【HDU】1693:Eat the Trees【插头DP】
Eat the Trees
Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 5079 Accepted Submission(s):
2628
the Ancient), Pudge is a strong hero in the first period of the game. When the
game goes to end however, Pudge is not a strong hero any more.
So Pudge’s
teammates give him a new assignment—Eat the Trees!
The trees are in a
rectangle N * M cells in size and each of the cells either has exactly one tree
or has nothing at all. And what Pudge needs to do is to eat all trees that are
in the cells.
There are several rules Pudge must follow:
I. Pudge must eat
the trees by choosing a circuit and he then will eat all trees that are in the
chosen circuit.
II. The cell that does not contain a tree is unreachable,
e.g. each of the cells that is through the circuit which Pudge chooses must
contain a tree and when the circuit is chosen, the trees which are in the cells
on the circuit will disappear.
III. Pudge may choose one or more circuits to
eat the trees.
Now Pudge has a question, how many ways are there to eat
the trees?
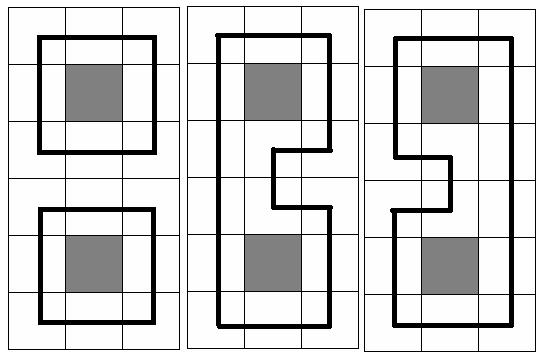
At the picture below three samples are given for N = 6 and M =
3(gray square means no trees in the cell, and the bold black line means the
chosen circuit(s))
line of the input is the number of the cases. There are no more than 10
cases.
For each case, the first line contains the integer numbers N and M,
1<=N, M<=11. Each of the next N lines contains M numbers (either 0 or 1)
separated by a space. Number 0 means a cell which has no trees and number 1
means a cell that has exactly one tree.
ways in one line. It is guaranteed, that it does not exceed 263 – 1.
Use the format in the sample.
6 3
1 1 1
1 0 1
1 1 1
1 1 1
1 0 1
1 1 1
2 4
1 1 1 1
1 1 1 1
Case 2: There are 2 ways to eat the trees.
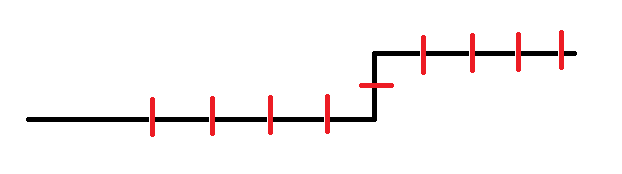
如上图,每根红线代表的是插头DP中状态的每一位,特别的地方就在最后一位,那条横线,表示的是当前格子被更新时左边是否有向右的插头,而当前格子上面的竖线表示上面是否有向下的插头...
这样,插头DP的状态就比普通轮廓线多一位。
这两个位置就是转移的重点。
在当前格子上面有插头或者左边有插头,那么可以转移到当前向右或者向下;如果两个状态同时存在,那么将两个状态合并,不能新增插头;如果两个状态都不存在,并且没有障碍格,那么同时增加两个新插头。
第一列、最后一排、最后一列需要特判。
空间要开足!!!
Code
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
#define LL long long
using namespace std; int n, m, G[][], ti;
LL dp[][( << )]; int main() {
int T;
scanf("%d", &T);
while(T --) {
scanf("%d%d", &n, &m);
for(int i = ; i <= n; i ++)
for(int j = ; j <= m; j ++)
scanf("%d", &G[i][j]);
memset(dp, , sizeof(dp));
int now = ;
dp[now][] = ;
for(int i = ; i <= n; i ++) {
for(int j = ; j <= m; j ++) {
now ^= ;
memset(dp[now], , sizeof(dp[now]));
for(int s = ; s < ( << m + ); s ++) {
int pre = s & ( << m);
int las = s & ;
if(!G[i][j]) {
int ss = (s << );
if(!pre && !las) dp[now][ss] += dp[now ^ ][s];
} else {
if(j != ) {
if(pre && las) {
int ss = (s ^ pre ^ las) << ;
dp[now][ss] += dp[now ^ ][s];
}
if(pre && !las) {
int ss = (s ^ pre) << | ;
if(j != m) dp[now][ss] += dp[now ^ ][s];
ss = (s ^ pre) << | ;
if(i != n) dp[now][ss] += dp[now ^ ][s];
}
if(!pre && las) {
int ss = (s ^ las) << | ;
if(j != m) dp[now][ss] += dp[now ^ ][s];
ss = (s ^ las) << | ;
if(i != n) dp[now][ss] += dp[now ^ ][s];
}
if(!pre && !las) {
int ss = s << | ;
dp[now][ss] += dp[now ^ ][s];
}
} else if(j == && !las) {
if(pre) {
int ss = (s ^ pre) << | ;
if(i != n) dp[now][ss] += dp[now ^ ][s];
ss = (s ^ pre) << | ;
if(j != m) dp[now][ss] += dp[now ^ ][s];
} else {
if(i != n && j != m) {
int ss = s << | ;
dp[now][ss] += dp[now ^ ][s];
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
printf("Case %d: There are %lld ways to eat the trees.\n", ++ti, dp[now][]);
}
}
【HDU】1693:Eat the Trees【插头DP】的更多相关文章
- hdu 1693 Eat the Trees——插头DP
题目:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1693 第一道插头 DP ! 直接用二进制数表示状态即可. #include<cstdio> # ...
- HDU 1693 Eat the Trees(插头DP)
题目链接 USACO 第6章,第一题是一个插头DP,无奈啊.从头看起,看了好久的陈丹琦的论文,表示木看懂... 大体知道思路之后,还是无法实现代码.. 此题是插头DP最最简单的一个,在一个n*m的棋盘 ...
- HDU 1693 Eat the Trees ——插头DP
[题目分析] 吃树. 直接插头DP,算是一道真正的入门题目. 0/1表示有没有插头 [代码] #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #inc ...
- hdu1693 Eat the Trees [插头DP经典例题]
想当初,我听见大佬们谈起插头DP时,觉得插头DP是个神仙的东西. 某大佬:"考场见到插头DP,直接弃疗." 现在,我终于懂了他们为什么这么说了. 因为-- 插头DP很毒瘤! 为什么 ...
- HDU 1693 Eat the Trees(插头DP、棋盘哈密顿回路数)+ URAL 1519 Formula 1(插头DP、棋盘哈密顿单回路数)
插头DP基础题的样子...输入N,M<=11,以及N*M的01矩阵,0(1)表示有(无)障碍物.输出哈密顿回路(可以多回路)方案数... 看了个ppt,画了下图...感觉还是挺有效的... 参考 ...
- HDU - 1693 Eat the Trees(多回路插头DP)
题目大意:要求你将全部非障碍格子都走一遍,形成回路(能够多回路),问有多少种方法 解题思路: 參考基于连通性状态压缩的动态规划问题 - 陈丹琦 下面为代码 #include<cstdio> ...
- HDU 1693 Eat the Trees(插头DP,入门题)
Problem Description Most of us know that in the game called DotA(Defense of the Ancient), Pudge is a ...
- HDU 1693 Eat the Trees (插头DP)
题意:给一个n*m的矩阵,为1时代表空格子,为0时代表障碍格子,问如果不经过障碍格子,可以画一至多个圆的话,有多少种方案?(n<12,m<12) 思路: 这题不需要用到最小表示法以及括号表 ...
- hdu 1693 : Eat the Trees 【插头dp 入门】
题目链接 题意: 给出一个n*m大小的01矩阵,在其中画线连成封闭图形,其中对每一个值为1的方格,线要恰好穿入穿出共两次,对每一个值为0的方格,所画线不能经过. 参考资料: <基于连通性状态压缩 ...
- HDU 1693 Eat the Trees
第一道(可能也是最后一道)插头dp.... 总算是领略了它的魅力... #include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstr ...
随机推荐
- Ubuntu 12.04下LVM2安装和操作实验
实验环境: VirtualBox v4.3.20 Lubuntu 12.04LTS 前期准备: 1.添加虚拟盘:菜单"控制"->"设置"->&quo ...
- 按需引入antd报错问题
1.使用create-react-app工具创建了一个项目 create-react-app antd-demo 2.安装babel-plugin-import npm install babel-p ...
- 你竟然在公钥中下毒!——如何在RSA公钥中添加后门
原文:http://www.hackdig.com/?01/hack-17893.htm 分享到: 当我知道它是如何运行时,我惊得下巴都掉了.这是一个非常简单的手法,但这篇文章会颠覆你之前对RSA的看 ...
- Service(二):通信
课程:http://www.jikexueyuan.com/course/715_3.html?ss=1 在activity和service之间通信. 首先使用的是启动服务来通信.注意是如何使用Int ...
- 如何学习React--[转]
如果你是一个 React (或者前端) 新手, 出于以下的原因, 你可能会对这个生态圈感到困惑: React 的目标群体历来是喜欢尝试新事物的开发者和前端专家. Facebook 只开源了他们在实际使 ...
- Luogu P2310 【loidc,看看海】
各位大佬都用的排序和杨颙大定理,蒟蒻的我怎么也不会做(瑟瑟发抖),那么,就来一发主席树吧.我们知道线段树可以维护区间,平衡树可以维护值域那么,我们可以用线段树套平衡树来解决这个区间值域的问题线段树套平 ...
- C++11之auto和decltype
auto自动类型推断,用于从初始表达式中推断出变量的类型. auto a;// 错误,没有初始化表达式,无法推断出a的类型 autoint a =10;// 错误,auto临时变量的语义在C++ 11 ...
- MIT6.006Lec01:Python实现
MIT6.006是Algo Intro这门课,据说语言使用python Lec01是讲peak finding,也就是峰值点 具体为: 一维情况下一个数组中a[i]>a[i-1]且a[i]> ...
- Jenkins+Ant+Git+Jmeter实现持续集成
个人记录: 基本的配置与Jenkins+Ant+SVN+Jmeter实现持续集成的配置一样,主要在Jenkins的配置上的区别会有所不同 安装的插件: enkins安装好之后,需要为其安装gitlab ...
- centos killall安装
https://blog.csdn.net/joeyon1985/article/details/46707865 https://blog.csdn.net/xupeng874395012/arti ...