省选算法学习-数据结构-splay
于是乎,在丧心病狂的noip2017结束之后,我们很快就要迎来更加丧心病狂的省选了-_-||
所以从写完上一篇博客开始到现在我一直深陷数据结构和网络流的漩涡不能自拔
今天终于想起来写博客(只是懒吧......)
言归正传。
省选级别的数据结构比NOIP要高到不知道哪里去了。
noip只考一点线段树啊st表啊并查集啊之类的简单数据结构,而且应用范围很窄
但是省选里面对数据结构,尤其是高级数据结构的要求就高了很多,更有一些题目看着就是数据结构题,也没有别的做法。
因此掌握高级数据结构就成了准备省选的一项大任务。
这一个月(2017.12-2018.1)来,我学习了平衡树、可持久化线段树、link-cut-tree和树套树四种数据结构。就在这里都记录下来。
第一篇是平衡树中的splay
在讲splay之前,需要先给出平衡树的定义。
平衡树是一棵二叉搜索树。它除了具有二叉搜索树的全部特征之外,还具有一个关键性的特征:“平衡”,即任意节点的左右子树高度差不超过1。
这个特性决定了它在面对特殊数据(例如那种专门卡普通二叉搜索树的数据)时,能够非常稳定的解决,只是牺牲了一些时间复杂度常数,但是基本不会被卡掉。
平衡树有非常多的实现方式,包括splay,treap,替罪羊树,红黑树,sbt(size balanced tree即严格平衡),AVL等
这篇文章则主要专注于splay
splay,意为“伸展”,故其中文名叫“伸展树”,核心是在二叉树上进行伸展操作,以此来保证树的平衡。
自然,伸展操作就成了splay树的核心,也是它和普通二叉树(二叉搜索树)的唯一的一点不同。
为方便描述,本文中统一称呼如下:
当前节点的编号为x,其父亲为fa[x],其左右儿子为ch[x][0]和ch[x][1],整棵树的根节点编号为root
splay操作的核心是旋转操作,又称rotate。它的特性是能够在不改变树的中序遍历(即满足原二叉搜索树性质)的条件下,改变树的形态,以此调整两棵子树之间的平衡。
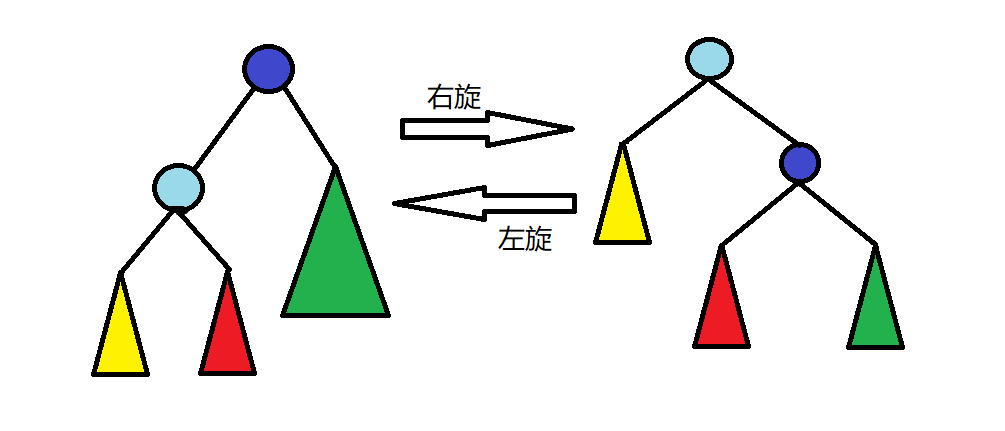
左右两图中三角形代表一整棵子树,圆则代表一个节点。
可以看到在两幅图中,整棵树的中序遍历都是“黄-浅蓝-红-深蓝-绿”,但是树的形态,以及根节点左右子树的深度却改变了。
因此可知,只要我们不断地进行左旋和右旋操作,一课不平衡的二叉树(例如一条链)一定可以被旋转成平衡的。
下面给出代码:
//get函数的作用是得到节点x是其父亲的左二子还是右儿子
int get(int x){
return ch[fa[x]][]==x;
}
//rotate函数将左旋和右旋集成。当x是左儿子的时候只能右旋,当x是右儿子的时候只能左旋
void rotate(int x){
int f=fa[x],ff=fa[f],son=get(x);
//f是x的父节点,ff是f的父节点
push(f);push(x);
ch[f][son]=ch[x][son^];
if(ch[f][son]) fa[ch[f][son]]=f;
ch[x][son^]=f;
fa[f]=x;
if(ff) ch[ff][ch[ff][]==f]=x;
fa[x]=ff;
update(f);update(x);
}
rotate(x)函数的时间复杂度为O(1)
接下来的就是splay操作
splay操作的的过程用一句话来说,就是多次调用rotate函数,使节点x成为目标节点to的儿子
首先显然可以想到调用循环,每次循环中rotate(x),并检测fa[x]是不是to。
很遗憾的是,这样的splay会被一些特殊数据卡掉,不能严格保证平衡
这种单旋splay因此被戏称为spaly
实际应用中为了保证平衡性,splay树的splay操作运用了双旋的技巧。
双旋,即为每次循环中依据不同的情况,每个循环节中调用两次rotate函数,分为以下两种情况:
情况一:get(x) == get(fa[x]) (其中get函数意义见上一代码块)
此时应该先rotate(fa[x]),再rotate(x),如图所示:
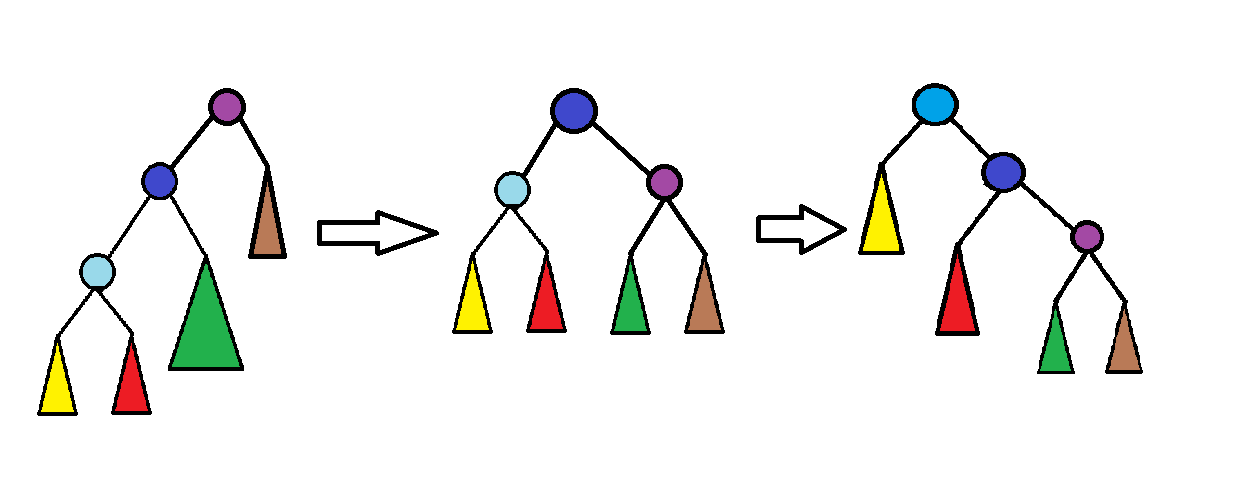
这样能够让原期望复杂度最大的,以浅蓝色节点为根的子树复杂度大大下降,平衡了三棵子树的复杂度
(其实这个具体原理非常复杂。若真正想搞清楚,可以去看tarjan教授的论文%%%)
情况二:get(x)!=get(fa[x])
这种情况下应该直接调用两次rotate(x),如下图:
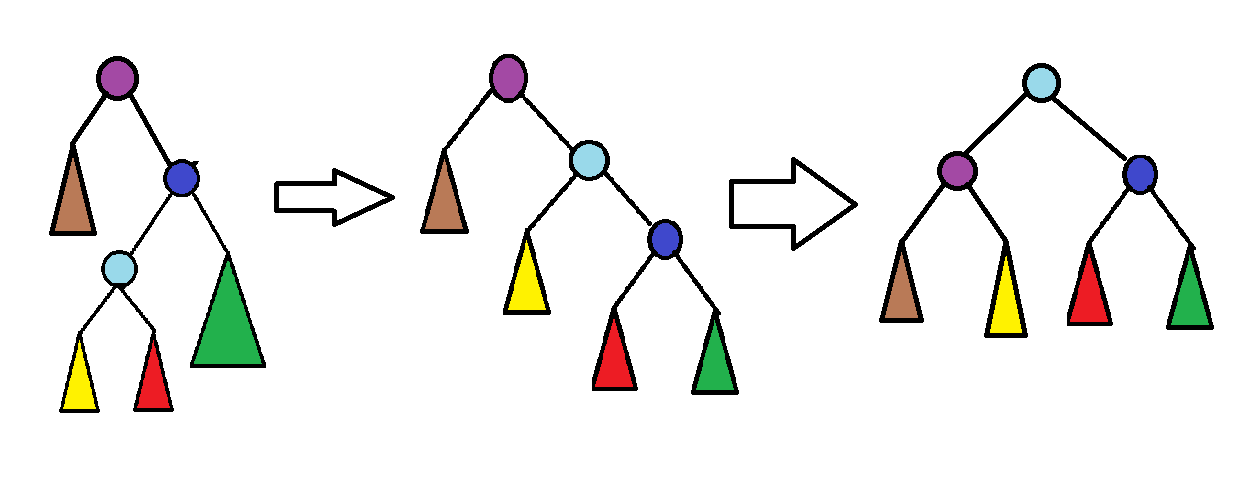
解释不多说,看图就清楚了,肯定平衡。
splay操作由于已经有rotate操作的集成函数,因此代码很短,如下:
//其实很多题目中并不涉及到splay(x,to),而是只涉及splay(x,fa[root]),即使x成为根节点。那样会简单很多。
void splay(int x,int to){
push(x);//push操作是在更下传azy标记,详见后文
if(x==to||fa[x]==to) return;
for(int f;(f=fa[x])&&f!=to;rotate(x)){
push(fa[fa[x]]);push(fa[x]);push(x);
if(fa[f]!=to)
rotate((get(x)==get(f))?f:x);
if(fa[x]==to) break;
}
update(x);
if(to==) root=x;
}
splay(x,to)函数的时间复杂度为均摊下O(log n)
好了,到这里splay树的核心操作splay已经讲完了。
splay因为本质是一棵二叉搜索树,因此它也可以实现和二叉搜索树相同的操作,包括求rank,给定初始数列建树,插入节点,删除节点等。这个时候它是作为一棵二叉搜索树存在的。唯一的不同就是它会在每一次操作结束以后调用splay函数,从某一个节点开始伸展,用这样的方式保证树的平衡。例如在插入操作结束后,从新插入的节点x开始splay(x)到树根,或者是在求第k大的元素时,找到该元素后将它splay到根。
一道例题:tyvj 1728 普通平衡树
实际上是treap模板题,也可以用普通的bst做,但会被卡。
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
inline int read(){
int re=,flag=;char ch=getchar();
while(ch>''||ch<''){
if(ch=='-') flag=-;
ch=getchar();
}
while(ch>=''&&ch<='') re=(re<<)+(re<<)+ch-'',ch=getchar();
return re*flag;
}
int n,m,cnt,root;
int fa[],ch[][],siz[],num[],w[];
void clear(int x){fa[x]=ch[x][]=ch[x][]=siz[x]=num[x]=w[x]=;}
void update(int x){siz[x]=siz[ch[x][]]+siz[ch[x][]]+num[x];}
int get(int x){return ch[fa[x]][]==x;}
void rotate(int x){
int f=fa[x],ff=fa[f],son=get(x);
ch[f][son]=ch[x][son^];
if(ch[f][son]) fa[ch[f][son]]=f;
fa[f]=x;ch[x][son^]=f;
fa[x]=ff;
if(ff) ch[ff][ch[ff][]==f]=x;
update(f);update(x);
}
void splay(int x){
for(int f;f=fa[x];rotate(x))
if(fa[f])
rotate((get(f)==get(x))?f:x);
root=x;
}
void insert(int x,int pos){
if(x==w[pos]){
num[pos]++;splay(pos);
return;
}
if(x<w[pos]){
if(!ch[pos][]){
clear(++cnt);
fa[cnt]=pos;w[cnt]=x;siz[cnt]=;num[cnt]=;
if(pos) ch[pos][]=cnt;
splay(cnt);
}
else insert(x,ch[pos][]);
}
else{
if(!ch[pos][]){
clear(++cnt);
fa[cnt]=pos;w[cnt]=x;siz[cnt]=;num[cnt]=;
if(pos) ch[pos][]=cnt;
splay(cnt);
}
else insert(x,ch[pos][]);
}
}
int getrank(int x,int pos){
if(w[pos]==x){
splay(pos);
return siz[ch[pos][]]+;
}
if(w[pos]>x) return getrank(x,ch[pos][]);
else return getrank(x,ch[pos][]);
}
int getrankval(int x,int pos){
if(x>siz[ch[pos][]]&&x<=siz[ch[pos][]]+num[pos]){
splay(pos);
return w[pos];
}
if(x<=siz[ch[pos][]]) return getrankval(x,ch[pos][]);
else return getrankval(x-siz[ch[pos][]]-num[pos],ch[pos][]);
}
//pre和suf函数是在splay结束后,从根节点(待求节点)开始,向左(向右)走一步,然后反过来一直走,走到没有右(左)儿子为止,把该节点的值返回。由二叉搜索树性质可得,这个点是比输入节点小的所有节点中最大的那个。
int pre(){
int pos=ch[root][];
while(ch[pos][]) pos=ch[pos][];
return pos;
}
int suf(){
int pos=ch[root][];
while(ch[pos][]) pos=ch[pos][];
return pos;
}
//del函数同样是在splay完以后,直接删除根节点(splay上去的所要求的节点)。方法是把左子树的最大值(即pre())splay到根,此时左子树树根没有右儿子,再把源根的右子树接上去即可。
void del(int x){
int rk=getrank(x,root);
if(num[root]>){
num[root]--;return;
}
if(!ch[root][]&&!ch[root][]){
clear(root);return;
}
if(!ch[root][]){
root=ch[root][];
clear(fa[root]);fa[root]=;
return;
}
if(!ch[root][]){
root=ch[root][];
clear(fa[root]);fa[root]=;
return;
}
int rt=root,left=pre();splay(left);
ch[root][]=ch[rt][];
fa[ch[rt][]]=root;
clear(rt);update(root);
}
int main(){
int i,t1,t2;
n=read();
for(i=;i<=n;i++){
t1=read();t2=read();
if(t1==) insert(t2,root);
if(t1==) del(t2);
if(t1==) insert(t2,root),printf("%d\n",getrank(t2,root)),del(t2);
if(t1==) printf("%d\n",getrankval(t2,root));
if(t1==) insert(t2,root),printf("%d\n",w[pre()]),del(t2);
if(t1==) insert(t2,root),printf("%d\n",w[suf()]),del(t2);
}
}
需要说明的是,splay树的每一个操作时间效率都是O(log n),但是它的常数在平衡树中是比较大的。因此若是有treap或者其他平衡树能实现的题目,用其他的平衡树可以避免卡常。
那么既然如此,splay又有什么特别的作用呢?
这就是接下来要讲的,splay的另一种用处。
先以一个小目标(雾)引入:
给出一个区间,长度为n,以及m次区间翻转操作(即把整个区间镜像过来),n,m <= 100,000
输出最后的序列。
如果不讨论某蜜汁无敌整体二分之类的方法,直接正面硬肛♂的话,好像有点难做。
不管是什么奇奇怪怪的结构都没法满足提取区间然后反过来这么一个蜜汁要求。
那么现在就是splay发挥大用处的时候了。
我们把这个序列建成一棵splay树,其中每一个节点的rank就是它在原序列中的位置。
例如某个splay树节点,它的中序遍历是全树的第x位,那么它也就是原数列的第x个数。
换句话说,这颗新建的splay树的中序遍历就是原数列。
理解了这一部分之后再往下看,我们现在引入splay区间提取的核心操作:
设将要提取的区间为 [l,r] ,则进行如下操作:
splay排名为 l-1 的点到根,再把排名为 r+1 的节点splay到 排名为 l-1 的节点下面。那么排名为 r+1 的节点的左子树就是节点区间 [l,r]。
如图:

因为这颗splay满足二叉搜索树性质,因此区间[l,r]的提取的正确性显然。
然后我们就可以在这颗子树上为所欲为了(≖ᴗ≖)✧
在这颗子树的根节点上加一个lazy标记,然后在每次修改树的形态之前push一下,就可以很好的维护了。
同理,splay也可以通过这种方式完成区间加、区间求和、区间求最小值之类的操作。
不过这种splay无法完成求第k大,因为求第k大的操作依赖于键值的有序性,但是这颗splay树并不满足,所以无法达成。
一道例题:poj 3580 SuperMemo
原题链接:http://poj.org/problem?id=3580
大意就是让你完成以下操作:单点插入,单点删除,区间加,区间翻转,区间旋转(见原题),求区间最小值。
可以用splay很好的维护,甚至可以说是一道很全的模板题了。
rev操作只要把前一半区间“剪”下来,再“粘”到后一半区间的后面即可。
代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#define inf 0x7fffffff
using namespace std;
int n,m,root,cnt,tmp[];
int fa[],ch[][],w[],siz[];
int minn[],lazy1[],lazy2[];
void _swap(int &l,int &r){l^=r;r^=l;l^=r;}
int _min(int l,int r){return (l>r)?r:l;}
void clear(int x){
fa[x]=ch[x][]=ch[x][]=w[x]=siz[x]=lazy1[x]=lazy2[x]=;
}
void add(int x,int f){
cnt++;
fa[cnt]=f;ch[cnt][]=ch[cnt][]=;w[cnt]=minn[cnt]=x;siz[cnt]=;lazy1[cnt]=lazy2[cnt]=;
}
int get(int x){
return ch[fa[x]][]==x;
}
void update_add(int x,int k){
if(x) lazy2[x]+=k,minn[x]+=k,w[x]+=k;
}
void update_rev(int x){
if(!x) return;
_swap(ch[x][],ch[x][]);
lazy1[x]^=;
}
void update(int x){
if(!x) return;
siz[x]=;minn[x]=w[x];
if(ch[x][]) siz[x]+=siz[ch[x][]],minn[x]=_min(minn[x],minn[ch[x][]]);
if(ch[x][]) siz[x]+=siz[ch[x][]],minn[x]=_min(minn[x],minn[ch[x][]]);
}
void push(int x){
if(!x) return;
if(lazy1[x]){
update_rev(ch[x][]);
update_rev(ch[x][]);
lazy1[x]=;
}
if(lazy2[x]){
update_add(ch[x][],lazy2[x]);
update_add(ch[x][],lazy2[x]);
lazy2[x]=;
}
}
void rotate(int x){
int f=fa[x],ff=fa[f],son=get(x);
push(f);push(x);
ch[f][son]=ch[x][son^];
if(ch[f][son]) fa[ch[f][son]]=f;
ch[x][son^]=f;
fa[f]=x;
if(ff) ch[ff][ch[ff][]==f]=x;
fa[x]=ff;
update(f);update(x);
}
void splay(int x,int to){
push(x);
if(x==to||fa[x]==to) return;
for(int f;(f=fa[x])&&f!=to;rotate(x)){
push(fa[fa[x]]);push(fa[x]);push(x);
if(fa[f]!=to)
rotate((get(x)==get(f))?f:x);
if(fa[x]==to) break;
}
update(x);
if(to==) root=x;
}
int build(int l,int r,int f){
int mid=(l+r)>>,tt;
add(tmp[mid],f);tt=cnt;
if(mid>l) ch[tt][]=build(l,mid-,tt);
if(mid<r) ch[tt][]=build(mid+,r,tt);
update(tt);
return tt;
}
int rank(int k,int pos){
push(pos);
if(siz[ch[pos][]]+==k) return pos;
if(siz[ch[pos][]]>=k) return rank(k,ch[pos][]);
else return rank(k-siz[ch[pos][]]-,ch[pos][]);
}
void add(int l,int r,int k){
int x=rank(l,root),y=rank(r+,root);
splay(x,);splay(y,x);
update_add(ch[y][],k);
}
void rev(int l,int r){
int x=rank(l,root),y=rank(r+,root);
splay(x,);splay(y,x);
lazy1[ch[y][]]^=;
_swap(ch[ch[y][]][],ch[ch[y][]][]);
}
void res(int l1,int r1,int l2,int r2){
int x=rank(l2,root),y=rank(r2+,root);
splay(x,);splay(y,x);
int tt=ch[y][];
ch[y][]=;fa[tt]=;
x=rank(l1,root);y=rank(l1+,root);
splay(x,);splay(y,x);
ch[y][]=tt;fa[tt]=y;
}
void ins(int p,int k){
int x=rank(p+,root),y=rank(p+,root);
splay(x,);splay(y,x);
add(k,y);ch[y][]=cnt;
push(y);update(y);
push(x);update(x);
splay(y,);
}
void del(int p){
int x=rank(p,root),y=rank(p+,root);
splay(x,);splay(y,x);
clear(ch[y][]);ch[y][]=;
update(y);update(x);
}
int getmin(int l,int r){
int x=rank(l,root),y=rank(r+,root);
splay(x,);splay(y,x);
return minn[ch[y][]];
}
int main(){
int i,t1,t2,t3;char s[];
scanf("%d",&n);
for(i=;i<=n;i++) scanf("%d",&tmp[i]);
tmp[]=tmp[n+]=inf;
root=build(,n+,);
scanf("%d",&m);
for(i=;i<=m;i++){
scanf("%s",s);
if(s[]=='A'){
scanf("%d%d%d",&t1,&t2,&t3);
add(t1,t2,t3);
}
if(s[]=='R'){
if(s[]=='O'){
scanf("%d%d%d",&t1,&t2,&t3);
t3=(t3%(t2-t1+)+t2-t1+)%(t2-t1+);
if(t3==) continue;
res(t1,t2-t3,t2-t3+,t2);
}
else{
scanf("%d%d",&t1,&t2);
rev(t1,t2);
}
}
if(s[]=='I'){
scanf("%d%d",&t1,&t2);
ins(t1,t2);
}
if(s[]=='D'){
scanf("%d",&t1);
del(t1);
}
if(s[]=='M'){
scanf("%d%d",&t1,&t2);
printf("%d\n",getmin(t1,t2));
}
}
system("pause");
}
由此可见,splay虽然效率上并不是特别高,但是能进行非常多的操作,缺点就是代码量稍大,而且调试难度高,在竞赛中一定要确保稳妥的情况下使用。
代码实现上需要注意的点:
1.逻辑运算符和位运算符的优先级都比赋值运算符高!
2.lazy数组有标记时,当前点一定是已经完成了翻转操作的!
UPDATE 2018.4.25
新版的普通平衡树代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#define ll long long
using namespace std;
inline int read(){
int re=,flag=;char ch=getchar();
while(ch>''||ch<''){
if(ch=='-') flag=-;
ch=getchar();
}
while(ch>=''&&ch<='') re=(re<<)+(re<<)+ch-'',ch=getchar();
return re*flag;
}
struct SplayTree{
int n,ch[][],siz[],num[],w[],fa[],root,cnt;
SplayTree(){n=root=cnt=;} int newnode(int f,int val){
// cout<<"new node "<<f<<ends<<val<<endl;
cnt++;ch[cnt][]=ch[cnt][]=;num[cnt]=siz[cnt]=;
w[cnt]=val;fa[cnt]=f;return cnt;
}
void delnode(int pos){
ch[pos][]=ch[pos][]=num[pos]=siz[pos]=w[pos]=fa[pos]=;
}
void update(int pos){siz[pos]=siz[ch[pos][]]+siz[ch[pos][]]+num[pos];}
bool get(int pos){return ch[fa[pos]][]==pos;} void rotate(int pos){
int f=fa[pos],ff=fa[f],son=get(pos);
// cout<<"rotate "<<pos<<ends<<f<<ends<<ff<<ends<<son<<ends<<ch[pos][son^1]<<ends<<ch[pos][son]<<endl;
ch[f][son]=ch[pos][son^];
if(ch[f][son]) fa[ch[f][son]]=f;
fa[f]=pos;ch[pos][son^]=f;
fa[pos]=ff;
if(ff) ch[ff][ch[ff][]==f]=pos;
// cout<<"finish rotate "<<ch[pos][son^1]<<ends<<ch[f][son]<<ends<<ch[f][son^1]<<ends<<fa[f]<<endl;
update(f);update(pos);
}
void splay(int pos,int to){
if((!pos)||(pos==to)) return;
// cout<<"splay "<<pos<<ends<<fa[pos]<<ends<<to<<endl;
for(int f;(f=fa[pos])!=to;rotate(pos))
if(fa[f]!=to)
rotate((get(f)==get(pos))?f:pos);
if(!to) root=pos;
}
int getpos(int pos,int rank){
if(rank>siz[ch[pos][]]&&rank<=(siz[ch[pos][]]+num[pos])){
splay(pos,);
return w[pos];
}
if(rank<=siz[ch[pos][]]) return getpos(ch[pos][],rank);
else return getpos(ch[pos][],rank-siz[ch[pos][]]-num[pos]);
}
int getrank(int pos,int val,int buff){
if(w[pos]==val){
splay(pos,);
return siz[ch[pos][]]+buff+;
}
if(w[pos]>val) return getrank(ch[pos][],val,buff);
else return getrank(ch[pos][],val,buff+siz[ch[pos][]]+num[pos]);
}
int getvalpos(int pos,int val){
if(w[pos]==val) return pos;
if(w[pos]>val) return getvalpos(ch[pos][],val);
else return getvalpos(ch[pos][],val);
}
int pre(){
int pos=ch[root][];
while(ch[pos][]) pos=ch[pos][];
return pos;
}
int suf(){
int pos=ch[root][];
while(ch[pos][]) pos=ch[pos][];
return pos;
}
void insert(int pos,int val){
// cout<<"insert "<<pos<<ends<<w[pos]<<ends<<val<<ends<<ch[pos][0]<<ends<<ch[pos][1]<<endl;
if(!pos){root=newnode(,val);return;}
if(w[pos]==val){num[pos]++;splay(pos,);return;}
if(w[pos]>val){
if(!ch[pos][]){
ch[pos][]=newnode(pos,val);
update(pos);splay(ch[pos][],);
}
else siz[pos]++,insert(ch[pos][],val);
}
else{
if(!ch[pos][]){
ch[pos][]=newnode(pos,val);
update(pos);splay(ch[pos][],);
}
else siz[pos]++,insert(ch[pos][],val);
}
}
void del(int val){
// cout<<"del "<<val<<endl;
int pos=getvalpos(root,val);splay(pos,);
if(num[pos]>){num[pos]--;return;}
if(!ch[pos][]){
root=ch[pos][];fa[root]=;
delnode(pos);
}
else{
int sec=pre();splay(sec,root);
root=ch[pos][];fa[root]=;
ch[root][]=ch[pos][];fa[ch[pos][]]=root;
update(root);delnode(pos);
}
}
}T;
int main(){
int i,t1,t2,Q=read();
for(i=;i<=Q;i++){
// cout<<"**************************query i "<<i<<endl;
t1=read();t2=read();
switch(t1){
case :T.insert(T.root,t2);break;
case :T.del(t2);break;
case :T.insert(T.root,t2);printf("%d\n",T.getrank(T.root,t2,));T.del(t2);break;
case :printf("%d\n",T.getpos(T.root,t2));break;
case :T.insert(T.root,t2);printf("%d\n",T.w[T.pre()]);T.del(t2);break;
case :T.insert(T.root,t2);printf("%d\n",T.w[T.suf()]);T.del(t2);break;
}
}
}
省选算法学习-数据结构-splay的更多相关文章
- 省选算法学习-插头dp
插头dp?你说的是这个吗? 好吧显然不是...... 所谓插头dp,实际上是“基于连通性的状态压缩dp”的简称,最先出现在cdq的论文里面 本篇博客致力于通过几道小小的例题(大部分都比较浅显)来介绍一 ...
- 省选算法学习-BSGS与exBSGS与二次剩余
前置知识 扩展欧几里得,快速幂 都是很基础的东西 扩展欧几里得 说实话这个东西我学了好几遍都没有懂,最近终于搞明白,可以考场现推了,故放到这里来加深印象 翡蜀定理 方程$ax+by=gcd(a,b)$ ...
- 省选算法学习-回文自动机 && 回文树
前置知识 首先你得会manacher,并理解manacher为什么是对的(不用理解为什么它是$O(n)$,这个大概记住就好了,不过理解了更方便做$PAM$的题) 什么是回文自动机? 回文自动机(Pal ...
- 省选算法学习-dp优化-四边形不等式
嗯......四边形不等式的确长得像个四边形[雾] 我们在dp中,经常见到这样一类状态以及转移方程: 设$dp\left[i\right]\left[j\right]$表示闭区间$\left[i,j\ ...
- 大数据学习之BigData常用算法和数据结构
大数据学习之BigData常用算法和数据结构 1.Bloom Filter 由一个很长的二进制向量和一系列hash函数组成 优点:可以减少IO操作,省空间 缺点:不支持删除,有 ...
- 在Object-C中学习数据结构与算法之排序算法
笔者在学习数据结构与算法时,尝试着将排序算法以动画的形式呈现出来更加方便理解记忆,本文配合Demo 在Object-C中学习数据结构与算法之排序算法阅读更佳. 目录 选择排序 冒泡排序 插入排序 快速 ...
- OI省选算法汇总及学习计划(转)
1.1 基本数据结构 数组(√) 链表(√),双向链表(√) 队列(√),单调队列(√),双端队列(√) 栈(√),单调栈(√) 1.2 中级数据结构 堆(√) 并查集与带权并查集(√) hash 表 ...
- AJPFX关于学习java遇到的问题:对算法和数据结构不熟悉
为什么我先拿“数据结构和算法”说事捏?这玩意是写程序最最基本的东东.不管你使用 Java 还是其它的什么语言,都离不开它.而且这玩意是跨语言的,学好之后不管在哪门语言中都能用得上. 既然“数据结构和算 ...
- OI省选算法汇总( 转发黄学长博客 )
[原文链接] http://hzwer.com/1234.html 注 : 蓝色为已学习算法 , 绿色为不熟练算法 , 灰色为未学习算法 1.1 基本数据结构 1. 数组 2. 链表,双向链表 3. ...
随机推荐
- vuejs课程简介及框架简介
vuejs准备知识: 1.前端开发基础 html css js 2.前端模块化基础 3.对es6有初步的了解 vuejs是一种轻量级的MVM框架,他吸收了react和angular的优点,强调re ...
- CUDA:Supercomputing for the Masses (用于大量数据的超级计算)-第一节
原文链接 第一节 CUDA 让你可以一边使用熟悉的编程概念,一边开发可在GPU上运行的软件. Rob Farber 是西北太平洋国家实验室(Pacific Northwest National Lab ...
- 搜狗浏览器特性页面JS
http://ie.sogou.com/features4.2.html <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Strict//EN ...
- Bootstrap 弹出框(Popover)插件
Bootstrap 弹出框(Popover)插件与Bootstrap 提示工具(Tooltip)插件类似,提供了一个扩展的视图,用户只需要把鼠标指针悬停到元素上面即可.弹出框的内容完全由Bootstr ...
- 【思维题 最大权闭合子图】loj#6045. 「雅礼集训 2017 Day8」价
又是经典模型的好题目 题目描述 人类智慧之神 zhangzj 最近有点胖,所以要减肥,他买了 NN 种减肥药,发现每种减肥药使用了若干种药材,总共正好有 NN 种不同的药材. 经过他的人脑实验,他发现 ...
- CentOS7 ngnix 的安装和配置
刚开始我也在纠结到底是该用Apache呢还是Nginx?然后网上各种查看了它俩的对比,总结了它俩最大区别在于apache是同步多进程模型,在处理动态有优势:nginx是异步的,并发性能比较好,cpu内 ...
- IDEA整合Mybatis+Struts2+Spring (二)--整合框架
二.搭建目录结构 我这里列出的是搭建完了之后所有的目录和文件,诸位先把目录文件建起来,然后我在给出文件内容 这里的目录建好之后还需要设置一下,让idea识别目录作用,选择File-Project St ...
- Emgu.CV.CvInvoke的类型初始值设定项引发异常
被这个问题蛋疼了一个下午,终于解决了.我的服务器出现这个问题的原因:可能是没有安装emgucv. 解决方法: 1.下载并安装emgucv 下载地址:链接: https://pan.baidu.com/ ...
- Python知识点入门笔记——特色数据类型(元组)
元组(tuple)是Python的另一种特色数据类型,元组和列表是相似的,可以存储不同类型的数据,但是元组是不可改变的,创建后就不能做任何修改操作. 创建元组 用逗号隔开的就是元组,但是为了美观和代码 ...
- Keepalivaed +Nginx proxy 高可用架构方案与实施过程细节
1.开源产品介绍 1)CMS介绍 官方网站http://www.dedecms.com/,是一个网站应用系统构建平台,也是一个强大的网站内容管理系统,既可以用来构建复杂的体系的企业信息门户或者电子商务 ...
