Sending e-mail with Spring MVC--转载
原文地址:http://www.codejava.net/frameworks/spring/sending-e-mail-with-spring-mvc
Table of contents:
1.Spring framework’s support for e-mail
3.Creating e-mail sending form
4.Configuring SMTP server settings and Spring MVC
5.Creating Spring MVC controller class
6.Creating result page and error page
8.Download Eclipse project/WAR file
This tutorial provides a sample spring MVC application that allows user sending an e-mail message by filling a web form. The e-mail form looks like following screenshot:
In this tutorial, you are supposed to familiar with Java EE development as well as developing Spring MVC-based applications.
1. Spring framework’s support for e-mail
Based on JavaMail, Spring framework provides high-level abstraction API which greatly simplifies e-mail sending process. Let’s take a brief look at this API in the following class diagram:
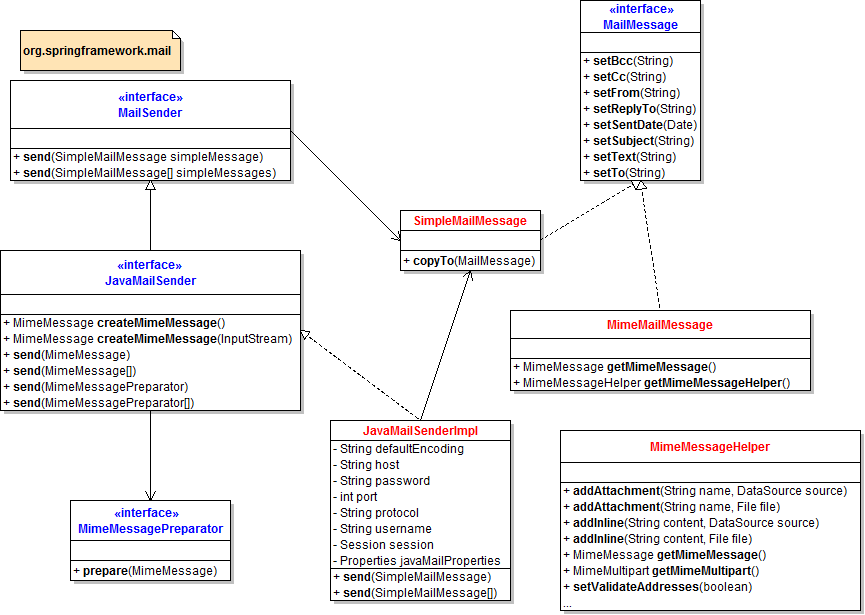
To send e-mail messages, we can use an implementation of interface MailSender – the JavaMailSenderImpl class which is built upon on JavaMail. It’s convenient to configure this implementation as a bean in Spring’s context:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
<bean id="mailSender" class="org.springframework.mail.javamail.JavaMailSenderImpl"> <!-- SMTP settings --> <property name="host" value="SMTP_HOST" /> <property name="port" value="SMTP_PORT" /> <property name="username" value="USER_NAME" /> <property name="password" value="PASSWORD" /> <property name="javaMailProperties"> <!-- additional properties specific to JavaMail --> <props> <prop key="mail.transport.protocol">smtp</prop> <prop key="mail.smtp.auth">true</prop> <prop key="mail.smtp.starttls.enable">true</prop> </props> </property></bean> |
This bean holds properties for SMTP and JavaMail and can be injected to a business/service class which needs to send an e-mail, for example:
|
1
|
mailSender.send(email); |
In which email is an object of a type that implements MailMessage interface, such as SimpleMailMessage class. We can construct the email object as follows:
|
1
2
3
4
|
SimpleMailMessage email = new SimpleMailMessage();email.setTo(toAddress);email.setSubject(subject);email.setText(body); |
That’s for a simple mail message (plain text). In case if we want to send HTML e-mail or attach files to the e-mail, we can use MimeMailMessage class with the help of MimeMessagePreparator class and MimeMessageHelper class. For example, sending an e-mail in HTML format with an attachment:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
mailSender.send(new MimeMessagePreparator() { public void prepare(MimeMessage mimeMessage) throws MessagingException { MimeMessageHelper message = new MimeMessageHelper(mimeMessage, true, "UTF-8"); message.setFrom(fromEmail); message.setTo(toEmail); message.setSubject("A file for you"); message.setText("<b>See the attached</b>", true); message.addAttachment("CoolStuff.doc", new File("CoolStuff.doc")); }}); |
The following table summarizes the interfaces and classes provided in org.springframework.mail package:
|
org.springframework.mail |
|
Click on a link in the table to see API documentation for the corresponding interface/class.
2. Required jar files
The application requires the following jar files copied to its WEB-INF\lib directory:
|
Required jar files |
|
|
mail.jar |
|
|
spring-beans-3.2.0.RELEASE.jar spring-context-3.2.0.RELEASE.jar spring-context-support-3.2.0.RELEASE.jar spring-core-3.2.0.RELEASE.jar spring-expression-3.2.0.RELEASE.jar spring-web-3.2.0.RELEASE.jar spring-webmvc-3.2.0.RELEASE.jar |
|
|
commons-logging-1.1.1.jar |
|
NOTE: Click on a hyperlink in the table above to download the corresponding software.
The sample application we are going to build contains the following key files:
- EmailForm.jsp: displays an e-mail form.
- Result.jsp: shows successful message after the e-mail has been sent.
- Error.jsp: shows error message in case of an exception is thrown.
- SendEmailController.java: the Spring controller class that takes input from e-mail form, calls Spring’s mailSender to send the e-mail, and redirects user to either successful page or error page.
- spring-mvc.xml: Spring’s context configuration file. Here we will configure SMTP server settings and various properties for JavaMail.
- web.xml: web deployment descriptor file.
3. Creating e-mail sending form
Create a JSP file called EmailForm.jsp with the following HTML code:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%><!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"><html><head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"><title>Email with Spring MVC</title></head><body> <center> <h1>Sending e-mail with Spring MVC</h1> <form method="post" action="sendEmail.do"> <table border="0" width="80%"> <tr> <td>To:</td> <td><input type="text" name="recipient" size="65" /></td> </tr> <tr> <td>Subject:</td> <td><input type="text" name="subject" size="65" /></td> </tr> <tr> <td>Message:</td> <td><textarea cols="50" rows="10" name="message"></textarea></td> </tr> <tr> <td colspan="2" align="center"> <input type="submit" value="Send E-mail" /> </td> </tr> </table> </form> </center></body></html> |
This is a simple form with three fields: To, Subject and Message – which are necessary attributes for a simple outgoing e-mail message. On submitting this form, the action named “sendEmail.do” will be called, as specified by the form’s actionattribute. We will implement a Spring controller class for handling this action in the next section.
4. Configuring SMTP server settings and Spring MVC
Create a Spring context configuration file called spring-mvc.xml with the following XML code:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd"> <context:component-scan base-package="net.codejava.spring" /> <bean id="mailSender" class="org.springframework.mail.javamail.JavaMailSenderImpl"> <property name="host" value="smtp.gmail.com" /> <property name="port" value="587" /> <property name="username" value="youremail" /> <property name="password" value="yourpassword" /> <property name="javaMailProperties"> <props> <prop key="mail.transport.protocol">smtp</prop> <prop key="mail.smtp.auth">true</prop> <prop key="mail.smtp.starttls.enable">true</prop> </props> </property> </bean> <bean id="viewResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"> <property name="prefix" value="/" /> <property name="suffix" value=".jsp" /> </bean> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleMappingExceptionResolver"> <property name="exceptionMappings"> <props> <prop key="java.lang.Exception">Error</prop> </props> </property> </bean> </beans> |
This configuration is pretty straightforward:
- <context:component-scan ... />: tells Spring to scan the package net.codejava.spring for initializing components which are annotated by Spring annotations (It’s a Spring controller class, in case of this application).
- Bean mailSender: this is the important part because it declares a Spring bean for e-mail implementation – theJavaMailSenderImpl class and configures SMTP server settings, which is for a Gmail account in this case. This bean will be injected to a Spring controller class which will be covered in the next section.
- Bean viewResolver: maps logical view names to real JSP file names.
- Bean SimpleMappingExceptionResolver: maps all exceptions of type java.lang.Exception to be handled byError.jsp page.
The web deployment descriptor file (web.xml) is configured as follows:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:web="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="3.0"> <display-name>EmailSpringMVC</display-name> <servlet> <servlet-name>SpringController</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>/WEB-INF/spring-mvc.xml</param-value> </init-param> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>SpringController</servlet-name> <url-pattern>*.do</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> <welcome-file-list> <welcome-file>EmailForm.jsp</welcome-file> </welcome-file-list></web-app> |
It declares Spring controller servlet with its context configuration file (/WEB-INF/spring-mvc.xml). The controller is configured to handle all requests whose URL end with pattern: *.do. And the default page when accessing the application is the email form (EmailForm.jsp).
5. Creating Spring MVC controller class
In order to handle submission from the e-mail form, we need to create a Spring controller class as follows:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
package net.codejava.spring;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.mail.SimpleMailMessage;import org.springframework.mail.javamail.JavaMailSender;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;@Controller@RequestMapping("/sendEmail.do")public class SendEmailController { @Autowired private JavaMailSender mailSender; @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST) public String doSendEmail(HttpServletRequest request) { // takes input from e-mail form String recipientAddress = request.getParameter("recipient"); String subject = request.getParameter("subject"); String message = request.getParameter("message"); // prints debug info System.out.println("To: " + recipientAddress); System.out.println("Subject: " + subject); System.out.println("Message: " + message); // creates a simple e-mail object SimpleMailMessage email = new SimpleMailMessage(); email.setTo(recipientAddress); email.setSubject(subject); email.setText(message); // sends the e-mail mailSender.send(email); // forwards to the view named "Result" return "Result"; }} |
This controller class is quite simple. It is declared as a Spring MVC controller by the annotation @Controller, and is mapped to the e-mail form’s action by the @RequestMapping annotation. We inject the mailSender bean declared inspring-mvc.xml file into this controller through the private field also named mailSender. The injection is done automatically by Spring as we use the @Autowired annotation.
The method doSendEmail()is responsible for capturing input from e-mail form, creating a SimpleMailMessage object and sending the e-mail by invoking the send() method on the mailSender bean. The e-mail is in plain text format. Finally, it returns a view named “Result” which causes Spring to use the viewResolver to find and load appropriate JSP file (Result.jsp).
6. Creating result page and error page
Code the Result.jsp file as follows:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%><!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"><html><head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"><title>Send e-mail result</title></head><body> <center> <h2>Thank you, your email has been sent.</h2> </center></body></html> |
And code the Error.jsp as follows:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%><!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"><html><head><meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"><title>Error</title></head><body> <center> <h2>Sorry, the email was not sent because of the following error:</h2> <h3>${exception.message}</h3> </center></body></html> |
As we can see, the result page simply tells the user that the e-mail has been sent, while the error page displays an error message if any exception thrown during the process of sending e-mail.
7. Run the application
So far we have created all the key pieces of the application. Let’s deploy it on a servlet container like Tomcat, and access the application by typing the following URL into browser’s address bar (your host name and port number maybe different, depending on server configuration):
http://localhost:8080/EmailSpringMVC
The e-mail form is displayed, type in required information:
Hit Send E-mail button, it may take a while for the e-mail to be sent. A successful message comes from the result page in case everything is going well:
In case of error (such as network failure or the SMTP server could not be reached), the error page displays:
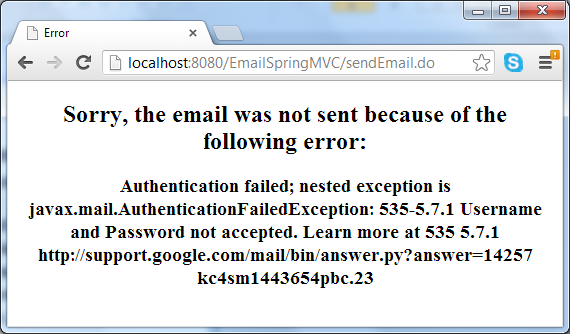
You can download the sample application as an Eclipse project or deployable WAR file in the attachment section, and remember to update SMTP settings to match your e-mail account.
Sending e-mail with Spring MVC--转载的更多相关文章
- 转载:如何让spring mvc web应用启动时就执行
转载:如何让spring mvc web应用启动时就执行特定处理 http://www.cnblogs.com/yjmyzz/p/4747251.html# Spring-MVC的应用中 一.Appl ...
- 转载 Spring、Spring MVC、MyBatis整合文件配置详解
Spring.Spring MVC.MyBatis整合文件配置详解 使用SSM框架做了几个小项目了,感觉还不错是时候总结一下了.先总结一下SSM整合的文件配置.其实具体的用法最好还是看官方文档. ...
- spring mvc入门教程 转载自【http://elf8848.iteye.com/blog/875830】
目录 一.前言二.spring mvc 核心类与接口三.spring mvc 核心流程图 四.spring mvc DispatcherServlet说明 五.spring mvc 父子上下文的说明 ...
- 转载:深入理解Spring MVC 思想
原文作者:赵磊 原文地址:http://elf8848.iteye.com/blog/875830 目录 一.前言二.spring mvc 核心类与接口三.spring mvc 核心流程图 四.sp ...
- 《转载》Spring MVC之@RequestBody, @ResponseBody 详解
引言: 接上一篇文章讲述处理@RequestMapping的方法参数绑定之后,详细介绍下@RequestBody.@ResponseBody的具体用法和使用时机: 简介: @RequestBody 作 ...
- (转载)spring mvc DispatcherServlet详解之一---处理请求深入解析
要深入理解spring mvc的工作流程,就需要先了解spring mvc的架构: 从上图可以看到 前端控制器DispatcherServlet在其中起着主导作用,理解了DispatcherServl ...
- 【转载】Spring MVC 整合 Freemarker
前言 1.为什么要使用Spring MVC呢? 2.为什么要使用Freemarker呢? 3.为什么不使用Struts2呢? 此示例出现的原因就是发现了struts2的性能太差,所以学习Spring ...
- Spring mvc 文件上传到文件夹(转载+心得)
spring mvc(注解)上传文件的简单例子,这有几个需要注意的地方1.form的enctype=”multipart/form-data” 这个是上传文件必须的2.applicationConte ...
- Spring mvc中@RequestMapping 6个基本用法小结(转载)
小结下spring mvc中的@RequestMapping的用法. 1)最基本的,方法级别上应用,例如: @RequestMapping(value="/departments" ...
- 解决 spring mvc 3.0 结合 hibernate3.2 使用<tx:annotation-driven>声明式事务无法提交的问题(转载)
1.问题复现 spring 3.0 + hibernate 3.2 spring mvc使用注解方式:service使用@service注解 事务使用@Transactional 事务配置使用 < ...
随机推荐
- libc.so.6: version GLIBC_2.14 not found
https://blog.csdn.net/heylun/article/details/78833050
- SpringBoot 增加 拦截器 判断是否登录
1.创建拦截器 package com.example.demo.interceptor; import org.slf4j.Logger; import org.slf4j.LoggerFactor ...
- Linux学习总结(2)——linux常用命令大全
玩过Linux的人都会知道,Linux中的命令的确是非常多,但是玩过Linux的人也从来不会因为Linux的命令如此之多而烦恼,因为我们只需要掌握我们最常用的命令就可以了.当然你也可以在使用时去找一下 ...
- iterator的使用和封个问题
这篇文章的内容还是不错的: http://www.cnblogs.com/zhuyf87/archive/2012/12/08/2808290.html for (vector<int>: ...
- android側滑菜单-DrawerLayout的基本使用
眼下主流App开发中,部分是以側滑菜单为主布局架构,曾经做android側滑菜单时.大多选择使用github上的第三方开源框架SildingMenu,可是这个框架还是稍显笨重.好消息是google已经 ...
- [转]Massive Model Rendering Techniques
Massive Model Rendering Techniques Andreas Dietrich Enrico Gobbetti Sung-Eui Yoon Abstract We presen ...
- 关于mysql数据库在输入password后,滴的一声直接退出界面的解决的方法(具体办法)
前一阵子.因为敲代码要用到数据库,便在本子上下载了一个,却出现非常多小问题(自己的台式机却没有该问题,可能是本人的本子太渣了吧),纠结了好一阵,回头想想.发现问题,分析问题,解决这个问题,不就是我们的 ...
- vue2留言板
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8&quo ...
- android framework 02
Android底层开发1.安装Ubuntu系统2.Ubuntu配置开发环境: sudo apt-get install git-core gnupg flex bison gperf zip sudo ...
- 79.QT解决迷宫问题(面向过程与面向对象)
面向过程: 创建一个类继承dialog,mydialog,添加两个变量 #ifndef MYDIALOG_H #define MYDIALOG_H #include <QDialog>&g ...
