LeetCode之“链表”:Linked List Cycle && Linked List Cycle II
1.Linked List Cycle
题目要求:
Given a linked list, determine if it has a cycle in it.
Follow up:
Can you solve it without using extra space?
刚看到这道题,很容易写出下边的程序:
bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {
ListNode *a = head, *b = head;
while(a)
{
b = a->next;
while(b)
{
if(a == b)
return true;
b = b->next;
}
a = a->next;
}
return false;
}
这个程序最大的问题在于“死循环”,例如在下边这种情况就会进入死循环:

要解决这个问题,我们可以定义两个指针slow、fast,slow每次前进一步,fast每次前进两步。如果链表存在环,则在循环一定次数后,slow与fast一定会重合(找个例子推导下就明白了)。具体从程序如下:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool hasCycle(ListNode *head) {
if(head == nullptr || head->next == nullptr)
return false; ListNode *slow = head, *fast = head;
while(fast != nullptr && fast->next != nullptr)
{
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if(slow == fast)
return true;
} return false;
}
};
2.Linked List Cycle II
题目要求:
Given a linked list, return the node where the cycle begins. If there is no cycle, return null.
Follow up:
Can you solve it without using extra space?
这道题难度还是挺大的。具体解法参考自一博文:
首先看图:
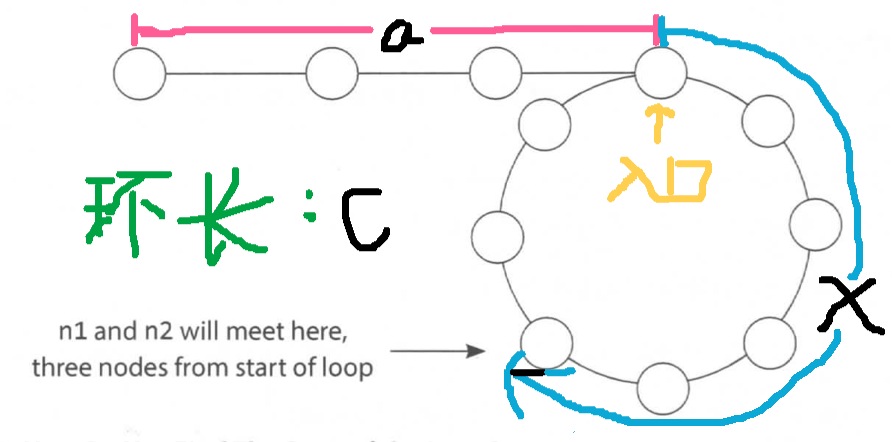
从链表起始处到环入口长度为:a,从环入口到Faster和Slower相遇点长度为:x,整个环长为:c。
假设从开始到相遇,Slower走过的路程长为s,由于Faster的步速是Slower的2倍,那么Faster在这段时间走的路程长为2s。
而对于Faster来说,他走的路程还等于之前绕整个环跑的n圈的路程nc,加上最后这一次遇见Slower的路程s。
所以我们有:
2s = nc + s
对于Slower来说,他走的路程长度s还等于他从链表起始处到相遇点的距离,所以有:
s = a + x
通过以上两个式子代入化简有:
a + x = nc
a = nc - x
a = (n-1)c + c-x
a = kc + (c-x)
那么可以看出,c-x,就是从相遇点继续走回到环入口的距离。上面整个式子可以看出,如果此时有个pointer1从起始点出发并且同时还有个pointer2从相遇点出发继续往前走(都只迈一步),那么绕过k圈以后, pointer2会和pointer1在环入口相遇。这样,换入口就找到了。
具体程序如下:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
ListNode* slow = head;
ListNode* fast = head;
while (true){
if(!fast || !fast->next)
return nullptr; slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
if (slow == fast)
break;
} slow = head;
while (slow != fast){
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next;
}
return slow;
}
};
LeetCode之“链表”:Linked List Cycle && Linked List Cycle II的更多相关文章
- [算法][LeetCode]Linked List Cycle & Linked List Cycle II——单链表中的环
题目要求 Linked List Cycle Given a linked list, determine if it has a cycle in it. Follow up: Can you so ...
- LeetCode解题报告:Linked List Cycle && Linked List Cycle II
LeetCode解题报告:Linked List Cycle && Linked List Cycle II 1题目 Linked List Cycle Given a linked ...
- LeetCode 430. Faltten a Multilevel Doubly Linked List
题目链接:LeetCode 430. Faltten a Multilevel Doubly Linked List class Node { public: int val = NULL; Node ...
- LeetCode 单链表专题 (一)
目录 LeetCode 单链表专题 <c++> \([2]\) Add Two Numbers \([92]\) Reverse Linked List II \([86]\) Parti ...
- leetcode 单链表相关题目汇总
leetcode-19-Remove Nth From End of List—移除链表中倒数第n个元素 leetcode-21-Merge Two Sorted Lists—两个已排序链表归并 ...
- Leetcode解题-链表(2.2.0)基础类
1 基类的作用 在开始练习LeetCode链表部分的习题之前,首先创建好一个Solution基类,其作用就是: Ø 规定好每个子Solution都要实现纯虚函数test做测试: Ø 提供了List ...
- 【算法题 14 LeetCode 147 链表的插入排序】
算法题 14 LeetCode 147 链表的插入排序: 解题代码: # Definition for singly-linked list. # class ListNode(object): # ...
- LeetCode 80. 删除排序数组中的重复项 II
LeetCode 80. 删除排序数组中的重复项 II
- Leetcode之二分法专题-240. 搜索二维矩阵 II(Search a 2D Matrix II)
Leetcode之二分法专题-240. 搜索二维矩阵 II(Search a 2D Matrix II) 编写一个高效的算法来搜索 m x n 矩阵 matrix 中的一个目标值 target.该矩阵 ...
- LeetCode:137. 只出现一次的数字 II
LeetCode:137. 只出现一次的数字 II 给定一个非空整数数组,除了某个元素只出现一次以外,其余每个元素均出现了三次.找出那个只出现了一次的元素. 说明: 你的算法应该具有线性时间复杂度. ...
随机推荐
- Spark:聚类算法之LDA主题模型算法
http://blog.csdn.net/pipisorry/article/details/52912179 Spark上实现LDA原理 LDA主题模型算法 [主题模型TopicModel:隐含狄利 ...
- ejabberd mod_echo 解析
ejabberd mod_echo 解析(金庆的专栏 2016.8)按开发入门的说明,mod_echo是最简单的模块之一.https://docs.ejabberd.im/developer/当然 m ...
- 【安卓开发】Android为什么选择binder
Binder (Android技术内幕): 在上面这些可供选择的方式中,Android使用得最多也最被认可的还是Binder机制. 为什么会选择Binder来作为进程之间的通信机制呢?因为Binder ...
- 快速索引 (对View的自定义)
快速索引 (对View的自定义) 快速索引应用场景: 微信好友列表, 联系人通讯录, 应用管理, 文件管理等. 快速索引7步曲: *1. A-Z索引的绘制. * 2. 处理Touch事件. * 3. ...
- activiti 动态配置 activiti 监听引擎启动和初始化(高级源码篇)
1.1.1. 前言 用户故事:现在有这样一个需求,第一个需求:公司的开发环境,测试环境以及线上环境,我们使用的数据库是不一样的,我们必须能够任意的切换数据库进行测试和发布,对数据库连接字符串我们需要加 ...
- JAVA面向对象-----instanceof 关键字
instanceof 关键字 1:快速演示instanceof Person p=new Person(); System.out.println( p instanceof Person); 2:i ...
- FFmpeg源代码简单分析:av_find_decoder()和av_find_encoder()
===================================================== FFmpeg的库函数源代码分析文章列表: [架构图] FFmpeg源代码结构图 - 解码 F ...
- GCD API记录(二)
前言 这是关于GCD的第二篇文章,GCD的API有100多个,通过快捷键Option + 单击,可以在Reference中的Grand Central Dispatch (GCD) Reference ...
- EBS HRMS数据表
4.1. 人员基本息 表 (PER_ALL_PEOPLE_F) ...
- 一个ExtJS实例
聊聊ExtJS 这几天接触了一个项目 前台用的是extjs 发现这个东西还是有点意思的 就把前台的部分 剥离了下来 有兴趣的朋友可以当做模板学习 不多说先上效果图 这篇文章 可以看作是ext知识的一 ...
