用Java实现红黑树
红黑树是众多“平衡的”搜索树模式中的一种,在最坏情况下,它相关操作的时间复杂度为O(log n)。
1、红黑树的属性
红黑树是一种二分查找树,与普通的二分查找树不同的一点是,红黑树的每个节点都有一个颜色(color)属性。该属性的值要么是红色,要么是黑色。
通过限制从根到叶子的任何简单路径上的节点颜色,红黑树确保没有比任何其他路径长两倍的路径,从而使树近似平衡。
假设红黑树节点的属性有键(key)、颜色(color)、左子节点(left)、右子节点(right),父节点(parent)。
一棵红黑树必须满足下面有下面这些特性(红黑树特性):
- 树中的每个节点要么是红色,要么是黑色;
- 根节点是黑色;
- 每个叶子节点(null)是黑色;
- 如果某节点是红色的,它的两个子节点都是黑色;
- 对于每个节点到后面任一叶子节点(null)的所有路径,都有相同数量的黑色节点。
为了在红黑树代码中处理边界条件方便,我们用一个哨兵变量代替null。对于一个红黑树tree,哨兵变量RedBlackTree.NULL(下文代码中)是一个和其它节点有同样属性的节点,它的颜色(color)属性是黑色,其它属性可以任意取值。
我们使用哨兵变量是因为我们可以把一个节点node的子节点null当成一个普通节点。
在这里,我们使用哨兵变量RedBlackTree.NULL代替树中所有的null(所有的叶子节点及根节点的父节点)。
我们把从一个节点n(不包括)到任一叶子节点路径上的黑色节点的个数称为黑色高度,用bh(n)表示。一棵红黑树的黑色高度是其根节点的黑色高度。
关于红黑树的搜索,求最小值,求最大值,求前驱,求后继这些操作的代码与二分查找树的这些操作的代码基本一致。可以在用java实现二分查找树查看。
结合上文给出下面的代码。
用一个枚举类Color表示颜色:
public enum Color {
Black("黑色"), Red("红色");
private String color;
private Color(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return color;
}
}
类Node表示节点:
public class Node {
public int key;
public Color color;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node parent;
public Node() {
}
public Node(Color color) {
this.color = color;
}
public Node(int key) {
this.key = key;
this.color = Color.Red;
}
public int height() {
return Math.max(left != RedBlackTree.NULL ? left.height() : 0, right != RedBlackTree.NULL ? right.height() : 0) + 1;
}
public Node minimum() {
Node pointer = this;
while (pointer.left != RedBlackTree.NULL)
pointer = pointer.left;
return pointer;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
String position = "null";
if (this.parent != RedBlackTree.NULL)
position = this.parent.left == this ? "left" : "right";
return "[key: " + key + ", color: " + color + ", parent: " + parent.key + ", position: " + position + "]";
}
}
类RedTreeNode表示红黑树:
public class RedBlackTree {
// 表示哨兵变量
public final static Node NULL = new Node(Color.Black);
public Node root;
public RedBlackTree() {
this.root = NULL;
}
}
2、旋转
红黑树的插入和删除操作,能改变红黑树的结构,可能会使它不再有前面所说的某些特性性。为了维持这些特性,我们需要改变树中某些节点的颜色和位置。
我们可以通过旋转改变节点的结构。主要有左旋转和右旋转两种方式。具体如下图所示。
左旋转:把一个节点n的右子节点right变为它的父节点,n变为right的左子节点,所以right不能为null。这时n的右指针空了出来,right的左子树被n挤掉,所以right原来的左子树称为n的右子树。
右旋转:把一个节点n的左子节点left变为它的父节点,n变为left的右子节点,所以left不能为null。这时n的左指针被空了出来,left的右子树被n挤掉,所以left原来的右子树被称为n的左子树。

可在RedTreeNode类中,加上如下实现代码:
public void leftRotate(Node node) {
Node rightNode = node.right;
node.right = rightNode.left;
if (rightNode.left != RedBlackTree.NULL)
rightNode.left.parent = node;
rightNode.parent = node.parent;
if (node.parent == RedBlackTree.NULL)
this.root = rightNode;
else if (node.parent.left == node)
node.parent.left = rightNode;
else
node.parent.right = rightNode;
rightNode.left = node;
node.parent = rightNode;
}
public void rightRotate(Node node) {
Node leftNode = node.left;
node.left = leftNode.right;
if (leftNode.right != RedBlackTree.NULL)
leftNode.right.parent = node;
leftNode.parent = node.parent;
if (node.parent == RedBlackTree.NULL) {
this.root = leftNode;
} else if (node.parent.left == node) {
node.parent.left = leftNode;
} else {
node.parent.right = leftNode;
}
leftNode.right = node;
node.parent = leftNode;
}
3、插入
红黑树的插入代码与二分查找树的插入代码非常相似。只不过红黑树的插入操作会改变红黑树的结构,使其不在有该有的特性。
在这里,新插入的节点默认是红色。
所以在插入节点之后,要有维护红黑树特性的代码。
public void insert(Node node) {
Node parentPointer = RedBlackTree.NULL;
Node pointer = this.root;
while (this.root != RedBlackTree.NULL) {
parentPointer = pointer;
pointer = node.key < pointer.key ? pointer.left : pointer.right;
}
node.parent = parentPointer;
if(parentPointer == RedBlackTree.NULL) {
this.root = node;
}else if(node.key < parentPointer.key) {
parentPointer.left = node;
}else {
parentPointer.right = node;
}
node.left = RedBlackTree.NULL;
node.right = RedBlackTree.NULL;
node.color = Color.Red;
// 维护红黑树属性的方法
this.insertFixUp(node);
}
用上述方法插入一个新节点的时候,有两类情况会违反红黑树的特性。
- 当树中没有节点时,此时插入的节点称为根节点,而此节点的颜色为红色。
- 当新插入的节点成为一个红色节点的子节点时,此时存在一个红色结点有红色子节点的情况。
对于第一类情况,可以直接把根结点设置为黑色;而针对第二类情况,需要根据具体条件,做出相应的解决方案。
具体代码如下:
public void insertFixUp(Node node) {
// 当node不是根结点,且node的父节点颜色为红色
while (node.parent.color == Color.Red) {
// 先判断node的父节点是左子节点,还是右子节点,这不同的情况,解决方案也会不同
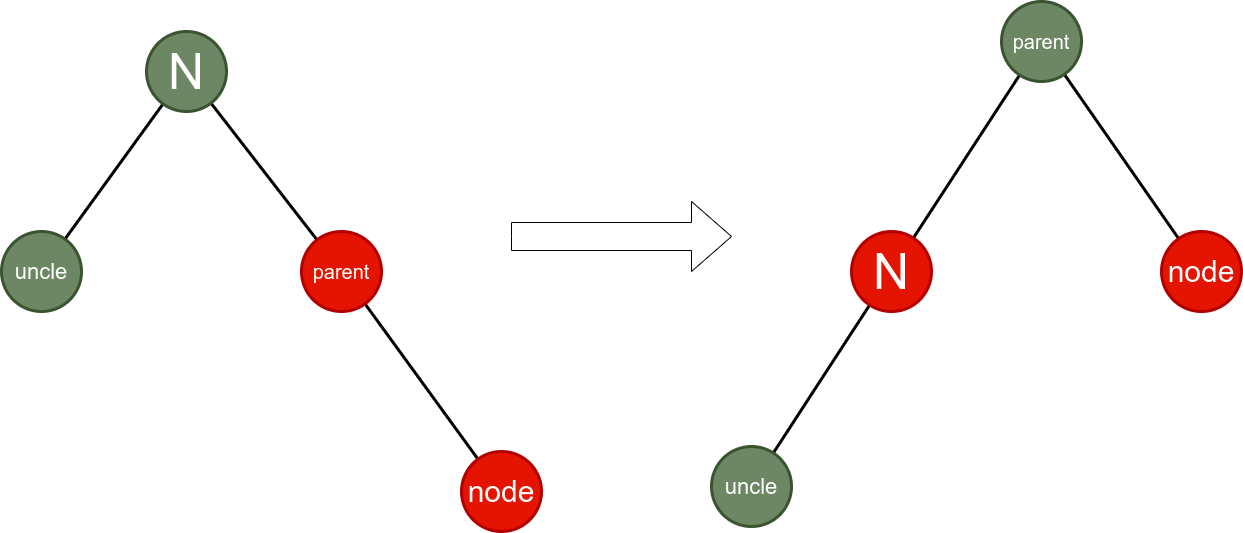
if (node.parent == node.parent.parent.left) {
Node uncleNode = node.parent.parent.right;
if (uncleNode.color == Color.Red) { // 如果叔叔节点是红色,则父父一定是黑色
// 通过把父父节点变成红色,父节点和兄弟节点变成黑色,然后在判断父父节点的颜色是否合适
uncleNode.color = Color.Black;
node.parent.color = Color.Black;
node.parent.parent.color = Color.Red;
node = node.parent.parent;
} else if (node == node.parent.right) {
node = node.parent;
this.leftRotate(node);
} else {
node.parent.color = Color.Black;
node.parent.parent.color = Color.Red;
this.rightRotate(node.parent.parent);
}
} else {
Node uncleNode = node.parent.parent.left;
if (uncleNode.color == Color.Red) {
uncleNode.color = Color.Black;
node.parent.color = Color.Black;
node.parent.parent.color = Color.Red;
node = node.parent.parent;
} else if (node == node.parent.left) {
node = node.parent;
this.rightRotate(node);
} else {
node.parent.color = Color.Black;
node.parent.parent.color = Color.Red;
this.leftRotate(node.parent.parent);
}
}
}
// 如果之前树中没有节点,那么新加入的点就成了新结点,而新插入的结点都是红色的,所以需要修改。
this.root.color = Color.Black;
}
下面的图分别对应第二类情况中的六种及相应处理结果。
情况1:

情况2:
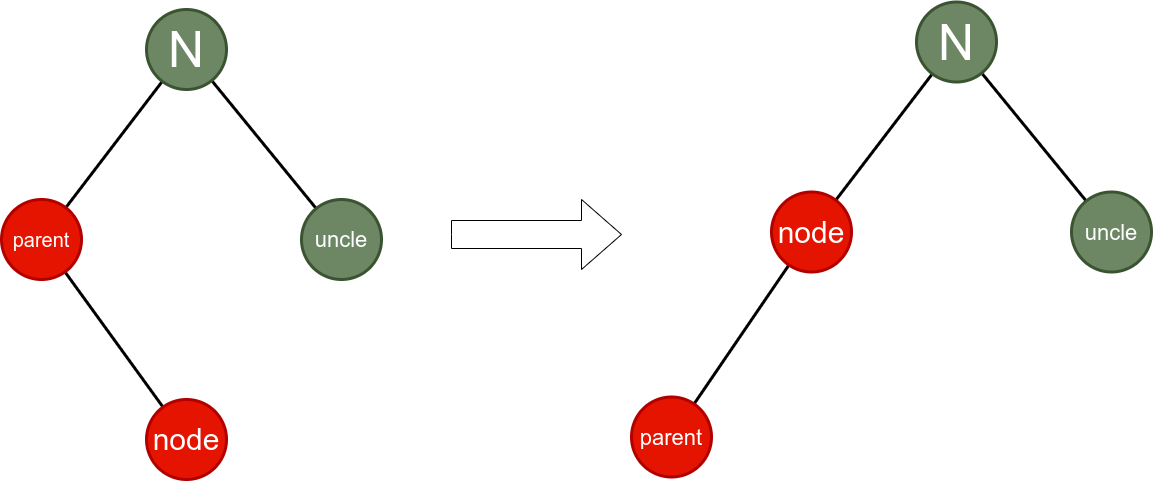
情况3:
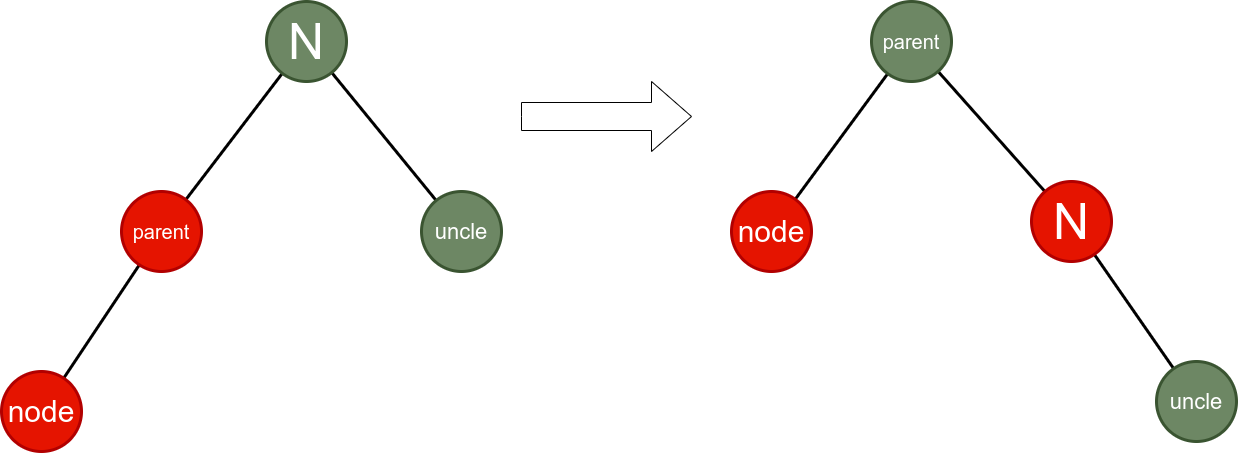
情况4:
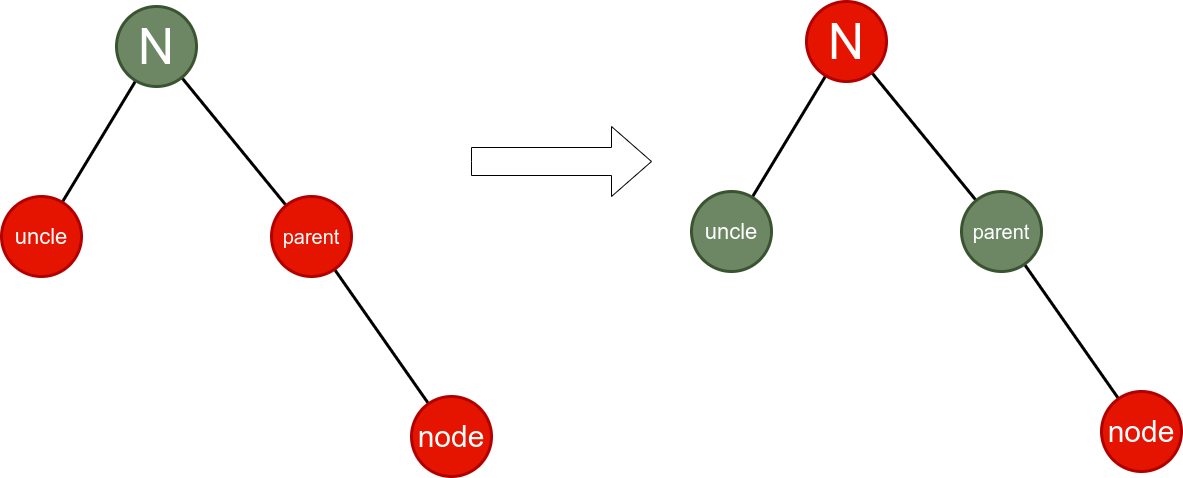
情况5:
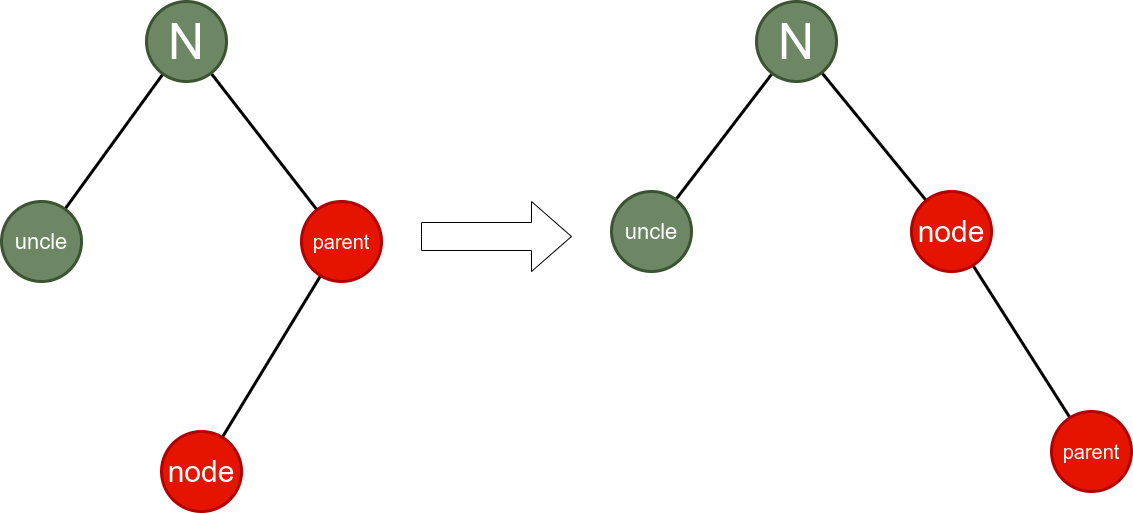
情况6:
4、删除
红黑树中节点的删除会使一个结点代替另外一个节点。所以先要实现这样的代码:
public void transplant(Node n1, Node n2) {
if(n1.parent == RedBlackTree.NULL){
this.root = n2;
}else if(n1.parent.left == n1) {
n1.parent.left = n2;
}else {
n1.parent.right = n2;
}
n2.parent = n1.parent;
}
红黑树的删除节点代码是基于二分查找树的删除节点代码而写的。
删除结点代码:
public void delete(Node node) {
Node pointer1 = node;
// 用于记录被删除的颜色,如果是红色,可以不用管,但如果是黑色,可能会破坏红黑树的属性
Color pointerOriginColor = pointer1.color;
// 用于记录问题的出现点
Node pointer2;
if (node.left == RedBlackTree.NULL) {
pointer2 = node.right;
this.transplant(node, node.right);
} else if (node.right == RedBlackTree.NULL) {
pointer2 = node.left;
this.transplant(node, node.left);
} else {
// 如要删除的字节有两个子节点,则找到其直接后继(右子树最小值),直接后继节点没有非空左子节点。
pointer1 = node.right.minimum();
// 记录直接后继的颜色和其右子节点
pointerOriginColor = pointer1.color;
pointer2 = pointer1.right;
// 如果其直接后继是node的右子节点,不用进行处理
if (pointer1.parent == node) {
pointer2.parent = pointer1;
} else {
// 否则,先把直接后继从树中提取出来,用来替换node
this.transplant(pointer1, pointer1.right);
pointer1.right = node.right;
pointer1.right.parent = pointer1;
}
// 用node的直接后继替换node,继承node的颜色
this.transplant(node, pointer1);
pointer1.left = node.left;
pointer1.left.parent = pointer1;
pointer1.color = node.color;
}
if (pointerOriginColor == Color.Black) {
this.deleteFixUp(pointer2);
}
}
当被删除节点的颜色是黑色时需要调用方法维护红黑树的特性。
主要有两类情况:
- 当node是红色时,直接变成黑色即可。
- 当node是黑色时,需要调整红黑树结构。,
private void deleteFixUp(Node node) {
// 如果node不是根节点,且是黑色
while (node != this.root && node.color == Color.Black) {
// 如果node是其父节点的左子节点
if (node == node.parent.left) {
// 记录node的兄弟节点
Node pointer1 = node.parent.right;
// 如果他兄弟节点是红色
if (pointer1.color == Color.Red) {
pointer1.color = Color.Black;
node.parent.color = Color.Red;
leftRotate(node.parent);
pointer1 = node.parent.right;
}
if (pointer1.left.color == Color.Black && pointer1.right.color == Color.Black) {
pointer1.color = Color.Red;
node = node.parent;
} else if (pointer1.right.color == Color.Black) {
pointer1.left.color = Color.Black;
pointer1.color = Color.Red;
rightRotate(pointer1);
pointer1 = node.parent.right;
} else {
pointer1.color = node.parent.color;
node.parent.color = Color.Black;
pointer1.right.color = Color.Black;
leftRotate(node.parent);
node = this.root;
}
} else {
// 记录node的兄弟节点
Node pointer1 = node.parent.left;
// 如果他兄弟节点是红色
if (pointer1.color == Color.Red) {
pointer1.color = Color.Black;
node.parent.color = Color.Red;
rightRotate(node.parent);
pointer1 = node.parent.left;
}
if (pointer1.right.color == Color.Black && pointer1.left.color == Color.Black) {
pointer1.color = Color.Red;
node = node.parent;
} else if (pointer1.left.color == Color.Black) {
pointer1.right.color = Color.Black;
pointer1.color = Color.Red;
leftRotate(pointer1);
pointer1 = node.parent.left;
} else {
pointer1.color = node.parent.color;
node.parent.color = Color.Black;
pointer1.left.color = Color.Black;
rightRotate(node.parent);
node = this.root;
}
}
}
node.color = Color.Black;
}
对第二类情况,有下面8种:
情况1:

情况2:
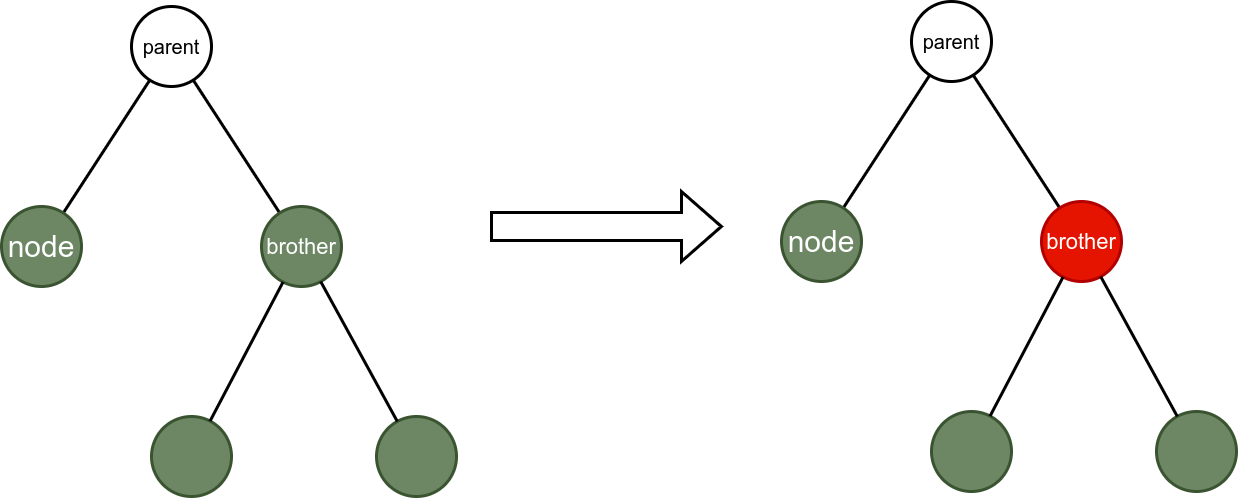
情况3:
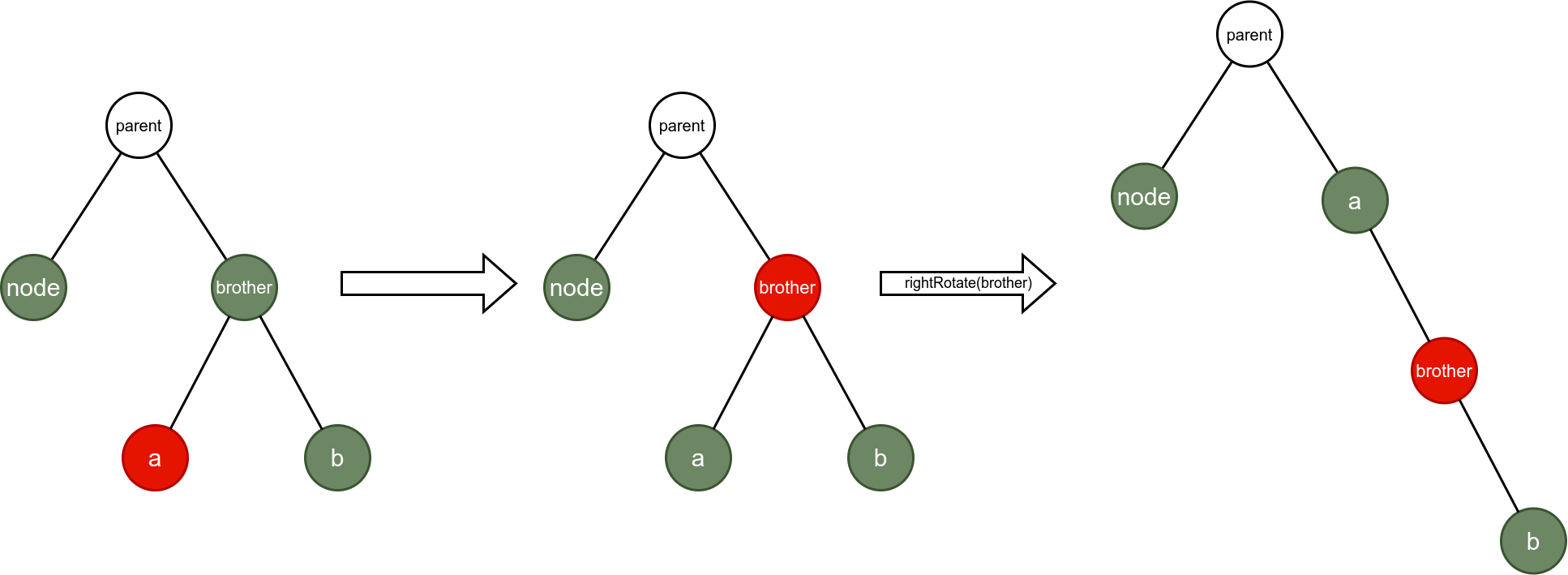
情况4:

情况5:
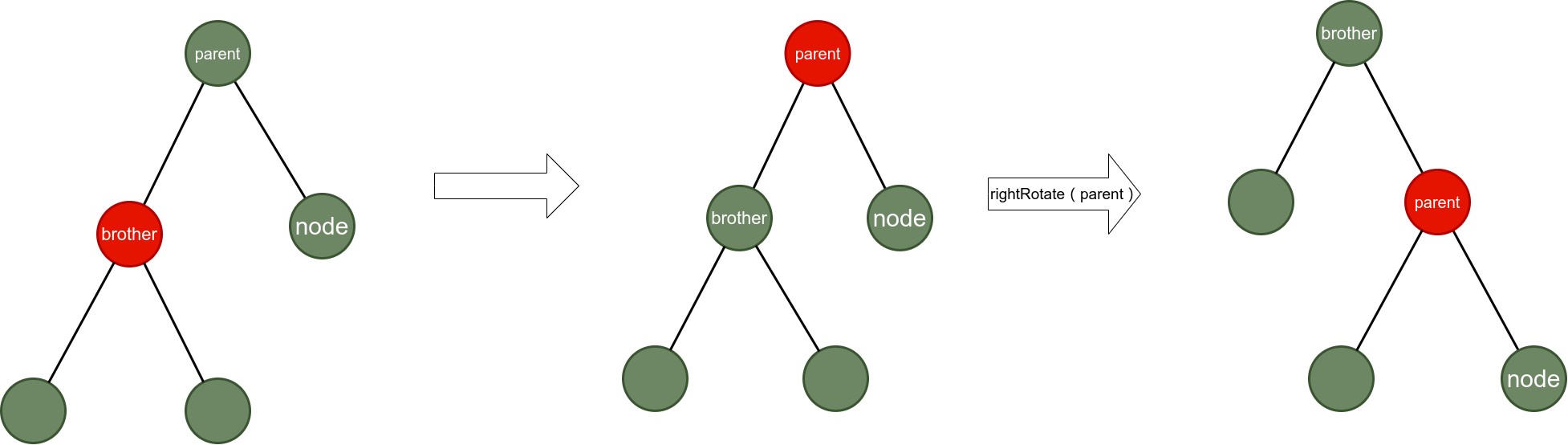
情况6:
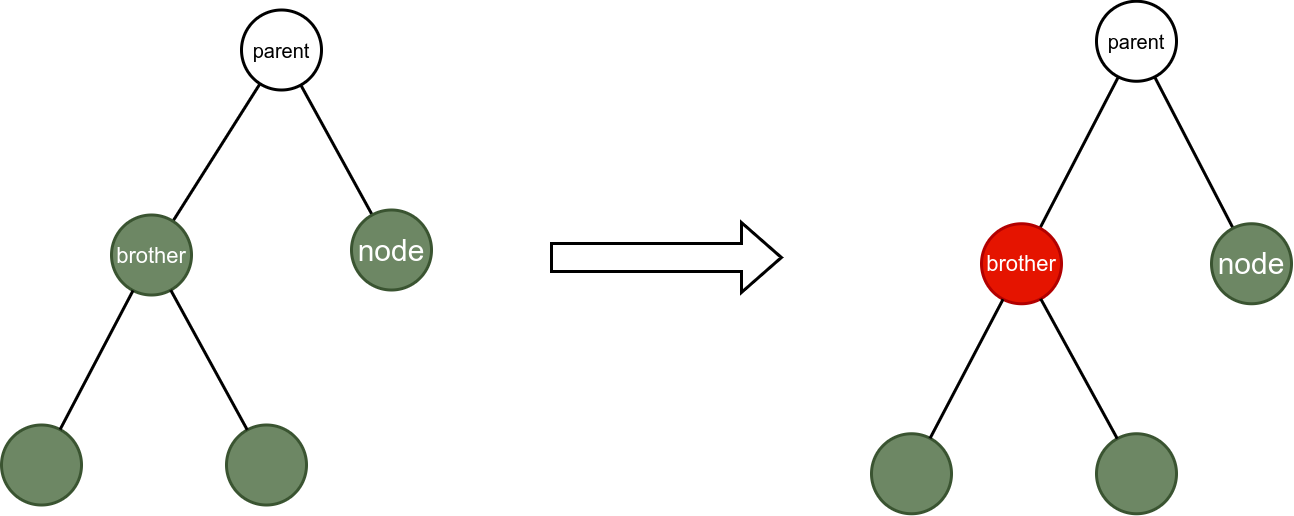
情况7:
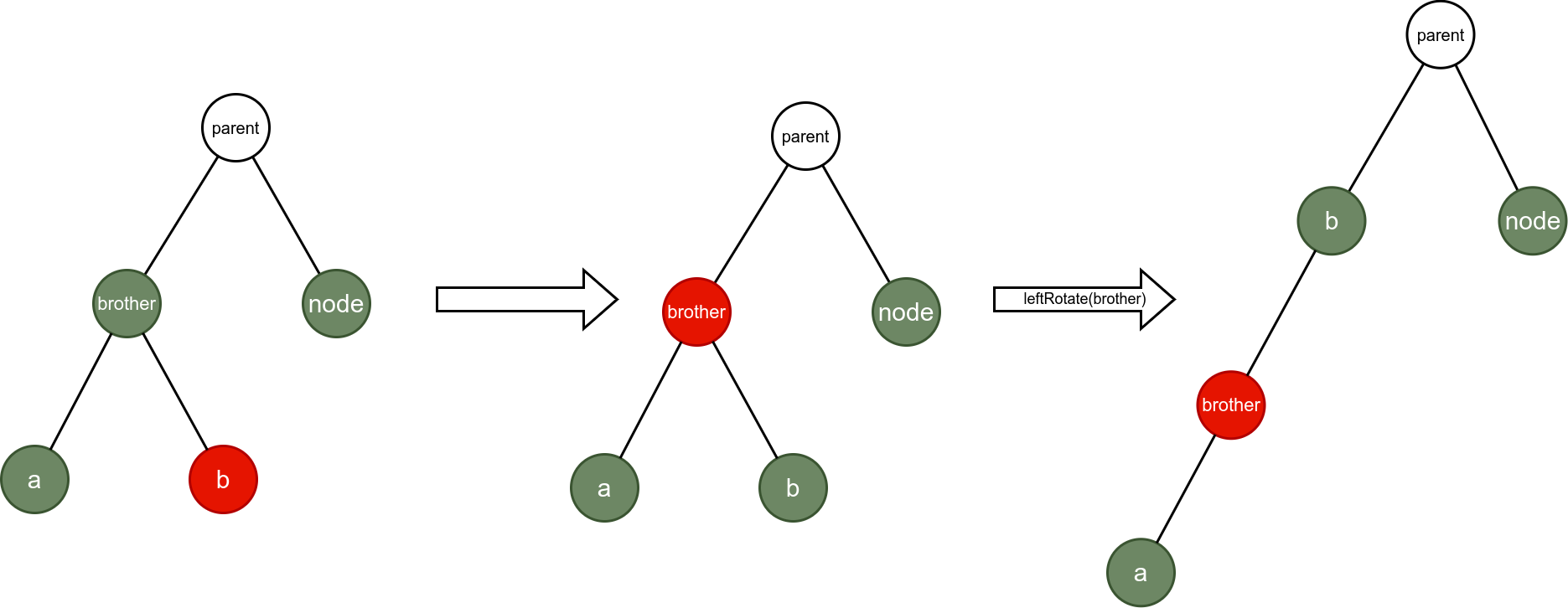
情况8:
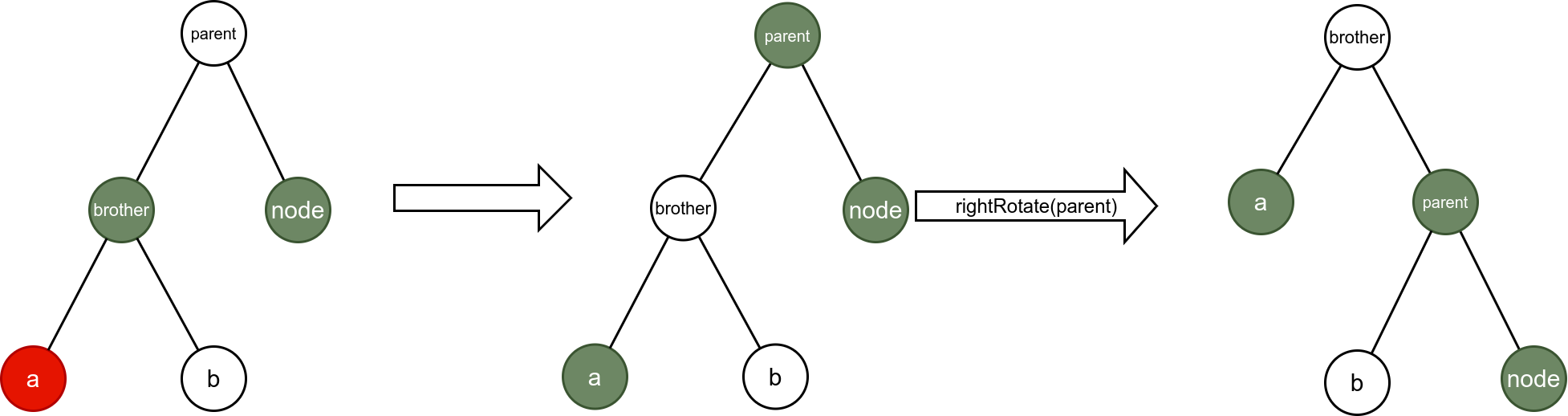
5、所有代码
public enum Color {
Black("黑色"), Red("红色");
private String color;
private Color(String color) {
this.color = color;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return color;
}
}
public class Node {
public int key;
public Color color;
public Node left;
public Node right;
public Node parent;
public Node() {
}
public Node(Color color) {
this.color = color;
}
public Node(int key) {
this.key = key;
this.color = Color.Red;
}
/**
* 求在树中节点的高度
*
* @return
*/
public int height() {
return Math.max(left != RedBlackTree.NULL ? left.height() : 0, right != RedBlackTree.NULL ? right.height() : 0) + 1;
}
/**
* 在以该节点为根节点的树中,求最小节点
*
* @return
*/
public Node minimum() {
Node pointer = this;
while (pointer.left != RedBlackTree.NULL)
pointer = pointer.left;
return pointer;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
String position = "null";
if (this.parent != RedBlackTree.NULL)
position = this.parent.left == this ? "left" : "right";
return "[key: " + key + ", color: " + color + ", parent: " + parent.key + ", position: " + position + "]";
}
}
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class RedBlackTree {
public final static Node NULL = new Node(Color.Black);
public Node root;
public RedBlackTree() {
this.root = NULL;
}
/**
* 左旋转
*
* @param node
*/
public void leftRotate(Node node) {
Node rightNode = node.right;
node.right = rightNode.left;
if (rightNode.left != RedBlackTree.NULL)
rightNode.left.parent = node;
rightNode.parent = node.parent;
if (node.parent == RedBlackTree.NULL)
this.root = rightNode;
else if (node.parent.left == node)
node.parent.left = rightNode;
else
node.parent.right = rightNode;
rightNode.left = node;
node.parent = rightNode;
}
/**
* 右旋转
*
* @param node
*/
public void rightRotate(Node node) {
Node leftNode = node.left;
node.left = leftNode.right;
if (leftNode.right != RedBlackTree.NULL)
leftNode.right.parent = node;
leftNode.parent = node.parent;
if (node.parent == RedBlackTree.NULL) {
this.root = leftNode;
} else if (node.parent.left == node) {
node.parent.left = leftNode;
} else {
node.parent.right = leftNode;
}
leftNode.right = node;
node.parent = leftNode;
}
public void insert(Node node) {
Node parentPointer = RedBlackTree.NULL;
Node pointer = this.root;
while (pointer != RedBlackTree.NULL) {
parentPointer = pointer;
pointer = node.key < pointer.key ? pointer.left : pointer.right;
}
node.parent = parentPointer;
if (parentPointer == RedBlackTree.NULL) {
this.root = node;
} else if (node.key < parentPointer.key) {
parentPointer.left = node;
} else {
parentPointer.right = node;
}
node.left = RedBlackTree.NULL;
node.right = RedBlackTree.NULL;
node.color = Color.Red;
this.insertFixUp(node);
}
private void insertFixUp(Node node) {
// 当node不是根结点,且node的父节点颜色为红色
while (node.parent.color == Color.Red) {
// 先判断node的父节点是左子节点,还是右子节点,这不同的情况,解决方案也会不同
if (node.parent == node.parent.parent.left) {
Node uncleNode = node.parent.parent.right;
if (uncleNode.color == Color.Red) { // 如果叔叔节点是红色,则父父一定是黑色
// 通过把父父节点变成红色,父节点和兄弟节点变成黑色,然后在判断父父节点的颜色是否合适
uncleNode.color = Color.Black;
node.parent.color = Color.Black;
node.parent.parent.color = Color.Red;
node = node.parent.parent;
} else if (node == node.parent.right) { // node是其父节点的右子节点,且叔叔节点是黑色
// 对node的父节点进行左旋转
node = node.parent;
this.leftRotate(node);
} else { // node如果叔叔节点是黑色,node是其父节点的左子节点,父父节点是黑色
// 把父节点变成黑色,父父节点变成红色,对父父节点进行右旋转
node.parent.color = Color.Black;
node.parent.parent.color = Color.Red;
this.rightRotate(node.parent.parent);
}
} else {
Node uncleNode = node.parent.parent.left;
if (uncleNode.color == Color.Red) {
uncleNode.color = Color.Black;
node.parent.color = Color.Black;
node.parent.parent.color = Color.Red;
node = node.parent.parent;
} else if (node == node.parent.left) {
node = node.parent;
this.rightRotate(node);
} else {
node.parent.color = Color.Black;
node.parent.parent.color = Color.Red;
this.leftRotate(node.parent.parent);
}
}
}
// 如果之前树中没有节点,那么新加入的点就成了新结点,而新插入的结点都是红色的,所以需要修改。
this.root.color = Color.Black;
}
/**
* n2替代n1
*
* @param n1
* @param n2
*/
private void transplant(Node n1, Node n2) {
if (n1.parent == RedBlackTree.NULL) { // 如果n1是根节点
this.root = n2;
} else if (n1.parent.left == n1) { // 如果n1是其父节点的左子节点
n1.parent.left = n2;
} else { // 如果n1是其父节点的右子节点
n1.parent.right = n2;
}
n2.parent = n1.parent;
}
/**
* 删除节点node
*
* @param node
*/
public void delete(Node node) {
Node pointer1 = node;
// 用于记录被删除的颜色,如果是红色,可以不用管,但如果是黑色,可能会破坏红黑树的属性
Color pointerOriginColor = pointer1.color;
// 用于记录问题的出现点
Node pointer2;
if (node.left == RedBlackTree.NULL) {
pointer2 = node.right;
this.transplant(node, node.right);
} else if (node.right == RedBlackTree.NULL) {
pointer2 = node.left;
this.transplant(node, node.left);
} else {
// 如要删除的字节有两个子节点,则找到其直接后继(右子树最小值),直接后继节点没有非空左子节点。
pointer1 = node.right.minimum();
// 记录直接后继的颜色和其右子节点
pointerOriginColor = pointer1.color;
pointer2 = pointer1.right;
// 如果其直接后继是node的右子节点,不用进行处理
if (pointer1.parent == node) {
pointer2.parent = pointer1;
} else {
// 否则,先把直接后继从树中提取出来,用来替换node
this.transplant(pointer1, pointer1.right);
pointer1.right = node.right;
pointer1.right.parent = pointer1;
}
// 用node的直接后继替换node,继承node的颜色
this.transplant(node, pointer1);
pointer1.left = node.left;
pointer1.left.parent = pointer1;
pointer1.color = node.color;
}
if (pointerOriginColor == Color.Black) {
this.deleteFixUp(pointer2);
}
}
/**
* The procedure RB-DELETE-FIXUP restores properties 1, 2, and 4
*
* @param node
*/
private void deleteFixUp(Node node) {
// 如果node不是根节点,且是黑色
while (node != this.root && node.color == Color.Black) {
// 如果node是其父节点的左子节点
if (node == node.parent.left) {
// 记录node的兄弟节点
Node pointer1 = node.parent.right;
// 如果node兄弟节点是红色
if (pointer1.color == Color.Red) {
pointer1.color = Color.Black;
node.parent.color = Color.Red;
leftRotate(node.parent);
pointer1 = node.parent.right;
}
if (pointer1.left.color == Color.Black && pointer1.right.color == Color.Black) {
pointer1.color = Color.Red;
node = node.parent;
} else if (pointer1.right.color == Color.Black) {
pointer1.left.color = Color.Black;
pointer1.color = Color.Red;
rightRotate(pointer1);
pointer1 = node.parent.right;
} else {
pointer1.color = node.parent.color;
node.parent.color = Color.Black;
pointer1.right.color = Color.Black;
leftRotate(node.parent);
node = this.root;
}
} else {
// 记录node的兄弟节点
Node pointer1 = node.parent.left;
// 如果他兄弟节点是红色
if (pointer1.color == Color.Red) {
pointer1.color = Color.Black;
node.parent.color = Color.Red;
rightRotate(node.parent);
pointer1 = node.parent.left;
}
if (pointer1.right.color == Color.Black && pointer1.left.color == Color.Black) {
pointer1.color = Color.Red;
node = node.parent;
} else if (pointer1.left.color == Color.Black) {
pointer1.right.color = Color.Black;
pointer1.color = Color.Red;
leftRotate(pointer1);
pointer1 = node.parent.left;
} else {
pointer1.color = node.parent.color;
node.parent.color = Color.Black;
pointer1.left.color = Color.Black;
rightRotate(node.parent);
node = this.root;
}
}
}
node.color = Color.Black;
}
private void innerWalk(Node node) {
if (node != NULL) {
innerWalk(node.left);
System.out.println(node);
innerWalk(node.right);
}
}
/**
* 中序遍历
*/
public void innerWalk() {
this.innerWalk(this.root);
}
/**
* 层次遍历
*/
public void print() {
Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(this.root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
Node temp = queue.poll();
System.out.println(temp);
if (temp.left != NULL)
queue.add(temp.left);
if (temp.right != NULL)
queue.add(temp.right);
}
}
// 查找
public Node search(int key) {
Node pointer = this.root;
while (pointer != NULL && pointer.key != key) {
pointer = pointer.key < key ? pointer.right : pointer.left;
}
return pointer;
}
}
6、演示
演示代码:
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 };
RedBlackTree redBlackTree = new RedBlackTree();
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
redBlackTree.insert(new Node(arr[i]));
}
System.out.println("树的高度: " + redBlackTree.root.height());
System.out.println("左子树的高度: " + redBlackTree.root.left.height());
System.out.println("右子树的高度: " + redBlackTree.root.right.height());
System.out.println("层次遍历");
redBlackTree.print();
// 要删除节点
Node node = redBlackTree.search(4);
redBlackTree.delete(node);
System.out.println("树的高度: " + redBlackTree.root.height());
System.out.println("左子树的高度: " + redBlackTree.root.left.height());
System.out.println("右子树的高度: " + redBlackTree.root.right.height());
System.out.println("层次遍历");
redBlackTree.print();
}
}
结果:
树的高度: 4
左子树的高度: 2
右子树的高度: 3
层次遍历
[key: 4, color: 黑色, parent: 0, position: null]
[key: 2, color: 红色, parent: 4, position: left]
[key: 6, color: 红色, parent: 4, position: right]
[key: 1, color: 黑色, parent: 2, position: left]
[key: 3, color: 黑色, parent: 2, position: right]
[key: 5, color: 黑色, parent: 6, position: left]
[key: 7, color: 黑色, parent: 6, position: right]
[key: 8, color: 红色, parent: 7, position: right]
树的高度: 3
左子树的高度: 2
右子树的高度: 2
层次遍历
[key: 5, color: 黑色, parent: 0, position: null]
[key: 2, color: 红色, parent: 5, position: left]
[key: 7, color: 红色, parent: 5, position: right]
[key: 1, color: 黑色, parent: 2, position: left]
[key: 3, color: 黑色, parent: 2, position: right]
[key: 6, color: 黑色, parent: 7, position: left]
[key: 8, color: 黑色, parent: 7, position: right]
7、参考
《算法导论》(第3版) 英文版
用Java实现红黑树的更多相关文章
- Java实现红黑树
转自:http://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/3624343.html 红黑树的介绍 红黑树(Red-Black Tree,简称R-B Tree),它一种特殊的二叉 ...
- 基于Java实现红黑树的基本操作
首先,在阅读文章之前,我希望读者对二叉树有一定的了解,因为红黑树的本质就是一颗二叉树.所以本篇博客中不在将二叉树的增删查的基本操作了,需要了解的同学可以到我之前写的一篇关于二叉树基本操作的博客:htt ...
- Java 集合 | 红黑树 | 前置知识
一.前言 0tnv1e.png 为啥要学红黑树吖? 因为笔者最近在赶项目的时候,不忘抽出时间来复习 Java 基础知识,现在准备看集合的源码啦啦.听闻,HashMap 在 jdk 1.8 的时候,底层 ...
- Java实现红黑树(平衡二叉树)
前言 在实现红黑树之前,我们先来了解一下符号表. 符号表的描述借鉴了Algorithms第四版,详情在:https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/home/ 符号表有时候被称为字典 ...
- java数据结构——红黑树(R-B Tree)
红黑树相比平衡二叉树(AVL)是一种弱平衡树,且具有以下特性: 1.每个节点非红即黑; 2.根节点是黑的; 3.每个叶节点(叶节点即树尾端NULL指针或NULL节点)都是黑的; 4.如图所示,如果一个 ...
- Java数据结构——红黑树
红黑树介绍红黑树(Red-Black Tree),它一种特殊的二叉查找树.执行查找.插入.删除等操作的时间复杂度为O(logn). 红黑树是特殊的二叉查找树,意味着它满足二叉查找树的特征:任意一个节点 ...
- 红黑树(五)之 Java的实现
概要 前面分别介绍红黑树的理论知识.红黑树的C语言和C++的实现.本章介绍红黑树的Java实现,若读者对红黑树的理论知识不熟悉,建立先学习红黑树的理论知识,再来学习本章.还是那句老话,红黑树的C/C+ ...
- 红黑树 Java实现
概要 前面分别介绍红黑树的理论知识.红黑树的C语言和C++的实现.本章介绍红黑树的Java实现,若读者对红黑树的理论知识不熟悉,建立先学习红黑树的理论知识,再来学习本章.还是那句老话,红黑树的C/C+ ...
- 从2-3-4树到红黑树(下) Java与C的实现
欢迎探讨,如有错误敬请指正 如需转载,请注明出处 http://www.cnblogs.com/nullzx/ 相关博客: 从2-3-4树到红黑树(上) 从2-3-4树到红黑树(中) 1. 实现技 ...
随机推荐
- 3、基于Python建立任意层数的深度神经网络
一.神经网络介绍: 神经网络算法参考人的神经元原理(轴突.树突.神经核),在很多神经元基础上构建神经网络模型,每个神经元可看作一个个学习单元.这些神经元采纳一定的特征作为输入,根据自身的模型得到输出. ...
- RSA算法之学习
一.RSA算法 RSA是非对称加密算法中的代表,它的重要性不言而喻,为了弄清楚RSA算法,我们一起来完成一项任务: 背景:现在是疫情时代,假如小明和女朋友被迫在两个城市,小明为了表达感情,想发给对方一 ...
- Nacos 笔记
Nacos 笔记 目录 Nacos 笔记 1. Nacos简介 1.1 主流配置中心对比 1.2 主流注册中心对比 1.3 Nacos特性 2. 安装启动 支持外部 MySQL 3. 配置管理 3.1 ...
- docker搭建kafka集群(高级版)
1. 环境docker, docker-compose 2.zookeeper集群 /data/zookeeper/zoo1/config/zoo.cfg # The number of millis ...
- golang 日志框架(zap)完整配置和使用
目录结构: logger.go文件: package log import ( rotatelogs "github.com/lestrrat-go/file-rotatelogs" ...
- msfvenom简介
写此文是因为网上资料杂乱,不方便查阅,辣眼睛 测试免杀的时候刚好用到这个功能,顺便写一下(0202年靠msfvenom生成的纯原生payload可以宣告死亡了,如果有查不出来的杀软可以退群了,这也叫杀 ...
- Internet的接入与IP地址 概述
文章目录 一.计算机接入Internet 1.公用交换电话网(PSTN)接入 2.有线电视(CATV)接入 3.局域网接入 4.无线接入 二.IP地址 1.IP地址的格式 2.IP地址分类 3.子网掩 ...
- Blazor+Dapr+K8s微服务之开发环境调试
1 安装Dapr开发调试环境 1.1 Dapr 完整安装模式不支持开发调试 在上一篇随笔<Blazor+Dapr+K8s微服务之服务调用>中,我们通过为每个 ...
- 关于Ajax异步提交登录及增删改查小项目制作-登录
一.登录的完成 先导包jquery和MySql //异步提交 <script type="text/javascript" src="js/jquery-1.8.2 ...
- docker 安装部署 jenkins
cd /data/docker-data/jenkins mkdir jenkins_home chmod 777 jenkins_home docker run -d -p 10240:8080 - ...
