Recommend ways to overwrite hashCode() in java
Perface
In the former chapter, I talk about topics about hashCode, And I will continue to finish the introduction to hashCode(). In this chapter, I will recommend several ways to overrwrite hashCode() to facilitate our work
Recommended by the author of "Effective Java"
Ideally, a hash function should distribute any reasonable collection of unequal instances uniformly across all possible hash values. Here is a simple recipe:
1. Store some constant nonzero value, say, 17, in an int variable called result.
2. For each significant field f in your object (each field taken into account by the equals method, that is), do the following:
a. Compute an int hash code c for the field:
i. If the field is a boolean, compute (f ? 1 : 0).
ii. If the field is a byte, char, short, or int, compute (int) f.
iii. If the field is a long, compute (int) (f ^ (f >>> 32)).
iv. If the field is a float, compute Float.floatToIntBits(f).
v. If the field is a double, compute Double.doubleToLongBits(f), and then hash the resulting long as in step 2.a.iii.
vi. If the field is an object reference and this class’s equals method compares the field by recursively invoking equals, recursively invoke hashCode on the field. If a more complex comparison is required, compute a “canonical representation” for this field and invoke hashCode on the canonical representation. If the value of the field is null, return 0.
vii. If the field is an array, treat it as if each element were a separate field. If every element in an array field is significant, you can use one of theArrays.hashCode methods.
b. Combine the hash code c computed in step 1) into result as follows:
result = 31 * result + c;
3. Return result.
Overriding hashCode() and equals() using Apache Commons Lang
Apache commons provide two excellent utility classes for generating hash code and equals methods. Below is its usage:
import org.apache.commons.lang3.builder.EqualsBuilder;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.builder.HashCodeBuilder;
public class Employee
{
private Integer id;
private String firstname;
private String lastName;
private String department;
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getFirstname() {
return firstname;
}
public void setFirstname(String firstname) {
this.firstname = firstname;
}
public String getLastName() {
return lastName;
}
public void setLastName(String lastName) {
this.lastName = lastName;
}
public String getDepartment() {
return department;
}
public void setDepartment(String department) {
this.department = department;
}
@Override
public int hashCode()
{
final int PRIME = 31;
return new HashCodeBuilder(getId()%2==0?getId()+1:getId(), PRIME).
toHashCode();
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == null)
return false;
if (o == this)
return true;
if (o.getClass() != getClass())
return false;
Employee e = (Employee) o;
return new EqualsBuilder().
append(getId(), e.getId()).
isEquals();
}
}
In the official doucment of HashCodeBuilder, it describes as follow:
This class enables a good hashCode method to be built for any class. It follows the rules laid out in the book Effective Java by Joshua Bloch. Writing a good hashCode method is actually quite difficult. This class aims to simplify the process.
The following is the approach taken. When appending a data field, the current total is multiplied by the multiplier then a relevant value for that data type is added. For example, if the current hashCode is 17, and the multiplier is 37, then appending the integer 45 will create a hashcode of 674, namely 17 * 37 + 45.
All relevant fields from the object should be included in the hashCode method. Derived fields may be excluded. In general, any field used in the equals method must be used in the hashCode method.
To use this class write code as follows:
public class Person {
String name;
int age;
boolean smoker;
...
public int hashCode() {
// you pick a hard-coded, randomly chosen, non-zero, odd number
// ideally different for each class
return new HashCodeBuilder(17, 37).
append(name).
append(age).
append(smoker).
toHashCode();
}
}
Automatically generated by eclipse IDE
if you are using any code editor, they also must be capable of generating some good structure for you. For example, Eclipse IDE has option under right click on class >> source > Generate hashCode() and equals() … will generate a very good implementation for you.
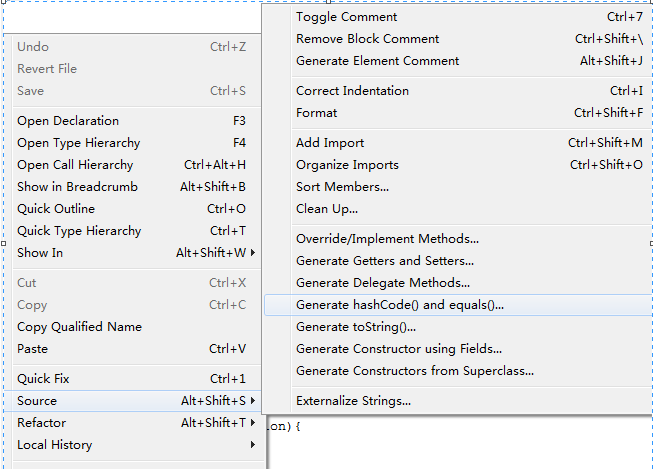
Summary
In general, it is not common to override the hashCode() method, but if we need to do it in practical work, it will be a troublesome experience. To make our work easier and more efficiently, it is a good idea to follow the recommendations in the chapter. But if you want to achieve a higher performance, you'd better to override the method yourself carefully.
References
Working with hashCode and equals methods in java
Recommend ways to overwrite hashCode() in java的更多相关文章
- String的hashcode(java)
hashCode就是我们所说的散列码,使用hashCode算法可以帮助我们进行高效率的查找,例如HashMap,说hashCode之前,先来看看Object类. Java程序中所有类的直接或间接父类, ...
- Java提高篇——equals()与hashCode()方法详解
java.lang.Object类中有两个非常重要的方法: 1 2 public boolean equals(Object obj) public int hashCode() Object类是类继 ...
- 【java基础学习-2--】关于Hashcode()的使用
摘要 Java中equals()和hashCode()有一个契约: 如果两个对象相等的话,它们的hash code必须相等: 但如果两个对象的hash code相等的话,这两个对象不一定相等; 这个约 ...
- Java中hashcode,equals和==
hashcode方法返回该对象的哈希码值. hashCode()方法可以用来来提高Map里面的搜索效率的,Map会根据不同的hashCode()来放在不同的位置,Map在搜索一个对象的时候先通过has ...
- java 覆盖hashCode()深入探讨 代码演示样例
java 翻盖hashCode()深入探讨 代码演示样例 package org.rui.collection2.hashcode; /** * 覆盖hashcode * 设计HashCode时最重要 ...
- JAVA中的各种 哈希码(HashCode) 与 equals方法在HIBERNATE的实际应用[转载]
1.什么是哈希码(HashCode) 在Java中,哈希码代表对象的特征.例如对象 Java代码 String str1 = “aa”, str1.hashCode= 3104 String str2 ...
- JAVA - hashcode与equals作用、关系
Hashcode的作用 总的来说,Java中的集合(Collection)有两类,一类是List,再有一类是Set.前者集合内的元素是有序的,元素可以重复:后者元素无序,但元素不可重复. ...
- Java equals 和 hashcode 方法
问题 面试时经常会问起字符串比较相关的问题, 总结一下,大体是如下几个: 1.字符串比较时用的什么方法,内部实现如何? 2.hashcode的作用,以及重写equal方法,为什么要重写hashcode ...
- 使用hashCode()和equals()方法 - Java
在这篇文章中,我将指出我对hashCode()和equals()方法的理解.我将讨论它们的默认实现以及如何正确地覆盖它们.我还将使用Apache Commons包中的实用工具类来实现这些方法. has ...
随机推荐
- python爬虫从入门到放弃(一)——试用bs4, request爬百度股票
文章实践主要来自于:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/FiKqb06nz0K0AD9VUWJapw 爬虫流程: 明确目的(哪些数据),确认网页可爬,查看源网页是否有需要的数据. b ...
- Flask系列03--Flask的路由 app.route中的参数, 动态参数路由
Flask–路由 添加路由的两种方式 第一种 @app.route("/my_de") def detail() 第二种(了解即可) app.add_url_rule(" ...
- 模仿 AppStore 顶部动画
App Store 顶部动画 App Store 中 Games.Apps.Updates 的顶部动画的特点: 自然状态下是大标题,右边有一个 button 顶上去时,变成小标题,右边按钮消失 导航栏 ...
- (转)IBM AIX系统为rootvg实现镜像
IBM AIX系统为rootvg实现镜像 AIX系统安装的时候,没有选择安装镜像,因此在系统安装完成后,出于安全方面的考虑,决定为rootvg创建镜像. 工具/原料 AIX rootvg lspv c ...
- 漫谈NIO(3)之Netty实现
1.前言 上一章结合Java的NIO例子,讲解了多路IO复用的一个基本使用方法,通过实际编码加深对其理解.本章开始进入Netty的环节,前面两章都是为了Netty进行铺垫说明.此节将对比Java的NI ...
- IE中的userData
之前做项目时用到了localstorage,但是考虑到浏览器存在IE8以下不兼容问题,所以来介绍以下IE中的userData. 本地存储解决方案很多,比如Flash SharedObject.Goog ...
- 【链表】Partition List
题目: Given a linked list and a value x, partition it such that all nodes less than x come before node ...
- Tomcat 访问manager app报403 解决方案(虚拟机可以正常使用,外面访问报错)
虚拟机中Tomcat启动后,可以访问项目(虚拟机里面和外面都可以).虚拟机中能够正常进入manager app进行热部署工作,但是在外面能访问tomcat首页,点击manager app报403错误. ...
- Centos虚拟机SVN的安装和使用http方式访问svn服务器
1.查看是否安装旧版SVNrpm -qa | grep subversion2.卸载旧版本SVNyum remove subversion3.安装SVNyum -y install subversio ...
- Golang gRPC 使用
一.概念 1.gRPC默认使用protocol buffers,这是google开源的一套成熟的结构数据序列化机制(当然也可以使用其他数据格式如JSON),可以用proto files创建gRPC服务 ...
