SpringBoot之使用Scheduled做定时任务
定时任务有好多开源框架比如Quartz,@Scheduled是Spring的一个定时任务注解,通过注解配置就能够轻量级的定时任务,简单方便。
一、@Scheduled注解介绍
这里先贴上@Scheduled注解。然后下面的这几个属性的介绍。
* Copyright 2002-2018 the original author or authors. package org.springframework.scheduling.annotation; import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Repeatable;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target; /**
* An annotation that marks a method to be scheduled. Exactly one of
* the {@link #cron()}, {@link #fixedDelay()}, or {@link #fixedRate()}
* attributes must be specified.
*
* <p>The annotated method must expect no arguments. It will typically have
* a {@code void} return type; if not, the returned value will be ignored
* when called through the scheduler.
*
* <p>Processing of {@code @Scheduled} annotations is performed by
* registering a {@link ScheduledAnnotationBeanPostProcessor}. This can be
* done manually or, more conveniently, through the {@code <task:annotation-driven/>}
* element or @{@link EnableScheduling} annotation.
*
* <p>This annotation may be used as a <em>meta-annotation</em> to create custom
* <em>composed annotations</em> with attribute overrides.
*
* @author Mark Fisher
* @author Dave Syer
* @author Chris Beams
* @since 3.0
* @see EnableScheduling
* @see ScheduledAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
* @see Schedules
*/
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.ANNOTATION_TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Repeatable(Schedules.class)
public @interface Scheduled { /**
* A cron-like expression, extending the usual UN*X definition to include
* triggers on the second as well as minute, hour, day of month, month
* and day of week. e.g. {@code "0 * * * * MON-FRI"} means once per minute on
* weekdays (at the top of the minute - the 0th second).
* @return an expression that can be parsed to a cron schedule
* @see org.springframework.scheduling.support.CronSequenceGenerator
*/
String cron() default ""; /**
* A time zone for which the cron expression will be resolved. By default, this
* attribute is the empty String (i.e. the server's local time zone will be used).
* @return a zone id accepted by {@link java.util.TimeZone#getTimeZone(String)},
* or an empty String to indicate the server's default time zone
* @since 4.0
* @see org.springframework.scheduling.support.CronTrigger#CronTrigger(String, java.util.TimeZone)
* @see java.util.TimeZone
*/
String zone() default ""; /**
* Execute the annotated method with a fixed period in milliseconds between the
* end of the last invocation and the start of the next.
* @return the delay in milliseconds
*/
long fixedDelay() default -1; /**
* Execute the annotated method with a fixed period in milliseconds between the
* end of the last invocation and the start of the next.
* @return the delay in milliseconds as a String value, e.g. a placeholder
* or a {@link java.time.Duration#parse java.time.Duration} compliant value
* @since 3.2.2
*/
String fixedDelayString() default ""; /**
* Execute the annotated method with a fixed period in milliseconds between
* invocations.
* @return the period in milliseconds
*/
long fixedRate() default -1; /**
* Execute the annotated method with a fixed period in milliseconds between
* invocations.
* @return the period in milliseconds as a String value, e.g. a placeholder
* or a {@link java.time.Duration#parse java.time.Duration} compliant value
* @since 3.2.2
*/
String fixedRateString() default ""; /**
* Number of milliseconds to delay before the first execution of a
* {@link #fixedRate()} or {@link #fixedDelay()} task.
* @return the initial delay in milliseconds
* @since 3.2
*/
long initialDelay() default -1; /**
* Number of milliseconds to delay before the first execution of a
* {@link #fixedRate()} or {@link #fixedDelay()} task.
* @return the initial delay in milliseconds as a String value, e.g. a placeholder
* or a {@link java.time.Duration#parse java.time.Duration} compliant value
* @since 3.2.2
*/
String initialDelayString() default ""; }
cron属性
这是一个时间表达式,可以通过简单的配置就能完成各种时间的配置,我们通过CRON表达式几乎可以完成任意的时间搭配,它包含了六或七个域:
Seconds : 可出现", - * /"四个字符,有效范围为0-59的整数
Minutes : 可出现", - * /"四个字符,有效范围为0-59的整数
Hours : 可出现", - * /"四个字符,有效范围为0-23的整数
DayofMonth : 可出现", - * / ? L W C"八个字符,有效范围为0-31的整数
Month : 可出现", - * /"四个字符,有效范围为1-12的整数或JAN-DEc
DayofWeek : 可出现", - * / ? L C #"四个字符,有效范围为1-7的整数或SUN-SAT两个范围。1表示星期天,2表示星期一, 依次类推
Year : 可出现", - * /"四个字符,有效范围为1970-2099年
"0 0 12 * * ?" 每天中午十二点触发
"0 15 10 ? * *" 每天早上10:15触发
"0 15 10 * * ?" 每天早上10:15触发
"0 15 10 * * ? *" 每天早上10:15触发
"0 15 10 * * ? 2005" 2005年的每天早上10:15触发
"0 * 14 * * ?" 每天从下午2点开始到2点59分每分钟一次触发
"0 0/5 14 * * ?" 每天从下午2点开始到2:55分结束每5分钟一次触发
"0 0/5 14,18 * * ?" 每天的下午2点至2:55和6点至6点55分两个时间段内每5分钟一次触发
"0 0-5 14 * * ?" 每天14:00至14:05每分钟一次触发
"0 10,44 14 ? 3 WED" 三月的每周三的14:10和14:44触发
"0 15 10 ? * MON-FRI" 每个周一、周二、周三、周四、周五的10:15触发
fixedRate属性
上一个调用开始后再次调用的延时(不用等待上一次调用完成),这样就会存在重复执行的问题,所以不是建议使用,但数据量如果不大时在配置的间隔时间内可以执行完也是可以使用的。
fixedDelay属性
该属性的功效与上面的fixedRate则是相反的,配置了该属性后会等到方法执行完成后延迟配置的时间再次执行该方法。
initialDelay属性
该属性跟上面的fixedDelay、fixedRate有着密切的关系,为什么这么说呢?该属性的作用是第一次执行延迟时间,只是做延迟的设定,并不会控制其他逻辑,所以要配合fixedDelay或者fixedRate来使用。
二、@Scheduled注解实例
package com.example.demo; import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date; import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.Scheduled;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component
public class SchedulerTask {
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss"); @Scheduled(fixedRate = 10000)
public void timerRate() {
System.out.println(dateFormat.format(new Date()));
} //第一次延迟1秒执行,当执行完后2秒再执行
@Scheduled(initialDelay = 1000, fixedDelay = 2000)
public void timerInit() {
System.out.println("init : "+dateFormat.format(new Date()));
} //每天21点41分50秒执行
@Scheduled(cron = "50 41 21 * * ?")
public void timerCron() {
System.out.println("current time : "+ dateFormat.format(new Date()));
}
}
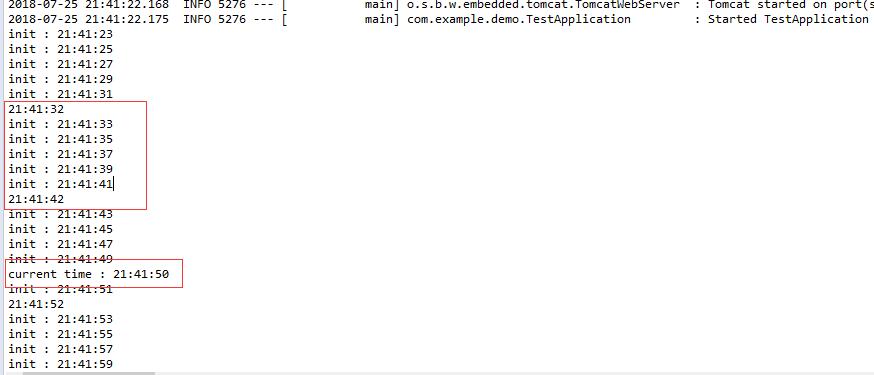
代码都使用了上了的@Scheduled属性。下图是执行打印的日志信息,timerInit方法是每隔2秒执行,timerCron设置在21点41分50秒执行,timerRate是每隔10秒执行。
三、添加@EnableScheduling注解
上面的定时任务并不能执行,还需要一步,需要设置开启定时任务,这个也很简单,只需在main方法上加上@EnableScheduling注解即可。
package com.example.demo; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableScheduling; @EnableScheduling
@SpringBootApplication
public class TestApplication { public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(TestApplication.class, args);
}
}
SpringBoot之使用Scheduled做定时任务的更多相关文章
- 定时任务-----Springboot中使用Scheduled做定时任务----http://www.cnblogs.com/lirenqing/p/6596557.html
Springboot中使用Scheduled做定时任务---http://www.cnblogs.com/lirenqing/p/6596557.html 已经验证的方案: pom文件加入依赖 < ...
- Springboot中使用Scheduled做定时任务
在开发中,定时任务是常见的功能,在spring boot 下开发定时任务其实很简单,具体代码如下: 1.配置依赖包pom.xml 由于默认的maven仓库经常访问不了,这里采用了阿里云的maven仓库 ...
- SpringBoot中使用@Scheduled创建定时任务
SpringBoot中使用@Scheduled创建定时任务 定时任务一般会在很多项目中都会用到,我们往往会间隔性的的去完成某些特定任务来减少服务器和数据库的压力.比较常见的就是金融服务系统推送回调,一 ...
- SpringBoot使用@Scheduled创建定时任务
定时任务一般会存在中大型企业级项目中,为了减少服务器.数据库的压力往往会采用时间段性的去完成某些业务逻辑.比较常见的就是金融服务系统推送回调,一般支付系统订单在没有收到成功的回调返回内容时会持续性的回 ...
- SpringBoot中使用task实现定时任务
定时任务实现的几种方式: Timer:这是java自带的java.util.Timer类,这个类允许你调度一个java.util.TimerTask任务.使用这种方式可以让你的程序按照某一个频度执行, ...
- spring的Scheduled(定时任务)和多线程
一.前言 在我们日常的开发中,经常用到数据同步的更新,这时我们采用的是spring的定时任务和java的多线程进行数据的更新,进行时实的服务调用. 二.实现思路 1.创建线程类 ...
- JFinal - scheduler 插件做定时任务
我在项目中遇到一个需求:服务运行期间,数据库要定期去监测某表并且更新. 正好项目是使用 jfinal 做的,于是就用了 jfinal-scheduler 插件来解决(jfinal-scheduler ...
- spring注解scheduled实现定时任务
只想说,spring注解scheduled实现定时任务使用真的非常简单. 一.配置spring.xml文件 1.在beans加入xmlns:task="http://www.springfr ...
- springboot+springmvc拦截器做登录拦截
springboot+springmvc拦截器做登录拦截 LoginInterceptor 实现 HandlerInterceptor 接口,自定义拦截器处理方法 LoginConfiguration ...
随机推荐
- qhfl-2 ContentType组件
一般商城里有很多的商品,计优惠券对应着活动类型商品,家电是一类商品,食物是一类商品,优惠券对应着不同的商品类别. from django.db import models class Applianc ...
- dom4j 使用原生xpath 处理带命名空间的文档
测试文件 <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.o ...
- Django积木块一——验证码
验证码 在github中搜验证码,那个有使用文档 # pip install django-simple-captcha==0.4.6 # setting app captcha # url url( ...
- Scanner 类的使用
/* Scanner类的使用: 1.导类 2.创建对象 3.调用对应的方法获取数据 */ import java.util.Scanner;//导入Scanner类 public class IfDe ...
- 初识Twisted(一)
pip install Twisted 安装Twisted库 from twisted.internet import reactor #开启事件循环 #不是简单的循环 #不会带来任何性能损失 rea ...
- 文件描述符fd、文件指针fp和vfork()
1. fd:在形式上是一个非负整数.实际上他是一个索引值.指向kernal为每一个进程所维护的该进程打开文件的记录表. 当程序打开一个文件或者创建一个新文件的时候kernal向进程返回一个文件描述符. ...
- mybatis分页查询,SqlServer 2008 查询速度很慢
一个业务场景,需要进行union查询: 查询速度非常慢,大概要37秒: 直接复制sql在数据库客户端执行,速度很快,由此可知是mybatis的原因,在网上搜索,可以配置fetchSize=" ...
- .NET Core微服务之路:利用DotNetty实现一个简单的通信过程
上一篇我们已经全面的介绍过<基于gRPC服务发现与服务治理的方案>,我们先复习一下RPC的调用过程(笔者会在这一节的几篇文章中反复的强调这个过程调用方案),看下图
- GET请求Referer限制绕过总结
作者:Vulkey_Chen 原文来自:GET请求Referer限制绕过总结 前言 在做测试的时候会遇见这样几个漏洞场景: JSONP跨域劫持 反射XSS GET请求类型攻击 但是,在相对安全的情况下 ...
- WebRTC 学习之 WebRTC 简介
本文使用的WebRTC相关API都是基于Intel® Collaboration Suite for WebRTC的. 相关文档链接:https://software.intel.com/sites/ ...
