstructorArgumentValues getConstructorArgumentValues();
default boolean hasConstructorArgumentValues() {
return !getConstructorArgumentValues().isEmpty();
}
// Bean 中的属性值,返回的实例在 bean factory post-processing 期间会被更改
MutablePropertyValues getPropertyValues();
default boolean hasPropertyValues() {
return !getPropertyValues().isEmpty();
}
void setInitMethodName(@Nullable String initMethodName);
@Nullable
String getInitMethodName();
void setDestroyMethodName(@Nullable String destroyMethodName);
@Nullable
String getDestroyMethodName();
void setRole(int role);
int getRole();
void setDescription(@Nullable String description);
@Nullable
String getDescription();
// Read-only attributes
boolean isSingleton();
boolean isPrototype();
boolean isAbstract();
@Nullable
String getResourceDescription();
@Nullable
BeanDefinition getOriginatingBeanDefinition();
}
AnnotationConfigUtils#processCommonDefinitionAnnotations(...)
static void processCommonDefinitionAnnotations(AnnotatedBeanDefinition abd, AnnotatedTypeMetadata metadata) {
AnnotationAttributes lazy = attributesFor(metadata, Lazy.class);
if (lazy != null) {
abd.setLazyInit(lazy.getBoolean("value"));
}
else if (abd.getMetadata() != metadata) {
lazy = attributesFor(abd.getMetadata(), Lazy.class);
if (lazy != null) {
abd.setLazyInit(lazy.getBoolean("value"));
}
}
if (metadata.isAnnotated(Primary.class.getName())) {
abd.setPrimary(true);
}
AnnotationAttributes dependsOn = attributesFor(metadata, DependsOn.class);
if (dependsOn != null) {
abd.setDependsOn(dependsOn.getStringArray("value"));
}
AnnotationAttributes role = attributesFor(metadata, Role.class);
if (role != null) {
abd.setRole(role.getNumber("value").intValue());
}
AnnotationAttributes description = attributesFor(metadata, Description.class);
if (description != null) {
abd.setDescription(description.getString("value"));
}
}
可以看到,processCommonDefinitionAnnotations 方法会根据注解来填充 AnnotatedBeanDefinition,这些注解有:
- Lazy
- Primary
- DependsOn
- Role
- Description
向上查看调用,发现会在 ConfigurationClassBeanDefinitionReader#registerBeanDefinitionForImportedConfigurationClass 将其注册为一个 bean definition。
private void registerBeanDefinitionForImportedConfigurationClass(ConfigurationClass configClass) {
AnnotationMetadata metadata = configClass.getMetadata();
AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition configBeanDef = new AnnotatedGenericBeanDefinition(metadata);
ScopeMetadata scopeMetadata = scopeMetadataResolver.resolveScopeMetadata(configBeanDef);
configBeanDef.setScope(scopeMetadata.getScopeName());
String configBeanName = this.importBeanNameGenerator.generateBeanName(configBeanDef, this.registry);
// 1. 通过注解填充 configBeanDef
AnnotationConfigUtils.processCommonDefinitionAnnotations(configBeanDef, metadata);
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder = new BeanDefinitionHolder(configBeanDef, configBeanName);
definitionHolder = AnnotationConfigUtils.applyScopedProxyMode(scopeMetadata, definitionHolder, this.registry);
// 2. 将 bean definition 注册到 registry 中
this.registry.registerBeanDefinition(definitionHolder.getBeanName(), definitionHolder.getBeanDefinition());
configClass.setBeanName(configBeanName);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Registered bean definition for imported class '" + configBeanName + "'");
}
}
最终会被 AbstractApplicationContext#refresh 的 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory) 方法调用。
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
...
}
}
BeanFactory 简介
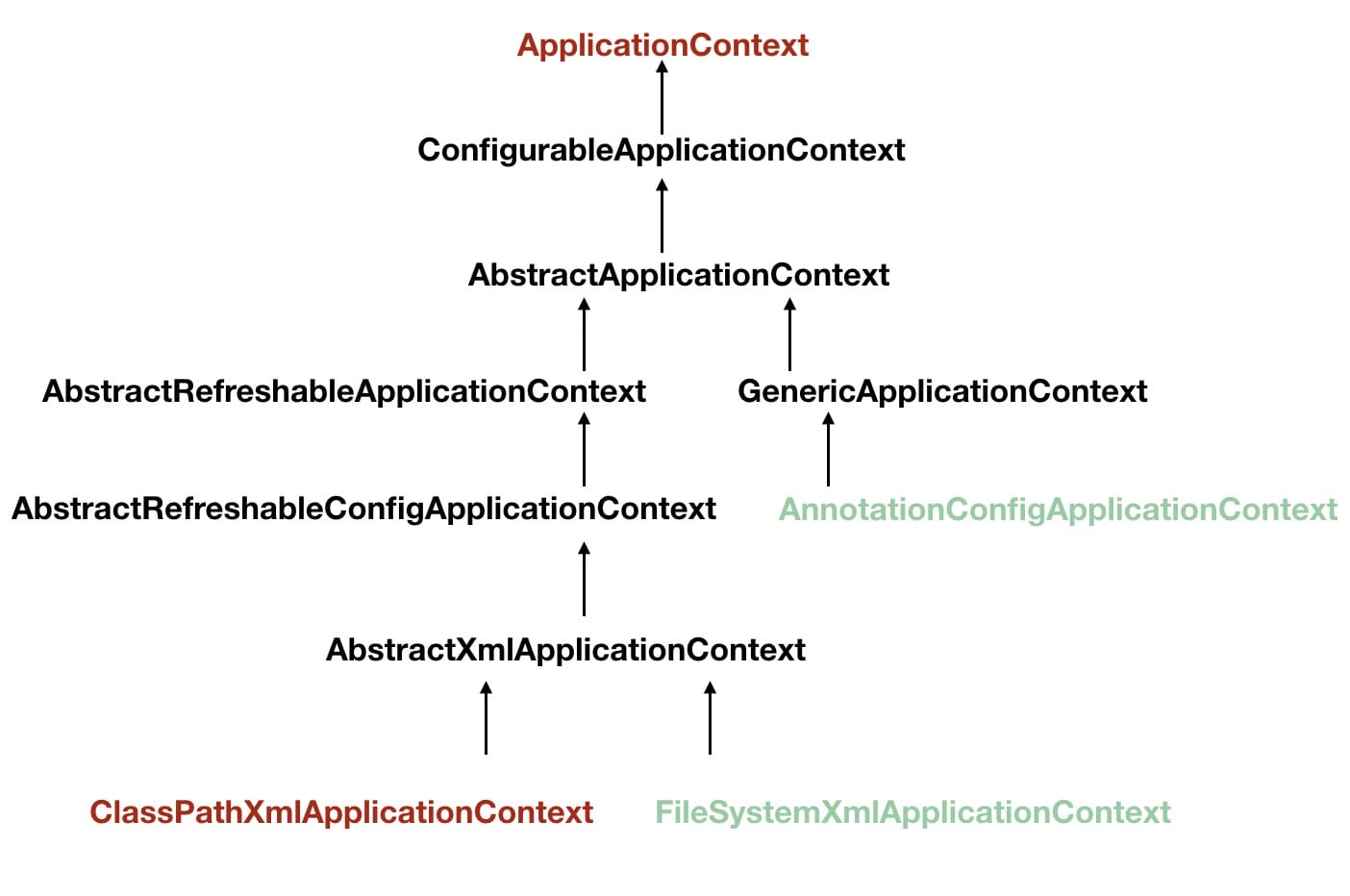
BeanFactory 是生产 bean 的工厂,它负责生产和管理各个 bean 实例。从下图可以看到,ApplicationContext 也是一个 BeanFactory。如果说 BeanFactory 是 Spring 的心脏,那么 ApplicationContext 就是完整的身躯。

ApplicationContext 是应用程序运行时提供配置信息的通用接口。ApplicationContext 在程序运行时是不可更改的,但是实现类可以重新再入配置信息。
ApplicationContext 的实现类有很多,比如 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext, AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext, ClassPathXmlApplicationContext, FileSystemXmlApplicationContext, XmlWebApplicationContext 等。我们上面分析的就是 AnnotationConfigApplicationContext,其采用注解的方式提供配置信息,这样我们就不用写 XML 配置文件了,非常简洁。
Web 容器启动过程
本文使用 Spring Boot 开发,其启动的代码是:
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableScheduling
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy
public class AppApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(AppApplication.class, args);
}
}
核心的点是这一句:
SpringApplication.run(AppApplication.class, args);
SpringApplication 的代码就不分析了,明确本次看源码的目的是分析容器源码,Spring Boot 的启动过程和其他信息都忽略了,因为 Spring 代码实在是庞杂。分析上面的 run 方法,最终会追踪到 SpringApplication#run(...) 方法。
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
context = createApplicationContext();
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
listeners.started(context);
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}
跟 context 相关的,是下面这 3 句代码:
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
refreshContext 方法就是刷新给定的 context:
private void refreshContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
refresh(context);
if (this.registerShutdownHook) {
try {
context.registerShutdownHook();
}
catch (AccessControlException ex) {
// Not allowed in some environments.
}
}
}
protected void refresh(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
Assert.isInstanceOf(AbstractApplicationContext.class, applicationContext);
((AbstractApplicationContext) applicationContext).refresh();
}
会发现最终调用到了 AbstractApplicationContext#refresh 方法。注释参考自:https://www.javadoop.com/post/spring-ioc
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
// 来个锁,不然 refresh() 还没结束,你又来个启动或销毁容器的操作,那不就乱套了嘛
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// 准备工作,记录下容器的启动时间、标记“已启动”状态、处理配置文件中的占位符
prepareRefresh();
// 这步比较关键,这步完成后,配置文件就会解析成一个个 Bean 定义,注册到 BeanFactory 中,
// 当然,这里说的 Bean 还没有初始化,只是配置信息都提取出来了,
// 注册也只是将这些信息都保存到了注册中心(说到底核心是一个 beanName-> beanDefinition 的 map)
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// 设置 BeanFactory 的类加载器,添加几个 BeanPostProcessor,手动注册几个特殊的 bean
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// 【这里需要知道 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 这个知识点,Bean 如果实现了此接口,
// 那么在容器初始化以后,Spring 会负责调用里面的 postProcessBeanFactory 方法。】
// 这里是提供给子类的扩展点,到这里的时候,所有的 Bean 都加载、注册完成了,但是都还没有初始化
// 具体的子类可以在这步的时候添加一些特殊的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的实现类或做点什么事
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// 调用 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 各个实现类的 postProcessBeanFactory(factory) 方法
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// 注册 BeanPostProcessor 的实现类,注意看和 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的区别
// 此接口两个方法: postProcessBeforeInitialization 和 postProcessAfterInitialization
// 两个方法分别在 Bean 初始化之前和初始化之后得到执行。注意,到这里 Bean 还没初始化
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// 初始化当前 ApplicationContext 的 MessageSource,国际化这里就不展开说了,不然没完没了了
initMessageSource();
// 初始化当前 ApplicationContext 的事件广播器,这里也不展开了
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// 从方法名就可以知道,典型的模板方法(钩子方法),
// 具体的子类可以在这里初始化一些特殊的 Bean(在初始化 singleton beans 之前)
onRefresh();
// 注册事件监听器,监听器需要实现 ApplicationListener 接口。这也不是我们的重点,过
registerListeners();
// 重点,重点,重点
// 初始化所有的 singleton beans
//(lazy-init 的除外)
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// 最后,广播事件,ApplicationContext 初始化完成
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
// 销毁已经初始化的 singleton 的 Beans,以免有些 bean 会一直占用资源
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
核心流程就是 try 代码块里的内容,我们应该了解整体原理,本篇文章并不能逐行逐句分析。如果那样做,完全就变成一部字典了……
bean 的加载
bean 加载的调用函数:org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory#doGetBean
protected <T> T doGetBean(final String name, @Nullable final Class<T> requiredType,
@Nullable final Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly) throws BeansException {
// 提取对应 bean 的名字
final String beanName = transformedBeanName(name);
Object bean;
// 1. 重要,重要,重要!
// 创建单例 bean 避免循环依赖,尝试从缓存中获取
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
if (isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
logger.trace("Returning eagerly cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName +
"' that is not fully initialized yet - a consequence of a circular reference");
}
else {
logger.trace("Returning cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
}
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null);
}
else {
// 存在循环依赖
if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
// 原型模式直接抛出异常(循环依赖仅能在单例模式下解决)
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName);
}
// Check if bean definition exists in this factory.
BeanFactory parentBeanFactory = getParentBeanFactory();
if (parentBeanFactory != null && !containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {
// Not found -> check parent.
String nameToLookup = originalBeanName(name);
if (parentBeanFactory instanceof AbstractBeanFactory) {
return ((AbstractBeanFactory) parentBeanFactory).doGetBean(
nameToLookup, requiredType, args, typeCheckOnly);
}
else if (args != null) {
// Delegation to parent with explicit args.
return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, args);
}
else if (requiredType != null) {
// No args -> delegate to standard getBean method.
return parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, requiredType);
}
else {
return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup);
}
}
// 如果不是仅仅做类型检查,则是创建 bean,需要做记录
if (!typeCheckOnly) {
markBeanAsCreated(beanName);
}
try {
// 获取 RootBeanDefinition,如果指定 beanName 是子 bean 的话,需要合并父类属性
final RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
checkMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanName, args);
// 若存在依赖,需要递归实例化依赖的 bean
String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn();
if (dependsOn != null) {
for (String dep : dependsOn) {
if (isDependent(beanName, dep)) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Circular depends-on relationship between '" + beanName + "' and '" + dep + "'");
}
registerDependentBean(dep, beanName);
try {
getBean(dep);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"'" + beanName + "' depends on missing bean '" + dep + "'", ex);
}
}
}
// 创建 bean 实例
// Singleton 模式的创建
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, () -> {
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
// Prototype 模式的创建
else if (mbd.isPrototype()) {
Object prototypeInstance = null;
try {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
else {
String scopeName = mbd.getScope();
final Scope scope = this.scopes.get(scopeName);
if (scope == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name '" + scopeName + "'");
}
try {
Object scopedInstance = scope.get(beanName, () -> {
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
try {
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
}
finally {
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
});
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
}
catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,
"Scope '" + scopeName + "' is not active for the current thread; consider " +
"defining a scoped proxy for this bean if you intend to refer to it from a singleton",
ex);
}
}
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
cleanupAfterBeanCreationFailure(beanName);
throw ex;
}
}
// 检测 requiredType 是否为 bean 的实际类型,不是则转换,不成功则抛出异常
if (requiredType != null && !requiredType.isInstance(bean)) {
try {
T convertedBean = getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(bean, requiredType);
if (convertedBean == null) {
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());
}
return convertedBean;
}
catch (TypeMismatchException ex) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Failed to convert bean '" + name + "' to required type '" +
ClassUtils.getQualifiedName(requiredType) + "'", ex);
}
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());
}
}
return (T) bean;
}
可以看到 bean 的加载是相当复杂的。加载的步骤大致如下:
- 转换对应 beanName
- 尝试从缓存中加载单例
- bean 的实例化
- 原型模式的依赖检查
- 检测 parentBeanFactory
- 将配置文件转换为 RootBeanDefinition
- 寻找依赖
- 针对不同的 scope 进行 bean 的创建
- 类型转换
FactoryBean
前面提到了 BeanFactory,这里又来了个 FactoryBean …… 据说 Spring 提供了 70 多个 FactoryBean 的实现,可见其在 Spring 框架中的地位。它们隐藏了实例化复杂 bean 的细节,给上层应用带来便捷。
public interface FactoryBean<T> {
// 返回 FactoryBean 创建的 bean 实例,如果 isSingleton() 返回 true,则该实例会放到 Spring 容器的单例缓存池中
@Nullable
T getObject() throws Exception;
// 返回 FactoryBean 创建的 bean 类型
@Nullable
Class<?> getObjectType();
default boolean isSingleton() {
return true;
}
}
循环依赖
循环依赖就是循环引用,两个或多个 bean 相互之间持有对方。那么 Spring 是如何解决循环依赖的?
在 Spring 中循环依赖一共有 3 种情况:
- 构造器循环依赖
- setter 循环依赖
- prototype 范围的依赖处理
其中构造器循环依赖是无法解决的,因为一个 bean 创建时首先要经过构造器,但是构造器相互依赖,就相当于 Java 中多线程死锁。
setter 注入造成的依赖是通过 Spring 容器提前暴露刚完成构造器注入但未完成其他步骤(如 setter 注入)的 bean 来完成的,而且只能解决单例作用域的 bean 循环依赖。通过提前暴露一个单例工厂方法,从而使其他 bean 能引用到该 bean,代码如下:
@Nullable
protected Object getSingleton(String beanName, boolean allowEarlyReference) {
Object singletonObject = this.singletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
synchronized (this.singletonObjects) {
singletonObject = this.earlySingletonObjects.get(beanName);
if (singletonObject == null && allowEarlyReference) {
ObjectFactory<?> singletonFactory = this.singletonFactories.get(beanName);
if (singletonFactory != null) {
singletonObject = singletonFactory.getObject();
this.earlySingletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
this.singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
}
}
}
}
return singletonObject;
}
其中 earlySingletonObjects 的定义为:
/** Cache of early singleton objects: bean name to bean instance. */
private final Map<String, Object> earlySingletonObjects = new HashMap<>(16);
对于 prototype 作用域的 bean,Spring 容器无法完成依赖注入,因为 Spring 容器不缓存 prototype 作用域的 bean。
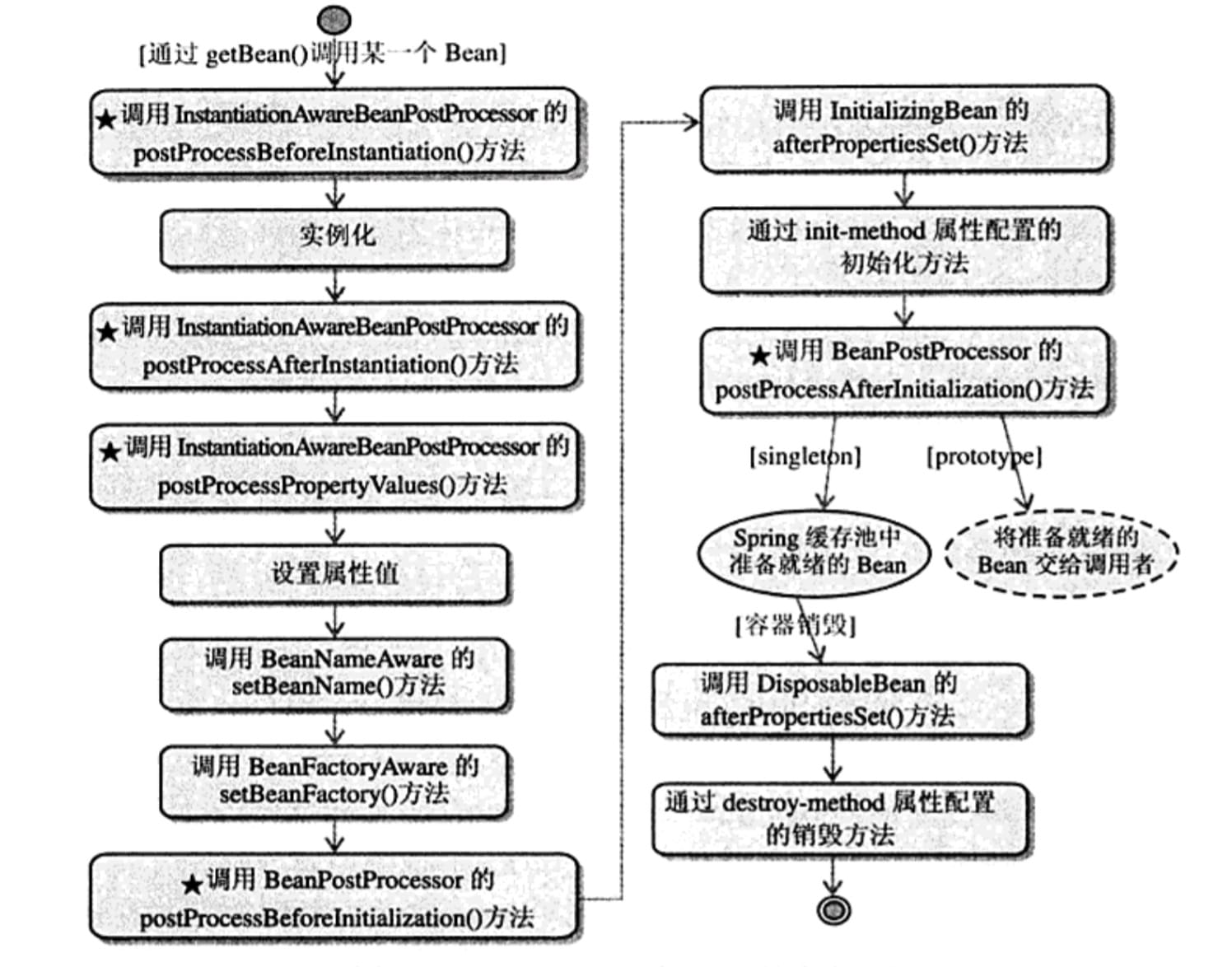
bean 生命周期
面试的话,Spring 的核心就在这里了,不过只要记住大体流程就行。
公众号
coding 笔记、点滴记录,以后的文章也会同步到公众号(Coding Insight)中,希望大家关注_
代码和思维导图在 GitHub 项目中,欢迎大家 star!

最简 Spring IOC 容器源码分析的更多相关文章
- Spring IOC 容器源码分析 - 余下的初始化工作
1. 简介 本篇文章是"Spring IOC 容器源码分析"系列文章的最后一篇文章,本篇文章所分析的对象是 initializeBean 方法,该方法用于对已完成属性填充的 bea ...
- Spring IOC 容器源码分析 - 填充属性到 bean 原始对象
1. 简介 本篇文章,我们来一起了解一下 Spring 是如何将配置文件中的属性值填充到 bean 对象中的.我在前面几篇文章中介绍过 Spring 创建 bean 的流程,即 Spring 先通过反 ...
- Spring IOC 容器源码分析 - 循环依赖的解决办法
1. 简介 本文,我们来看一下 Spring 是如何解决循环依赖问题的.在本篇文章中,我会首先向大家介绍一下什么是循环依赖.然后,进入源码分析阶段.为了更好的说明 Spring 解决循环依赖的办法,我 ...
- Spring IOC 容器源码分析 - 创建原始 bean 对象
1. 简介 本篇文章是上一篇文章(创建单例 bean 的过程)的延续.在上一篇文章中,我们从战略层面上领略了doCreateBean方法的全过程.本篇文章,我们就从战术的层面上,详细分析doCreat ...
- Spring IOC 容器源码分析 - 创建单例 bean 的过程
1. 简介 在上一篇文章中,我比较详细的分析了获取 bean 的方法,也就是getBean(String)的实现逻辑.对于已实例化好的单例 bean,getBean(String) 方法并不会再一次去 ...
- Spring IOC 容器源码分析 - 获取单例 bean
1. 简介 为了写 Spring IOC 容器源码分析系列的文章,我特地写了一篇 Spring IOC 容器的导读文章.在导读一文中,我介绍了 Spring 的一些特性以及阅读 Spring 源码的一 ...
- Spring IOC 容器源码分析系列文章导读
1. 简介 Spring 是一个轻量级的企业级应用开发框架,于 2004 年由 Rod Johnson 发布了 1.0 版本.经过十几年的迭代,现在的 Spring 框架已经非常成熟了.Spring ...
- Spring IOC 容器源码分析
声明!非原创,本文出处 Spring 最重要的概念是 IOC 和 AOP,本篇文章其实就是要带领大家来分析下 Spring 的 IOC 容器.既然大家平时都要用到 Spring,怎么可以不好好了解 S ...
- Spring IOC 容器源码分析(转)
原文地址 Spring 最重要的概念是 IOC 和 AOP,本篇文章其实就是要带领大家来分析下 Spring 的 IOC 容器.既然大家平时都要用到 Spring,怎么可以不好好了解 Spring 呢 ...
随机推荐
- Ubuntu18.04上安装CUDA_10.1(nvidia-driver)和cuDNN_7.6.5
本文是在Ubuntu18.04.5服务器上安装CUDA_10.1(nvidia-driver455)和cuDNN_7.6.5, Ubuntu 18.04.5 CUDA_10.1 (nvidia-dri ...
- 13Linux之磁盘管理
13Linux之磁盘管理 目录 13Linux之磁盘管理 13 磁盘管理 13.1 两种分区格式 13.1.1 磁盘命名 13.1.2 mbr 13.1.3 gpt 13.2 制作文件系统并且挂载 1 ...
- cephfs删除报nospace的问题
ceph Vol 45 Issue 2 CephFS: No space left on device After upgrading to 10.2.3 we frequently see mess ...
- PDF技术 -Java实现Html转PDF文件
转载:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_34190023/article/details/82999702 html转换为pdf的关键技术是如何处理网页中复杂的css样式.以及中文乱码 ...
- 网络发布工具 Apache/Nginx
四大主流发布服务器 注:发布服务器的背后都是socket套接字 1.Apache阿帕奇 - 多进程 2.IIS -多线程 3.Nginx (engine x)(新) -支持异步IO,是现在最快的发布服 ...
- 源码分析:Semaphore之信号量
简介 Semaphore 又名计数信号量,从概念上来讲,信号量初始并维护一定数量的许可证,使用之前先要先获得一个许可,用完之后再释放一个许可.信号量通常用于限制线程的数量来控制访问某些资源,从而达到单 ...
- LeetCode-Python-删除链表解题思路
给定一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个节点,并且返回链表的头结点. image.png 解题思路: 使用双指针,快指针与慢指针的间隔为n: 涉及到最后要删除慢指针的节点,为了方便,先开辟一个nod ...
- Unity CommandBuffer物体轮廓
1.command buffer具有很高的灵活性,它的作用是预定义一些渲染指令,然后在我们想要执行的时候去执行这些指令(见图1),绿点表示可以在"Forward Rendering Path ...
- php 进行图片裁剪
<?php $src_path = '1.jpg'; //创建源图的实例 $src = imagecreatefromstring(file_get_contents($src_path)); ...
- ABBYY FineReader 14新建任务窗口给我们哪些帮助?
当您启动ABBYY FineReader时, 新任务 将打开一个窗口,在其中您可以轻松打开.扫描.创建或对比文档. 如果您没有看到此 内置任务 窗口(比如,如果您关闭了该窗口,或者您通过在 Windo ...
