kaggle 欺诈信用卡预测——不平衡训练样本的处理方法 综合结论就是:随机森林+过采样(直接复制或者smote后,黑白比例1:3 or 1:1)效果比较好!记得在smote前一定要先做标准化!!!其实随机森林对特征是否标准化无感,但是svm和LR就非常非常关键了
先看数据:
Number of seconds elapsed between each transaction (over two days)
abc
Amount of money for this transaction
Fraud or Not-Fraud
Introduction
from:https://www.kaggle.com/nikitaivanov/getting-high-sensitivity-for-imbalanced-data 主要使用了smote和聚类两种思路!
In this notebook we will try to predict fraud transactions from a given data set. Given that the data is imbalanced, standard metrics for evaluating classification algorithm (such as accuracy) are invalid. We will focus on the following metrics: Sensitivity (true positive rate) and Specificity (true negative rate). Of course, they are dependent on each other, so we want to find optimal trade-off between them. Such trade-off usually depends on the application of the algorithm, and in case of fraud detection I would prefer to see high sensitivity (e.g. given that a transaction is fraud, I want to be able to detect it with high probability).
For dealing with skewed data I am going to use SMOTE algorithm. In two words, the idea is to create synthetic samples (in opposite to oversampling with replacement) through finding nearest examples (KNN), calculating difference between them, multiplying this difference by a random number between 0 and 1 and adding the result to the initial sample. For this purpose we are going to use SMOTE function from DMwR package.
Algorithms I am going to implement are Support Vector Machine (SVM), Logistic regression and Random Forest. Models will be trained on the original and SMOTEd data and their performance will be measured on the entire data set.
As a bonus, we are going to have some fun and use K-means centroids of the negative examples together with the original positive examples as a new dataset and train our algorithm on it. We then compare results.
##Loading required packeges
library(ggplot2) #visualization
library(caret) #train model
library(dplyr) #data manipulation
library(kernlab) #svm
library(nnet) #models (logit, neural nets)
library(DMwR) #SMOTE data ##Load data
d = read.csv("../input/creditcard.csv")
n = ncol(d)
str(d)
d$Class = ifelse(d$Class == 0, 'No', 'Yes') %>% as.factor()
Loading required package: lattice
Attaching package: ‘dplyr’
The following objects are masked from ‘package:stats’:
filter, lag
The following objects are masked from ‘package:base’:
intersect, setdiff, setequal, union
Attaching package: ‘kernlab’
The following object is masked from ‘package:ggplot2’:
alpha
Loading required package: grid
'data.frame': 284807 obs. of 31 variables:
$ Time : num 0 0 1 1 2 2 4 7 7 9 ...
$ V1 : num -1.36 1.192 -1.358 -0.966 -1.158 ...
$ V2 : num -0.0728 0.2662 -1.3402 -0.1852 0.8777 ...
$ V3 : num 2.536 0.166 1.773 1.793 1.549 ...
$ V4 : num 1.378 0.448 0.38 -0.863 0.403 ...
$ V5 : num -0.3383 0.06 -0.5032 -0.0103 -0.4072 ...
$ V6 : num 0.4624 -0.0824 1.8005 1.2472 0.0959 ...
$ V7 : num 0.2396 -0.0788 0.7915 0.2376 0.5929 ...
$ V8 : num 0.0987 0.0851 0.2477 0.3774 -0.2705 ...
$ V9 : num 0.364 -0.255 -1.515 -1.387 0.818 ...
$ V10 : num 0.0908 -0.167 0.2076 -0.055 0.7531 ...
$ V11 : num -0.552 1.613 0.625 -0.226 -0.823 ...
$ V12 : num -0.6178 1.0652 0.0661 0.1782 0.5382 ...
$ V13 : num -0.991 0.489 0.717 0.508 1.346 ...
$ V14 : num -0.311 -0.144 -0.166 -0.288 -1.12 ...
$ V15 : num 1.468 0.636 2.346 -0.631 0.175 ...
$ V16 : num -0.47 0.464 -2.89 -1.06 -0.451 ...
$ V17 : num 0.208 -0.115 1.11 -0.684 -0.237 ...
$ V18 : num 0.0258 -0.1834 -0.1214 1.9658 -0.0382 ...
$ V19 : num 0.404 -0.146 -2.262 -1.233 0.803 ...
$ V20 : num 0.2514 -0.0691 0.525 -0.208 0.4085 ...
$ V21 : num -0.01831 -0.22578 0.248 -0.1083 -0.00943 ...
$ V22 : num 0.27784 -0.63867 0.77168 0.00527 0.79828 ...
$ V23 : num -0.11 0.101 0.909 -0.19 -0.137 ...
$ V24 : num 0.0669 -0.3398 -0.6893 -1.1756 0.1413 ...
$ V25 : num 0.129 0.167 -0.328 0.647 -0.206 ...
$ V26 : num -0.189 0.126 -0.139 -0.222 0.502 ...
$ V27 : num 0.13356 -0.00898 -0.05535 0.06272 0.21942 ...
$ V28 : num -0.0211 0.0147 -0.0598 0.0615 0.2152 ...
$ Amount: num 149.62 2.69 378.66 123.5 69.99 ...
$ Class : int 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ...
It is always a good idea first to plot a response variable to check for skewness in data:
qplot(x = d$Class, geom = 'bar') + xlab('Fraud (Yes/No)') + ylab('Number of transactions')

Classification on the original data
Keeping in mind that the data is highly skewed we proceed. First split the data into training and test sets.
idx = createDataPartition(d$Class, p = 0.7, list = F)
d[, -n] = scale(d[, -n]) #perform scaling
train = d[idx, ]
test = d[-idx, ]
Calculate baseline accuracy for future reference
blacc = nrow(d[d$Class == 'No', ])/nrow(d)*100
cat('Baseline accuracy:', blacc)
Baseline accuracy: 99.82725
To begin with, let's train our models on the original dataset to see what we get if use unbalanced data. Due to computational limitations of my laptop, I will only run logistic regression for this purpose.
m1 = multinom(data = train, Class ~ .)
p1 = predict(m1, test[, -n], type = 'class')
cat(' Accuracy of the model', mean(p1 == test[, n])*100, '\n', 'Baseline accuracy', blacc)
# weights: 32 (31 variable)
initial value 138189.980799
final value 31315.159746
converged
Accuracy of the model 99.92744
Baseline accuracy 99.82725
Though accuracy (99.92%) of the model might look impressive at a first glance, in fact it isn't. Simply predicting 'not a fraud' for all transactions will give 99.83% accuracy. To really evaluate model's perfomance we need to check confusion matrix.
confusionMatrix(p1, test[, n], positive = 'Yes')
Confusion Matrix and Statistics
Reference
Prediction No Yes
No 85287 55
Yes 7 92
Accuracy : 0.9993
95% CI : (0.9991, 0.9994)
No Information Rate : 0.9983
P-Value [Acc > NIR] : 1.779e-15
Kappa : 0.7476
Mcnemar's Test P-Value : 2.387e-09
Sensitivity : 0.625850
Specificity : 0.999918
Pos Pred Value : 0.929293
Neg Pred Value : 0.999356
Prevalence : 0.001720
Detection Rate : 0.001077
Detection Prevalence : 0.001159
Balanced Accuracy : 0.812884
'Positive' Class : Yes
From the confusion matrix we see that while model has high accuracy (99.92%) and high specificity (99.98%), it has low sensitivity of 64%. In other words, only 64% of all fraudulent transactions were detected.
Classification on the SMOTEd data
Now let's preprocess our data using SMOTE algorithm:
table(d$Class) #check initial distribution
newData <- SMOTE(Class ~ ., d, perc.over = 500,perc.under=100)
table(newData$Class) #check SMOTed distribution
No Yes
284315 492
No Yes
2460 2952
To train SVM (with RBF kernel) we are going to use train function from caret package. It allows to choose optimal parameters of the model (cost and sigma in this case). Cost refers to penalty for misclassifying examples and sigma is a parameter of RBF which measures similarity between examples. To choose best model we use 5-fold cross-validation. We then evaluate our model on the entire data set.
gr = expand.grid(C = c(1, 50, 150), sigma = c(0.01, 0.05, 1))
tr = trainControl(method = 'cv', number = 5)
m2 = train(data = newData, Class ~ ., method = 'svmRadial', trControl = tr, tuneGrid = gr)
m2
Support Vector Machines with Radial Basis Function Kernel 5412 samples
30 predictor
2 classes: 'No', 'Yes' No pre-processing
Resampling: Cross-Validated (5 fold)
Summary of sample sizes: 4330, 4329, 4329, 4330, 4330
Resampling results across tuning parameters: C sigma Accuracy Kappa
1 0.01 0.9445668 0.8891865
1 0.05 0.9626774 0.9250408
1 1.00 0.9672934 0.9344234
50 0.01 0.9717300 0.9430408
50 0.05 0.9863262 0.9723782
50 1.00 0.9695108 0.9388440
150 0.01 0.9789351 0.9574955
150 0.05 0.9850335 0.9697552
150 1.00 0.9695108 0.9388440 Accuracy was used to select the optimal model using the largest value.
The final values used for the model were sigma = 0.05 and C = 50.
As wee see, best tuning parameters are C = 50 and sigma = 0.05
Let's look at a confusion matrix
p2 = predict(m2, d[, -n])
confusionMatrix(p2, d[, n], positive = 'Yes')
Confusion Matrix and Statistics
Reference
Prediction No Yes
No 278470 2
Yes 5845 490
Accuracy : 0.9795
95% CI : (0.9789, 0.98)
No Information Rate : 0.9983
P-Value [Acc > NIR] : 1
Kappa : 0.1408
Mcnemar's Test P-Value : <2e-16
Sensitivity : 0.995935
Specificity : 0.979442
Pos Pred Value : 0.077348
Neg Pred Value : 0.999993
Prevalence : 0.001727
Detection Rate : 0.001720
Detection Prevalence : 0.022243
Balanced Accuracy : 0.987688
'Positive' Class : Yes
(Numbers may differ due to randomness of k-fold cv)
As expected we were able to achieve sensitivity of 99.59%. In other words, out of all fraudulent transactions we correctly detected 99.59% of them. This came in price of slightly lower accuracy (in comparison to the first model) - 97.95% vs. 99.92% and lower specificity 97.94% vs. 99.98%. The main disadvantage is low level of positive predicted value (i.e. given that prediction is positive, what is probability that the true state is positive) which this case is 7.74% vs. 85% for initial (unbalanced dataset) model. As was mentioned in the beginning, one should choose a model that matches certain goals. If the goal is to correctly identify fraudulent transactions even in price of low positive predicted value (which I believe the case), then the latter model (based on SMOTed data) should be used. Looking at confusion matrix we see that almost all fraudulent transactions were correctly identified and only 2.5% were mislabeled as fraudulent.
I'm planning to try couple more models and also use more sophisticated algorithm that uses K-means centroids of the majority class as samples for non fraudulent transactions.
m3 = randomForest(data = newData, Class ~ .)
p3 = predict(m3, d[, -n])
confusionMatrix(p3, d[, n], positive = 'Yes')
Error in eval(expr, envir, enclos): could not find function "randomForest"
Traceback:
library(randomForest)
m3 = randomForest(data = newData, Class ~ .)
p3 = predict(m3, d[, -n])
confusionMatrix(p3, d[, n], positive = 'Yes')
randomForest 4.6-12
Type rfNews() to see new features/changes/bug fixes. Attaching package: ‘randomForest’ The following object is masked from ‘package:dplyr’: combine The following object is masked from ‘package:ggplot2’: margin
Confusion Matrix and Statistics
Reference
Prediction No Yes
No 282105 0
Yes 2210 492
Accuracy : 0.9922
95% CI : (0.9919, 0.9926)
No Information Rate : 0.9983
P-Value [Acc > NIR] : 1
Kappa : 0.306
Mcnemar's Test P-Value : <2e-16
Sensitivity : 1.000000
Specificity : 0.992227
Pos Pred Value : 0.182087
Neg Pred Value : 1.000000
Prevalence : 0.001727
Detection Rate : 0.001727
Detection Prevalence : 0.009487
Balanced Accuracy : 0.996113
'Positive' Class : Yes
Random forest performs really well. Sensitivity 100% and high specificity (more than 99%). All fraudulent transactions were detected and less than 1% of all transactions were falsely classified as fraud. Hence, Random Forest + SMOTE algorithm shloud be considered as final model.
K-means centroids as a new sample
For curiosity, let's take another approach in dealing with imbalanced data. We are going to separate the examples for positive and negative and from the latter one extract centroids (generated using K-means clustering). Number of clusters will be equal to the number of positive examples. We then use these centroids together with positive examples as a new sample.(思路就是聚类,将major class聚类为k个点,其中k为欺诈信用卡的样本数!)
neg = d[d$Class == 'No', ] #negative examples
pos = d[d$Class == 'Yes', ] #positive examples
n_pos = sum(d$Class == 'Yes') #calculate number of positive examples
clus = kmeans(neg[, -n], centers = n_pos, iter.max = 100) #perform K-means
neg = as.data.frame(clus$centers) #extract centroids as new sample
neg$Class = 'No'
newData = rbind(neg, pos) #merge positive and negative examples
newData$Class = factor(newData$Class)
We run random forest on the new dataset, newData, and check confusion matrix.
m4 = randomForest(data = newData, Class ~ .)
p4 = predict(m4, d[, -n])
confusionMatrix(p4, d[, n], positive = 'Yes')
Confusion Matrix and Statistics
Reference
Prediction No Yes
No 210086 0
Yes 74229 492
Accuracy : 0.7394
95% CI : (0.7378, 0.741)
No Information Rate : 0.9983
P-Value [Acc > NIR] : 1
Kappa : 0.0097
Mcnemar's Test P-Value : <2e-16
Sensitivity : 1.000000
Specificity : 0.738920
Pos Pred Value : 0.006584
Neg Pred Value : 1.000000
Prevalence : 0.001727
Detection Rate : 0.001727
Detection Prevalence : 0.262357
Balanced Accuracy : 0.869460
'Positive' Class : Yes
Well, while sensitivity is still 100%, specificity dropped to 72% leading to a big fraction of false positive predictions. Learning on the data that was transformed using SMOTE algorithm gave much better results.
from:https://www.kaggle.com/themlguy/undersample-and-oversample-approach-explored
# This Python 3 environment comes with many helpful analytics libraries installed
# It is defined by the kaggle/python docker image: https://github.com/kaggle/docker-python
# For example, here's several helpful packages to load in import numpy as np # linear algebra
import pandas as pd # data processing, CSV file I/O (e.g. pd.read_csv) # Input data files are available in the "../input/" directory.
# For example, running this (by clicking run or pressing Shift+Enter) will list the files in the input directory import os
print(os.listdir("../input")) # Any results you write to the current directory are saved as output.
['creditcard.csv']
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
import seaborn as sns
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix,recall_score,precision_recall_curve,auc,roc_curve,roc_auc_score,classification_report
/opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages/sklearn/cross_validation.py:41: DeprecationWarning: This module was deprecated in version 0.18 in favor of the model_selection module into which all the refactored classes and functions are moved. Also note that the interface of the new CV iterators are different from that of this module. This module will be removed in 0.20.
"This module will be removed in 0.20.", DeprecationWarning)
creditcard_data=pd.read_csv("../input/creditcard.csv")
creditcard_data['Amount']=StandardScaler().fit_transform(creditcard_data['Amount'].values.reshape(-1, 1))
creditcard_data.drop(['Time'], axis=1, inplace=True)
def generatePerformanceReport(clf,X_train,y_train,X_test,y_test,bool_):
if bool_==True:
clf.fit(X_train,y_train.values.ravel())
pred=clf.predict(X_test)
cnf_matrix=confusion_matrix(y_test,pred)
tn, fp, fn, tp=cnf_matrix.ravel()
print('---------------------------------')
print('Length of training data:',len(X_train))
print('Length of test data:', len(X_test))
print('---------------------------------')
print('True positives:',tp)
print('True negatives:',tn)
print('False positives:',fp)
print('False negatives:',fn)
#sns.heatmap(cnf_matrix,cmap="coolwarm_r",annot=True,linewidths=0.5)
print('----------------------Classification report--------------------------')
print(classification_report(y_test,pred))
#generate 50%, 66%, 75% proportions of normal indices to be combined with fraud indices 也就是说采样后的黑白样本比例是:0.5,0.66,0.75
#undersampled data
normal_indices=creditcard_data[creditcard_data['Class']==0].index
fraud_indices=creditcard_data[creditcard_data['Class']==1].index
for i in range(1,4):
normal_sampled_data=np.array(np.random.choice(normal_indices, i*len(fraud_indices),replace=False)) #a random sample is generated from normal_indices 主要是随机欠采样
undersampled_data=np.concatenate([fraud_indices, normal_sampled_data])
undersampled_data=creditcard_data.iloc[undersampled_data]
print('length of undersampled data ', len(undersampled_data))
print('% of fraud transactions in undersampled data ',len(undersampled_data.loc[undersampled_data['Class']==1])/len(undersampled_data))
#get feature and label data
feature_data=undersampled_data.loc[:,undersampled_data.columns!='Class']
label_data=undersampled_data.loc[:,undersampled_data.columns=='Class']
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test=train_test_split(feature_data,label_data,test_size=0.30)
for j in [LogisticRegression(),SVC(),RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100)]:
clf=j
print(j)
generatePerformanceReport(clf,X_train,y_train,X_test,y_test,True)
#the above code classifies X_test which is part of undersampled data
#now, let us consider the remaining rows of dataset and use that as test set
remaining_indices=[i for i in creditcard_data.index if i not in undersampled_data.index]
testdf=creditcard_data.iloc[remaining_indices]
testdf_label=creditcard_data.loc[:,testdf.columns=='Class']
testdf_feature=creditcard_data.loc[:,testdf.columns!='Class']
generatePerformanceReport(clf,X_train,y_train,testdf_feature,testdf_label,False)
length of undersampled data 984
% of fraud transactions in undersampled data 0.5
LogisticRegression(C=1.0, class_weight=None, dual=False, fit_intercept=True,
intercept_scaling=1, max_iter=100, multi_class='ovr', n_jobs=1,
penalty='l2', random_state=None, solver='liblinear', tol=0.0001,
verbose=0, warm_start=False)
---------------------------------
Length of training data: 688
Length of test data: 296
---------------------------------
True positives: 144
True negatives: 134
False positives: 11
False negatives: 7
----------------------Classification report--------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 0.95 0.92 0.94 145
1 0.93 0.95 0.94 151 avg / total 0.94 0.94 0.94 296 ---------------------------------
Length of training data: 688
Length of test data: 284807
---------------------------------
True positives: 461
True negatives: 270879
False positives: 13436
False negatives: 31
----------------------Classification report--------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 1.00 0.95 0.98 284315
1 0.03 0.94 0.06 492 #可以看到LR在测试数据集上表现并不好 avg / total 1.00 0.95 0.97 284807 SVC(C=1.0, cache_size=200, class_weight=None, coef0=0.0,
decision_function_shape='ovr', degree=3, gamma='auto', kernel='rbf',
max_iter=-1, probability=False, random_state=None, shrinking=True,
tol=0.001, verbose=False)
---------------------------------
Length of training data: 688
Length of test data: 296
---------------------------------
True positives: 144
True negatives: 140
False positives: 5
False negatives: 7
----------------------Classification report--------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 0.95 0.97 0.96 145
1 0.97 0.95 0.96 151 avg / total 0.96 0.96 0.96 296 ---------------------------------
Length of training data: 688
Length of test data: 284807
---------------------------------
True positives: 463
True negatives: 267084
False positives: 17231
False negatives: 29
----------------------Classification report--------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 1.00 0.94 0.97 284315
1 0.03 0.94 0.05 492 #看来svm在测试数据集上也不行啊 avg / total 1.00 0.94 0.97 284807 RandomForestClassifier(bootstrap=True, class_weight=None, criterion='gini',
max_depth=None, max_features='auto', max_leaf_nodes=None,
min_impurity_decrease=0.0, min_impurity_split=None,
min_samples_leaf=1, min_samples_split=2,
min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.0, n_estimators=100, n_jobs=1,
oob_score=False, random_state=None, verbose=0,
warm_start=False)
---------------------------------
Length of training data: 688
Length of test data: 296
---------------------------------
True positives: 144
True negatives: 142
False positives: 3
False negatives: 7
----------------------Classification report--------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 0.95 0.98 0.97 145
1 0.98 0.95 0.97 151 avg / total 0.97 0.97 0.97 296 ---------------------------------
Length of training data: 688
Length of test data: 284807
---------------------------------
True positives: 485
True negatives: 275060
False positives: 9255
False negatives: 7
----------------------Classification report--------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 1.00 0.97 0.98 284315
1 0.05 0.99 0.09 492 #Rf也不行???? avg / total 1.00 0.97 0.98 284807 length of undersampled data 1476
% of fraud transactions in undersampled data 0.3333333333333333
LogisticRegression(C=1.0, class_weight=None, dual=False, fit_intercept=True,
intercept_scaling=1, max_iter=100, multi_class='ovr', n_jobs=1,
penalty='l2', random_state=None, solver='liblinear', tol=0.0001,
verbose=0, warm_start=False)
---------------------------------
Length of training data: 1033
Length of test data: 443
---------------------------------
True positives: 130
True negatives: 291
False positives: 5
False negatives: 17
----------------------Classification report--------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 0.94 0.98 0.96 296
1 0.96 0.88 0.92 147 avg / total 0.95 0.95 0.95 443 ---------------------------------
Length of training data: 1033
Length of test data: 284807
---------------------------------
True positives: 442
True negatives: 278887
False positives: 5428
False negatives: 50
----------------------Classification report--------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 1.00 0.98 0.99 284315
1 0.08 0.90 0.14 492 avg / total 1.00 0.98 0.99 284807 SVC(C=1.0, cache_size=200, class_weight=None, coef0=0.0,
decision_function_shape='ovr', degree=3, gamma='auto', kernel='rbf',
max_iter=-1, probability=False, random_state=None, shrinking=True,
tol=0.001, verbose=False)
---------------------------------
Length of training data: 1033
Length of test data: 443
---------------------------------
True positives: 133
True negatives: 286
False positives: 10
False negatives: 14
----------------------Classification report--------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 0.95 0.97 0.96 296
1 0.93 0.90 0.92 147 avg / total 0.95 0.95 0.95 443 ---------------------------------
Length of training data: 1033
Length of test data: 284807
---------------------------------
True positives: 453
True negatives: 274909
False positives: 9406
False negatives: 39
----------------------Classification report--------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 1.00 0.97 0.98 284315
1 0.05 0.92 0.09 492 avg / total 1.00 0.97 0.98 284807 RandomForestClassifier(bootstrap=True, class_weight=None, criterion='gini',
max_depth=None, max_features='auto', max_leaf_nodes=None,
min_impurity_decrease=0.0, min_impurity_split=None,
min_samples_leaf=1, min_samples_split=2,
min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.0, n_estimators=100, n_jobs=1,
oob_score=False, random_state=None, verbose=0,
warm_start=False)
---------------------------------
Length of training data: 1033
Length of test data: 443
---------------------------------
True positives: 128
True negatives: 293
False positives: 3
False negatives: 19
----------------------Classification report--------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 0.94 0.99 0.96 296
1 0.98 0.87 0.92 147 avg / total 0.95 0.95 0.95 443 ---------------------------------
Length of training data: 1033
Length of test data: 284807
---------------------------------
True positives: 473
True negatives: 281560
False positives: 2755
False negatives: 19
----------------------Classification report--------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 1.00 0.99 1.00 284315
1 0.15 0.96 0.25 492 avg / total 1.00 0.99 0.99 284807 length of undersampled data 1968
% of fraud transactions in undersampled data 0.25
LogisticRegression(C=1.0, class_weight=None, dual=False, fit_intercept=True,
intercept_scaling=1, max_iter=100, multi_class='ovr', n_jobs=1,
penalty='l2', random_state=None, solver='liblinear', tol=0.0001,
verbose=0, warm_start=False)
---------------------------------
Length of training data: 1377
Length of test data: 591
---------------------------------
True positives: 116
True negatives: 451
False positives: 5
False negatives: 19
----------------------Classification report--------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 0.96 0.99 0.97 456
1 0.96 0.86 0.91 135 avg / total 0.96 0.96 0.96 591 ---------------------------------
Length of training data: 1377
Length of test data: 284807
---------------------------------
True positives: 433
True negatives: 282245
False positives: 2070
False negatives: 59
----------------------Classification report--------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 1.00 0.99 1.00 284315
1 0.17 0.88 0.29 492 avg / total 1.00 0.99 1.00 284807 SVC(C=1.0, cache_size=200, class_weight=None, coef0=0.0,
decision_function_shape='ovr', degree=3, gamma='auto', kernel='rbf',
max_iter=-1, probability=False, random_state=None, shrinking=True,
tol=0.001, verbose=False)
---------------------------------
Length of training data: 1377
Length of test data: 591
---------------------------------
True positives: 118
True negatives: 447
False positives: 9
False negatives: 17
----------------------Classification report--------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 0.96 0.98 0.97 456
1 0.93 0.87 0.90 135 avg / total 0.96 0.96 0.96 591 ---------------------------------
Length of training data: 1377
Length of test data: 284807
---------------------------------
True positives: 445
True negatives: 279369
False positives: 4946
False negatives: 47
----------------------Classification report--------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 1.00 0.98 0.99 284315
1 0.08 0.90 0.15 492 avg / total 1.00 0.98 0.99 284807 RandomForestClassifier(bootstrap=True, class_weight=None, criterion='gini',
max_depth=None, max_features='auto', max_leaf_nodes=None,
min_impurity_decrease=0.0, min_impurity_split=None,
min_samples_leaf=1, min_samples_split=2,
min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.0, n_estimators=100, n_jobs=1,
oob_score=False, random_state=None, verbose=0,
warm_start=False)
---------------------------------
Length of training data: 1377
Length of test data: 591
---------------------------------
True positives: 112
True negatives: 455
False positives: 1
False negatives: 23
----------------------Classification report--------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 0.95 1.00 0.97 456
1 0.99 0.83 0.90 135 avg / total 0.96 0.96 0.96 591 ---------------------------------
Length of training data: 1377
Length of test data: 284807
---------------------------------
True positives: 469
True negatives: 283466
False positives: 849
False negatives: 23
----------------------Classification report--------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 1.00 1.00 1.00 284315
1 0.36 0.95 0.52 492 avg / total 1.00 1.00 1.00 284807 整体来看,因为欠采样只是用了一个模型,因此预测效果很差!!!因为没有用到全量数据特征,所以在全部数据集上表现并不好!
#oversampled_data data
normal_sampled_indices=creditcard_data.loc[creditcard_data['Class']==0].index
oversampled_data=creditcard_data.iloc[normal_sampled_indices]
fraud_data=creditcard_data.loc[creditcard_data['Class']==1]
oversampled_data=oversampled_data.append([fraud_data]*300, ignore_index=True) #此处过采样处理是直接将欺诈样本复制300份!!!
print('length of oversampled_data data ', len(oversampled_data))
print('% of fraud transactions in oversampled_data data ',len(oversampled_data.loc[oversampled_data['Class']==1])/len(oversampled_data))
#get feature and label data
feature_data=oversampled_data.loc[:,oversampled_data.columns!='Class']
label_data=oversampled_data.loc[:,oversampled_data.columns=='Class']
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test=train_test_split(feature_data,label_data,test_size=0.30)
for j in [LogisticRegression(),RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100)]:
clf=j
print(j)
generatePerformanceReport(clf,X_train,y_train,X_test,y_test,True)
#the above code classifies X_test which is part of undersampled data
#now, let us consider the remaining rows of dataset and use that as test set
remaining_indices=[i for i in creditcard_data.index if i not in oversampled_data.index]
testdf=creditcard_data.iloc[remaining_indices]
testdf_label=creditcard_data.loc[:,testdf.columns=='Class']
testdf_feature=creditcard_data.loc[:,testdf.columns!='Class']
generatePerformanceReport(clf,X_train,y_train,testdf_feature,testdf_label,False)
length of oversampled_data data 431915
% of fraud transactions in oversampled_data data 0.3417339059768704 最后复制后的欺诈样本比例为白样本的33%
LogisticRegression(C=1.0, class_weight=None, dual=False, fit_intercept=True,
intercept_scaling=1, max_iter=100, multi_class='ovr', n_jobs=1,
penalty='l2', random_state=None, solver='liblinear', tol=0.0001,
verbose=0, warm_start=False)
---------------------------------
Length of training data: 302340
Length of test data: 129575
---------------------------------
True positives: 39803
True negatives: 84311
False positives: 1027
False negatives: 4434
----------------------Classification report--------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 0.95 0.99 0.97 85338
1 0.97 0.90 0.94 44237 avg / total 0.96 0.96 0.96 129575 ---------------------------------
Length of training data: 302340
Length of test data: 284807
---------------------------------
True positives: 444
True negatives: 281055
False positives: 3260
False negatives: 48
----------------------Classification report--------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 1.00 0.99 0.99 284315
1 0.12 0.90 0.21 492 #效果也不咋的啊! avg / total 1.00 0.99 0.99 284807 RandomForestClassifier(bootstrap=True, class_weight=None, criterion='gini',
max_depth=None, max_features='auto', max_leaf_nodes=None,
min_impurity_decrease=0.0, min_impurity_split=None,
min_samples_leaf=1, min_samples_split=2,
min_weight_fraction_leaf=0.0, n_estimators=100, n_jobs=1,
oob_score=False, random_state=None, verbose=0,
warm_start=False)
---------------------------------
Length of training data: 302340
Length of test data: 129575
---------------------------------
True positives: 44237
True negatives: 85327
False positives: 11
False negatives: 0
----------------------Classification report--------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 1.00 1.00 1.00 85338
1 1.00 1.00 1.00 44237 avg / total 1.00 1.00 1.00 129575 ---------------------------------
Length of training data: 302340
Length of test data: 284807
---------------------------------
True positives: 492
True negatives: 284304
False positives: 11
False negatives: 0
----------------------Classification report--------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 1.00 1.00 1.00 284315
1 0.98 1.00 0.99 492 #随机森林还是不错的!!! avg / total 1.00 1.00 1.00 284807
Random forest classifier with oversampled approach performs better compared to undersampled approach!!!
from:https://www.kaggle.com/gargmanish/how-to-handle-imbalance-data-study-in-detail
Hi all as we know credit card fraud detection will have a imbalanced data i.e having more number of normal class than the number of fraud class
In this I will use Basic method of handling imbalance data which are
This all I have done by using Analytics Vidya's blog please find the link Analytics Vidya
Undersampling:- it means taking the less number of majority class (In our case taking less number of Normal transactions so that our new data will be balanced
Oversampling: it means using replicating the data of minority class (fraud class) so that we can have a balanced data
SMOTE: it is also a type of oversampling but in this we will make the synthetic example of Minority data and will give as a balanced data
First I will start with the Undersampling and will try to classify using these Models
Decision Tree Classifier/ Random Forest Classifier
Logistic regression
SVM
XGboost
# This Python 3 environment comes with many helpful analytics libraries installed
# It is defined by the kaggle/python docker image: https://github.com/kaggle/docker-python
# For example, here's several helpful packages to load in import numpy as np # linear algebra
import pandas as pd # data processing, CSV file I/O (e.g. pd.read_csv) # Input data files are available in the "../input/" directory.
# For example, running this (by clicking run or pressing Shift+Enter) will list the files in the input directory from subprocess import check_output
print(check_output(["ls", "../input"]).decode("utf8")) # Any results you write to the current directory are saved as output.
creditcard.csv
Lets start with Importing Libraries and data
import pandas as pd # to import csv and for data manipulation
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt # to plot graph
import seaborn as sns # for intractve graphs
import numpy as np # for linear algebra
import datetime # to dela with date and time
%matplotlib inline
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler # for preprocessing the data
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier # Random forest classifier
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier # for Decision Tree classifier
from sklearn.svm import SVC # for SVM classification
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.cross_validation import train_test_split # to split the data
from sklearn.cross_validation import KFold # For cross vbalidation
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV # for tunnig hyper parameter it will use all combination of given parameters
from sklearn.model_selection import RandomizedSearchCV # same for tunning hyper parameter but will use random combinations of parameters
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix,recall_score,precision_recall_curve,auc,roc_curve,roc_auc_score,classification_report
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
/opt/conda/lib/python3.6/site-packages/sklearn/cross_validation.py:43: DeprecationWarning: This module was deprecated in version 0.18 in favor of the model_selection module into which all the refactored classes and functions are moved. Also note that the interface of the new CV iterators are different from that of this module. This module will be removed in 0.20.
"This module will be removed in 0.20.", DeprecationWarning)
data = pd.read_csv("../input/creditcard.csv",header = 0)
Now explore the data to get insight in it
data.info()
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 284807 entries, 0 to 284806
Data columns (total 31 columns):
Time 284807 non-null float64
V1 284807 non-null float64
V2 284807 non-null float64
V3 284807 non-null float64
V4 284807 non-null float64
V5 284807 non-null float64
V6 284807 non-null float64
V7 284807 non-null float64
V8 284807 non-null float64
V9 284807 non-null float64
V10 284807 non-null float64
V11 284807 non-null float64
V12 284807 non-null float64
V13 284807 non-null float64
V14 284807 non-null float64
V15 284807 non-null float64
V16 284807 non-null float64
V17 284807 non-null float64
V18 284807 non-null float64
V19 284807 non-null float64
V20 284807 non-null float64
V21 284807 non-null float64
V22 284807 non-null float64
V23 284807 non-null float64
V24 284807 non-null float64
V25 284807 non-null float64
V26 284807 non-null float64
V27 284807 non-null float64
V28 284807 non-null float64
Amount 284807 non-null float64
Class 284807 non-null int64
dtypes: float64(30), int64(1)
memory usage: 67.4 MB
- Hence we can see there are 284,807 rows and 31 columns which is a huge data
- Time is also in float here mean it can be only seconds starting from a particular time
# Now lets check the class distributions
sns.countplot("Class",data=data)
<matplotlib.axes._subplots.AxesSubplot at 0x7f6dabaaf128>

- As we know data is imbalanced and this graph also confirmed it
# now let us check in the number of Percentage
Count_Normal_transacation = len(data[data["Class"]==0]) # normal transaction are repersented by 0
Count_Fraud_transacation = len(data[data["Class"]==1]) # fraud by 1
Percentage_of_Normal_transacation = Count_Normal_transacation/(Count_Normal_transacation+Count_Fraud_transacation)
print("percentage of normal transacation is",Percentage_of_Normal_transacation*100)
Percentage_of_Fraud_transacation= Count_Fraud_transacation/(Count_Normal_transacation+Count_Fraud_transacation)
print("percentage of fraud transacation",Percentage_of_Fraud_transacation*100)
percentage of normal transacation is 99.82725143693798
percentage of fraud transacation 0.1727485630620034
- Hence in data there is only 0.17 % are the fraud transcation while 99.83 are valid transcation
- So now we have to do resampling of this data
- before doing resampling lets have look at the amount related to valid transcation and fraud transcation
Fraud_transacation = data[data["Class"]==1]
Normal_transacation= data[data["Class"]==0]
plt.figure(figsize=(10,6))
plt.subplot(121)
Fraud_transacation.Amount.plot.hist(title="Fraud Transacation")
plt.subplot(122)
Normal_transacation.Amount.plot.hist(title="Normal Transaction")
<matplotlib.axes._subplots.AxesSubplot at 0x7f6da691cf60>

# the distribution for Normal transction is not clear and it seams that all transaction are less than 2.5 K
# So plot graph for same
Fraud_transacation = data[data["Class"]==1]
Normal_transacation= data[data["Class"]==0]
plt.figure(figsize=(10,6))
plt.subplot(121)
Fraud_transacation[Fraud_transacation["Amount"]<= 2500].Amount.plot.hist(title="Fraud Tranascation")
plt.subplot(122)
Normal_transacation[Normal_transacation["Amount"]<=2500].Amount.plot.hist(title="Normal Transaction")
<matplotlib.axes._subplots.AxesSubplot at 0x7f6d98ecb0f0>

- Here now after exploring data we can say there is no pattern in data
- Now lets start with resmapling of data
ReSampling - Under Sampling
Before re sampling lets have look at the different accuracy matrices
Accuracy = TP+TN/Total
Precison = TP/(TP+FP)
Recall = TP/(TP+FN)
TP = True possitive means no of possitve cases which are predicted possitive
TN = True negative means no of negative cases which are predicted negative
FP = False possitve means no of negative cases which are predicted possitive
FN= False Negative means no of possitive cases which are predicted negative
Now for our case recall will be a better option because in these case no of normal transacations will be very high than the no of fraud cases and sometime a fraud case will be predicted as normal. So, recall will give us a sense of only fraud cases
Resampling
in this we will resample our data with different size
then we will try to use this resampled data to train our model
then we will use this model to predict for our original data
# for undersampling we need a portion of majority class and will take whole data of minority class
# count fraud transaction is the total number of fraud transaction
# now lets us see the index of fraud cases
fraud_indices= np.array(data[data.Class==1].index)
normal_indices = np.array(data[data.Class==0].index)
#now let us a define a function for make undersample data with different proportion
#different proportion means with different proportion of normal classes of data
def undersample(normal_indices,fraud_indices,times):#times denote the normal data = times*fraud data
Normal_indices_undersample = np.array(np.random.choice(normal_indices,(times*Count_Fraud_transacation),replace=False)) #和上面例子是一样的!!!
undersample_data= np.concatenate([fraud_indices,Normal_indices_undersample])
undersample_data = data.iloc[undersample_data,:] print("the normal transacation proportion is :",len(undersample_data[undersample_data.Class==0])/len(undersample_data[undersample_data.Class]))
print("the fraud transacation proportion is :",len(undersample_data[undersample_data.Class==1])/len(undersample_data[undersample_data.Class]))
print("total number of record in resampled data is:",len(undersample_data[undersample_data.Class]))
return(undersample_data)
## first make a model function for modeling with confusion matrix
def model(model,features_train,features_test,labels_train,labels_test):
clf= model
clf.fit(features_train,labels_train.values.ravel())
pred=clf.predict(features_test)
cnf_matrix=confusion_matrix(labels_test,pred)
print("the recall for this model is :",cnf_matrix[1,1]/(cnf_matrix[1,1]+cnf_matrix[1,0]))
fig= plt.figure(figsize=(6,3))# to plot the graph
print("TP",cnf_matrix[1,1,]) # no of fraud transaction which are predicted fraud
print("TN",cnf_matrix[0,0]) # no. of normal transaction which are predited normal
print("FP",cnf_matrix[0,1]) # no of normal transaction which are predicted fraud
print("FN",cnf_matrix[1,0]) # no of fraud Transaction which are predicted normal
sns.heatmap(cnf_matrix,cmap="coolwarm_r",annot=True,linewidths=0.5)
plt.title("Confusion_matrix")
plt.xlabel("Predicted_class")
plt.ylabel("Real class")
plt.show()
print("\n----------Classification Report------------------------------------")
print(classification_report(labels_test,pred))
def data_prepration(x): # preparing data for training and testing as we are going to use different data
#again and again so make a function
x_features= x.ix[:,x.columns != "Class"]
x_labels=x.ix[:,x.columns=="Class"]
x_features_train,x_features_test,x_labels_train,x_labels_test = train_test_split(x_features,x_labels,test_size=0.3) #30%用于测试
print("length of training data")
print(len(x_features_train))
print("length of test data")
print(len(x_features_test))
return(x_features_train,x_features_test,x_labels_train,x_labels_test)
# before starting we should standridze our ampount column
data["Normalized Amount"] = StandardScaler().fit_transform(data['Amount'].reshape(-1, 1))
data.drop(["Time","Amount"],axis=1,inplace=True)
data.head()
| V1 | V2 | V3 | V4 | V5 | V6 | V7 | V8 | V9 | V10 | ... | V21 | V22 | V23 | V24 | V25 | V26 | V27 | V28 | Class | Normalized Amount | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | -1.359807 | -0.072781 | 2.536347 | 1.378155 | -0.338321 | 0.462388 | 0.239599 | 0.098698 | 0.363787 | 0.090794 | ... | -0.018307 | 0.277838 | -0.110474 | 0.066928 | 0.128539 | -0.189115 | 0.133558 | -0.021053 | 0 | 0.244964 |
| 1 | 1.191857 | 0.266151 | 0.166480 | 0.448154 | 0.060018 | -0.082361 | -0.078803 | 0.085102 | -0.255425 | -0.166974 | ... | -0.225775 | -0.638672 | 0.101288 | -0.339846 | 0.167170 | 0.125895 | -0.008983 | 0.014724 | 0 | -0.342475 |
| 2 | -1.358354 | -1.340163 | 1.773209 | 0.379780 | -0.503198 | 1.800499 | 0.791461 | 0.247676 | -1.514654 | 0.207643 | ... | 0.247998 | 0.771679 | 0.909412 | -0.689281 | -0.327642 | -0.139097 | -0.055353 | -0.059752 | 0 | 1.160686 |
| 3 | -0.966272 | -0.185226 | 1.792993 | -0.863291 | -0.010309 | 1.247203 | 0.237609 | 0.377436 | -1.387024 | -0.054952 | ... | -0.108300 | 0.005274 | -0.190321 | -1.175575 | 0.647376 | -0.221929 | 0.062723 | 0.061458 | 0 | 0.140534 |
| 4 | -1.158233 | 0.877737 | 1.548718 | 0.403034 | -0.407193 | 0.095921 | 0.592941 | -0.270533 | 0.817739 | 0.753074 | ... | -0.009431 | 0.798278 | -0.137458 | 0.141267 | -0.206010 | 0.502292 | 0.219422 | 0.215153 | 0 | -0.073403 |
5 rows × 30 columns
Logistic Regression with Undersample Data
# Now make undersample data with differnt portion
# here i will take normal trasaction in 0..5 %, 0.66% and 0.75 % proportion of total data now do this for
for i in range(1,4):
print("the undersample data for {} proportion".format(i))
print()
Undersample_data = undersample(normal_indices,fraud_indices,i)
print("------------------------------------------------------------")
print()
print("the model classification for {} proportion".format(i))
print()
undersample_features_train,undersample_features_test,undersample_labels_train,undersample_labels_test=data_prepration(Undersample_data)
print()
clf=LogisticRegression()
model(clf,undersample_features_train,undersample_features_test,undersample_labels_train,undersample_labels_test)
print("________________________________________________________________________________________________________") # here 1st proportion conatain 50% normal transaction
#Proportion 2nd contains 66% noraml transaction
#proportion 3rd contains 75 % normal transaction
the undersample data for 1 proportion the normal transacation proportion is : 0.5
the fraud transacation proportion is : 0.5
total number of record in resampled data is: 984
------------------------------------------------------------ the model classification for 1 proportion length of training data
688
length of test data
296 the recall for this model is : 0.897260273973
TP 131
TN 147
FP 3
FN 15

----------Classification Report------------------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 0.91 0.98 0.94 150
1 0.98 0.90 0.94 146 #测试集上???咋会这么高!!! avg / total 0.94 0.94 0.94 296 ________________________________________________________________________________________________________
the undersample data for 2 proportion the normal transacation proportion is : 0.6666666666666666
the fraud transacation proportion is : 0.3333333333333333
total number of record in resampled data is: 1476
------------------------------------------------------------ the model classification for 2 proportion length of training data
1033
length of test data
443 the recall for this model is : 0.929078014184
TP 131
TN 296
FP 6
FN 10

----------Classification Report------------------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 0.97 0.98 0.97 302
1 0.96 0.93 0.94 141 avg / total 0.96 0.96 0.96 443 ________________________________________________________________________________________________________
the undersample data for 3 proportion the normal transacation proportion is : 0.75
the fraud transacation proportion is : 0.25
total number of record in resampled data is: 1968
------------------------------------------------------------ the model classification for 3 proportion length of training data
1377
length of test data
591 the recall for this model is : 0.892086330935
TP 124
TN 446
FP 6
FN 15

----------Classification Report------------------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 0.97 0.99 0.98 452
1 0.95 0.89 0.92 139 avg / total 0.96 0.96 0.96 591 ________________________________________________________________________________________________________
- As the number of normal transaction is increasing the recall for fraud transcation is decreasing
- TP = no of fraud transaction which are predicted fraud
- TN = no. of normal transaction which are predicted normal
- FP = no of normal transaction which are predicted fraud
- FN =no of fraud Transaction which are predicted normal
#let us train this model using undersample data and test for the whole data test set #用欠采样训练的模型来预测全量数据集
for i in range(1,4):
print("the undersample data for {} proportion".format(i))
print()
Undersample_data = undersample(normal_indices,fraud_indices,i)
print("------------------------------------------------------------")
print()
print("the model classification for {} proportion".format(i))
print()
undersample_features_train,undersample_features_test,undersample_labels_train,undersample_labels_test=data_prepration(Undersample_data)
data_features_train,data_features_test,data_labels_train,data_labels_test=data_prepration(data)
#the partion for whole data
print()
clf=LogisticRegression()
model(clf,undersample_features_train,data_features_test,undersample_labels_train,data_labels_test)
# here training for the undersample data but tatsing for whole data
print("_________________________________________________________________________________________")
the undersample data for 1 proportion the normal transacation proportion is : 0.5
the fraud transacation proportion is : 0.5
total number of record in resampled data is: 984
------------------------------------------------------------ the model classification for 1 proportion length of training data
688
length of test data
296
length of training data
199364
length of test data
85443 the recall for this model is : 0.923076923077
TP 132
TN 81568
FP 3732
FN 11

----------Classification Report------------------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 1.00 0.96 0.98 85300
1 0.03 0.92 0.07 143 #果然是预测全量数据不好!!! avg / total 1.00 0.96 0.98 85443 _________________________________________________________________________________________
the undersample data for 2 proportion the normal transacation proportion is : 0.6666666666666666
the fraud transacation proportion is : 0.3333333333333333
total number of record in resampled data is: 1476
------------------------------------------------------------ the model classification for 2 proportion length of training data
1033
length of test data
443
length of training data
199364
length of test data
85443 the recall for this model is : 0.913333333333
TP 137
TN 84232
FP 1061
FN 13

----------Classification Report------------------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 1.00 0.99 0.99 85293
1 0.11 0.91 0.20 150 avg / total 1.00 0.99 0.99 85443 _________________________________________________________________________________________
the undersample data for 3 proportion the normal transacation proportion is : 0.75
the fraud transacation proportion is : 0.25
total number of record in resampled data is: 1968
------------------------------------------------------------ the model classification for 3 proportion length of training data
1377
length of test data
591
length of training data
199364
length of test data
85443 the recall for this model is : 0.894366197183
TP 127
TN 84750
FP 551
FN 15

----------Classification Report------------------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 1.00 0.99 1.00 85301
1 0.19 0.89 0.31 142 avg / total 1.00 0.99 1.00 85443 _________________________________________________________________________________________
Here we can see it is following same recall pattern as it was for under sample data that's sounds good but if we have look at the precision is very less
So we should built a model which is correct overall
Precision is less means we are predicting other class wrong like as for our third part there were 953 transaction are predicted fraud it means we and recall is good then it means we are catching fraud transaction very well but we are catching innocent transaction also i.e which are not fraud.
So with recall our precision should be better
if we go by this model then we are going to put 953 innocents in jail with the all criminal who have actually done this
- Hence we are mainly lacking in the precision how can we increase our precision
- Don't get confuse with above output showing that the two training data and two test data first one is for undersample data while another one is for our whole data
1.Try with SVM and then Random Forest in same Manner
- from Random forest we can get which features are more important
SVM with Undersample data
for i in range(1,4):
print("the undersample data for {} proportion".format(i))
print()
Undersample_data = undersample(normal_indices,fraud_indices,i)
print("------------------------------------------------------------")
print()
print("the model classification for {} proportion".format(i))
print()
undersample_features_train,undersample_features_test,undersample_labels_train,undersample_labels_test=data_prepration(Undersample_data)
print()
clf= SVC()# here we are just changing classifier
model(clf,undersample_features_train,undersample_features_test,undersample_labels_train,undersample_labels_test)
print("________________________________________________________________________________________________________")
the undersample data for 1 proportion the normal transacation proportion is : 0.5
the fraud transacation proportion is : 0.5
total number of record in resampled data is: 984
------------------------------------------------------------ the model classification for 1 proportion length of training data
688
length of test data
296 the recall for this model is : 0.933734939759
TP 155
TN 117
FP 13
FN 11

----------Classification Report------------------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 0.91 0.90 0.91 130
1 0.92 0.93 0.93 166 avg / total 0.92 0.92 0.92 296 ________________________________________________________________________________________________________
the undersample data for 2 proportion the normal transacation proportion is : 0.6666666666666666
the fraud transacation proportion is : 0.3333333333333333
total number of record in resampled data is: 1476
------------------------------------------------------------ the model classification for 2 proportion length of training data
1033
length of test data
443 the recall for this model is : 0.923076923077
TP 120
TN 302
FP 11
FN 10

----------Classification Report------------------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 0.97 0.96 0.97 313
1 0.92 0.92 0.92 130 avg / total 0.95 0.95 0.95 443 ________________________________________________________________________________________________________
the undersample data for 3 proportion the normal transacation proportion is : 0.75
the fraud transacation proportion is : 0.25
total number of record in resampled data is: 1968
------------------------------------------------------------ the model classification for 3 proportion length of training data
1377
length of test data
591 the recall for this model is : 0.858974358974
TP 134
TN 428
FP 7
FN 22

----------Classification Report------------------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 0.95 0.98 0.97 435
1 0.95 0.86 0.90 156 avg / total 0.95 0.95 0.95 591 ________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Here recall and precision are approximately equal to Logistic Regression
Lets try for whole data
#let us train this model using undersample data and test for the whole data test set
for i in range(1,4):
print("the undersample data for {} proportion".format(i))
print()
Undersample_data = undersample(normal_indices,fraud_indices,i)
print("------------------------------------------------------------")
print()
print("the model classification for {} proportion".format(i))
print()
undersample_features_train,undersample_features_test,undersample_labels_train,undersample_labels_test=data_prepration(Undersample_data)
data_features_train,data_features_test,data_labels_train,data_labels_test=data_prepration(data)
#the partion for whole data
print()
clf=SVC()
model(clf,undersample_features_train,data_features_test,undersample_labels_train,data_labels_test)
# here training for the undersample data but tatsing for whole data
print("_________________________________________________________________________________________")
the undersample data for 1 proportion the normal transacation proportion is : 0.5
the fraud transacation proportion is : 0.5
total number of record in resampled data is: 984
------------------------------------------------------------ the model classification for 1 proportion length of training data
688
length of test data
296
length of training data
199364
length of test data
85443 the recall for this model is : 0.941176470588
TP 128
TN 81207
FP 4100
FN 8

----------Classification Report------------------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 1.00 0.95 0.98 85307
1 0.03 0.94 0.06 136 avg / total 1.00 0.95 0.97 85443 _________________________________________________________________________________________
the undersample data for 2 proportion the normal transacation proportion is : 0.6666666666666666
the fraud transacation proportion is : 0.3333333333333333
total number of record in resampled data is: 1476
------------------------------------------------------------ the model classification for 2 proportion length of training data
1033
length of test data
443
length of training data
199364
length of test data
85443 the recall for this model is : 0.922580645161
TP 143
TN 82552
FP 2736
FN 12

----------Classification Report------------------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 1.00 0.97 0.98 85288
1 0.05 0.92 0.09 155 avg / total 1.00 0.97 0.98 85443 _________________________________________________________________________________________
the undersample data for 3 proportion the normal transacation proportion is : 0.75
the fraud transacation proportion is : 0.25
total number of record in resampled data is: 1968
------------------------------------------------------------ the model classification for 3 proportion length of training data
1377
length of test data
591
length of training data
199364
length of test data
85443 the recall for this model is : 0.888888888889
TP 136
TN 83261
FP 2029
FN 17

----------Classification Report------------------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 1.00 0.98 0.99 85290
1 0.06 0.89 0.12 153 avg / total 1.00 0.98 0.99 85443 _________________________________________________________________________________________
- A better recall but precision is not improving much
2 .so to improve precision we must have to tune the hyper parameter of these models
3 That I will do in next version
4 For now lets try with my favorite Random Forest classifier
# Random Forest Classifier with undersample data only
for i in range(1,4):
print("the undersample data for {} proportion".format(i))
print()
Undersample_data = undersample(normal_indices,fraud_indices,i)
print("------------------------------------------------------------")
print()
print("the model classification for {} proportion".format(i))
print()
undersample_features_train,undersample_features_test,undersample_labels_train,undersample_labels_test=data_prepration(Undersample_data)
print()
clf= RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100)# here we are just changing classifier
model(clf,undersample_features_train,undersample_features_test,undersample_labels_train,undersample_labels_test)
print("________________________________________________________________________________________________________")
the undersample data for 1 proportion the normal transacation proportion is : 0.5
the fraud transacation proportion is : 0.5
total number of record in resampled data is: 984
------------------------------------------------------------ the model classification for 1 proportion length of training data
688
length of test data
296 the recall for this model is : 0.858064516129
TP 133
TN 139
FP 2
FN 22

----------Classification Report------------------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 0.86 0.99 0.92 141
1 0.99 0.86 0.92 155 avg / total 0.93 0.92 0.92 296 ________________________________________________________________________________________________________
the undersample data for 2 proportion the normal transacation proportion is : 0.6666666666666666
the fraud transacation proportion is : 0.3333333333333333
total number of record in resampled data is: 1476
------------------------------------------------------------ the model classification for 2 proportion length of training data
1033
length of test data
443 the recall for this model is : 0.890410958904
TP 130
TN 294
FP 3
FN 16

----------Classification Report------------------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 0.95 0.99 0.97 297
1 0.98 0.89 0.93 146 avg / total 0.96 0.96 0.96 443 ________________________________________________________________________________________________________
the undersample data for 3 proportion the normal transacation proportion is : 0.75
the fraud transacation proportion is : 0.25
total number of record in resampled data is: 1968
------------------------------------------------------------ the model classification for 3 proportion length of training data
1377
length of test data
591 the recall for this model is : 0.863636363636
TP 133
TN 436
FP 1
FN 21

----------Classification Report------------------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 0.95 1.00 0.98 437
1 0.99 0.86 0.92 154 avg / total 0.96 0.96 0.96 591 ________________________________________________________________________________________________________
#let us train this model using undersample data and test for the whole data test set
for i in range(1,4):
print("the undersample data for {} proportion".format(i))
print()
Undersample_data = undersample(normal_indices,fraud_indices,i)
print("------------------------------------------------------------")
print()
print("the model classification for {} proportion".format(i))
print()
undersample_features_train,undersample_features_test,undersample_labels_train,undersample_labels_test=data_prepration(Undersample_data)
data_features_train,data_features_test,data_labels_train,data_labels_test=data_prepration(data)
#the partion for whole data
print()
clf=RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100)
model(clf,undersample_features_train,data_features_test,undersample_labels_train,data_labels_test)
# here training for the undersample data but tatsing for whole data
print("_________________________________________________________________________________________")
the undersample data for 1 proportion the normal transacation proportion is : 0.5
the fraud transacation proportion is : 0.5
total number of record in resampled data is: 984
------------------------------------------------------------ the model classification for 1 proportion length of training data
688
length of test data
296
length of training data
199364
length of test data
85443 the recall for this model is : 0.971631205674
TP 137
TN 83064
FP 2238
FN 4

----------Classification Report------------------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 1.00 0.97 0.99 85302
1 0.06 0.97 0.11 141 avg / total 1.00 0.97 0.99 85443 _________________________________________________________________________________________
the undersample data for 2 proportion the normal transacation proportion is : 0.6666666666666666
the fraud transacation proportion is : 0.3333333333333333
total number of record in resampled data is: 1476
------------------------------------------------------------ the model classification for 2 proportion length of training data
1033
length of test data
443
length of training data
199364
length of test data
85443 the recall for this model is : 0.967320261438
TP 148
TN 84448
FP 842
FN 5

----------Classification Report------------------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 1.00 0.99 1.00 85290
1 0.15 0.97 0.26 153 avg / total 1.00 0.99 0.99 85443 _________________________________________________________________________________________
the undersample data for 3 proportion the normal transacation proportion is : 0.75
the fraud transacation proportion is : 0.25
total number of record in resampled data is: 1968
------------------------------------------------------------ the model classification for 3 proportion length of training data
1377
length of test data
591
length of training data
199364
length of test data
85443 the recall for this model is : 0.967948717949
TP 151
TN 84964
FP 323
FN 5

----------Classification Report------------------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 1.00 1.00 1.00 85287
1 0.32 0.97 0.48 156 avg / total 1.00 1.00 1.00 85443 _________________________________________________________________________________________
for the third proportion the precision is 0.33 which is better than others
Lets try to get only import features using Random Forest Classifier
After it i will do analysis only for one portion that is 0.5 %
featimp = pd.Series(clf.feature_importances_,index=data_features_train.columns).sort_values(ascending=False)
print(featimp) # this is the property of Random Forest classifier that it provide us the importance
# of the features use
V14 0.206364
V10 0.134424
V11 0.098375
V12 0.097194
V17 0.088706
V4 0.075658
V3 0.071006
V16 0.034599
V2 0.020407
V18 0.019018
V7 0.017165
V21 0.014312
V27 0.011712
V19 0.011044
V8 0.010244
V1 0.008564
Normalized Amount 0.007908
V9 0.007183
V20 0.007094
V15 0.006852
V26 0.006653
V5 0.006597
V22 0.006507
V13 0.005839
V24 0.005519
V28 0.005390
V6 0.005303
V25 0.005210
V23 0.005154
dtype: float64
we can see this is showing the importance of feature for the making decision
V14 is having a very good importance compare to other features
Lets use only top 5 (V14,V10,V12,V17,V4) feature to predict using Random forest classifier only for 0.5 % 特征选择使用top 5特征
# make a new data with only class and V14
data1=data[["V14","V10","V12","V17","V4","Class"]]
data1.head()
| V14 | V10 | V12 | V17 | V4 | Class | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | -0.311169 | 0.090794 | -0.617801 | 0.207971 | 1.378155 | 0 |
| 1 | -0.143772 | -0.166974 | 1.065235 | -0.114805 | 0.448154 | 0 |
| 2 | -0.165946 | 0.207643 | 0.066084 | 1.109969 | 0.379780 | 0 |
| 3 | -0.287924 | -0.054952 | 0.178228 | -0.684093 | -0.863291 | 0 |
| 4 | -1.119670 | 0.753074 | 0.538196 | -0.237033 | 0.403034 | 0 |
Undersample_data1 = undersample(normal_indices,fraud_indices,1)
#only for 50 % proportion it means normal transaction and fraud transaction are equal so passing
Undersample_data1_features_train,Undersample_data1_features_test,Undersample_data1_labels_train,Undersample_data1_labels_test = data_prepration(Undersample_data1)
the normal transacation proportion is : 0.5
the fraud transacation proportion is : 0.5
total number of record in resampled data is: 984
length of training data
688
length of test data
296
clf= RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100)
model(clf,Undersample_data1_features_train,Undersample_data1_features_test,Undersample_data1_labels_train,Undersample_data1_labels_test)
the recall for this model is : 0.93006993007
TP 133
TN 149
FP 4
FN 10

----------Classification Report------------------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 0.94 0.97 0.96 153
1 0.97 0.93 0.95 143 avg / total 0.95 0.95 0.95 296
Over Sampling
In my previous version I got the 100 recall and 98 % precision by using Random forest with the over sampled data but in real it was due to over fitting because i was taking whole fraud data and was training for that and I was doing the testing on the same data.
Please find link of previous version for more understanding Link
- Thanks to Mr. Dominik Stuerzer for help
# now we will divied our data sets into two part and we will train and test and will oversample the train data and predict for test data
# lets import data again
data = pd.read_csv("../input/creditcard.csv",header = 0)
print("length of training data",len(data))
print("length of normal data",len(data[data["Class"]==0]))
print("length of fraud data",len(data[data["Class"]==1]))
length of training data 284807
length of normal data 284315
length of fraud data 492
data_train_X,data_test_X,data_train_y,data_test_y=data_prepration(data)
data_train_X.columns
data_train_y.columns
length of training data
199364
length of test data
85443
Index(['Class'], dtype='object')
# ok Now we have a traing data
data_train_X["Class"]= data_train_y["Class"] # combining class with original data
data_train = data_train_X.copy() # for naming conevntion
print("length of training data",len(data_train))
# Now make data set of normal transction from train data
normal_data = data_train[data_train["Class"]==0]
print("length of normal data",len(normal_data))
fraud_data = data_train[data_train["Class"]==1]
print("length of fraud data",len(fraud_data))
length of training data 199364
length of normal data 199009
length of fraud data 355
# Now start oversamoling of training data
# means we will duplicate many times the value of fraud data #直接复制365份!!!
for i in range (365): # the number is choosen by myself on basis of nnumber of fraud transaction
normal_data= normal_data.append(fraud_data)
os_data = normal_data.copy()
print("length of oversampled data is ",len(os_data))
print("Number of normal transcation in oversampled data",len(os_data[os_data["Class"]==0]))
print("No.of fraud transcation",len(os_data[os_data["Class"]==1]))
print("Proportion of Normal data in oversampled data is ",len(os_data[os_data["Class"]==0])/len(os_data))
print("Proportion of fraud data in oversampled data is ",len(os_data[os_data["Class"]==1])/len(os_data))
length of oversampled data is 328584
Number of normal transcation in oversampled data 199009
No.of fraud transcation 129575
Proportion of Normal data in oversampled data is 0.6056563922771651
Proportion of fraud data in oversampled data is 0.39434360772283494
- The proportion now becomes the 60 % and 40 % that is good now
# before applying any model standerdize our data amount
os_data["Normalized Amount"] = StandardScaler().fit_transform(os_data['Amount'].reshape(-1, 1))
os_data.drop(["Time","Amount"],axis=1,inplace=True) 其实随机森林对特征是否标准化无感,但是svm和LR就非常非常关键了
os_data.head()
| V1 | V2 | V3 | V4 | V5 | V6 | V7 | V8 | V9 | V10 | ... | V21 | V22 | V23 | V24 | V25 | V26 | V27 | V28 | Class | Normalized Amount | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 82656 | 1.356574 | -1.535896 | 1.014585 | -0.980949 | -1.840651 | 0.495094 | -1.535552 | 0.235415 | -0.847601 | 1.180545 | ... | -0.578444 | -0.948479 | 0.038288 | -0.051798 | 0.350549 | -0.338308 | 0.073518 | 0.017247 | 0 | -0.240655 |
| 202761 | 0.078384 | 0.693709 | -0.282273 | -1.007720 | 1.058216 | -0.035670 | 0.838345 | 0.070423 | -0.094317 | -0.221217 | ... | -0.303203 | -0.775385 | -0.086534 | -1.414806 | -0.360046 | 0.208073 | 0.234031 | 0.072388 | 0 | -0.371265 |
| 85985 | -3.549282 | -3.403880 | 2.389801 | 1.080311 | 1.683676 | -1.100104 | -0.699287 | 0.171644 | 0.935805 | -0.256182 | ... | -0.284722 | 0.428109 | 2.844650 | 0.006528 | 0.466552 | 0.421108 | 0.260494 | -0.472237 | 0 | -0.383217 |
| 215180 | 2.084961 | 0.009129 | -3.842413 | -0.551511 | 3.139773 | 2.743495 | 0.130580 | 0.552759 | -0.030368 | -0.295843 | ... | 0.034740 | 0.187883 | -0.014668 | 0.682901 | 0.410981 | 0.734260 | -0.081080 | -0.064606 | 0 | -0.374769 |
| 75855 | 1.193268 | -0.071682 | 0.611175 | -0.232721 | -0.478724 | -0.216029 | -0.329775 | 0.071921 | 0.009225 | -0.112748 | ... | -0.043944 | -0.080370 | 0.101692 | 0.090155 | 0.041104 | 0.914386 | -0.053130 | -0.002135 | 0 | -0.388278 |
5 rows × 30 columns
# Now use this oversampled data for trainig the model and predict value for the test data that we created before
# now let us try within the the oversampled data itself
# for that we need to split our oversampled data into train and test
# so call our function data Prepration with oversampled data
os_train_X,os_test_X,os_train_y,os_test_y=data_prepration(os_data)
clf= RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100)
model(clf,os_train_X,os_test_X,os_train_y,os_test_y)
length of training data
230008
length of test data
98576
the recall for this model is : 1.0
TP 38975
TN 59596
FP 5
FN 0

----------Classification Report------------------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 1.00 1.00 1.00 59601
1 1.00 1.00 1.00 38975 avg / total 1.00 1.00 1.00 98576
Observations
- As it have too many sample of same fraud data so may be the all which are present in train data are present in test data also so we can say it is over fitting #重复样本太多,过拟合严重
- So lets try with test data that one which we created in starting of oversampling segment no fraud transaction from that data have been repeated here #在过采样前先拿出一点数据出来做测试,而不是过采样之后!!!
- Lets try
# now take all over sampled data as trainging and test it for test data
os_data_X = os_data.ix[:,os_data.columns != "Class"]
os_data_y = os_data.ix[:,os_data.columns == "Class"]
#for that we have to standrdize the normal amount and drop the time from it
data_test_X["Normalized Amount"] = StandardScaler().fit_transform(data_test_X['Amount'].reshape(-1, 1))
data_test_X.drop(["Time","Amount"],axis=1,inplace=True)
data_test_X.head()
| V1 | V2 | V3 | V4 | V5 | V6 | V7 | V8 | V9 | V10 | ... | V20 | V21 | V22 | V23 | V24 | V25 | V26 | V27 | V28 | Normalized Amount | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11514 | 1.451038 | -0.603389 | 0.007125 | -0.616909 | -0.260790 | 0.474328 | -0.826944 | 0.042607 | 1.101926 | 0.110945 | ... | -0.054708 | -0.249080 | -0.389480 | -0.151185 | -1.380077 | 0.610950 | -0.163068 | -0.005513 | -0.013058 | -0.320476 |
| 162269 | -6.697569 | 4.179960 | -4.866476 | -0.626586 | -3.024024 | -1.324855 | -0.835983 | 2.692196 | 1.844012 | 2.825418 | ... | 0.649757 | 0.035932 | 0.852066 | 0.245004 | 1.155756 | 0.098178 | -0.214949 | 0.996161 | 1.252345 | 0.050478 |
| 158202 | 2.104037 | 0.065442 | -1.428655 | 0.323540 | 0.393572 | -0.720375 | 0.054806 | -0.347347 | 2.082360 | -0.464191 | ... | -0.271997 | 0.093486 | 0.657963 | -0.007259 | 0.431328 | 0.360900 | -0.474799 | -0.024631 | -0.056532 | -0.357576 |
| 203014 | -2.602873 | -1.593223 | 0.029747 | -3.264885 | 1.156256 | 0.930955 | -0.477817 | 0.828043 | -0.543710 | -0.592860 | ... | -1.154639 | -0.680829 | -1.305820 | 0.841971 | -1.009959 | -0.495993 | 0.056765 | -0.434924 | 0.375225 | -0.176200 |
| 129141 | -1.325968 | 1.418993 | -0.531978 | -1.422122 | 2.635501 | 3.223994 | 0.477654 | 0.538505 | 0.756693 | 1.527077 | ... | 0.941600 | -0.599390 | -1.053070 | -0.004289 | 0.917391 | 0.221693 | 0.059054 | 0.459664 | -0.018905 | -0.324681 |
5 rows × 29 columns
# now use it for modeling
clf= RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100)
model(clf,os_data_X,data_test_X,os_data_y,data_test_y)
the recall for this model is : 0.773722627737
TP 106
TN 85300
FP 6
FN 31

----------Classification Report------------------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 1.00 1.00 1.00 85306
1 0.95 0.77 0.85 137 avg / total 1.00 1.00 1.00 85443
Observations
- Now here we can see recall decrease to only 83 % which is not bad but not good also
- The precision is 0.93 which is good
- from these observation we can say that the oversampling is better than the Under sampling because on Under sampling we were loosing a large amount of data or we can say a good amount of information so why the there precision was very low
SMOTE
# Lets Use SMOTE for Sampling
# As I mentioned it is also a type of oversampling but in this the data is not replicated but they are created
#lets start with importing libraries
from imblearn.over_sampling import SMOTE
data = pd.read_csv('../input/creditcard.csv')
os = SMOTE(random_state=0) # We are using SMOTE as the function for oversampling
# now we can devided our data into training and test data
# Call our method data prepration on our dataset
data_train_X,data_test_X,data_train_y,data_test_y=data_prepration(data)
columns = data_train_X.columns
length of training data
199364
length of test data
85443
# now use SMOTE to oversample our train data which have features data_train_X and labels in data_train_y
os_data_X,os_data_y=os.fit_sample(data_train_X,data_train_y)
os_data_X = pd.DataFrame(data=os_data_X,columns=columns )
os_data_y= pd.DataFrame(data=os_data_y,columns=["Class"])
# we can Check the numbers of our data
print("length of oversampled data is ",len(os_data_X))
print("Number of normal transcation in oversampled data",len(os_data_y[os_data_y["Class"]==0]))
print("No.of fraud transcation",len(os_data_y[os_data_y["Class"]==1]))
print("Proportion of Normal data in oversampled data is ",len(os_data_y[os_data_y["Class"]==0])/len(os_data_X))
print("Proportion of fraud data in oversampled data is ",len(os_data_y[os_data_y["Class"]==1])/len(os_data_X))
length of oversampled data is 398078
Number of normal transcation in oversampled data 199039
No.of fraud transcation 199039 # smote后1:1了
Proportion of Normal data in oversampled data is 0.5
Proportion of fraud data in oversampled data is 0.5
By using Smote we are getting a 50 - 50 each
No need of checking here in over sampled data itself from previous we know it will be overfitting
let us check with the test data direct
# Let us first do our amount normalised and other that we are doing above #过采样前一定一定要标准化!!!
os_data_X["Normalized Amount"] = StandardScaler().fit_transform(os_data_X['Amount'].reshape(-1, 1))
os_data_X.drop(["Time","Amount"],axis=1,inplace=True)
data_test_X["Normalized Amount"] = StandardScaler().fit_transform(data_test_X['Amount'].reshape(-1, 1))
data_test_X.drop(["Time","Amount"],axis=1,inplace=True)
# Now start modeling
clf= RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100)
# train data using oversampled data and predict for the test data
model(clf,os_data_X,data_test_X,os_data_y,data_test_y)
the recall for this model is : 0.862275449102
TP 144
TN 85253
FP 23
FN 23

----------Classification Report------------------------------------
precision recall f1-score support 0 1.00 1.00 1.00 85276
1 0.86 0.86 0.86 167 avg / total 1.00 1.00 1.00 85443
observation
- The recall is nearby the previous one done by over sampling
- The precision decrease in this case
综合结论就是:随机森林+过采样(直接复制或者smote后,黑白比例1:3)效果比较好!
from:http://www.dataguru.cn/article-11449-1.html
用Python作信用卡欺诈预测 ——欠采样、效果不好

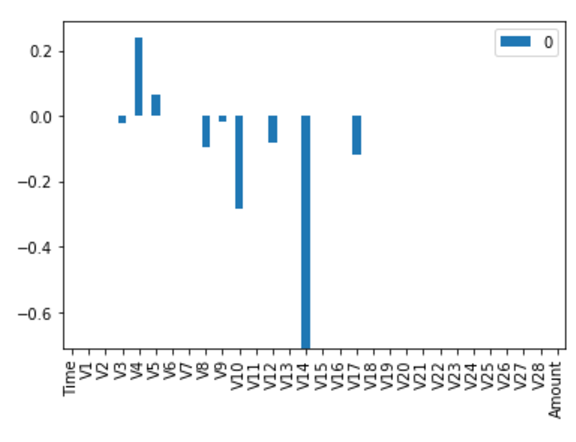
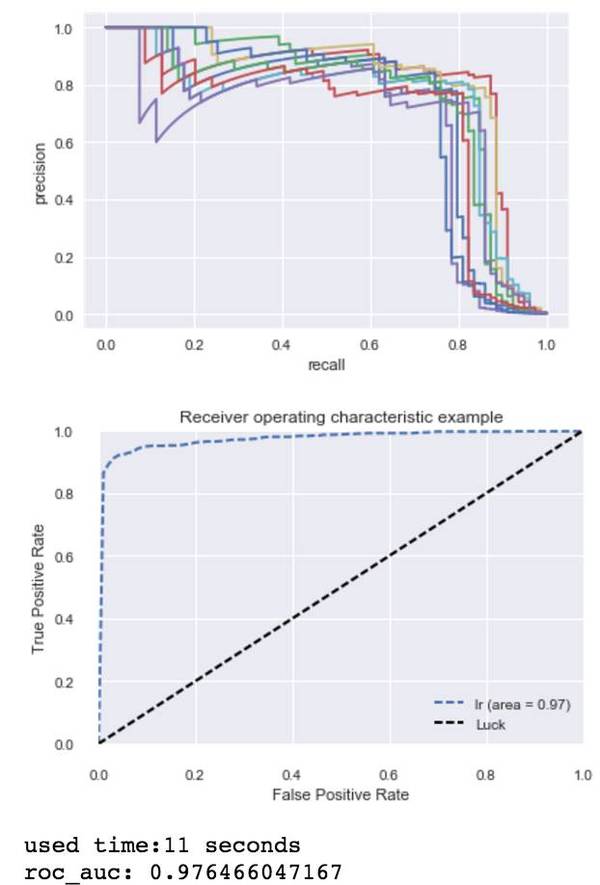


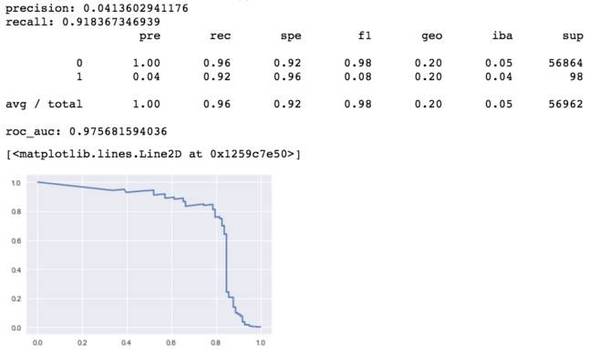
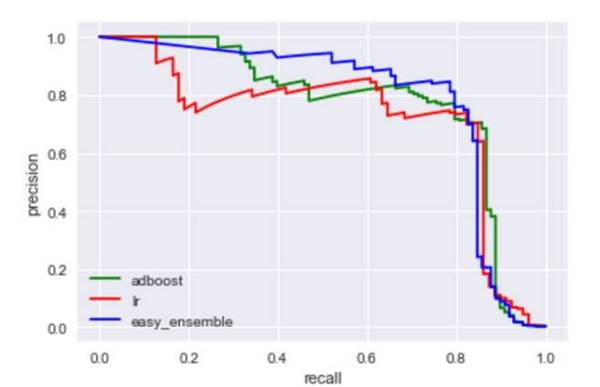
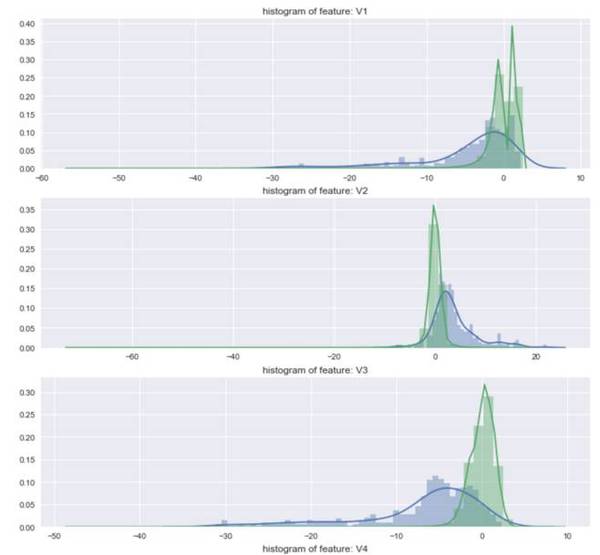

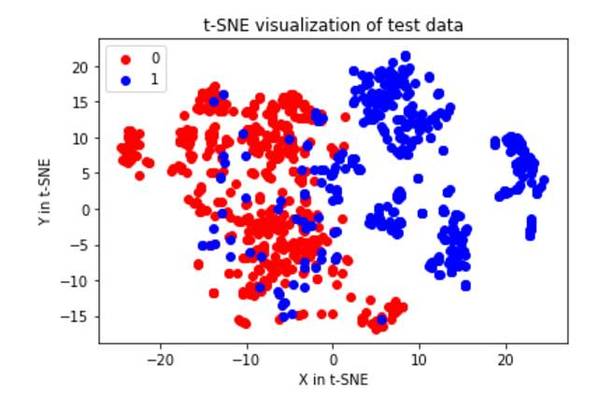
kaggle 欺诈信用卡预测——不平衡训练样本的处理方法 综合结论就是:随机森林+过采样(直接复制或者smote后,黑白比例1:3 or 1:1)效果比较好!记得在smote前一定要先做标准化!!!其实随机森林对特征是否标准化无感,但是svm和LR就非常非常关键了的更多相关文章
- kaggle 欺诈信用卡预测——Smote+LR
from:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/30461746 本项目需解决的问题 本项目通过利用信用卡的历史交易数据,进行机器学习,构建信用卡反欺诈预测模型,提前发现客户信用卡 ...
- 从信用卡欺诈模型看不平衡数据分类(1)数据层面:使用过采样是主流,过采样通常使用smote,或者少数使用数据复制。过采样后模型选择RF、xgboost、神经网络能够取得非常不错的效果。(2)模型层面:使用模型集成,样本不做处理,将各个模型进行特征选择、参数调优后进行集成,通常也能够取得不错的结果。(3)其他方法:偶尔可以使用异常检测技术,IF为主
总结:不平衡数据的分类,(1)数据层面:使用过采样是主流,过采样通常使用smote,或者少数使用数据复制.过采样后模型选择RF.xgboost.神经网络能够取得非常不错的效果.(2)模型层面:使用模型 ...
- Kaggle 自行车租赁预测比赛项目实现
作者:大树 更新时间:01.20 email:59888745@qq.com 数据处理,机器学习 回主目录:2017 年学习记录和总结 .caret, .dropup > .btn > . ...
- Kaggle网站流量预测任务第一名解决方案:从模型到代码详解时序预测
Kaggle网站流量预测任务第一名解决方案:从模型到代码详解时序预测 2017年12月13日 17:39:11 机器之心V 阅读数:5931 近日,Artur Suilin 等人发布了 Kaggl ...
- Spring Cloud实战 | 最八篇:Spring Cloud +Spring Security OAuth2+ Axios前后端分离模式下无感刷新实现JWT续期
一. 前言 记得上一篇Spring Cloud的文章关于如何使JWT失效进行了理论结合代码实践的说明,想当然的以为那篇会是基于Spring Cloud统一认证架构系列的最终篇.但关于JWT另外还有一个 ...
- ASHRAE KAGGLE大能源预测(前三名方案总结+相关知识点讲解+python实现)
@ 目录 1 概述 2 处理思想学习 2.1 移除异常值 2.2 缺失值 2.3 目标函数 2.4 特征工程 2.4.1 Savitzky-Golay filter 2.4.2 Bayesian ta ...
- Kaggle 商品销量预测季军方案出炉,应对时间序列问题有何妙招
https://www.leiphone.com/news/201803/fPnpTdrkvUHf7uAj.html 雷锋网 AI 研习社消息,Kaggle 上 Corporación Favorit ...
- Kaggle竞赛 —— 房价预测 (House Prices)
完整代码见kaggle kernel 或 Github 比赛页面:https://www.kaggle.com/c/house-prices-advanced-regression-technique ...
- 教程 | Kaggle网站流量预测任务第一名解决方案:从模型到代码详解时序预测
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/JwRXBNmXBaQM2GK6BDRqMw 选自GitHub 作者:Artur Suilin 机器之心编译 参与:蒋思源.路雪.黄小天 近日,A ...
随机推荐
- 过年啦!小B高兴的不行了,她收到了很多红包,可以实现好多的愿望呢。小B可是对商店货架上心仪的货物红眼好久了,只因囊中羞涩作罢,这次她可是要大大的shopping一番。小B想去购物时,总是习惯性的把要买的东西列在一个购买清单上,每个物品单独列一行(即便要买多个某种物品),这次也不例外。
include "stdafx.h" #include<iostream> #include<vector> #include <algorithm& ...
- Java深入 - Java 内存分配和回收机制-转
Java的GC机制是自动进行的,和c语言有些区别需要程序员自己保证内存的使用和回收. Java的内存分配和回收也主要在Java的堆上进行的,Java的堆中存储了大量的对象实例,所以Java的堆也叫GC ...
- Java 异常介绍
Java标准库内建了一些通用的异常,这些类以 Throwable 为顶层父类.Throwable又派生出 Error 类和 Exception 类. 错误:Error类以及他的子类的实例,代表了JVM ...
- java并发阻塞队列
Java 并发编程利用 Condition 来实现阻塞队列 You are here: 开发&语言 - Java 文章 发布于 2017年06月26日 阅读 944 并发编程 什么是阻 ...
- CSS改变字体下划线颜色
下图是网页中一个非常普通的列表. watermark/2/text/aHR0cDovL2Jsb2cuY3Nkbi5uZXQvQXVndXMzMzQ0/font/5a6L5L2T/fontsize/40 ...
- Latex中參考文献排序
\bibliographystyle{unsrt}:依照引用的先后排序 \bibliographystyle{plain}:按字母的顺序排列,比較次序为作者.年度和标题.当中作者中姓氏字母优先. 关于 ...
- c#中关于compare比较的一点注意事项
一直没有太注意,今天发现在compare比较两个字符串的时候出了点小问题 如果我设置了两个字符串 一个是“2”,一个是“12” 那么在比较的时候 第一个会大于第二个: 如果第一个是“02”,第二个是“ ...
- random随机模块,time时间模块
random /随机模块: 作用: 在某个范围内取到每一个值得概率是相通的. 一.随机小数 random.random() import random print(random.random()) ...
- 星球大战starwar(并查集)
1015: [JSOI2008]星球大战starwar Time Limit: 3 Sec Memory Limit: 162 MBSubmit: 5253 Solved: 2395[Submit ...
- 牛人blog汇总
1.天一思维: https://blog.csdn.net/tszty1997?t=1
