老男孩Day4作业:员工信息查询系统
1、作业需求:
(1).工信息表程序,实现增删改查操作:
(2).可进行模糊查询,语法至少支持下面3种:
select name,age from staff_table where age > 22
select * from staff_table where dept = "IT"
select * from staff_table where enroll_date like "2013"
(3).查到的信息,打印后,最后面还要显示查到的条数
(4).可创建新员工纪录,以phone做唯一键,staff_id需自增
(5).可删除指定员工信息纪录,输入员工id,即可删除
(6).可修改员工信息,语法如下:
UPDATE staff_table SET dept = "Market" where dept = "IT"
注意:以上需求,要充分使用函数,请尽你的最大限度来减少重复代码
2、流程图
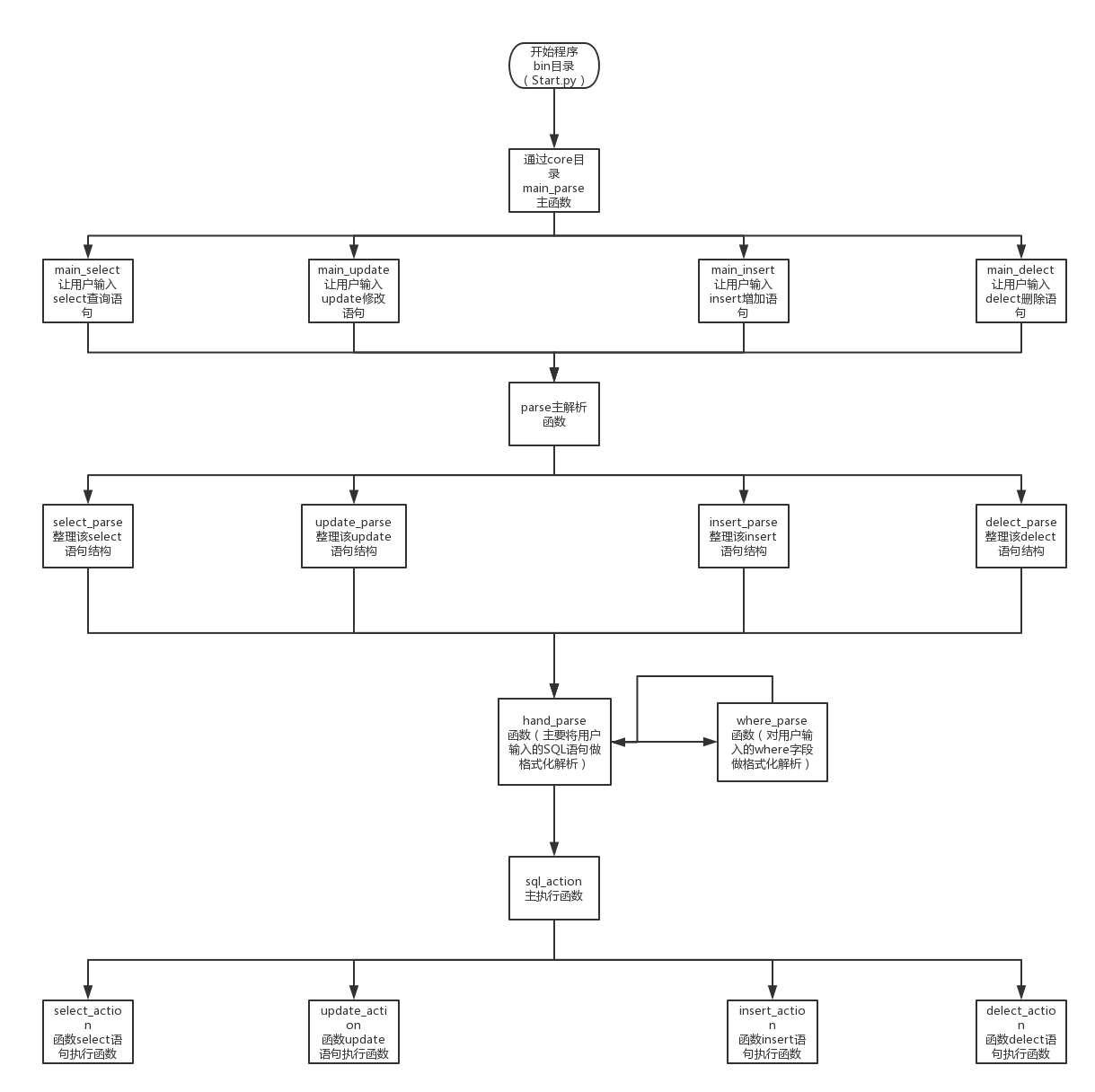
3、目录结构
|——员工信息查询系统
|——bin目录
| |—— _init.py
| |____ Stary.py ——>程序运行文件
|
|——core目录
| |—— __init__.py
| |—— main.py ——>主逻辑函数模块
| |—— parses.py ——>语句解析模块
| |____ action.py ——>语句执行模块
|
|——db目录
| |—— emp ——>数据库txt文件
| |___ xmp ——>数据库txt文件
|
|__ __init.py__
4、core目录
main主逻辑模块
#-*- Coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author: D.Gray
import os,sys
# BASE_DIR = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__)))
# sys.path.append(BASE_DIR)
# print("PATH",sys.path) from core import parses def main_parse(user_input):
'''
定义一个main_parse函数,来接受用户操作菜单的选择,并根据用户输入的操作序号进入相应的模块
:param user_input:用户输入操作菜单序号
:return:
'''
main_dict = {
'': main_select,
'': main_add,
'': main_update,
'': main_delect,
}
if user_input in main_dict.keys():
main_dict[user_input]() # 执行输入号码对应的函数
#main_select等主函数没有定义形参所以main_dict[user_input]()括号里不要传参数
if user_input == '':
exit("已退出程序,欢迎下次使用")
else:
print("\033[31;1m输入格式无效\033[0m") def main_select():
'''
定义main_select函数——select查询信息管理模块
用来接受解析并完成的select语句,并显示查询结果
:return:
'''
print('''\t\t\t-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
语法示例:
select name,age from db.emp where age > 22
select * from db.xmp where dept like IT
select * from db.emp where id >= 2
select * from db.emp where id <5 limit 3
\t\t\t-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------''')
while True:
user_sql = input('请输入查询sql语句>>>:').strip()
sql_list = user_sql.split(' ') # 将用户输入的sql语句转换成列表格式
func = sql_list[0] if func != 'select':
print('\033[31;1m请输入相应sql关键字\033[0m')
if user_sql == 'b':
break
else:
parses.parse(user_sql,func,sql_list) def main_add():
'''
定义main_add函数——insert查询信息管理模块
用来接受解析并完成的insert语句,并显示查询结果
:return:
'''
print('''\t\t\t-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
语法示例:
insert db.emp value Mark,32,13655818285,CTO,2014-08-08
insert db.xmp value Mark,32,13655818285,CTO,2014-08-08
\t\t\t-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------''')
while True:
user_sql = input('请输入查询sql语句>>>:').strip()
sql_list = user_sql.split(' ') # 将用户输入的sql语句转换成列表格式
# split()输出结果为[]此时会报错 建议split(' ')输出结果['']
# 以空格为分隔符切分成列表形式
func = sql_list[0]
if func != 'insert':
print('\033[31;1m请输入相应sql关键字\033[0m')
if user_sql == 'b':
break
else:
parses.parse(user_sql,func,sql_list) def main_update():
'''
定义main_update函数——update查询信息管理模块
用来接受解析并完成的update语句,并显示查询结果
:return:
'''
print('''\t\t\t-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
语法示例:
update db.xmp set dept = Market where dept like IT
update db.emp set phone = 15618285621 where phone = 110
update db.emp set enroll_data = 2014-08-11 where dept like 运维
\t\t\t-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------''')
while True:
user_sql = input('请输入查询sql语句>>>:').strip()
sql_list = user_sql.split(' ') # 将用户输入的sql语句转换成列表格式
func = sql_list[0]
if func != 'update':
print('\033[31;1m请输入相应sql关键字\033[0m')
if user_sql == 'b':
break
else:
parses.parse(user_sql,func,sql_list) def main_delect():
'''
定义main_delect函数——delect查询信息管理模块
用来接受解析并完成的delect语句,并显示查询结果
:return:
'''
print('''\t\t\t-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
语法示例:
delect from db.emp
delect from db.emp where id = 3
delect from db.emp where id < 10 and name like alex
\t\t\t-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------''')
while True:
user_sql = input('请输入查询sql语句>>>:').strip()
sql_list = user_sql.split(' ') # 将用户输入的sql语句转换成列表格式
func = sql_list[0] if func != 'delect':
print('\033[31;1m请输入相应sql关键字\033[0m')
if user_sql == 'b':
break
else:
parses.parse(user_sql,func,sql_list)
parse语句解析模块
#-*- Coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author: D.Gray
import os,sys
from core import action
def parse(user_sql,func,sql_list):
'''
定义用户输入的sql并统一格式化后分配到各个sql解析模块
:param user_sql:用户输入的sql语句
:return:
'''
parse_dic = {
'select':select_parse,
'update':update_parse,
'delect':delect_parse,
'insert':insert_parse
}
par_res = ''
if func in parse_dic.keys(): #根据用户输入的sql关键字,分配到相应函数中进行解析
par_res = parse_dic[func](sql_list) #将parse_dic[func](sql_list)中的(sql_list)作为位置参数传给select_parse()
#select_parse()有定义个形参,所以parse_dic[func]()后要定义一个位置参数给select_parse()
return par_res #定义一个函数返回值,传给相应的解析函数 def select_parse(par_res):
'''
定义select_parse函数,接受用户输入的查询sql语句(parse()函数传递过来的返回值 res=parse_dic[func](sql_list))
并返回参数给hand_parse(res,sql_dic)函数进行sql解析
:param sql:
:return:
'''
sql_dic = {
'par_res': action.select_action,
'select':[],
'from':[],
'where':[],
'limit':[]
}
#print('in the select_parse-parse_res:',par_res,sql_dic)
return hand_parse(par_res,sql_dic) def insert_parse(par_res):
'''
定义insert_parse函数,接受用户输入的查询sql语句并进行sql解析
:param sql:
:return:
'''
sql_dic = {
'par_res': action.insert_action,
'insert': [],
'value': [],
'into':[]
}
print('in the insert_parse:', par_res)
return hand_parse(par_res, sql_dic) def update_parse(par_res):
'''
定义update_parse函数,接受用户输入的查询sql语句并进行sql解析
:param sql:
:return:
'''
sql_dic = {
'par_res': action.update_action,
'update': [],
'set': [],
'where': [],
}
#print('in the update_parse:',par_res)
return hand_parse(par_res, sql_dic) def delect_parse(par_res):
'''
定义delect_parse函数,接受用户输入的查询sql语句并进行sql解析
:param sql:
:return:
'''
sql_dic = {
'par_res':action.delect_action,
'delect': [],
'from': [],
'where':[]
}
#print('in the delect_parse:',par_res)
return hand_parse(par_res, sql_dic) def hand_parse(par_res,sql_dic):
'''
该函数把接受过来的函数进行格式化解析操作,并将整合后的sql字典作为返回值传参给 sql_action()语句主执行函数
:param sql_list:
:param sql_dic:各sql模块所对应的sql语句结构字典
:return:
'''
for item in par_res: #循环遍历select_parse()函数传过来的:用户输入的sql语句
if item in sql_dic: #判断语句中的关键字是否在相应函数sql_dic字典中
key = item
else:
sql_dic[key].append(item) #将字典转化为 select:[*] from:[db.emp] 格式
#print('in the hand_parse:',sql_dic) if sql_dic.get('where'): #整理并格式化where[id < 10...]字段内容
res_list = []
key = ['and','or','not']
char = ''
for item in sql_dic.get('where'):
if len(item) == 0:
continue
if item in key:
if len(char) != 0:
char = where_parse(char) #将char最为实参传参给where_parse()函数。例:char = 'id ','>','10'
res_list.append(char)
res_list.append(item)
char = ''
else:
char += item
else:
char = where_parse(char) ##将char最为实参传参给where_parse()函数。例:char = 'id ','>','10'
res_list.append(char),
sql_dic['where'] = res_list #将where列表内容整理成 where['id > 10','and','id < 20']的格式
#print('where字段列表元素:',sql_dic['where'],sql_dic)
return action.sql_action(sql_dic) #将where['id > 10','and','id < 20']的列表格式作为返回值,
# 传参给where_parse()函数进行最终整理 def where_parse(where_char):
'''
该函数接收hand_parse()传递过来的char参数,并把这些参数整理成['id ','>','10']这样的格式,并返回一个where_res_list值
:param where_char: where_parse(where_char)函数中where_char形参接收的是hand_parse()传递过来的char参数
:return: 把整理完毕的参数格式作为一个 where_res_list列表 的返回值
'''
key = ['<','>','=']
where_res_list = []
opt = ''
char = ''
tag = False
for item in where_char: #循环遍历where_char字符串,如: 'id > 10'
if len(item) == 0:
continue
if item in key:
tag = True #将tag状态变为True
if len(char) != 0 :
where_res_list.append(char)
char = ''
opt += item
if not tag: #判断tag状态是否是False
char += item
if tag and item not in key: #判断tag状态为False并且不在key列表中
tag = False #将tag状态变为False
where_res_list.append(opt)
opt = ''
char += item
else:
where_res_list.append(char) if len(where_res_list) == 1 : # 将列表中'namelikealex'字符串内容转换成['name','like','alex']格式
where_res_list = where_res_list[0].split('like')
where_res_list.insert(1,'like')
#print('in the where_parse:', where_res_list)
return where_res_list
action语句执行模块
#-*- Coding:utf-8 -*-
# Author: D.Gray
import os,sys,re #语句主分配模块
def sql_action(sql_dic):
'''
该函数接收hand_parse()传过来的整理完毕后的字典sql_dic,并根据字典中 par_res键分配调用相应的语句执行模块函数
:return:
'''
return sql_dic.get('par_res')(sql_dic) #根据字典中 par_res为键 将sql_dic做为参数分配调用相应的语句执行模块函数 #select查询语句执行模块
def select_action(sql_dic):
'''
该函数通过sql_action主语句执行函数传来的参数‘sql_dic字典’进行语句执行操作
:param sql_dic: sql_action主语句执行函数传来的参数
:return:
'''
#优先处理最高from部分
if len(sql_dic.get('from')) == 0:
print('\033[31;1mfrom字段不能为空\033[0m')
else:
db,table = sql_dic.get('from')[0].split('.') #将{from:['db.emp'}中['db.emp']拆分成 table = emp db = db
db_pash = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))) + r'/%s/%s'%(db,table)
with open(db_pash,'r',encoding='utf-8')as fh: #其次处理where部分
where_res = where_action(fh,sql_dic.get('where')) #定义where_res变量存储where_action的执行处理结果
# 再次处理limit部分
limit_res = limit_action(where_res,sql_dic.get('limit'))
# 最后处理select部分
select_res = select(limit_res,sql_dic.get('select'))
for record in select_res:
print("查询结果为: \033[34;1m%s\033[0m"% record)
print('查询结果数量为: \033[34;1m%s\033[0m'%len(record))
return select_res def where_action(fh, where_l):
'''
该函数将接收过来的db.emp文件变成字典形式,并将该字典与用户输入的where条件进行对比解析,最后将对比结果为True的查询
条件储存在where_action_res列表中
:param fh: 接收select_action函数传过来的db.emp文件路径
:param where_l:接收 select_action函数传过来的sql_dic.get(where')
:return:
'''
where_action_res = []
title = 'id,name,age,phone,dept,enroll_data'
if len(where_l) != 0:
for item in fh:
db_dic = dict(zip(title.split(','), item.split(',')))
'''
定义db_dic函数以字典形式将emp文件中的内容为值,title
为字典中的键做下拉链拼接。例:db_dic = {
'name':'Mark'
'age':'4'
......
}
'''
logice_res = logic_action(where_l,db_dic) # logice_res = logic_action_res
if logice_res: # 判断logic_action的返回结果是否为True
where_action_res.append(item.split()) # 将fh和where_l比对后都为True的那条记录添加到where_action_res列表
else: # 查询结果都为False,给出提示
print('正在努力为您查询请稍后...')
else:
where_action_res = fh.readlines()
#print('in the where_action_res: \033[32;1m%s\033[0m'%where_action_res)
return where_action_res def logic_action(where_l,db_dic):
'''
该函数处理where部分与db.emp文件中的信息进行逻辑分析和对比。并将对比结果为True的信息返回给where_action
:param where_l:
:param db_dic:
:return:
'''
logic_action_res = []
for exp in where_l:
if type(exp) is list: # 判断exp是否是列表形式 ['id','>','10']
exp_k, opt, exp_v = exp # 将该列表参数赋值成 exp_k=='id' opt = '>' ,exp_v = '10'
if exp[1] == '=':
opt = "%s=" % exp[1] # 将exp列表中 '=' 变为 '=='
if db_dic[exp_k].isdigit(): # 判断 db_dic['id'] 是否是数字 如:10
dic_v = int(db_dic[exp_k]) # 将 db_dic['id']的值变成int类型
exp_v = int(exp_v)
else:
dic_v = '%s' % db_dic[exp_k] # 将不是数字的例如: 员工姓名 alex,Jim
if opt != 'like':
exp = str(eval('%s%s%s' % (dic_v, opt, exp_v))) # 将emp表中员工db_dic[exp_k]值与exp_v值进行eval字符串比较
else:
if exp_v in dic_v:
exp = 'True'
else:
exp = 'False'
logic_action_res.append(exp) # 将exp "'True',and,'False'" 字符串变成['True',and,'False']形式
logic_action_res = eval(' '.join(logic_action_res)) # 先将['True',and,'False']使用join函数变成'Falase',然后在用
# eval函数最终将logic_action_res变成False
#print('in the logic_action_res\033[33;1m%s\033[0m' %logic_action_res)
return logic_action_res def limit_action(where_res,limit_l):
limit_res = []
if len(limit_l) != 0:
index = int(limit_l[0]) #定义index变量取 limit_l[0]所对应的值 如 limit['3'] index=3
limit_res = where_res[0:index] #将where_res里面的内容进行切片,从0-index
else:
limit_res = where_res
return limit_res def select(limit_res,select_l):
'''
该函数为执行select[name,id]模块查询语句,也是其最终查询结果。如用户输入 select * from db.emp则显示所有字段结果
若 select name,id,dept from db.emp 则只显示 name,age,dept字段的查询结果
:param limit_res: limit_res函数过滤后的查询结果
:param select_l: 用户输入的 select ['name','age','dept']列表信息
:return:
'''
select_list = []
exp = []
char = ''
if len(select_l) != 0:
if select_l[0] != '*':
title = 'id,name,age,phone,dept,enroll_data'
for item in limit_res: for index in item:
select_dic = dict(zip(title.split(','),index.split(',')))
exp = select_l[0].split(',')
for i in exp:
select_list.append(select_dic[i].strip())
else:
select_list = limit_res
else:
print('\033[31;1m请输入有效select * 语句\033[0m')
return exp,select_list #insert语句执行模块
def insert_action(sql_dic):
'''
该函数接收用户输入的insert语句,并分配给指定的insert执行函数进行原文件对比和执行程序
:param sql_dic:
:return:
'''
#首先处理insert部分
if len(sql_dic.get('insert')) == 0:
print('\033[31;1m insert 字段不能为空\033[0m')
else:
db,table = sql_dic.get('insert')[0].split('.') #将{from:['db.emp'}中['db.emp']拆分成 table = emp db = db
db_pash = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))) + r'/%s/%s'%(db,table)
with open(db_pash,'r',encoding='utf-8')as fh:
#其次处理value值
value_res = value_action(fh,sql_dic.get('value'),db_pash)
return value_res def value_action(fh,value_l,db_pash):
'''
该函数接收insert_action()函数传递过来的fh,value_l,db_pash值,并相应变量进行解析整理并执行用户输入的insert语句
:param fh: 数据库文件
:param value_l: 用户输入的 value字段参数
:param db_pash: 数据库文件路径
:return:
'''
phone = []
for index in value_l:
index_l = index.split(',') #遍历用户输入的value值,并将其转换为['5','Mark','32'....]格式
for item in fh: #遍历数据库表文件也将其转换为['5','Mark','32'....]格式
info = item.strip().split(',')
phone.append(info[3]) tag = True
if index_l[2] in phone: #以手机号作唯一键,判断用户输入的value值是否存在数据文件中
tag = False
tag_res = print('\033[31;1m该用户已存在不能重复添加\033[0m')
if tag and len(index_l) < 5:
tag = False
tag_res = print('\033[31;1m用户输入value信息不够\033[0m')
if tag:
index_l[0] = int(info[0][-1]) + 1 # 完成id自增:info[0][-1] 取info列表 id的字段最后一个值,然后自动+1
with open(db_pash,'a',encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(''.join('\n%s,'%index_l[0]+index)) #使用join函数将['6','mark','32'...]拼接字符串成 8,Mark,32的样式
tag_res = print("已成功添加信息: \033[34;1m%s\033[0m" %index)
return tag_res,index_l #update语句执行模块
def update_action(sql_dic):
#优先处理update字段
db,table = sql_dic.get('update')[0].split('.') #将{from:['db.emp'}中['db.emp']拆分成 table = emp db = db
db_pash = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))) + r'/%s/%s'%(db,table)
with open(db_pash,'r',encoding='utf-8') as fh: #其次处理where部分
where_res = where_action(fh,sql_dic.get('where')) # 定义where_res变量存储where_action的执行处理结果
#最后处理set部分
set_res = set_action(where_res,sql_dic.get('set'),fh,db_pash)
print('参数已修改完成: \033[36;1m %s \033[0m' %set_res)
return set_res def set_action(where_res,set_l,fh,db_pash):
'''
该函数对用户输入的set字段进行处理执行,返回添加结果和修改数据库文本内容
:param where_res: 接收where_action()函数传递过来的where_res返回值
:param set_l: 用户输入的 set列表参数
:param fh:
:param db_pash:
:return:
'''
set_list = []
change_list = []
title = 'id,name,age,phone,dept,enroll_data'
if len(set_l) == 0 or set_l[0] == 'id':
print('\033[31;1m用户id不能修改\033[0m')
else:
for item in where_res:
for index in item: # index参数格式: 1,'Alex',22...
index_l= index.split(',') #index_l参数格式:['1','Alex','22'...]
set_dic = dict(zip(title.split(','),index_l)) change_list.append(set_dic[set_l[0]]) # 将未修改的字段参数值添加到change_list列表
change_list.append(set_l[2]) # 将需要修改的参数添加到change_list列表 set_dic[set_l[0]] = set_l[2] # 将字典根据用户输入的要修改的字段 如: dept,age 修改成 相应的数值 set_list = (list(set_dic.values())) #将重新赋值后的值取出并以列表形式存储,作为修改后的列表
with open(db_pash, 'r', encoding='utf-8')as fh:
fh_r = fh.readlines() with open(db_pash,'w',encoding='utf-8') as f:
for line in fh_r:
if change_list[0] in line : #判断未修改的参数值是否存在数据库表中
line = line.replace(change_list[0],change_list[1]) #修改文件中所对应的参数值
f.write(line) #print('in the set_action: \033[36;1m %s \033[0m'%set_list)
return set_list #delect语句执行模块
def delect_action(sql_dic):
'''
delect主执行函数,对用户输入的delect语句各字段进行分配到相应函数进行解析执行
:param sql_dic:
:return:
'''
# 优先处理from字段
if len(sql_dic.get('from')) == 0:
print('\033[31;1m insert 字段不能为空\033[0m')
else:
db, table = sql_dic.get('from')[0].split('.') # 将{from:['db.emp'}中['db.emp']拆分成 table = emp db = db
db_pash = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))) + r'/%s/%s' % (db, table)
with open(db_pash, 'r', encoding='utf-8')as fh:
#其次处理where字段
where_res = where_action(fh,sql_dic.get('where')) # 定义where_res变量存储where_action的执行处理结果
#最后处理delect字段
delect_res = delect(fh,where_res,where_l=sql_dic.get('where'),db_pash=db_pash)
print('已删除\033[34;1m %s \033[0m员工信息:'%delect_res)
return delect_res def delect(fh,where_res,where_l,db_pash):
'''
该函数执行用户输入的 where条件参数解析并执行delect操作,并相应文本内容
:param fh:
:param where_res:
:param where_l:
:param db_pash:
:return:
'''
delect_list = []
for i in where_res:
for i in i:
pass
if len(where_l) != 0:
with open(db_pash,'r',encoding='utf-8') as fh:
lines = fh.readlines()
for line in lines:
if not re.search(i,line): #循环遍历出 不包含 想要删除的文本信息
delect_list.append(line) #并将这些信息存储到字典中
with open(db_pash,'w',encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.writelines(delect_list) #将不包含想要删除的文本信息 写入数据库文本中
else:
print('\033[31;1m无删除条件记录\033[0m')
return where_res
5、db数据库目录
1,zhiww,29,18898564892,Market,2013-02-12
2,wangying,12,100861343251,Market,2014-08-11
3,zhoujielun,29,15618285621,运维,2014-08-11
4,zhangsan,36,100861221,HR,2014-08-11
5,zhoujielun,29,114550,测试,2007-02-12
6,alex,25,13798708765,测试,2015-06-15
7,chen,29,1889856413,Market,2013-02-12
8,zjlun,25,13569856669,HR,2014-08-11
9,Mark,32,13655818285,CTO,2014-08-08
老男孩Day4作业:员工信息查询系统的更多相关文章
- python 写的员工信息查询
#!/use/bin/env pythonn#_*_ coding:utf-8 _*_import timedef Bre(): while True: Bre_falg = ra ...
- C语言身份证信息查询系统(修改版)
很久以前写了一个<C语言身份证信息查询系统>,如果你点击链接进去看了. 估计也会被我那磅礴大气的代码震惊到的,最近复习/学习文件操作,把代码改了改,算是对以前还不会文件操作的时候的愿望,哈 ...
- day12 python作业:员工信息表
作业要求: 周末大作业:实现员工信息表文件存储格式如下:id,name,age,phone,job1,Alex,22,13651054608,IT2,Egon,23,13304320533,Tearc ...
- python作业员工信息表程序(第四周)
作业需求: 1. 员工信息表程序,实现增删改查操作: 2. 可进行模糊查询,语法至少支持下面3种: select name,age from staff_table where age > 22 ...
- Day4作业:蛋疼CRM系统
先上流程图,还得27寸4K显示器,画图各种爽: ReadMe: 运行程序前的提示: 1.抱歉,你得装prettytable模块...... 2.还得抱歉,如果shell中运行,最好把字体调得小点,表格 ...
- day4作业之信息表
实在是太low了,终究是自己写的,记录下 #!/usr/bin/env python # coding=utf8 import os, re #这里我把查询这块分为3个函数了,纠结了很久是放一起还是分 ...
- 用户信息查询系统_daoImpl
package com.hopetesting.dao.impl;import com.hopetesting.dao.UserDao;import com.hopetesting.domain.Us ...
- 老男孩Day5作业:电子银行购物商城
1.作业需求: 模拟实现一个ATM + 购物商城程序 额度 15000或自定义 实现购物商城,买东西加入 购物车,调用信用卡接口结账 可以提现,手续费5% 支持多账户登录支持账户间转账 记录每月日常消 ...
- python-查询员工信息表
python查询员工信息表 基本要求: 用户可以模糊查询员工信息 显示匹配了多少条,匹配字符需要高亮显示 代码: #!/usr/env python #coding:utf-8 import time ...
随机推荐
- jenkins学习 01 jenkins介绍
jenkins 是一个可扩展的持续集成引擎. 使用Jenkins目的: 持续.自动地构建/测试软件项目. 监控一些定时执行的任务. jenkins拥有的特性: 易于安装,只要jenkins.war部署 ...
- ruby 异常处理
begin raise 'A test exception.' rescue Exception => e puts e.message puts e.backtrace.inspect end
- SpringMVC---依赖注入与面向切面
1.依赖注入与面向切面 1.1.出现背景 ——如何简化java开发? 其中很重要的一点是“组件化”. ——如何更好的“组件化”? 松耦合,以及尽可能的让组件专注于本身. ——Spring框架的目的也只 ...
- sass实用知识点
本文总结sass相关核心知识点 说明:本文的内容是,我在开发实践中总结的实用性比较强的sass知识点,其他未涉及的知识,如果对你有作用请自行查阅 sass知识目录 嵌套 注释 SassScript @ ...
- 第十四章 Spring MVC的工作机制与设计模式(待续)
Spring MVC的总体设计 Control设计 Model设计 View设计 框架设计的思考 设计模式解析之模版模式
- pa15-三省吾身
序号 项 1 凡事提前10分钟 凡事提前10分钟,会让你有充裕的时间应对可能的突发事件,更加从容. 试着把起床闹钟提前10分钟,你就会发现你出门不必急匆匆,早饭也可慢慢享用,一整天的状态也 ...
- UIBezierPath和CAShapeLayer配合肆意画图
一.CAShapeLayer CAShapeLayer 是 CALayer 的子类,但是比 CALayer 更灵活,可以画出各种图形 使用CAShapeLayer 绘制一个矩形 let layer ...
- MyBatis总结八:缓存介绍(一级缓存,二级缓存)
简介 为数据库的查询进行缓存,是减少数据库压力的主要途径.分为一级缓存和二级缓存. 一级缓存:session级别缓存,作用于当前会话. 二级缓存:SessionFactory级别缓存,作用于整个Ses ...
- java中一些常用的英语
abstract (关键字 ) 抽象 ['.bstr.kt] access vt.访问,存取 ['.kses]'(n.入口,使用权) algorithm n.算法 ['.lg.rie ...
- 【总结整理】行内标签span设置position:absolute/float属性可以设置宽度与高度
postion:absolute 跳出文本流,不是行内元素,设置宽高有效,我的理解. 引用下曹刘阳写的<编写高质量代码-web前端开发修炼之道>一书中看到的一句话:position:abs ...
