K-D tree入门
久仰K-D tree大名已久,终于在合适的时候遇见了合适的水题入了坑入了门
K-D tree是什么##
K-D tree是什么? 按名字上翻译来就是K维的树,就是一个用来维护K维空间的点的平衡二叉树
K-D tree有什么用##
K-D tree可以进行空间上的操作,最经典的就是查询最近/最远 点对
还有很多我不知道
K-D tree的原理与实现##
K-D tree,又有一个名字叫做划分树,与其原理相联系
类似于普通的平衡树,对于普通的平衡树的节点u,其左右子树分别是权值小于u的和权值大于u的,该节点就相当于在一个值域上在u的值处进行了分割
而kd-tree对于多维空间进行分割,一个节点储存着以下信息:
struct node{
int d[K],s[2],x[2],y[2],......;
}e[maxn];
d就是该节点储存的点的K维坐标
s储存着其左右儿子
剩余的若干数组储存着以该节点为根的子树的各维度的最值
也就是说,一棵子树实际上对应着一个空间区域,而根节点将该空间区域划分为左右两部分
而该空间的信息就储存在子树的根节点中
但是这是在一个多维空间,将空间区域划分有多种方式
一般地,kd-tree垂直于其中一个坐标轴将平面划分开
以2维为例,如下图所示
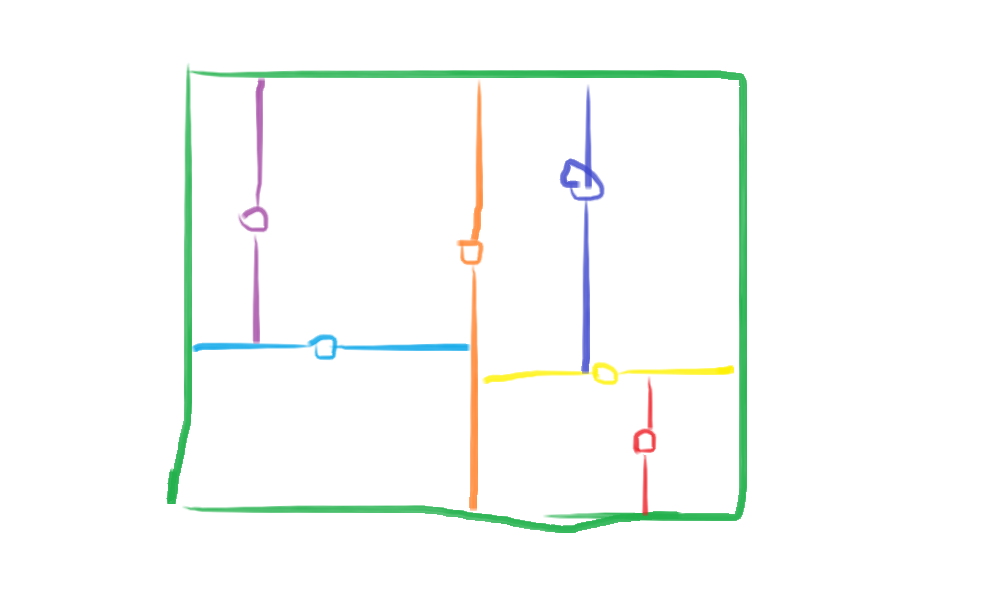
如图圆圈表示节点,将区域进行划分
一般遵循以下规律构造:
①各层节点交替划分各维空间
根节点划分x坐标
其儿子划分y坐标
其孙子划分z坐标
......
②每一层的区域中,按该层划分的坐标排序,选取其中位数作为划分点进行划分
切点作为父节点,左边的点划分到左子树中,右边的点划分到右子树中
③逐层划分,直至划分区域无节点
在C++的STL中,有一个函数nth_element()可以在\(O(n)\)时间内将一个数组第k大找出,并将小于的放在左边,大于的放在右边
具体实现类似快排
对于K维空间,建树复杂度\(O(Knlogn)\)
二维建树代码如下:
#define ls e[u].s[0]
#define rs e[u].s[1]
#define cmin(x,y) (x > y ? x = y : x)
#define cmax(x,y) (x < y ? x = y : x)
struct point{int d[2];}a[maxn];
struct node{int d[2],s[2],x[2],y[2];}e[maxn];
int n,rt,D,x,y;
bool operator <(const point& a,const point& b){
return a.d[D] == b.d[D] ? a.d[D ^ 1] < b.d[D ^ 1] : a.d[D] < b.d[D];
}
void pup(int u){
if (ls){
cmin(e[u].x[0],e[ls].x[0]); cmax(e[u].x[1],e[ls].x[1]);
cmin(e[u].y[0],e[ls].y[0]); cmax(e[u].y[1],e[ls].y[1]);
}
if (rs){
cmin(e[u].x[0],e[rs].x[0]); cmax(e[u].x[1],e[rs].x[1]);
cmin(e[u].y[0],e[rs].y[0]); cmax(e[u].y[1],e[rs].y[1]);
}
}
int build(int l,int r,int d){
D = d; int u = l + r >> 1;
nth_element(a + l,a + u,a + r + 1);
e[u].d[0] = e[u].x[0] = e[u].x[1] = a[u].d[0];
e[u].d[1] = e[u].y[0] = e[u].y[1] = a[u].d[1];
if (l < u) ls = build(l,u - 1,d ^ 1);
if (r > u) rs = build(u + 1,r,d ^ 1);
pup(u);
return u;
}
查询最近/远点对##
以最近为例
与普通的暴力不同,在KDtree中查询最近点对,预期复杂度为\(O(logn)\),可以被卡为\(O(\sqrt{N})\)
我们到一个节点时,用该节点更新答案,并计算左右子树的估价函数
由于每棵子树都对应一个区域,可以由此计算出每棵子树的最近值
如果最近的点的贡献都比当前答案大,那么就不用访问该子树了
以2维为例,估价函数可以这样写:
#define getd(u) (max(x - e[u].x[1],0) + max(e[u].x[0] - x,0) + max(y - e[u].y[1],0) + max(e[u].y[0] - y,0))
#define getdx(u) (max(abs(e[u].x[0] - x),abs(e[u].x[1] - x)) + max(abs(e[u].y[0] - y),abs(e[u].y[1] - y)))
实际上就是求与四个顶点距离的最值
由此可以写出搜索函数:
void qmx(int u){
LL t = equal(u) ? -INF : (abs(e[u].d[0] - x) + abs(e[u].d[1] - y)),d[2];
if (ls) d[0] = getdx(ls); else d[0] = -INF;
if (rs) d[1] = getdx(rs); else d[1] = -INF;
cmax(mx,t); t = d[0] <= d[1];
if (d[t] > mx) qmx(e[u].s[t]); t ^= 1;
if (d[t] > mx) qmx(e[u].s[t]);
}
void qmn(int u){
int t = equal(u) ? INF : (abs(e[u].d[0] - x) + abs(e[u].d[1] - y)),d[2];
if (ls) d[0] = getd(ls); else d[0] = INF;
if (rs) d[1] = getd(rs); else d[1] = INF;
cmin(mn,t); t = d[0] >= d[1];
if (d[t] < mn) qmn(e[u].s[t]); t ^= 1;
if (d[t] < mn) qmn(e[u].s[t]);
}
插入##
类似平衡树插入
void insert(int u,int d){
if (e[u].d[d] < dd[d]){
if (ls) insert(ls,d ^ 1);
else {
ls = ++n;
e[ls].d[0] = e[ls].x[0] = e[ls].x[1] = dd[0];
e[ls].d[1] = e[ls].y[0] = e[ls].y[1] = dd[1];
}
}
else {
if (rs) insert(rs,d ^ 1);
else {
rs = ++n;
e[rs].d[0] = e[rs].x[0] = e[rs].x[1] = dd[0];
e[rs].d[1] = e[rs].y[0] = e[rs].y[1] = dd[1];
}
}
pup(u);
}
例题##
由以上基础,我们就可以轻松A掉SDOI2010 hideseek了
用每个点搜一次就好
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#define LL long long int
#define Redge(u) for (int k = h[u],to; k; k = ed[k].nxt)
#define REP(i,n) for (int i = 1; i <= (n); i++)
#define BUG(s,n) for (int i = 1; i <= (n); i++) cout<<s[i]<<' '; puts("");
#define ls e[u].s[0]
#define rs e[u].s[1]
#define cmin(x,y) (x > y ? x = y : x)
#define cmax(x,y) (x < y ? x = y : x)
#define getd(u) (max(x - e[u].x[1],0) + max(e[u].x[0] - x,0) + max(y - e[u].y[1],0) + max(e[u].y[0] - y,0))
#define getdx(u) (max(abs(e[u].x[0] - x),abs(e[u].x[1] - x)) + max(abs(e[u].y[0] - y),abs(e[u].y[1] - y)))
#define equal(u) (e[u].d[0] == x && e[u].d[1] == y)
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 100005,maxm = 100005,INF = 2100000000;
inline int read(){
int out = 0,flag = 1; char c = getchar();
while (c < 48 || c > 57){if (c == '-') flag = -1; c = getchar();}
while (c >= 48 && c <= 57){out = (out << 3) + (out << 1) + c - 48; c = getchar();}
return out * flag;
}
struct point{int d[2];}a[maxn];
struct node{int d[2],s[2],x[2],y[2];}e[maxn];
int n,rt,D,x,y; LL mx,mn;
bool operator <(const point& a,const point& b){
return a.d[D] == b.d[D] ? a.d[D ^ 1] < b.d[D ^ 1] : a.d[D] < b.d[D];
}
void pup(int u){
if (ls){
cmin(e[u].x[0],e[ls].x[0]); cmax(e[u].x[1],e[ls].x[1]);
cmin(e[u].y[0],e[ls].y[0]); cmax(e[u].y[1],e[ls].y[1]);
}
if (rs){
cmin(e[u].x[0],e[rs].x[0]); cmax(e[u].x[1],e[rs].x[1]);
cmin(e[u].y[0],e[rs].y[0]); cmax(e[u].y[1],e[rs].y[1]);
}
}
int build(int l,int r,int d){
D = d; int u = l + r >> 1;
nth_element(a + l,a + u,a + r + 1);
e[u].d[0] = e[u].x[0] = e[u].x[1] = a[u].d[0];
e[u].d[1] = e[u].y[0] = e[u].y[1] = a[u].d[1];
if (l < u) ls = build(l,u - 1,d ^ 1);
if (r > u) rs = build(u + 1,r,d ^ 1);
pup(u);
return u;
}
void qmx(int u){
LL t = equal(u) ? -INF : (abs(e[u].d[0] - x) + abs(e[u].d[1] - y)),d[2];
if (ls) d[0] = getdx(ls); else d[0] = -INF;
if (rs) d[1] = getdx(rs); else d[1] = -INF;
cmax(mx,t); t = d[0] <= d[1];
if (d[t] > mx) qmx(e[u].s[t]); t ^= 1;
if (d[t] > mx) qmx(e[u].s[t]);
}
void qmn(int u){
int t = equal(u) ? INF : (abs(e[u].d[0] - x) + abs(e[u].d[1] - y)),d[2];
if (ls) d[0] = getd(ls); else d[0] = INF;
if (rs) d[1] = getd(rs); else d[1] = INF;
cmin(mn,t); t = d[0] >= d[1];
if (d[t] < mn) qmn(e[u].s[t]); t ^= 1;
if (d[t] < mn) qmn(e[u].s[t]);
}
int main(){
n = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) a[i].d[0] = read(),a[i].d[1] = read();
rt = build(1,n,0);
LL ans = INF;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
x = a[i].d[0]; y = a[i].d[1];
mx = 0; qmx(rt);
mn = INF; qmn(rt);
ans = min(ans,mx - mn);
}
printf("%lld\n",ans);
return 0;
}
BZOJ2648 / BZOJ2716 两道比较卡常数
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#define LL long long int
#define max(a,b) (a > b ? a : b)
#define min(a,b) (a < b ? a : b)
#define cmax(a,b) (a < b ? a = b : a)
#define cmin(a,b) (a > b ? a = b : a)
#define ls e[u].s[0]
#define rs e[u].s[1]
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1000005,maxm = 500005,INF = 1000000000;
inline int read(){
int out = 0,flag = 1; char c = getchar();
while (c < 48 || c > 57){if (c == '-') flag = -1; c = getchar();}
while (c >= 48 && c <= 57){out = (out << 3) + (out << 1) + c - 48; c = getchar();}
return out * flag;
}
struct node{
int d[2],s[2],x[2],y[2];
}e[maxn];
int m,n,x,y,D,dd[2],ans,rt;
struct point{int d[2];}p[maxm];
inline bool cmp(const point& a,const point& b){
return a.d[D] < b.d[D];
}
int getd(int u){
int tmp = 0;
tmp += max(e[u].x[0] - x,0);
tmp += max(x - e[u].x[1],0);
tmp += max(e[u].y[0] - y,0);
tmp += max(y - e[u].y[1],0);
return tmp;
}
inline void pup(int u){
if (ls){
cmin(e[u].x[0],e[ls].x[0]); cmax(e[u].x[1],e[ls].x[1]);
cmin(e[u].y[0],e[ls].y[0]); cmax(e[u].y[1],e[ls].y[1]);
}
if (rs){
cmin(e[u].x[0],e[rs].x[0]); cmax(e[u].x[1],e[rs].x[1]);
cmin(e[u].y[0],e[rs].y[0]); cmax(e[u].y[1],e[rs].y[1]);
}
}
int build(int l,int r,int d){
D = d; int u = l + r >> 1;
nth_element(p + l,p + u,p + r + 1,cmp);
e[u].d[0] = e[u].x[0] = e[u].x[1] = p[u].d[0];
e[u].d[1] = e[u].y[0] = e[u].y[1] = p[u].d[1];
if (l < u) ls = build(l,u - 1,d ^ 1);
if (r > u) rs = build(u + 1,r,d ^ 1);
pup(u);
return u;
}
void insert(int u,int d){
if (e[u].d[d] < dd[d]){
if (ls) insert(ls,d ^ 1);
else {
ls = ++n;
e[ls].d[0] = e[ls].x[0] = e[ls].x[1] = dd[0];
e[ls].d[1] = e[ls].y[0] = e[ls].y[1] = dd[1];
}
}
else {
if (rs) insert(rs,d ^ 1);
else {
rs = ++n;
e[rs].d[0] = e[rs].x[0] = e[rs].x[1] = dd[0];
e[rs].d[1] = e[rs].y[0] = e[rs].y[1] = dd[1];
}
}
pup(u);
}
void query(int u){
int t = abs(e[u].d[0] - x) + abs(e[u].d[1] - y),d[2];
if (ls) d[0] = getd(ls); else d[0] = INF;
if (rs) d[1] = getd(rs); else d[1] = INF;
cmin(ans,t); t = d[0] >= d[1];
if (d[t] < ans) query(e[u].s[t]); t ^= 1;
if (d[t] < ans) query(e[u].s[t]);
}
int main(){
n = read(); m = read();
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
p[i].d[0] = read();
p[i].d[1] = read();
}
rt = build(1,n,0);
int t;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
t = read(); x = read(); y = read();
if (t & 1){
dd[0] = x; dd[1] = y;
insert(rt,0);
}
else {
ans = INF;
query(rt);
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
}
return 0;
}
K-D tree入门的更多相关文章
- bzoj2049 [Sdoi2008]Cave 洞穴勘测 link cut tree入门
link cut tree入门题 首先说明本人只会写自底向上的数组版(都说了不写指针.不写自顶向下QAQ……) 突然发现link cut tree不难写... 说一下各个函数作用: bool isro ...
- link cut tree 入门
鉴于最近写bzoj还有51nod都出现写不动的现象,决定学习一波厉害的算法/数据结构. link cut tree:研究popoqqq那个神ppt. bzoj1036:维护access操作就可以了. ...
- dsu on tree入门
先瞎扯几句 说起来我跟这个算法好像还有很深的渊源呢qwq.当时在学业水平考试的考场上,题目都做完了不会做,于是开始xjb出题.突然我想到这么一个题 看起来好像很可做的样子,然而直到考试完我都只想出来一 ...
- POJ 3468 A Simple Problem with Integers (splay tree入门)
A Simple Problem with Integers Time Limit: 5000MS Memory Limit: 131072K Total Submissions: 47944 ...
- [HNOI2002]营业额统计 Splay tree入门题
题目连接:http://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=1588 1588: [HNOI2002]营业额统计 Time Limit: 5 Sec ...
- poj3481(splay tree 入门题)
平衡树都能做. // // main.cpp // splay // // Created by 陈加寿 on 16/3/25. // Copyright © 2016年 chenhuan001. A ...
- 手撸红黑树-Red-Black Tree 入门
一.学习红黑树前的准备: 熟悉基础数据结构 了解二叉树概念 二.红黑树的规则和规则分析: 根节点是黑色的 所有叶子节点(Null)是黑色的,一般会认定节点下空节点全部为黑色 如果节点为红色,那么子节点 ...
- dsu on tree 入门
Dus on tree 树上并查集?. 啊这,并不是的啦,他利用了树上启发式合并的思想. 他主要解决不带修改且主要询问子树信息的树上问题. 先来看到例题,CF600E . 这不就是树上莫队的经典题吗? ...
- 第46届ICPC澳门站 K - Link-Cut Tree // 贪心 + 并查集 + DFS
原题链接:K-Link-Cut Tree_第46屆ICPC 東亞洲區域賽(澳門)(正式賽) (nowcoder.com) 题意: 要求一个边权值总和最小的环,并从小到大输出边权值(2的次幂):若不存在 ...
随机推荐
- 压力测试工具segie的使用
压力测试工具segie的使用 使用文档参考地址:https://www.joedog.org/siege-manual/ siege4地址:http://download.joedog.org/sie ...
- 洛谷 P1181 数列分段Section I(水题日常)
题目描述 对于给定的一个长度为N的正整数数列A[i],现要将其分成连续的若干段,并且每段和不超过M(可以等于M),问最少能将其分成多少段使得满足要求. 输入输出格式 输入格式: 输入文件divide_ ...
- codeforce Gym 100203I I WIN (网络流)
把'I'拆成容量为1一条边,一个入点一个出点,入点和相邻的'W'连一条容量为1的边,出点和相邻的'N'连一条容量为1,所有的'W'和源点连一条容量为1边,所有的'N'和汇点连一条容量为1的边,表示只能 ...
- Codeforces Round #290 (Div. 2) _B找矩形环的三种写法
http://codeforces.com/contest/510/status/B 题目大意 给一个n*m 找有没有相同字母连起来的矩形串 第一种并查集 瞎搞一下 第一次的时候把val开成字符串了 ...
- iOS7.1企业应用"无法安装应用程序 因为证书无效"的解决方案
今天升级了iOS7.1后发现通过之前的url无法安装企业应用了,一直提示“无法安装应用程序 因为http://xxx.xxx.xxx证书无效”,折腾了一番,终于在StackOverFlow上找到了答案 ...
- Bootstrap历练实例:响应式导航栏
响应式的导航栏 为了给导航栏添加响应式特性,您要折叠的内容必须包裹在带有 classes .collapse..navbar-collapse 的 <div> 中.折叠起来的导航栏实际上是 ...
- ios 点餐系统
这个程序的主要界面就是一个TabBarController.总共三个标签,第一个是所有的可点的菜,第二个是已点的菜,第三个是可以留言或者查看所有留言. 下面是第一个页面: 右上角的i按钮是添加新菜,每 ...
- Vue构建项目
构建Vue项目 按照官网教程安装 //先安装脚手架 cnpm i -g vue-cli //查看项目目标列表: webpack browserify pwa 等项目模板 vue list //使用we ...
- nginx 无法加载css/js图片等文件 404 not fund
刚配置Nginx反向代理,Nginx可能会出现无法加载css.js或者图片等文件,这里需要在配置文件*.conf里面加上如下配置项. location ~ .*\.(js|css|png|jpg)$ ...
- History Api以及hash操作
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000002447556#articleHeader12 https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs ...
