【关键字】c++关键字
1. alignas (c++11)
设置类和struct的字节对齐方式
默认取值是: 2n : 0, 1, 2, 4 , 6, 8.....
2. alignof
区分sizeof(), alignof得到字节对齐的字节数
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; //对结构体或类进行表示, 设置对齐方式为8字节
struct alignas() S {}; //struct alignas(1) U { S s; } // warning //有字节对齐(以4字节为对齐方式)
struct Foo
{
int i;
float f;
char c;
}; struct Empty {}; struct alignas() Empty64 {}; struct alignas() Double {
double d;
}; //以四字节为对齐方式, 即sizeof(Obj) == 8
struct Obj {
char a;
int b;
}; void alignInfo()
{
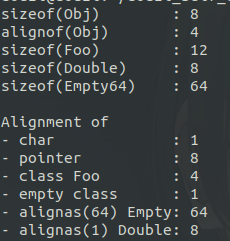
cout << "sizeof(Obj) : " << sizeof(Obj) << endl; //
cout << "alignof(Obj) : " << alignof(Obj) << endl; //
cout << "sizeof(Foo) : " << sizeof(Foo) << endl; //
cout << "sizeof(Double) : " << sizeof(Double) << endl; //
cout << "sizeof(Empty64) : " << sizeof(Empty64) << endl; // cout << "\n"; cout << "Alignment of " << endl;
cout << "- char : " << alignof(char) << endl; //
cout << "- pointer : " << alignof(int*) << endl; //
cout << "- class Foo : " << alignof(Foo) << endl; //
cout << "- empty class : " << alignof(Empty) << endl; //
cout << "- alignas(64) Empty: " << alignof(Empty64) << endl; //
cout << "- alignas(1) Double: " << alignof(Double) << endl; //
} int main()
{
alignInfo(); return ;
}
3. auto (c++11)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; double add(double a, double b)
{
return a + b;
} double get_fun(int a)
{
return a;
} void showAuto()
{
int aa = + ;
auto a = + ;
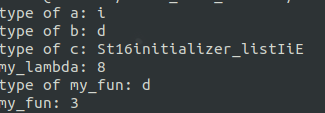
cout << "type of a: " << typeid(a).name() << endl; auto b = add(, 1.2);
cout << "type of b: " << typeid(b).name() << endl; auto c = {, };
cout << "type of c: " << typeid(c).name() << endl; auto my_lambda = [](int x) { return x + ; };
std::cout << "my_lambda: " << my_lambda() << endl; auto my_fun = get_fun();
cout << "type of my_fun: " << typeid(my_fun).name() << endl;
cout << "my_fun: " << get_fun() << endl; } int main()
{ showAuto();
return ;
}
4. bitand 和 bitor
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; void showBitAndOr()
{
auto a = 3L;
auto b = ; //long
auto c = a bitand b; // &
auto d = a bitor b; // | cout << c << endl; cout << d << endl;
} int main()
{
showBitAndOr(); return ;
}
5. constexpr: 常量表达式(c++11)
- 用于编译时的常量与常量函数。
- 声明为constexpr函数的意义是:如果其参数均为合适的编译期常量,则对这个constexpr函数的调用就可用于 期望常量表达式 的场合(如模板的非类型参数,或枚举常量的值)。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std; int fact(int n)
{
return n < ? : (n * fact(n - ));
} //编译器在编译器时, 就求出来返回的值了
constexpr int factorial(int n)
{
return n <= ? : (n * factorial(n - ));
} template<int N>
struct NN {
void print()
{
cout << N << endl;
}
}; int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{ //在编译器编译时调用的
if (argc > ) factorial(atoi(argv[])); auto aa = fact();
auto bb = factorial();
char group[factorial()]; //编译器在编译时, 就求出来了 NN<factorial()> nn;
nn.print(); return ; }
输出: 6
6. const_cast(避免使用)
7. decltype指定符(c++11)
检查实体的声明类型或表达式的类型及值分类。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std; struct A {
double x;
A(double t) : x(t) {} }; void testDecltype()
{
A* a = new A(); auto aa = a->x; // aa : double
decltype(a->x) y; // decltype(a->x) : double
decltype((a->x)) z = y; // decltype((a->x)) : double&
z = 23.5;
cout << y << endl; // 23.5 //其他用法
} //c++11, 后置返回类型, 返回值类型由 后面的表达式确定的
//返回值不损失任何精度
template<typename T, typename U>
auto add(T a, U b) -> decltype(a + b)
{
return a + b;
} template<typename T, typename U>
auto add(T a, U b) {
auto c = a + b;
//return c; //返回值
//return (c); //返回引用
return c;
} int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
testDecltype(); return ;
}
8. dynamic_cast转换
沿继承层级向上、向下及侧向转换到类的指针和引用。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std; struct Base
{
virtual ~Base() {}
}; struct Derived : public Base
{
virtual void name() {}
}; void testDynatic_cast()
{
Base *b1 = new Base();
//拥有基类指针, base指针-->derived指针, 失败
if (Derived *d = dynamic_cast<Derived *> (b1))
{
cout << "donwcast from b1 to d successful\n";
d->name(); // safe to call
} Base *b2 = new Derived();
//成功, 因为b2的确指向derived
if (Derived *d = dynamic_cast<Derived *> (b2))
{
cout << "donwcast from b2 to d successful\n";
d->name(); // safe to call
}
} int main(int argc, char **argv)
{ testDynatic_cast(); return ;
}
9. explicit
struct A
{
A(int) { } // 转换构造函数
A(int, int) { } // 转换构造函数 (C++11)
operator bool() const { return true; }
}; struct B
{
explicit B(int) { }
explicit B(int, int) { }
explicit operator bool() const { return true; }
}; int main()
{
A a1 = ; // OK :复制初始化选择 A::A(int)
A a2(); // OK :直接初始化选择 A::A(int)
A a3 {, }; // OK :直接列表初始化选择 A::A(int, int)
A a4 = {, }; // OK :复制列表初始化选择 A::A(int, int)
A a5 = (A); // OK :显式转型进行 static_cast
if (a1) ; // OK :A::operator bool()
bool na1 = a1; // OK :复制初始化选择 A::operator bool()
bool na2 = static_cast<bool>(a1); // OK :static_cast 进行直接初始化 // B b1 = 1; // 错误:复制初始化不考虑 B::B(int)
B b2(); // OK :直接初始化选择 B::B(int)
B b3 {, }; // OK :直接列表初始化选择 B::B(int, int)
// B b4 = {4, 5}; // 错误:复制列表初始化不考虑 B::B(int,int)
B b5 = (B); // OK :显式转型进行 static_cast
if (b2) ; // OK :B::operator bool()
// bool nb1 = b2; // 错误:复制初始化不考虑 B::operator bool()
bool nb2 = static_cast<bool>(b2); // OK :static_cast 进行直接初始化
}
10. static_assert: 编译时检查
#include <iostream>
using namespace std; template<typename T>
void func(T t)
{
static_assert(alignof(T) == , "only for alignof 4");
} int main()
{
int a = ; func(a); return ;
}
【关键字】c++关键字的更多相关文章
- JAVA基础复习与总结<二>构造方法_static关键字_final关键字
构造方法详解 构造器也叫做构造方法(constructor),用于对象的初始化. class Person2 { String name; int age; public Person2(String ...
- oracle: 分割字符串,或者查找字段里面的关键字(关键字1,关键字2,关键字3)
表中有一个字段:keyword, keyword里面的存储的字符一般是:[关键字1,关键字2,关键字3] 那么,在搜索的时候,不能用like 来模糊查询,因为这样会,多查询出一下不相干的关键字, hi ...
- 对象的反序列化流_ObjectInputStream和transient关键字瞬态关键字
对象的反序列化流_ObjectInputStream package com.yang.Test.ObjectStreamStudy; import java.io.FileInputStream; ...
- OC基础--self关键字&super关键字
PS:OC中的self关键字可以与C#中的this关键字区分记忆,虽然区别还是很大的. OC中的super关键字指的是父类指针 一.self关键字必须了解的知识: 1.使用场合:只能用在方法中(对象方 ...
- final关键字+const关键字
final关键字 1.如果我们希望某个类不被其它的类来继承(可能因为安全考虑),可以使用final. 例题 <? final class A{} class B extends A{};//会报 ...
- ref 关键字out关键字
using System;using System.Collections.Generic;using System.Linq;using System.Text;using System.Threa ...
- 织梦dedecms后台文章搜索关键字,关键字包含文章内容的代码修改
1.织梦dedecms后台文章搜索功能在哪里找?织梦dedecms后台-->核心-->常用操作-->所有档案列表(或)织梦dedecms后台-->核心-->内容管理--& ...
- grep 满足多个关键字 任意关键字 排除多个关键字
① grep -E "word1|word2|word3" file.txt 满足任意条件(word1.word2和word3之一)将匹配. ② grep word1 f ...
- static_cast关键字 dynamic_cast关键字
前言 说起C++中的继承.多态.虚函数等概念,可能很多同学都有所了解,但是要说真正熟知的同学可能就不是很多了.最近在编程过程中了解到C++类型的层次转换(这就涉及到了多态和继承的相关概率),通常C语言 ...
- static关键字 weak关键字
1.static关键字 static HAL_StatusTypeDef UART_Receive_IT(UART_HandleTypeDef *huart){ ...} 在函数前面加了一个stati ...
随机推荐
- JS 实现DIV 滚动至顶部后固定
JS 实现DIV 滚动至顶部后固定 <!DOCTYPE HTML> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8" ...
- 「AtCoder Grand018B」Sports Festival(暴力)
题目链接B - Sports Festival 题意 n(1~300)个人m(1~300)个活动,\(A_{ij}\)表示i第j喜欢的活动,每个人选择在举办的活动里最喜欢的,因此可以通过选择一些活动来 ...
- Nagios 使用 NSClient++ 监控Windows Server
在被监控的Windows server 主机上安装NSClinet++下载地址:https://www.nsclient.org/download/32bit:http://files.nsclien ...
- 【Luogu4781】【模板】拉格朗日插值
[Luogu4781][模板]拉格朗日插值 题面 洛谷 题解 套个公式就好 #include<cstdio> #define ll long long #define MOD 998244 ...
- Neko's loop HDU-6444(网络赛1007)
题意就是给出n个数,在n个数上每次跳k个数,最多可以跳m次,你可以选择跳任意次,也可以都不跳,问你为了达到目标了快乐值至少在开始的需要多少快乐值. 题目可以转换成找出循环节,然后再循环节上疯狂试探我可 ...
- 【mysql】数据库中的DML DDL DCL TCL 及 Online DDL
DDL(data definition language) : 数据库定义语言 用来定义创建操作表的时候用到的一些sql命令,比如CREATE.ALTER.DROP等等. DML(data manip ...
- long long
1. ll a; scanf("%d",&a); 数据读入后,产生错误 2. const ll inf=1e18; 3. int * ll = ll ll * int = ...
- pip的更新问题
OSX系统中在利用pip安装有些模块的时候出现”you are using pip version 9.0.1, however version 10.0.0 is available. You sh ...
- 改xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?><LinearLayout xmlns:android=" ...
- (链表 set) leetcode 817. Linked List Components
We are given head, the head node of a linked list containing unique integer values. We are also give ...
