D. Mike and distribution 首先学习了一个玄学的东西
http://codeforces.com/contest/798/problem/D
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Mike has always been thinking about the harshness of social inequality. He's so obsessed with it that sometimes it even affects him while solving problems. At the moment, Mike has two sequences of positive integersA = [a1, a2, ..., an] and B = [b1, b2, ..., bn] of length n each which he uses to ask people some quite peculiar questions.
To test you on how good are you at spotting inequality in life, he wants you to find an "unfair" subset of the original sequence. To be more precise, he wants you to select k numbers P = [p1, p2, ..., pk] such that 1 ≤ pi ≤ n for1 ≤ i ≤ k and elements in P are distinct. Sequence P will represent indices of elements that you'll select from both sequences. He calls such a subset P "unfair" if and only if the following conditions are satisfied: 2·(ap1 + ... + apk)is greater than the sum of all elements from sequence A, and 2·(bp1 + ... + bpk) is greater than the sum of all elements from the sequence B. Also, k should be smaller or equal to 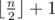 because it will be to easy to find sequence P if he allowed you to select too many elements!
because it will be to easy to find sequence P if he allowed you to select too many elements!
Mike guarantees you that a solution will always exist given the conditions described above, so please help him satisfy his curiosity!
The first line contains integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105) — the number of elements in the sequences.
On the second line there are n space-separated integers a1, ..., an (1 ≤ ai ≤ 109) — elements of sequence A.
On the third line there are also n space-separated integers b1, ..., bn (1 ≤ bi ≤ 109) — elements of sequence B.
On the first line output an integer k which represents the size of the found subset. k should be less or equal to 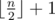 .
.
On the next line print k integers p1, p2, ..., pk (1 ≤ pi ≤ n) — the elements of sequence P. You can print the numbers in any order you want. Elements in sequence P should be distinct.
5
8 7 4 8 3
4 2 5 3 7
3
1 4 5
用了一个叫random_shuffle的东西,每次都乱选,然后暴力前k个。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <assert.h>
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
using namespace std;
#define inf (0x3f3f3f3f)
typedef long long int LL; #include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <string>
#include <bitset>
const int maxn = 1e5 + ;
int a[maxn], b[maxn]; bool in[maxn];
LL sumA, sumB;
LL allA, allB;
int c[maxn];
int n, en;
bool ok() {
LL ta = , tb = ;
for (int i = ; i <= en; ++i) {
ta += * a[c[i]];
tb += * b[c[i]];
if (ta > allA && tb > allB) return true;
}
return false;
}
void work() {
cin >> n;
for (int i = ; i <= n; ++i) {
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
allA += a[i];
}
for (int i = ; i <= n; ++i) {
scanf("%d", &b[i]);
allB += b[i];
c[i] = i;
}
en = (n) / + ;
while (!ok()) {
random_shuffle(c + , c + + n);
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; ++i) {
// cout << c[i] << " ";
// }
// cout << endl;
}
cout << en<< endl;
for (int i = ; i <= en; ++i) {
printf("%d ", c[i]);
}
} int main() {
#ifdef LOCAL
freopen("data.txt", "r", stdin);
// freopen("data.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif
work();
return ;
}
正解:
首先注意到,选出n / 2 + 1个数,2倍的和大于总和,等价于选出n / 2 + 1个数,总和大于剩下的数。
因为可以取n / 2 + 1个,那么先对A排序,B不动,先把A[1]选了(这个是用在证明A数组成立用的),A【1】是当前A中最大的了。当然了也选了一个B,就是选了B[A[1].id],
然后每两个做一pair,选一个比较大的B,也就是max(B[A[i].id], B[A[i + 1].id])
这样,B数组是满足的,这很容易证明,因为没一对中,都选了一个较大的。然后加上第一个,总和肯定大于剩下 的。
也就是
max(b[1], b[2]) >= min(b[1], b[2])
max(b[3], b[4]) >= min(b[3], b[4])
max(b[5], b[6]) >= min(b[5], b[6])
那么全部相加,不等号方向不变。而且开头还有一个b[A[1].id]加了进来,所以是严格大于的。
再来看看A的证明。
第一是选了a[1]
然后选a[2]和a[3]的那个呢?不固定的,还要看B,但是不管,有以下不等式。
a[1] >= any(a[2], a[3])
any(a[2], a[3]) >= any(a[4], a[5])
any(a[4], a[5]) >= any(a[5], a[6])
也就是,你选了一个a[1],然后a[2]和a[3]选那个是没关系的,可以用a[1]和它比较,然后又因为选了any(a[2], a[3]),那么你a[4]和a[5]选那个是没所谓的,因为可以用any(a[2], a[3])和它比较。
最后,any(a[n - 1], a[n]) > 0,所以是严格大于的。
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <assert.h>
#define IOS ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
using namespace std;
#define inf (0x3f3f3f3f)
typedef long long int LL; #include <iostream>
#include <sstream>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <string>
#include <bitset>
const int maxn = 1e5 + ;
struct Node {
int a, id;
bool operator < (const struct Node & rhs) const {
return a > rhs.a;
}
}a[maxn];
int b[maxn];
vector<int>ans;
void work() {
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = ; i <= n; ++i) {
cin >> a[i].a;
a[i].id = i;
}
for (int i = ; i <= n; ++i) {
cin >> b[i];
}
sort(a + , a + + n);
int sel = n / + ;
ans.push_back(a[].id);
for (int i = ; i <= n; i += ) {
int want = a[i].id;
if (i + <= n && b[want] < b[a[i + ].id]) {
want = a[i + ].id;
}
ans.push_back(want);
}
cout << ans.size() << endl;
for (int i = ; i < ans.size(); ++i) {
cout << ans[i] << " ";
}
} int main() {
#ifdef local
freopen("data.txt", "r", stdin);
// freopen("data.txt", "w", stdout);
#endif
IOS;
work();
return ;
}
2017-4-23 22:22:03
要开始补sg函数(博弈)和构造题。先复习下字符串准备省赛。
D. Mike and distribution 首先学习了一个玄学的东西的更多相关文章
- codeforces 798 D. Mike and distribution
D. Mike and distribution time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input sta ...
- CF798D Mike and distribution
CF798D Mike and distribution 洛谷评测传送门 题目描述 Mike has always been thinking about the harshness of socia ...
- [深度学习]实现一个博弈型的AI,从五子棋开始(1)
好久没有写过博客了,多久,大概8年???最近重新把写作这事儿捡起来……最近在折腾AI,写个AI相关的给团队的小伙伴们看吧. 搞了这么多年的机器学习,从分类到聚类,从朴素贝叶斯到SVM,从神经网络到深度 ...
- [深度学习]实现一个博弈型的AI,从五子棋开始(2)
嗯,今天接着来搞五子棋,从五子棋开始给小伙伴们聊AI. 昨天晚上我们已经实现了一个五子棋的逻辑部分,其实讲道理,有个规则在,可以开始搞AI了,但是考虑到不够直观,我们还是顺带先把五子棋的UI也先搞出来 ...
- 学习建一个spring-Mvc项目
学习建一个spring-Mvc项目 首先要有jdk1.8以上,spring,mybatis,以及整合jar包,tomcat ,然后配置环境(前面有配置得方法). 1)右键new project,--& ...
- 6、GNU makefile工程管理学习的一个例子
在之前我们已经学习了一个文件的编译过程,但是做过项目的都知道,一个工程中的源文件不计其数,其按类型.功能.模块会分别放在若干个目录中,而这些文件如何编译就需要有一个编译规则,虽然现在很多大型的项目都是 ...
- PDNN: 深度学习的一个Python工具箱
PDNN: 深度学习的一个Python工具箱 PDNN是一个在Theano环境下开发出来的一个Python深度学习工具箱.它由苗亚杰(Yajie Miao)原创.现在仍然在不断努力去丰富它的功能和扩展 ...
- #410div2D. Mike and distribution
D. Mike and distribution time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input sta ...
- Codeforces 798D Mike and distribution(贪心或随机化)
题目链接 Mike and distribution 题目意思很简单,给出$a_{i}$和$b_{i}$,我们需要在这$n$个数中挑选最多$n/2+1$个,使得挑选出来的 $p_{1}$,$p_{2} ...
随机推荐
- BZOJ_2259_ [Oibh]新型计算机 _最短路
Description Tim正在摆弄着他设计的“计算机”,他认为这台计算机原理很独特,因此利用它可以解决许多难题. 但是,有一个难题他却解决不了,是这台计算机的输入问题.新型计算机的输入也很独特,假 ...
- 微信开放平台开发-授权、全网发布(PHP)
这两天做了微信开发平台的开发,梳理下... 浙江百牛信息技术bainiu.ltd整理发布于博客园 先看看授权的流程: 第一步:接收component_verify_ticket: 1.微信服务器每隔1 ...
- zk 01之 ZooKeeper概述
Zookeeper产生的背景 ZooKeeper---译名为“动物园管理员”.动物园里当然有好多的动物,游客可以根据动物园提供的向导图到不同的场馆观赏各种类型的动物,而不是像走在原始丛林里,心惊胆颤的 ...
- 算法导论笔记——第二十章 van Emde Boas树
当关键字是有界范围内的整数时,能够规避Ω(lglgn)下界的限制,那么在类似的场景下,我们应弄清楚o(lgn)时间内是否可以完成优先队列的每个操作.在本章中,我们将看到:van Emde Boas树支 ...
- Springboot学习七 spring的一些注解
一 事务控制 @Service public class CityServiceImpl implements CityService { @Autowired private CityMapper ...
- shader之顶点着色器
Vertex Shader 是渲染管道中一个可编程的模块,用于处理独立的顶点.Vertex Shader接收Vertex Attribute Data,由定点数组对象通过渲染指令来生成. Vertex ...
- Django 之验证码实现
1. django-simple-captcha 模块 安装 django-simple-captcha pip install django-simple-captcha pip install P ...
- Vee-validate 父组件获取子组件表单校验结果
vee-validate 是为 Vue.js 量身打造的表单校验框架,允许您校验输入的内容并显示对应的错误提示信息.它内置了很多常见的校验规则,可以组合使用多种校验规则,大部分场景只需要配置就能实现开 ...
- 基于selenium+java的12306自动抢票
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit; import org.openqa.selenium.By;import org.openqa.selenium.Keys; ...
- ue4 enable input
actor: enable input 这个可以使多个actor接收输入 pawn: possese pawn使用enable input是不生效的 貌似不允许多个pawn同时接收输入,可以考虑直接 ...
