chapter3——逻辑回归手动+sklean版本
1 导入numpy包
- import numpy as np
2 sigmoid函数
- def sigmoid(x):
- return 1/(1+np.exp(-x))
- demox = np.array([1,2,3])
- print(sigmoid(demox))
- #报错
- #demox = [1,2,3]
- # print(sigmoid(demox))
结果:
- [0.73105858 0.88079708 0.95257413]
3 定义逻辑回归模型主体
- ### 定义逻辑回归模型主体
- def logistic(x, y, w, b):
- # 训练样本量
- num_train = x.shape[0]
- # 逻辑回归模型输出
- y_hat = sigmoid(np.dot(x,w)+b)
- # 交叉熵损失
- cost = -1/(num_train)*(np.sum(y*np.log(y_hat)+(1-y)*np.log(1-y_hat)))
- # 权值梯度
- dW = np.dot(x.T,(y_hat-y))/num_train
- # 偏置梯度
- db = np.sum(y_hat- y)/num_train
- # 压缩损失数组维度
- cost = np.squeeze(cost)
- return y_hat, cost, dW, db
4 初始化函数
- def init_parm(dims):
- w = np.zeros((dims,1))
- b = 0
- return w ,b
5 定义逻辑回归模型训练过程
- ### 定义逻辑回归模型训练过程
- def logistic_train(X, y, learning_rate, epochs):
- # 初始化模型参数
- W, b = init_parm(X.shape[1])
- cost_list = []
- for i in range(epochs):
- # 计算当前次的模型计算结果、损失和参数梯度
- a, cost, dW, db = logistic(X, y, W, b)
- # 参数更新
- W = W -learning_rate * dW
- b = b -learning_rate * db
- if i % 100 == 0:
- cost_list.append(cost)
- if i % 100 == 0:
- print('epoch %d cost %f' % (i, cost))
- params = {
- 'W': W,
- 'b': b
- }
- grads = {
- 'dW': dW,
- 'db': db
- }
- return cost_list, params, grads
6 定义预测函数
- def predict(X,params):
- y_pred = sigmoid(np.dot(X,params['W'])+params['b'])
- y_preds = [1 if y_pred[i]>0.5 else 0 for i in range(len(y_pred))]
- return y_preds
7 生成数据
- # 导入matplotlib绘图库
- import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
- # 导入生成分类数据函数
- from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
- # 生成100*2的模拟二分类数据集
- x ,label = make_classification(
- n_samples=100,# 样本个数
- n_classes=2,# 样本类别
- n_features=2,#特征个数
- n_redundant=0,#冗余特征个数(有效特征的随机组合)
- n_informative=2,#有效特征,有价值特征
- n_repeated=0, # 重复特征个数(有效特征和冗余特征的随机组合)
- n_clusters_per_class=2 ,# 簇的个数
- random_state=1,
- )
- print("x.shape =",x.shape)
- print("label.shape = ",label.shape)
- print("np.unique(label) =",np.unique(label))
- print(set(label))
- # 设置随机数种子
- rng = np.random.RandomState(2)
- # 对生成的特征数据添加一组均匀分布噪声https://blog.csdn.net/vicdd/article/details/52667709
- x += 2*rng.uniform(size=x.shape)
- # 标签类别数
- unique_label = set(label)
- # 根据标签类别数设置颜色
- print(np.linspace(0,1,len(unique_label)))
- colors = plt.cm.Spectral(np.linspace(0,1,len(unique_label)))
- print(colors)
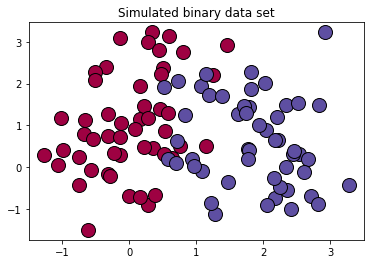
- # 绘制模拟数据的散点图
- for k,col in zip(unique_label , colors):
- x_k=x[label==k]
- plt.plot(x_k[:,0],x_k[:,1],'o',markerfacecolor=col,markeredgecolor="k",
- markersize=14)
- plt.title('Simulated binary data set')
- plt.show();
结果:
- x.shape = (100, 2)
- label.shape = (100,)
- np.unique(label) = [0 1]
- {0, 1}
- [0. 1.]
- [[0.61960784 0.00392157 0.25882353 1. ]
- [0.36862745 0.30980392 0.63529412 1. ]]
复习
- # 复习
- mylabel = label.reshape((-1,1))
- data = np.concatenate((x,mylabel),axis=1)
- print(data.shape)
结果:
- (100, 3)
8 划分数据集
- offset = int(x.shape[0]*0.7)
- x_train, y_train = x[:offset],label[:offset].reshape((-1,1))
- x_test, y_test = x[offset:],label[offset:].reshape((-1,1))
- print(x_train.shape)
- print(y_train.shape)
- print(x_test.shape)
- print(y_test.shape)
结果:
- (70, 2)
- (70, 1)
- (30, 2)
- (30, 1)
9 训练
- cost_list, params, grads = logistic_train(x_train, y_train, 0.01, 1000)
- print(params['b'])
结果:
- epoch 0 cost 0.693147
- epoch 100 cost 0.568743
- epoch 200 cost 0.496925
- epoch 300 cost 0.449932
- epoch 400 cost 0.416618
- epoch 500 cost 0.391660
- epoch 600 cost 0.372186
- epoch 700 cost 0.356509
- epoch 800 cost 0.343574
- epoch 900 cost 0.332689
- -0.6646648941379839
10 准确率计算
- from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score,classification_report
- y_pred = predict(x_test,params)
- print("y_pred = ",y_pred)
- print(y_pred)
- print(y_test.shape)
- print(accuracy_score(y_pred,y_test)) #不需要都是1维的,貌似会自动squeeze()
- print(classification_report(y_test,y_pred))
结果:
- y_pred = [0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0]
- [0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 1, 0]
- (30, 1)
- 0.9333333333333333
- precision recall f1-score support
- 0 0.92 0.92 0.92 12
- 1 0.94 0.94 0.94 18
- accuracy 0.93 30
- macro avg 0.93 0.93 0.93 30
- weighted avg 0.93 0.93 0.93 30
11 绘制逻辑回归决策边界
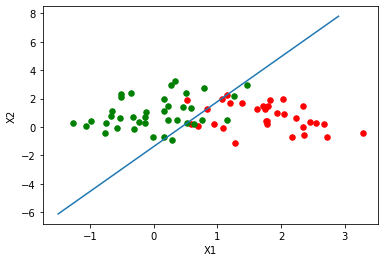
- ### 绘制逻辑回归决策边界
- def plot_logistic(X_train, y_train, params):
- # 训练样本量
- n = X_train.shape[0]
- xcord1,ycord1,xcord2,ycord2 = [],[],[],[]
- # 获取两类坐标点并存入列表
- for i in range(n):
- if y_train[i] == 1:
- xcord1.append(X_train[i][0])
- ycord1.append(X_train[i][1])
- else:
- xcord2.append(X_train[i][0])
- ycord2.append(X_train[i][1])
- fig = plt.figure()
- ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
- ax.scatter(xcord1,ycord1,s = 30,c = 'red')
- ax.scatter(xcord2,ycord2,s = 30,c = 'green')
- # 取值范围
- x =np.arange(-1.5,3,0.1)
- # 决策边界公式
- y = (-params['b'] - params['W'][0] * x) / params['W'][1]
- # 绘图
- ax.plot(x, y)
- plt.xlabel('X1')
- plt.ylabel('X2')
- plt.show()
- plot_logistic(x_train, y_train, params)
结果:
11 sklearn实现
- from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
- clf = LogisticRegression(random_state=0).fit(x_train,y_train)
- y_pred = clf.predict(x_test)
- print(y_pred)
- accuracy_score(y_test,y_pred)
结果:
- [0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 0]
- 0.9333333333333333
chapter3——逻辑回归手动+sklean版本的更多相关文章
- numpy+sklearn 手动实现逻辑回归【Python】
逻辑回归损失函数: from sklearn.datasets import load_iris,make_classification from sklearn.model_selection im ...
- 逻辑回归原理_挑战者飞船事故和乳腺癌案例_Python和R_信用评分卡(AAA推荐)
sklearn实战-乳腺癌细胞数据挖掘(博客主亲自录制视频教程) https://study.163.com/course/introduction.htm?courseId=1005269003&a ...
- 逻辑回归算法的原理及实现(LR)
Logistic回归虽然名字叫"回归" ,但却是一种分类学习方法.使用场景大概有两个:第一用来预测,第二寻找因变量的影响因素.逻辑回归(Logistic Regression, L ...
- Theano3.3-练习之逻辑回归
是官网上theano的逻辑回归的练习(http://deeplearning.net/tutorial/logreg.html#logreg)的讲解. Classifying MNIST digits ...
- PRML读书会第四章 Linear Models for Classification(贝叶斯marginalization、Fisher线性判别、感知机、概率生成和判别模型、逻辑回归)
主讲人 planktonli planktonli(1027753147) 19:52:28 现在我们就开始讲第四章,第四章的内容是关于 线性分类模型,主要内容有四点:1) Fisher准则的分类,以 ...
- Spark Mllib逻辑回归算法分析
原创文章,转载请注明: 转载自http://www.cnblogs.com/tovin/p/3816289.html 本文以spark 1.0.0版本MLlib算法为准进行分析 一.代码结构 逻辑回归 ...
- Python实践之(七)逻辑回归(Logistic Regression)
机器学习算法与Python实践之(七)逻辑回归(Logistic Regression) zouxy09@qq.com http://blog.csdn.net/zouxy09 机器学习算法与Pyth ...
- 学习Machine Leaning In Action(四):逻辑回归
第一眼看到逻辑回归(Logistic Regression)这个词时,脑海中没有任何概念,读了几页后,发现这非常类似于神经网络中单个神经元的分类方法. 书中逻辑回归的思想是用一个超平面将数据集分为两部 ...
- Andrew Ng机器学习课程笔记--week3(逻辑回归&正则化参数)
Logistic Regression 一.内容概要 Classification and Representation Classification Hypothesis Representatio ...
随机推荐
- Docker 与 K8S学习笔记(九)—— 容器间通信
容器之间可通过IP.Docker DNS Server或joined三种方式进行通信,今天我们来详细学习一下. 一.IP通信 IP通信很简单,前一篇中已经有所涉及了,只要容器使用相同网络,那么就可以使 ...
- griffin环境搭建及功能测试
目录 1 准备 mysql hive hadoop spark livy es maven 配置环境变量 2 安装griffin 配置配置文件 编译 部署jar包 3 批处理测试 准确度度量 Accu ...
- (原创)WinForm中莫名其妙的小BUG——RichTextBox自动选择字词问题
一.前言 使用WinForm很久了,多多少少会遇到一些小BUG. 这些小BUG影响并不严重,而且稍微设置一下就能正常使用,而且微软一直也没有修复这些小BUG. 写本系列文章,是为了记录一下这些无伤大雅 ...
- DAGs with NO TEARS: Continuous Optimization for Structure Learning
DAGs with NO TEARS: Continuous Optimization for Structure Learning 目录 DAGs with NO TEARS: Continuous ...
- MA8601升级版 PL2586|USB HUB 工控级芯片方案PL2586|可直接替代FE1.1S芯片方案
MA8601升级版 PL2586|USB HUB 工控级芯片方案PL2586|可直接替代FE1.1S芯片方案 旺玖在2022年新推出的一款USB HUB 芯片其性能和参数可以完全替代FE1.1S,是M ...
- C语言string操作
创建方式 字符数组:空间已定 字符指针:未分配空间 初始化 字符数组: 创建与赋值必须在同一行 指定大小:未填满部分用'\0'填充 用字符串初始化:末尾自动添加'\0' 不初始化赋值则乱值 字符指针: ...
- 高效位运算 __builtin_系列函数
•int __builtin_ffs (unsigned int x) 返回x的最后一位1的是从后向前第几位,比如7368(1110011001000)返回4. •int __builtin_clz ...
- Java Web程序设计笔记 • 【第2章 JSP基础】
全部章节 >>>> 本章目录 2.1 JSP 简介 2.1.1 JSP 概述 2.1.2 开发第一个 JSP 页面 2.1.3 JSP 处理流程 2.1.4 实践练习 2. ...
- SQL Server 数据库添加主键,唯一键,外键约束脚本
-- 声明使用数据库use 数据库;go -- 添加主键(primary key)约束-- 基本语法-- 判断主键约束是否存在,如果存在则删除,不存在则添加if exists(select * fro ...
- Python3.7 发送邮件 报‘[WinError 10061] 由于目标计算机积极拒绝,无法连接’错误的解决方法
背景: 最近在练习Python 的邮件发送功能 照着教程写了一个简单的demo 结果运行时报如下错误:[WinError 10061] 由于目标计算机积极拒绝,无法连接. 如图: 解决路径如下: St ...
