爬虫----BeautifulSoup模块
一、介绍
Beautiful Soup 是一个可以从HTML或XML文件中提取数据的Python库.它能够通过你喜欢的转换器实现惯用的文档导航,查找,修改文档的方式.Beautiful Soup会帮你节省数小时甚至数天的工作时间.你可能在寻找 Beautiful Soup3 的文档,Beautiful Soup 3 目前已经停止开发,官网推荐在现在的项目中使用Beautiful Soup 4, 移植到BS4
#安装 Beautiful Soup
pip3 install beautifulsoup4 #安装解析器
Beautiful Soup支持Python标准库中的HTML解析器,还支持一些第三方的解析器,其中一个是 lxml .根据操作系统不同,可以选择下列方法来安装lxml: $ apt-get install Python-lxml $ easy_install lxml $ pip install lxml 另一个可供选择的解析器是纯Python实现的 html5lib , html5lib的解析方式与浏览器相同,可以选择下列方法来安装html5lib: $ apt-get install Python-html5lib $ easy_install html5lib $ pip install html5lib
下表列出了主要的解析器,以及它们的优缺点,官网推荐使用lxml作为解析器,因为效率更高. 在Python2.7.3之前的版本和Python3中3.2.2之前的版本,必须安装lxml或html5lib, 因为那些Python版本的标准库中内置的HTML解析方法不够稳定.
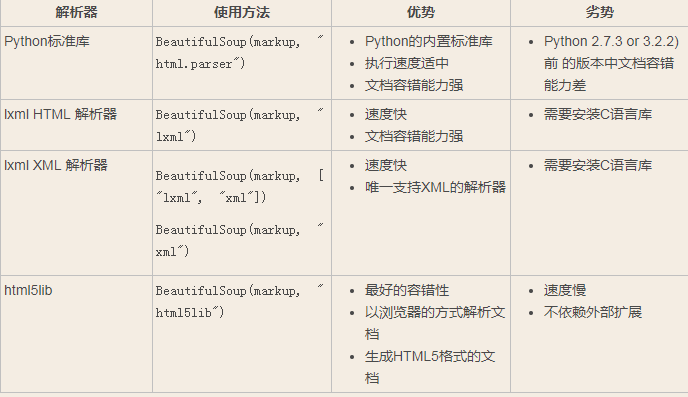
二、基本使用
html_doc = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p> <p class="story">...</p>
""" #基本使用:容错处理,文档的容错能力指的是在html代码不完整的情况下,使用该模块可以识别该错误。使用BeautifulSoup解析上述代码,能够得到一个 BeautifulSoup 的对象,并能按照标准的缩进格式的结构输出
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup=BeautifulSoup(html_doc,'lxml') #具有容错功能
res=soup.prettify() #处理好缩进,结构化显示
print(res)
三、遍历文档树
#遍历文档树:即直接通过标签名字选择,特点是选择速度快,但如果存在多个相同的标签则只返回第一个
#1、用法
#2、获取标签的名称
#3、获取标签的属性
#4、获取标签的内容
#5、嵌套选择
#6、子节点、子孙节点
#7、父节点、祖先节点
#8、兄弟节点
#遍历文档树:即直接通过标签名字选择,特点是选择速度快,但如果存在多个相同的标签则只返回第一个
html_doc = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p id="my p" class="title"><b id="bbb" class="boldest">The Dormouse's story</b></p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p> <p class="story">...</p>
""" #1、用法
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup=BeautifulSoup(html_doc,'lxml')
# soup=BeautifulSoup(open('a.html'),'lxml') print(soup.p) #存在多个相同的标签则只返回第一个
print(soup.a) #存在多个相同的标签则只返回第一个 #2、获取标签的名称
print(soup.p.name) #3、获取标签的属性
print(soup.p.attrs) #4、获取标签的内容
print(soup.p.string) # p下的文本只有一个时,取到,否则为None
print(soup.p.strings) #拿到一个生成器对象, 取到p下所有的文本内容
print(soup.p.text) #取到p下所有的文本内容
for line in soup.stripped_strings: #去掉空白
print(line) '''
如果tag包含了多个子节点,tag就无法确定 .string 方法应该调用哪个子节点的内容, .string 的输出结果是 None,如果只有一个子节点那么就输出该子节点的文本,比如下面的这种结构,soup.p.string 返回为None,但soup.p.strings就可以找到所有文本
<p id='list-1'>
哈哈哈哈
<a class='sss'>
<span>
<h1>aaaa</h1>
</span>
</a>
<b>bbbbb</b>
</p>
''' #5、嵌套选择
print(soup.head.title.string)
print(soup.body.a.string) #6、子节点、子孙节点
print(soup.p.contents) #p下所有子节点
print(soup.p.children) #得到一个迭代器,包含p下所有子节点 for i,child in enumerate(soup.p.children):
print(i,child) print(soup.p.descendants) #获取子孙节点,p下所有的标签都会选择出来
for i,child in enumerate(soup.p.descendants):
print(i,child) #7、父节点、祖先节点
print(soup.a.parent) #获取a标签的父节点
print(soup.a.parents) #找到a标签所有的祖先节点,父亲的父亲,父亲的父亲的父亲... #8、兄弟节点
print('=====>')
print(soup.a.next_sibling) #下一个兄弟
print(soup.a.previous_sibling) #上一个兄弟 print(list(soup.a.next_siblings)) #下面的兄弟们=>生成器对象
print(soup.a.previous_siblings) #上面的兄弟们=>生成器对象
soup = BeautifulSoup(html_doc,"lxml") #第一个参数指定文本内容,第二个参数解析器
# soup = BeautifulSoup(open("a.html"),"lxml") #也可以打开一个文件创建实例
print(soup.prettify()) #容错性的体现,自动补全
print(soup.a) #只找到了一个,而且是从整个文档树找
print(soup.a.text) #找到a标签里面的文本
print(soup.text) #找整个文档树种所有的文本
print(soup.a.attrs) #找a标签的所有属性,字典形式
print(soup.a.attrs["href"]) #找a标签的href属性
print(soup.p.b) #嵌套查找,这是只找一个
print(soup.p.contents) #子节点,找到的是一个闭标签
print(list(soup.p.children )) #得到生成器
print(list(soup.p.descendants)) #所有的子子孙孙
print(soup.a.parent)#找父亲
print(list(soup.a.parent))#父亲的父亲的父亲
print(soup.p.find_all() ) #标签名可以和find可以结合在一起使用
基本使用
四、搜索文档数
1、五种过滤器
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
html_doc = '''<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title"><b>The Dormouse's story</b></p>
<p class="title"><b>$75</b></p>
<p id="meiyuan">啦啦啦啦啦啦</p> <p class="story">Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">Elsie</a>,
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
and they lived at the bottom of a well.</p>'''
soup= BeautifulSoup(html_doc,"lxml")
# 1、字符串:特点:是一种完全匹配的
print(soup.find_all(name="a")) #找到所有的a标签
print(soup.find_all(name="a aa")) #找不到,会打印一个[]
print(soup.find_all(attrs={"class":"sister"}))
print(soup.find_all(text="The Dormouse's story")) #按照文本来找
print(soup.find_all(name="b",text="The Dormouse's story")) #找标签名是b,并且文本是The Dormouse's story
print(soup.p.find(name="b").text) #第一个p标签的b里面的文本
print(soup.find_all(name="p",attrs={"class":"story"})) #找到标签名是p,属性名是class,
print(soup.find(name="p",attrs={"class":"story"}).find_all(name="a")[2]) #找到标签名是p,属性名是class的第二个a标签
# 2、正则
import re
print(soup.find_all(name=re.compile("^b"))) #找b开头的的标签
print(soup.find_all(attrs={"id":re.compile("link")})) #找到id属性是link的
print(soup.find_all(text=re.compile(r"\$"))) #找带有$价钱的文本
#
# # 3、列表:如果传入列表参数,Beautiful Soup会将与列表中任一元素匹配的内容返回.
print(soup.find_all(name=["a",re.compile("^b")])) #找a标签或者b标签开头的所有的标签
print(soup.find_all(text=["$",])) #找不到
print(soup.find_all(text=[re.compile(r"\$")])) #['$75']
print(soup.find_all(text=["a",re.compile(r"\$")])) # # 4、True:可以匹配任何值
print(soup.find_all(name=True)) #找到所有标签的标签名
print(soup.find_all(attrs={"id":True}))#找到只要有id属性的
#
print(soup.find_all(name="p",attrs={"id":True}))# 找到有id属性的p标签
# 5、方法:如果没有合适过滤器,那么还可以定义一个方法,方法只接受一个元素参数 ,如果这个方法返回 True 表示当前元素匹配并且被找到,如果不是则反回 False
#
# # 有class属性没有id属性的
def has_class_not_id(tag):
return tag.has_attr('class') and not tag.has_attr('id')
# return tag.has_attr('id') and not tag.has_attr('class') # return tag.name =="a" and tag.has_attr("class") and not tag.has_attr("id")
# # #只找a标签
print(soup.find_all(has_class_not_id)) #默认是按照标签来找的 print(soup.find_all(name="a",limit=2))#找所有的a标签,只找前两个
print(soup.body.find_all(attrs={"class":"sister"},recursive=False))#找属性为sister的
print(soup.html.find_all('a'))
print(soup.html.find_all('a',recursive=False))
# recursive = True #从子子孙孙都找到了
# recursive = False #如果只想搜索tag的直接子节点(就不往里面找了),可以使用参数 recursive=False . # **kwargs
print(soup.find_all(attrs={"class":"sister"}))
print(soup.find_all(class_="sister")) #这两个是一样的 print(soup.find_all(attrs={"id":"link3"})) #这两个是一样的,只是表示方式不一样
print(soup.find_all(id="link3"))
2、find_all( name , attrs , recursive , text , **kwargs )
#2、find_all( name , attrs , recursive , text , **kwargs )
#2.1、name: 搜索name参数的值可以使任一类型的 过滤器 ,字符窜,正则表达式,列表,方法或是 True .
print(soup.find_all(name=re.compile('^t'))) #2.2、keyword: key=value的形式,value可以是过滤器:字符串 , 正则表达式 , 列表, True .
print(soup.find_all(id=re.compile('my')))
print(soup.find_all(href=re.compile('lacie'),id=re.compile('\d'))) #注意类要用class_
print(soup.find_all(id=True)) #查找有id属性的标签 # 有些tag属性在搜索不能使用,比如HTML5中的 data-* 属性:
data_soup = BeautifulSoup('<div data-foo="value">foo!</div>','lxml')
# data_soup.find_all(data-foo="value") #报错:SyntaxError: keyword can't be an expression
# 但是可以通过 find_all() 方法的 attrs 参数定义一个字典参数来搜索包含特殊属性的tag:
print(data_soup.find_all(attrs={"data-foo": "value"}))
# [<div data-foo="value">foo!</div>] #2.3、按照类名查找,注意关键字是class_,class_=value,value可以是五种选择器之一
print(soup.find_all('a',class_='sister')) #查找类为sister的a标签
print(soup.find_all('a',class_='sister ssss')) #查找类为sister和sss的a标签,顺序错误也匹配不成功
print(soup.find_all(class_=re.compile('^sis'))) #查找类为sister的所有标签 #2.4、attrs
print(soup.find_all('p',attrs={'class':'story'})) #2.5、text: 值可以是:字符,列表,True,正则
print(soup.find_all(text='Elsie'))
print(soup.find_all('a',text='Elsie')) #2.6、limit参数:如果文档树很大那么搜索会很慢.如果我们不需要全部结果,可以使用 limit 参数限制返回结果的数量.效果与SQL中的limit关键字类似,当搜索到的结果数量达到 limit 的限制时,就停止搜索返回结果
print(soup.find_all('a',limit=2)) #2.7、recursive:调用tag的 find_all() 方法时,Beautiful Soup会检索当前tag的所有子孙节点,如果只想搜索tag的直接子节点,可以使用参数 recursive=False .
print(soup.html.find_all('a'))
print(soup.html.find_all('a',recursive=False)) '''
像调用 find_all() 一样调用tag
find_all() 几乎是Beautiful Soup中最常用的搜索方法,所以我们定义了它的简写方法. BeautifulSoup 对象和 tag 对象可以被当作一个方法来使用,这个方法的执行结果与调用这个对象的 find_all() 方法相同,下面两行代码是等价的:
soup.find_all("a")
soup("a")
这两行代码也是等价的:
soup.title.find_all(text=True)
soup.title(text=True)
'''
3、find( name , attrs , recursive , text , **kwargs )
#3、find( name , attrs , recursive , text , **kwargs )
find_all() 方法将返回文档中符合条件的所有tag,尽管有时候我们只想得到一个结果.比如文档中只有一个<body>标签,那么使用 find_all() 方法来查找<body>标签就不太合适, 使用 find_all 方法并设置 limit=1 参数不如直接使用 find() 方法.下面两行代码是等价的: soup.find_all('title', limit=1)
# [<title>The Dormouse's story</title>]
soup.find('title')
# <title>The Dormouse's story</title> 唯一的区别是 find_all() 方法的返回结果是值包含一个元素的列表,而 find() 方法直接返回结果.
find_all() 方法没有找到目标是返回空列表, find() 方法找不到目标时,返回 None .
print(soup.find("nosuchtag"))
# None soup.head.title 是 tag的名字 方法的简写.这个简写的原理就是多次调用当前tag的 find() 方法: soup.head.title
# <title>The Dormouse's story</title>
soup.find("head").find("title")
# <title>The Dormouse's story</title>
4、其他方法
见官网:https://www.crummy.com/software/BeautifulSoup/bs4/doc/index.zh.html#find-parents-find-parent
5、CSS选择器
#该模块提供了select方法来支持css,详见官网:https://www.crummy.com/software/BeautifulSoup/bs4/doc/index.zh.html#id37
html_doc = """
<html><head><title>The Dormouse's story</title></head>
<body>
<p class="title">
<b>The Dormouse's story</b>
Once upon a time there were three little sisters; and their names were
<a href="http://example.com/elsie" class="sister" id="link1">
<span>Elsie</span>
</a>
<a href="http://example.com/lacie" class="sister" id="link2">Lacie</a> and
<a href="http://example.com/tillie" class="sister" id="link3">Tillie</a>;
<div class='panel-1'>
<ul class='list' id='list-1'>
<li class='element'>Foo</li>
<li class='element'>Bar</li>
<li class='element'>Jay</li>
</ul>
<ul class='list list-small' id='list-2'>
<li class='element'><h1 class='yyyy'>Foo</h1></li>
<li class='element xxx'>Bar</li>
<li class='element'>Jay</li>
</ul>
</div>
and they lived at the bottom of a well.
</p>
<p class="story">...</p>
"""
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
soup=BeautifulSoup(html_doc,'lxml') #1、CSS选择器
print(soup.p.select('.sister'))
print(soup.select('.sister span')) print(soup.select('#link1'))
print(soup.select('#link1 span')) print(soup.select('#list-2 .element.xxx')) print(soup.select('#list-2')[0].select('.element')) #可以一直select,但其实没必要,一条select就可以了 # 2、获取属性
print(soup.select('#list-2 h1')[0].attrs) # 3、获取内容
print(soup.select('#list-2 h1')[0].get_text())
五、修改文档数
链接:https://www.crummy.com/software/BeautifulSoup/bs4/doc/index.zh.html#id40
六、总结
总结:
#1、推荐使用lxml解析库
#2、讲了三种选择器:标签选择器,find与find_all,css选择器
1、标签选择器筛选功能弱,但是速度快
2、建议使用find,find_all查询匹配单个结果或者多个结果
3、如果对css选择器非常熟悉建议使用select
#3、记住常用的获取属性attrs和文本值get_text()的方法
爬虫----BeautifulSoup模块的更多相关文章
- 【爬虫入门手记03】爬虫解析利器beautifulSoup模块的基本应用
[爬虫入门手记03]爬虫解析利器beautifulSoup模块的基本应用 1.引言 网络爬虫最终的目的就是过滤选取网络信息,因此最重要的就是解析器了,其性能的优劣直接决定这网络爬虫的速度和效率.Bea ...
- 【网络爬虫入门03】爬虫解析利器beautifulSoup模块的基本应用
[网络爬虫入门03]爬虫解析利器beautifulSoup模块的基本应用 1.引言 网络爬虫最终的目的就是过滤选取网络信息,因此最重要的就是解析器了,其性能的优劣直接决定这网络爬虫的速度和效率.B ...
- Python 爬虫三 beautifulsoup模块
beautifulsoup模块 BeautifulSoup模块 BeautifulSoup是一个模块,该模块用于接收一个HTML或XML字符串,然后将其进行格式化,之后遍可以使用他提供的方法进行快速查 ...
- Python爬虫之Beautifulsoup模块的使用
一 Beautifulsoup模块介绍 Beautiful Soup 是一个可以从HTML或XML文件中提取数据的Python库.它能够通过你喜欢的转换器实现惯用的文档导航,查找,修改文档的方式.Be ...
- requests和BeautifulSoup模块的使用
用python写爬虫时,有两个很好用第三方模块requests库和beautifulsoup库,简单学习了下模块用法: 1,requests模块 Python标准库中提供了:urllib.urllib ...
- requsets模块和beautifulsoup模块
2.requests模块方法 requests是基于Python开发的HTTP库,使用Requests可以轻而易举的完成浏览器可有的任何操作. request.get() request.post() ...
- BeautifulSoup 模块详解
BeautifulSoup 模块详解 BeautifulSoup是一个模块,该模块用于接收一个HTML或XML字符串,然后将其进行格式化,之后遍可以使用他提供的方法进行快速查找指定元素,从而使得在HT ...
- 03 解析库之Beautifulsoup模块
Beautifulsoup模块 一 介绍 Beautiful Soup 是一个可以从HTML或XML文件中提取数据的Python库.它能够通过你喜欢的转换器实现惯用的文档导航,查找,修改文档的方式 ...
- python之爬虫_模块
目录 一.requests模块二.Beautifulsoup模块 一.requests模块 1.介绍 Python标准库中提供了:urllib.urllib2.httplib等模块以供Http请求,但 ...
随机推荐
- Cuda9.1+cunn7.1+Tensorflow1.7-GUP
Cuda9.1下载地址 cudnn下载 需要注册英伟达账号 cuda安装完成后默认的环境变量配置不对,CUDA_PATH是C:\Program Files\NVIDIA GPU Computing ...
- 内存(RAM或ROM)和FLASH存储的真正区别总结
转载自:http://blog.csdn.net/liangkaiyang/article/details/59556531.什么是内存 什么是内存呢?在计算机的组成结构中,有一个很重要的部分 ...
- Scikit-learn使用总结
在机器学习和数据挖掘的应用中,scikit-learn是一个功能强大的python包.在数据量不是过大的情况下,可以解决大部分问题.学习使用scikit-learn的过程中,我自己也在补充着机器学习和 ...
- css3 - 纯css实现一个轮播图
这是我上一次的面试题.一晃两个月过去了. 从前都是拿原理骗人,把怎么实现的思路说出来. 我今天又被人问到了,才想起来真正码出来.码出来效果说明一切: 以上gif,只用到了5张图片,一个html+css ...
- Android新特性介绍,ConstraintLayout完全解析
今天给大家带来2017年的第一篇文章,这里先祝大家新年好. 本篇文章的主题是ConstraintLayout.其实ConstraintLayout是Android Studio 2.2中主要的新增功能 ...
- linux搭建mysql集群
一.公共配置 请在三个虚拟机上分别配置此处的配置项. 1. 安装虚拟机 虚拟机操作系统安装CentOS 6.5的x86_64版本. 2. 拷贝mysql cluster 下载以下版本的MySQL-Cl ...
- electron+react
yarn create react-app electron-react cd electron-react yarn run eject // 修改react-app打包的路径 / -> ./ ...
- 大数据和Hadoop时代的维度建模和Kimball数据集市
小结: 1. Hadoop 文件系统中的存储是不可变的,换句话说,只能插入和追加记录,不能修改数据.如果你熟悉的是关系型数据仓库,这看起来可能有点奇怪.但是从内部机制看,数据库是以类似的机制工作,在一 ...
- sass基础学习(一)
移动端布局各种问题 pc端布局各种问题sass 组件模块化面向对象编程ajax 框架学习 webpack 打包 性能优化 gulp是基于Nodejs的自动任务运行器她能自动化地完成 javascrip ...
- caffe报错:cudnn.hpp:86] Check failed: status == CUDNN_STATUS_SUCCESS (3 vs. 0) CUDNN_STATUS_BAD_PARAM 原因
在实际项目中出现的该问题,起初以为是cudnn版本的问题,后来才定位到在网络进行reshape操作的时候 input_layer->Reshape({(), input_layer->sh ...
