使用Graphlab参加Kaggle比赛(2017-08-20 发布于知乎)

之前用学生证在graphlab上申了一年的graphlab使用权(华盛顿大学机器学习课程需要)然后今天突然想到完全可以用这个东东来参加kaggle.
下午参考了一篇教程,把notebook上面的写好了
本文很多代码参考了turi官网的一个教程,有兴趣的同学可以去看原版 https://turi.com/learn/gallery/notebooks/who_survived_the_titanic.html
代码
import graphlab as gl
%matplotlib inline
import matplotlib.pyplot as mpl
mpl.rcParams['figure.figsize']=(15.0,8.0)
import numpy as np
第一步:数据探索
导入数据
train = graphlab.SFrame.read_csv('train.csv')
数据探索与数据可视化
#看看除了Survived这一列以外其他列的缺值情况
columns = ("Pclass", "Name", "Sex", "Age", "SibSp", "Parch", "Ticket", "Fare", "Cabin", "Embarked")
not_null=[sum(1 for el in train[column] if el or el == 0)for column in columns]
null = [len(train) - el for el in not_null]
#数字指代第几列
indexes = np.arange(len(columns))
width = 0.5
#用柱形图表示缺值情况
not_null_bar = mpl.bar(indexes, not_null, width, color='green', edgecolor='white', alpha=0.8)#非空为绿,底色为白
null_bar = mpl.bar(indexes, null, width, color='red', edgecolor='white', bottom=not_null, alpha=0.8)#空值为红,底色为白
mpl.xlim( indexes[0] - 0.5, indexes[-1] + 1)#横轴的范围
#柱形图标题
mpl.title('Null values for each column', fontsize=20, weight='bold')
#x轴单位长度
mpl.xticks(indexes + width/2., columns, fontsize=16)
#y轴单位长度
mpl.yticks(np.arange(0,1200,100))
#右上角为图例
mpl.legend( (not_null_bar[0], null_bar[0]), ('Not Null', 'Null') )
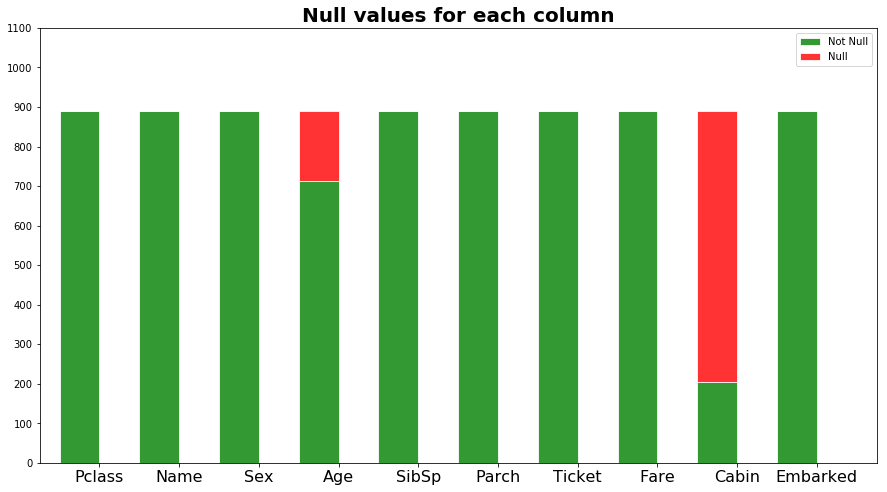
观察上图我们知道Age列有少量缺值,Cabin列有大量的缺值,于是我们需要补全Age缺值,但是把Cabin列整个忽略
直接用Age的均值补全空值
train = train.fillna('Age',train['Age'].mean())
#看看除了Survived这一列以外其他列的缺值情况
columns = ("Pclass", "Name", "Sex", "Age", "SibSp", "Parch", "Ticket", "Fare", "Cabin", "Embarked")
not_null=[sum(1 for el in train[column] if el or el == 0)for column in columns]
null = [len(train) - el for el in not_null]
#数字指代第几列
indexes = np.arange(len(columns))
width = 0.5
#用柱形图表示缺值情况
not_null_bar = mpl.bar(indexes, not_null, width, color='green', edgecolor='white', alpha=0.8)#非空为绿,底色为白
null_bar = mpl.bar(indexes, null, width, color='red', edgecolor='white', bottom=not_null, alpha=0.8)#空值为红,底色为白
mpl.xlim( indexes[0] - 0.5, indexes[-1] + 1)#横轴的范围
#柱形图标题
mpl.title('Null values for each column', fontsize=20, weight='bold')
#x轴单位长度
mpl.xticks(indexes + width/2., columns, fontsize=16)
#y轴单位长度
mpl.yticks(np.arange(0,1200,100))
#右上角为图例
mpl.legend( (not_null_bar[0], null_bar[0]), ('Not Null', 'Null') )

我们看看Pclass与生存率的关系
passenger_class = train["Pclass"].astype(str)
#观察每个Pclass的存活率
#用groupby方法
class_distribution = train.groupby(["Pclass", "Survived"], {'count':gl.aggregate.COUNT()})
#用0和1过滤出生存和死亡
survived = class_distribution.filter_by(1,'Survived').sort("Pclass")
died = class_distribution.filter_by(0,'Survived').sort("Pclass") width = 0.5
#柱形图的参数
survived_bar = mpl.bar(survived["Pclass"], survived["count"], width, color='green', edgecolor='white', alpha=0.8)
died_bar = mpl.bar(died["Pclass"], died["count"], width, color='red', edgecolor='white', bottom=survived["count"], alpha=0.8)
mpl.xlim( indexes[0] - 0.5, indexes[-1] + 1) mpl.title('Survived by Passengers Class', fontsize=20, weight='bold')
mpl.xticks(survived["Pclass"] + width/2., survived["Pclass"], fontsize=16)
mpl.xlim(0.5,4)
mpl.yticks(np.arange(0,600,50))
mpl.legend( (survived_bar[0], died_bar[0]), ('Survived', 'Died') ) for ind in np.arange(len(survived)):
ind = int(ind)
x = 1 + ind + width / 2.
y = survived["count"][ind] + died["count"][ind] + 10
percentage = survived["count"][ind] / float( survived["count"][ind] + died["count"][ind]) * 100
mpl.text(x, y, "%5.2f%%" % percentage, fontsize=20, ha='center')
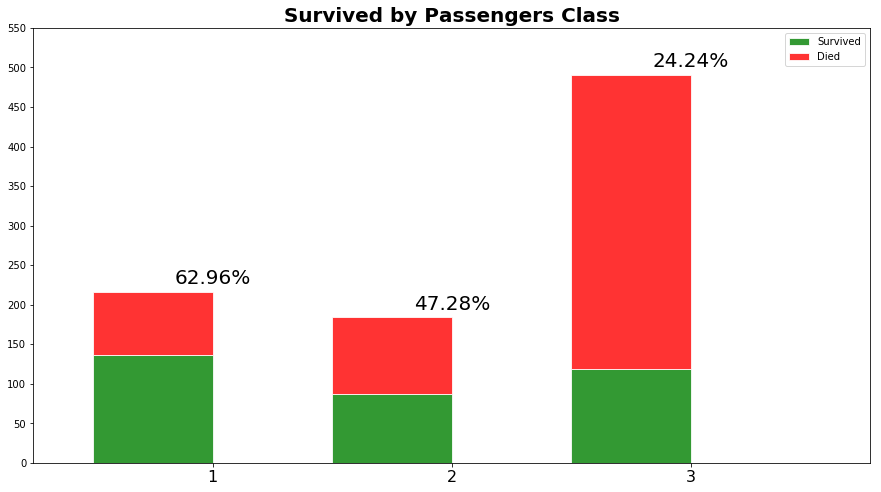
由此可见,Pclass的存活率从1到3逐次下降
我们看看性别与生存率的关系
sex_distribution = train.groupby(["Sex", "Survived"], {'count':gl.aggregate.COUNT()})
survived = sex_distribution.filter_by(1,'Survived').sort("Sex")
died = sex_distribution.filter_by(0,'Survived').sort("Sex")
indexes = np.arange(len(survived["Sex"]))
width = 0.5
survived_bar = mpl.bar(indexes, survived["count"], width, color='green', edgecolor='white', alpha=0.8)
died_bar = mpl.bar(indexes, died["count"], width, color='red', edgecolor='white', bottom=survived["count"], alpha=0.8)
mpl.xlim( indexes[0] - 0.5, indexes[-1] + 1)
mpl.title('Survived by Sex', fontsize=20, weight='bold')
survived["Sex"] = [sex.capitalize() for sex in survived["Sex"]]
mpl.xticks(indexes + width/2., survived["Sex"], fontsize=16)
mpl.xlim(-0.5,2)
mpl.yticks(np.arange(0,700, 50))
mpl.legend( (survived_bar[0], died_bar[0]), ('Survived', 'Died') )
for ind in indexes:
ind = int(ind)
x = ind + width / 2.
y = survived["count"][ind] + died["count"][ind] + 10
percentage = survived["count"][ind] / float( survived["count"][ind] + died["count"][ind]) * 100
mpl.text(x, y, "%5.2f%%" % percentage, fontsize=20, ha='center')
mpl.show()

我们看看年龄与生存率的关系
为了更加直观的体现成人与小孩的区别,我再增加一个"Categorized_Age"列
我们使用apply方法来对每个元素进行作用,小于18岁称为小孩,其余均为大人。
#增加列,18以下称为child
train['Categorized_Age'] = train['Age'].apply(lambda x: "Child" if x <= 18 else "Adult")
#用groupby方法把二者关联
age_distribution = train.groupby(["Categorized_Age", "Survived"], {'count':gl.aggregate.COUNT()}).dropna()
#过滤数据
survived = age_distribution.filter_by(1,'Survived').sort("Categorized_Age")
died = age_distribution.filter_by(0,'Survived').sort("Categorized_Age")
#柱形图参数设置
indexes = np.arange(len(survived["Categorized_Age"])) width = 0.5 survived_bar = mpl.bar(indexes, survived["count"], width, color='green', edgecolor='white', alpha=0.8)
died_bar = mpl.bar(indexes, died["count"], width, color='red', edgecolor='white', bottom=survived["count"], alpha=0.8)
mpl.xlim( indexes[0] - 0.5, indexes[-1] + 1) mpl.title('Survived by Age Categorization', fontsize=20, weight='bold')
survived["Categorized_Age"] = [sex.capitalize() for sex in survived["Categorized_Age"]]
mpl.xticks(indexes + width/2., survived["Categorized_Age"], fontsize=16)
mpl.xlim(-0.5,2)
mpl.yticks(np.arange(0,700, 50))
mpl.legend( (survived_bar[0], died_bar[0]), ('Survived', 'Died') ) for ind in indexes:
ind = int(ind)
x = ind + width / 2.
y = survived["count"][ind] + died["count"][ind] + 10
percentage = survived["count"][ind] / float( survived["count"][ind] + died["count"][ind]) * 100
mpl.text(x, y, "%5.2f%%" % percentage, fontsize=20, ha='center') mpl.show()
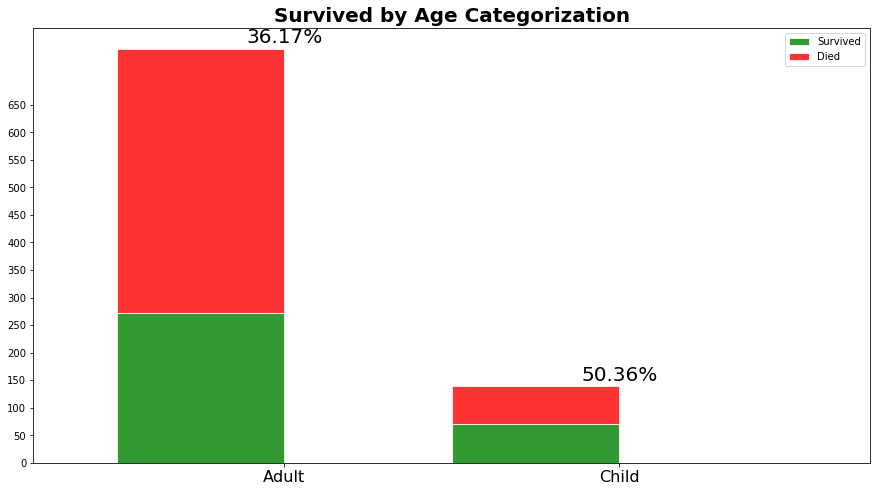
由上图可知,未成年人的存活率远大于成人
我们看看家眷人数与生存率的关系
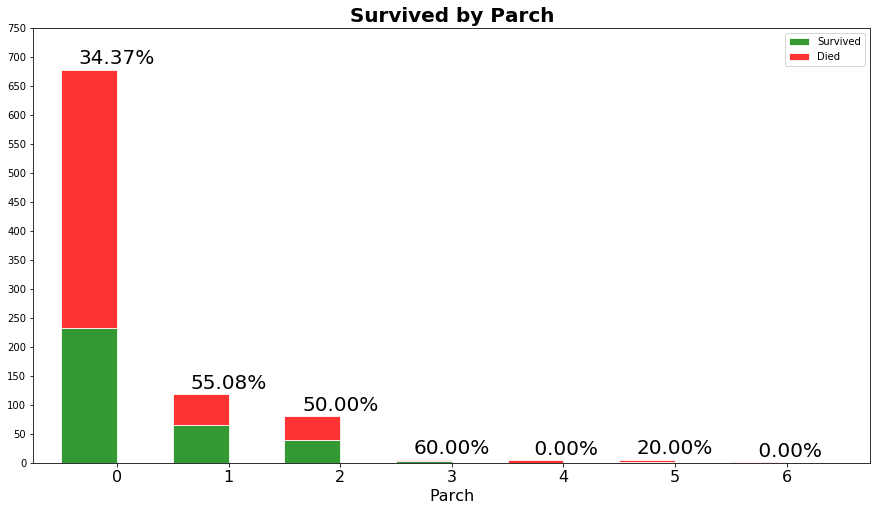
下面的代码算出了家眷人数与生存率的关系。第一个for循环(line 6)是画图需要,遍历分组完生存率的各个家庭,若某个规模的所有家庭没有人生存,还是要加上一列。事实上,bar方法(line 12,13) 希望在每一个家庭规模都要对应的生存率,但是有5或者8个家眷的家庭都gg了。因此,我们用append方法 (line 8) 增加了两列,生存率记为0。
sibling_spouses = train["SibSp"].astype(str)
sibsp_distribution = train.groupby(["SibSp", "Survived"], {'count':gl.aggregate.COUNT()}).sort(["SibSp"]) survived = sibsp_distribution.filter_by(1,"Survived")
died = sibsp_distribution.filter_by(0,"Survived") for sibsp in sibsp_distribution["SibSp"]:
if not survived.filter_by(sibsp, "SibSp"):
survived = survived.append(gl.SFrame({'SibSp': [sibsp], 'Survived': [1], 'count':[0]})) width = 0.5 survived_bar = mpl.bar(survived["SibSp"], survived["count"], width, color='green', edgecolor='white', alpha=0.8)
died_bar = mpl.bar(died["SibSp"], died["count"], width, color='red', edgecolor='white', bottom=survived["count"], alpha=0.8)
mpl.xlim( indexes[0] - 0.5, indexes[-1] + 1) mpl.title('Survived by SibSp', fontsize=20, weight='bold')
mpl.xticks(survived["SibSp"] + width/2., survived["SibSp"], fontsize=16)
mpl.xlim(-0.5,9)
mpl.yticks(np.arange(0,750,50))
mpl.xlabel("SibSp", fontsize=16)
mpl.legend( (survived_bar[0], died_bar[0]), ('Survived', 'Died') ) for ind in np.arange(len(survived)):
ind = int(ind)
x = survived["SibSp"][ind] + width / 2.
y = survived["count"][ind] + died["count"][ind] + 10
percentage = survived["count"][ind] / float( survived["count"][ind] + died["count"][ind]) * 100
mpl.text(x, y, "%5.2f%%" % percentage, fontsize=20, ha='center') mpl.show()

由上图可知,有一个配偶的家庭生存率最高,三口之家次之,接下来才是单身狗,而家眷超过三人生存希望渺茫.
我们看看有没有孩子与生存率的关系
parents_children = train["Parch"].astype(str)
parch_distribution = train.groupby(["Parch", "Survived"], {'count':gl.aggregate.COUNT()}) survived = parch_distribution.filter_by(1,"Survived")
died = parch_distribution.filter_by(0,"Survived") for parch in parch_distribution["Parch"]:
if not survived.filter_by(parch, "Parch"):
survived = survived.append(gl.SFrame({'Parch': [parch], 'Survived': [1], 'count':[0]})) survived = survived.sort("Parch")
died = died.sort("Parch") width = 0.5 survived_bar = mpl.bar(survived["Parch"], survived["count"], width, color='green', edgecolor='white', alpha=0.8)
died_bar = mpl.bar(died["Parch"], died["count"], width, color='red', edgecolor='white', bottom=survived["count"], alpha=0.8)
mpl.xlim( indexes[0] - 0.5, indexes[-1] + 1) mpl.title('Survived by Parch', fontsize=20, weight='bold')
mpl.xticks(survived["Parch"] + width/2., survived["Parch"], fontsize=16)
mpl.xlim(-0.5,7)
mpl.yticks(np.arange(0,800,50))
mpl.xlabel("Parch", fontsize=16)
mpl.legend( (survived_bar[0], died_bar[0]), ('Survived', 'Died') ) for ind in np.arange(len(survived)):
ind = int(ind)
x = survived["Parch"][ind] + width / 2.
y = survived["count"][ind] + died["count"][ind] + 10
percentage = survived["count"][ind] / float( survived["count"][ind] + died["count"][ind]) * 100
mpl.text(x, y, "%5.2f%%" % percentage, fontsize=20, ha='center') mpl.show()
我们看看船费与生存率的关系(有钱人可能有特权
fare = train["Fare"]
survived = train.filter_by(1,'Survived')["Fare"]
died = train.filter_by(0,'Survived')["Fare"] data_to_plot = [died, survived] bp = mpl.boxplot(data_to_plot,patch_artist=True, vert=0) ## change outline color, fill color and linewidth of the boxes
for box in bp['boxes']:
# change outline color
box.set( color='#7570b3', linewidth=2)
# change fill color
box.set( facecolor = '#1b9e77' ) ## change color and linewidth of the whiskers
for whisker in bp['whiskers']:
whisker.set(color='#7570b3', linewidth=2) ## change color and linewidth of the caps
for cap in bp['caps']:
cap.set(color='#7570b3', linewidth=2) ## change color and linewidth of the medians
for median in bp['medians']:
median.set(color='#b2df8a', linewidth=2) ## change the style of fliers and their fill
for flier in bp['fliers']:
flier.set(marker='o', color='#e7298a', alpha=0.5) mpl.yticks([1,2],['Died', 'Survived'], fontsize=20)
mpl.xticks(np.arange(0,700, 20))
mpl.xlim(-10,515)
mpl.title("Survived by Fare", fontsize=20, weight='bold')
mpl.show()

这个图是反着看的,活下来的人跟死去的人花的船费对比。活下来的人普遍花了较多的船费,均值在35刀。而死去的人花费均值才几美刀。(注意有个花500多刀的真·土豪
我们看看上船渡口与生存率的关系
port = train["Embarked"].apply(
lambda el: el + " (S = Southampton)" if el == "S"
else ( el + " (C = Cherbourg)" if el == "C"
else (el + " (Q = Queenstown)" if el == "Q" else None)))
port.tail(1) # force the lambda to materialize before .show() is processed
port.show() embarked_distribution = train.groupby(["Embarked", "Survived"], {'count':gl.aggregate.COUNT()}).dropna() survived = embarked_distribution.filter_by(1,'Survived').sort("Embarked")
survived = survived[1:]
died = embarked_distribution.filter_by(0,'Survived').sort("Embarked") indexes = np.arange(len(survived["Embarked"])) width = 0.5 survived_bar = mpl.bar(indexes, survived["count"], width, color='green', edgecolor='white', alpha=0.8)
died_bar = mpl.bar(indexes, died["count"], width, color='red', edgecolor='white', bottom=survived["count"], alpha=0.8)
mpl.xlim( indexes[0] - 0.5, indexes[-1] + 1) mpl.title('Survived by Port of Embarkation', fontsize=20)
labels = [ el + "\n(S = Southampton)" if el == "S" else ( el + "\n(C = Cherbourg)" if el == "C" else el + "\n(Q = Queenstown)") for el in survived["Embarked"]]
mpl.xticks(np.arange(len(survived["Embarked"])) + width/2.,labels, fontsize=16) for ind in indexes:
ind = int(ind)
x = ind + width / 2.
y = survived["count"][ind] + died["count"][ind] + 10
percentage = survived["count"][ind] / float( survived["count"][ind] + died["count"][ind]) * 100
mpl.text(x, y, "%5.2f%%" % percentage, fontsize=20, ha='center') mpl.legend( (survived_bar[0], died_bar[0]), ('Survived', 'Died') ) mpl.show()
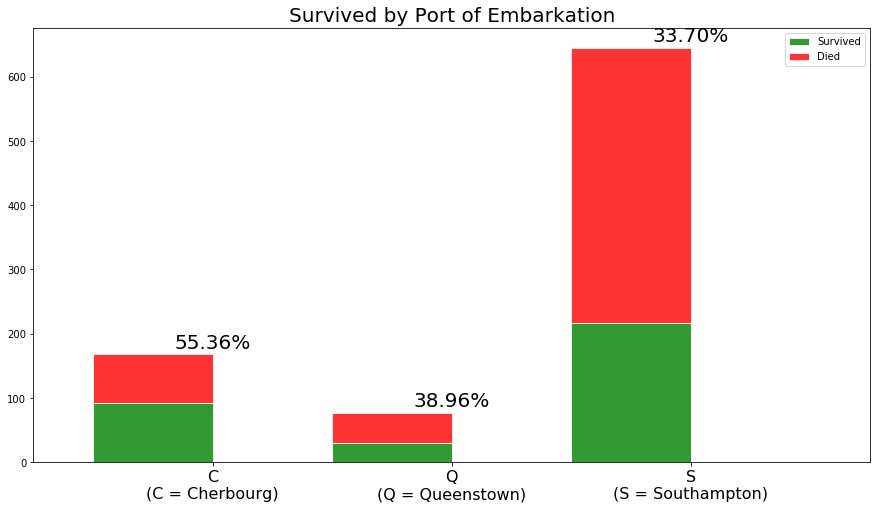
所以Cherbourg上船的人存活率巨高……我个人不太明白为什么
第二步:模型构建
在Embarked列中有一些缺值,我们补全一下
train["Embarked"] = train["Embarked"].apply(lambda x: x if x != '' else "S")
port_of_embarkation = train["Embarked"]
port_of_embarkation.tail(1)
port_of_embarkation.show()
在训练集中再取80%来训练模型,20%来验证模型。
train_set, test_set = train.random_split(0.8, seed=4)
print "Rows for training:", train_set.num_rows()
print "Rows for testing:", test_set.num_rows()
试一下 gradient boosted tree 这个模型
model_4 = gl.boosted_trees_regression.create(train_set,target='Survived',
features=['Sex', 'Age', 'Pclass', 'SibSp', 'Parch', 'Embarked', 'Fare'])
result_4 = model_4.evaluate(test_set) print result_4
下面是训练过程PROGRESS: Creating a validation set from 5 percent of training data. This may take a while.
You can set ``validation_set=None`` to disable validation tracking. Boosted trees regression:
--------------------------------------------------------
Number of examples : 663
Number of features : 7
Number of unpacked features : 7
+-----------+--------------+--------------------+----------------------+---------------+-----------------+
| Iteration | Elapsed Time | Training-max_error | Validation-max_error | Training-rmse | Validation-rmse |
+-----------+--------------+--------------------+----------------------+---------------+-----------------+
| 1 | 0.094067 | 0.640132 | 0.640625 | 0.413718 | 0.452089 |
| 2 | 0.095066 | 0.736341 | 0.741699 | 0.361147 | 0.435120 |
| 3 | 0.097067 | 0.799792 | 0.795940 | 0.326181 | 0.414205 |
| 4 | 0.098068 | 0.843834 | 0.853179 | 0.300373 | 0.418672 |
| 5 | 0.099068 | 0.866550 | 0.875894 | 0.284084 | 0.414071 |
| 6 | 0.100069 | 0.886572 | 0.895917 | 0.268531 | 0.401603 |
+-----------+--------------+--------------------+----------------------+---------------+-----------------+
{'max_error': 0.9767722487449646, 'rmse': 0.3790493668897309}
三、导入测试集进行预测
test = graphlab.SFrame.read_csv('test.csv')
model_4.predict(test)
dtype: float
Rows: 418
[0.24605900049209595, 0.1579868197441101, 0.09492728114128113, 0.08076220750808716, 0.820347249507904, 0.13742545247077942, 0.46745458245277405, 0.08334535360336304, 0.6385629177093506, 0.053301453590393066, 0.7933655977249146, 0.10734456777572632, 0.9794546365737915, 0.0696893036365509, 0.9803991913795471, 0.9651352167129517, 0.08926722407341003, 0.32400867342948914, 0.8363758325576782, 0.1579868197441101, 0.4781973361968994, 0.6420668363571167, 0.4161583185195923, 0.28341546654701233, 0.9170076847076416, 0.0696893036365509, 0.9794546365737915, 0.17743894457817078, 0.5841416120529175, 0.7112432718276978, 0.0696893036365509, 0.09834089875221252, 0.7118383646011353, 0.36395323276519775, 0.47720423340797424, 0.2933708429336548, 0.4699748754501343, 0.16753268241882324, 0.0941736102104187, 0.5083406567573547, 0.2918650507926941, 0.7348397970199585, 0.10613331198692322, 0.9710206985473633, 0.9803991913795471, 0.14958679676055908, 0.42003297805786133, 0.5664023756980896, 0.9672679901123047, 0.7332731485366821, 0.5267215967178345, 0.1717779040336609, 0.9495010375976562, 0.9067643880844116, 0.8308284282684326, 0.05739110708236694, 0.08792659640312195, 0.11708483099937439, 0.8308284282684326, 0.9750292301177979, 0.06759494543075562, 0.13685157895088196, 0.10684752464294434, 0.7940642237663269, 0.1582772135734558, 0.7426018714904785, 0.7501979470252991, 0.1021573543548584, 0.2818759083747864, 0.8806270360946655, 0.7940642237663269, 0.06759494543075562, 0.7951251268386841, 0.2818759083747864, 0.9750292301177979, 0.28711044788360596, 0.8174170255661011, 0.9488879442214966, 0.13685157895088196, 0.7940642237663269, 0.893699049949646, 0.04857367277145386, 0.20609065890312195, 0.7933655977249146, 0.6543059349060059, 0.8308284282684326, 0.9047337770462036, 0.16753268241882324, 0.8481748104095459, 0.9108253717422485, 0.5572522878646851, 0.7125066518783569, 0.35652855038642883, 0.8174170255661011, 0.28670477867126465, 0.28864753246307373, 0.9726588726043701, 0.16057392954826355, 0.70356285572052, 0.1119779646396637, ... ]
使用Graphlab参加Kaggle比赛(2017-08-20 发布于知乎)的更多相关文章
- Kaggle比赛:从何着手?
介绍 参加Kaggle比赛,我必须有哪些技能呢? 你有没有面对过这样的问题?最少在我大二的时候,我有过.过去我仅仅想象Kaggle比赛的困难度,我就感觉害怕.这种恐惧跟我怕水的感觉相似.怕水,让我无法 ...
- kaggle比赛流程(转)
一.比赛概述 不同比赛有不同的任务,分类.回归.推荐.排序等.比赛开始后训练集和测试集就会开放下载. 比赛通常持续 2 ~ 3 个月,每个队伍每天可以提交的次数有限,通常为 5 次. 比赛结束前一周是 ...
- Kaggle比赛总结
做完 Kaggle 比赛已经快五个月了,今天来总结一下,为秋招做个准备. 题目要求:根据主办方提供的超过 4 天约 2 亿次的点击数据,建立预测模型预测用户是否会在点击移动应用广告后下载应用程序. 数 ...
- 用python参加Kaggle的经验总结【转】
用python参加Kaggle的经验总结 转载自:http://www.jianshu.com/p/32def2294ae6,作者 JxKing 最近挤出时间,用python在kaggle上试了 ...
- 用python参加Kaggle的些许经验总结(收藏)
Step1: Exploratory Data Analysis EDA,也就是对数据进行探索性的分析,一般就用到pandas和matplotlib就够了.EDA一般包括: 每个feature的意义, ...
- Kaggle比赛冠军经验分享:如何用 RNN 预测维基百科网络流量
Kaggle比赛冠军经验分享:如何用 RNN 预测维基百科网络流量 from:https://www.leiphone.com/news/201712/zbX22Ye5wD6CiwCJ.html 导语 ...
- http://www.cnblogs.com/jqyp/archive/2010/08/20/1805041.html
http://www.cnblogs.com/jqyp/archive/2010/08/20/1805041.html
- Visual Studio 2017正式版发布全纪录
又是一年发布季,微软借着Visual Studio品牌20周年之际,于美国太平洋时间2017年3月7日9点召开发布会议,宣布正式发布新一代开发利器Visual Studio 2017.同时发布的还有 ...
- .NET Core 2.0版本预计于2017年春季发布
英文原文: NET Core 2.0 Planned for Spring 2017 微软项目经理 Immo Landwerth 公布了即将推出的 .NET Core 2.0 版本的细节,该版本预计于 ...
随机推荐
- C++学习书籍推荐《C++编程思想第二版第二卷》下载
百度云及其他网盘下载地址:点我 编辑推荐 “经典原版书库”是响应教育部提出的使用原版国外教材的号召,为国内高校的计算机教学度身订造的.<C++编程思想>(英文版第2版)是书库中的一本,在广 ...
- 异常——cmd下javac错误:编码GBK不可映射字符
在看菜鸟教程时候用记事本创建文件,之后用notepad++编辑后,运行出现错误. 首先从信息上知道这是编码的问题了.开始试了下再notepad++上打开文件选择标签栏的“Encoding”中的“enc ...
- AKKA 集群中的发布与订阅Distributed Publish Subscribe in Cluster
Distributed Publish Subscribe in Cluster 基本定义 在单机环境下订阅与发布是很常用的,然而在集群环境是比较麻烦和不好实现的: AKKA已经提供了相应的实现,集群 ...
- 庖丁解牛Linux内核分析 0x00:《庖丁解牛》
庖丁解牛 吾生也有涯,而知也无涯 .以有涯随无涯,殆已!已而为知者,殆而已矣!为善无近名,为恶无近刑.缘督以为经,可以保身,可以全生,可以养亲,可以尽年. 庖丁为文惠君解牛,手之所触,肩之所倚,足之 ...
- Java 集合框架部分面试题
1.Java集合框架是什么?说出一些集合框架的优点? 每种编程语言中都有集合,最初的Java版本包含几种集合类:Vector.Stack.HashTable和Array.随着集合的广泛使用,Java1 ...
- 【git】15分钟学会使用Git和远程代码库
Git是个了不起但却复杂的源代码管理系统.它能支持复杂的任务,却因此经常被认为太过复杂而不适用于简单的日常工作.让我们诚实一记吧:Git是复杂的,我们不要装作它不是.但我仍然会试图教会你用(我的)基本 ...
- C# Winform程序如何使用ClickOnce发布并自动升级(图解)
有不少朋友问到C#Winform程序怎么样配置升级,怎么样打包,怎么样发布的,在这里我解释一下打包和发布关于打包的大家可以看我的文章C# winform程序怎么打包成安装项目(图解)其实打包是打包,发 ...
- MyBatis映射,抛出Cause: org.apache.ibatis.reflection.ReflectionException: There is no getter for property named 'oid' in 'class java.lang.String'
原因在于: 在MyBatis中使用动态语句的判断时,传入的参数(parameterType)为Java基本数据类型,获取的结果(resultType)为JavaBean对象,此时就会抛出该异常,此时可 ...
- Swagger UI使用指南
1:认识Swagger Swagger 是一个规范和完整的框架,用于生成.描述.调用和可视化 RESTful 风格的 Web 服务.总体目标是使客户端和文件系统作为服务器以同样的速度来更新.文件的方法 ...
- Mac 使用小结
小白使用 Mac 的点点滴滴总结,更新中…… 1. 显示/隐藏 文件的命令: a) 显示文件: defaults write com.apple.finder AppleShowAllFiles -b ...
