How to receive a million packets per second
Last week during a casual conversation I overheard a colleague saying: "The Linux network stack is slow! You can't expect it to do more than 50 thousand packets per second per core!"
That got me thinking. While I agree that 50kpps per core is probably the limit for any practical application, what is the Linux networking stack capable of? Let's rephrase that to make it more fun:
On Linux, how hard is it to write a program that receives 1 million UDP packets per second?
Hopefully, answering this question will be a good lesson about the design of a modern networking stack.

CC BY-SA 2.0 image by Bob McCaffrey
First, let us assume:
Measuring packets per second (pps) is much more interesting than measuring bytes per second (Bps). You can achieve high Bps by better pipelining and sending longer packets. Improving pps is much harder.
Since we're interested in pps, our experiments will use short UDP
messages. To be precise: 32 bytes of UDP payload. That means 74
bytes on the Ethernet layer.For the experiments we will use two physical servers: "receiver" and
"sender".They both have two six core 2GHz Xeon processors. With hyperthreading (HT) enabled that counts to 24 processors on each box. The boxes have a multi-queue 10G network card by Solarflare, with 11 receive queues configured. More on that later.
The source code of the test programs is available here:
udpsender,udpreceiver.
Prerequisites
Let's use port 4321 for our UDP packets. Before we start we must ensure the traffic won't be interfered with by the iptables:
receiver$ iptables -I INPUT 1 -p udp --dport 4321 -j ACCEPT
receiver$ iptables -t raw -I PREROUTING 1 -p udp --dport 4321 -j NOTRACK
A couple of explicitly defined IP addresses will later become handy:
receiver$ for i in `seq 1 20`; do \
ip addr add 192.168.254.$i/24 dev eth2; \
done
sender$ ip addr add 192.168.254.30/24 dev eth3
- The naive approach
To start let's do the simplest experiment. How many packets will be delivered for a naive send and receive?
The sender pseudo code:
fd = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
fd.bind(("0.0.0.0", 65400)) # select source port to reduce nondeterminism
fd.connect(("192.168.254.1", 4321))
while True:
fd.sendmmsg(["\x00" * 32] * 1024)
While we could have used the usual send syscall, it wouldn't be efficient. Context switches to the kernel have a cost and it is be better to avoid it. Fortunately a handy syscall was recently added to Linux: sendmmsg. It allows us to send many packets in one go. Let's do 1,024 packets at once.
The receiver pseudo code:
fd = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET, socket.SOCK_DGRAM)
fd.bind(("0.0.0.0", 4321))
while True:
packets = [None] * 1024
fd.recvmmsg(packets, MSG_WAITFORONE)
Similarly, recvmmsg is a more efficient version of the common recv syscall.
Let's try it out:
sender$ ./udpsender 192.168.254.1:4321
receiver$ ./udpreceiver1 0.0.0.0:4321
0.352M pps 10.730MiB / 90.010Mb
0.284M pps 8.655MiB / 72.603Mb
0.262M pps 7.991MiB / 67.033Mb
0.199M pps 6.081MiB / 51.013Mb
0.195M pps 5.956MiB / 49.966Mb
0.199M pps 6.060MiB / 50.836Mb
0.200M pps 6.097MiB / 51.147Mb
0.197M pps 6.021MiB / 50.509Mb
With the naive approach we can do between 197k and 350k pps. Not too bad. Unfortunately there is quite a bit of variability. It is caused by the kernel shuffling our programs between cores. Pinning the processes to CPUs will help:
sender$ taskset -c 1 ./udpsender 192.168.254.1:4321
receiver$ taskset -c 1 ./udpreceiver1 0.0.0.0:4321
0.362M pps 11.058MiB / 92.760Mb
0.374M pps 11.411MiB / 95.723Mb
0.369M pps 11.252MiB / 94.389Mb
0.370M pps 11.289MiB / 94.696Mb
0.365M pps 11.152MiB / 93.552Mb
0.360M pps 10.971MiB / 92.033Mb
Now, the kernel scheduler keeps the processes on the defined CPUs. This improves processor cache locality and makes the numbers more consistent, just what we wanted.
- Send more packets
While 370k pps is not bad for a naive program, it's still quite far from the goal of 1Mpps. To receive more, first we must send more packets. How about sending independently from two threads:
sender$ taskset -c 1,2 ./udpsender \
192.168.254.1:4321 192.168.254.1:4321
receiver$ taskset -c 1 ./udpreceiver1 0.0.0.0:4321
0.349M pps 10.651MiB / 89.343Mb
0.354M pps 10.815MiB / 90.724Mb
0.354M pps 10.806MiB / 90.646Mb
0.354M pps 10.811MiB / 90.690Mb
The numbers on the receiving side didn't increase. ethtool -S will reveal where the packets actually went:
receiver$ watch 'sudo ethtool -S eth2 |grep rx'
rx_nodesc_drop_cnt: 451.3k/s
rx-0.rx_packets: 8.0/s
rx-1.rx_packets: 0.0/s
rx-2.rx_packets: 0.0/s
rx-3.rx_packets: 0.5/s
rx-4.rx_packets: 355.2k/s
rx-5.rx_packets: 0.0/s
rx-6.rx_packets: 0.0/s
rx-7.rx_packets: 0.5/s
rx-8.rx_packets: 0.0/s
rx-9.rx_packets: 0.0/s
rx-10.rx_packets: 0.0/s
Through these stats, the NIC reports that it had successfully delivered around 350kpps to RX queue number #4. The rx_nodesc_drop_cnt is a Solarflare specific counter saying the NIC failed to deliver 450kpps to the kernel.
Sometimes it's not obvious why the packets weren't delivered. In our case though, it's very clear: the RX queue #4 delivers packets to CPU #4. And CPU #4 can't do any more work - it's totally busy just reading the 350kpps. Here's how that looks in htop:
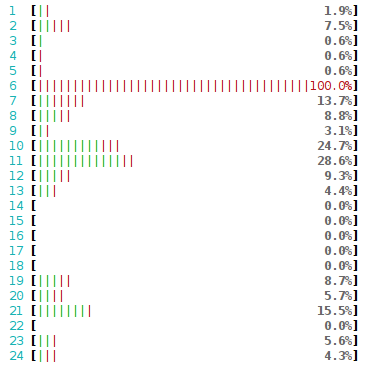
Crash course to multi-queue NICs
Historically, network cards had a single RX queue that was used to pass packets between hardware and kernel. This design had an obvious limitation - it was impossible to deliver more packets than a single CPU could handle.
To utilize multicore systems, NICs began to support multiple RX queues. The design is simple: each RX queue is pinned to a separate CPU, therefore, by delivering packets to all the RX queues a NIC can utilize all CPUs. But it raises a question: given a packet, how does the NIC decide to which RX queue to push it?
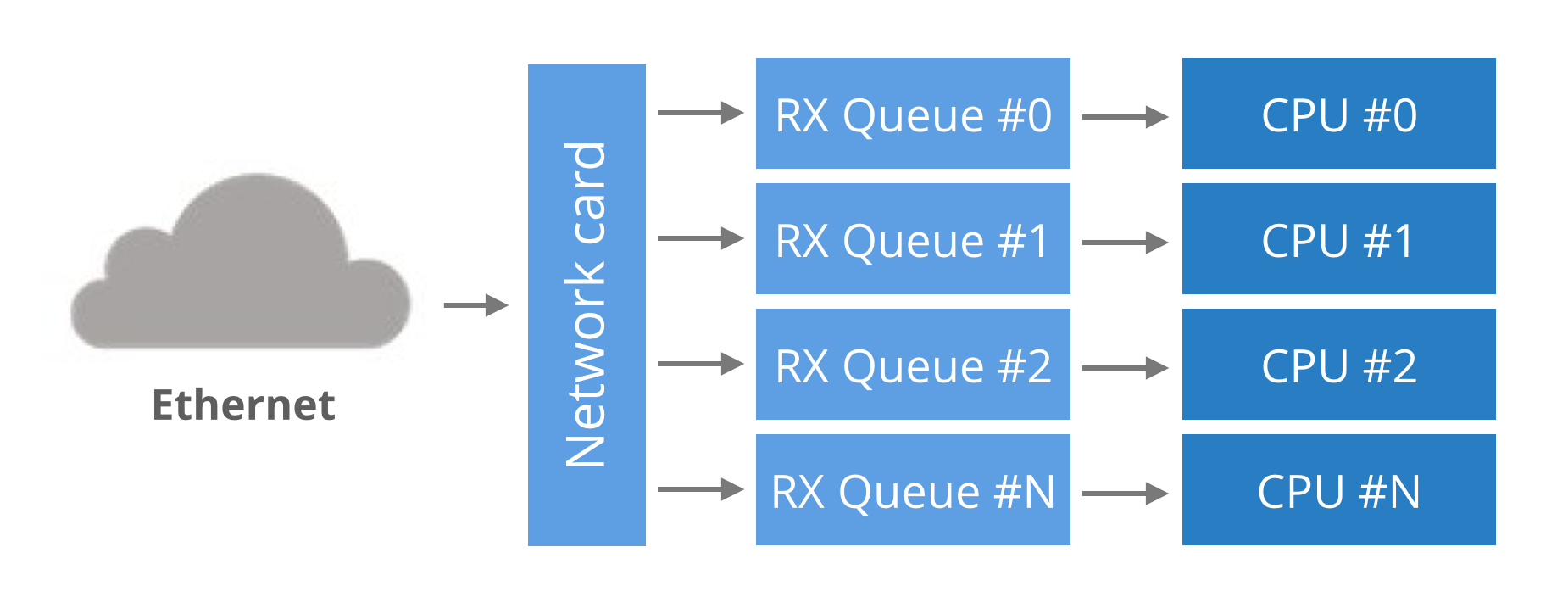
Round-robin balancing is not acceptable, as it might introduce reordering of packets within a single connection. An alternative is to use a hash from packet to decide the RX queue number. The hash is usually counted from a tuple (src IP, dst IP, src port, dst port). This guarantees that packets for a single flow will always end up on exactly the same RX queue, and reordering of packets within a single flow can't happen.
In our case, the hash could have been used like this:
RX_queue_number = hash('192.168.254.30', '192.168.254.1', 65400, 4321) % number_of_queues
Multi-queue hashing algorithms
The hash algorithm is configurable with ethtool. On our setup it is:
receiver$ ethtool -n eth2 rx-flow-hash udp4
UDP over IPV4 flows use these fields for computing Hash flow key:
IP SA
IP DA
This reads as: for IPv4 UDP packets, the NIC will hash (src IP, dst IP) addresses. i.e.:
RX_queue_number = hash('192.168.254.30', '192.168.254.1') % number_of_queues
This is pretty limited, as it ignores the port numbers. Many NICs allow customization of the hash. Again, using ethtool we can select the tuple (src IP, dst IP, src port, dst port) for hashing:
receiver$ ethtool -N eth2 rx-flow-hash udp4 sdfn
Cannot change RX network flow hashing options: Operation not supported
Unfortunately our NIC doesn't support it - we are constrained to (src IP, dst IP) hashing.
A note on NUMA performance
So far all our packets flow to only one RX queue and hit only one CPU. Let's use this as an opportunity to benchmark the performance of different CPUs. In our setup the receiver host has two separate processor banks, each is a different NUMA node.
We can pin the single-threaded receiver to one of four interesting CPUs in our setup. The four options are:
Run receiver on another CPU, but on the same NUMA node as the RX queue. The performance as we saw above is around 360kpps.
With receiver on exactly same CPU as the RX queue we can get up to ~430kpps. But it creates high variability. The performance drops down to zero if the NIC is overwhelmed with packets.
When the receiver runs on the HT counterpart of the CPU handling RX queue, the performance is half the usual number at around 200kpps.
With receiver on a CPU on a different NUMA node than the RX queue we get ~330k pps. The numbers aren't too consistent though.
While a 10% penalty for running on a different NUMA node may not sound too bad, the problem only gets worse with scale. On some tests I was able to squeeze out only 250kpps per core. On all the cross-NUMA tests the variability was bad. The performance penalty across NUMA nodes is even more visible at higher throughput. In one of the tests I got a 4x penalty when running the receiver on a bad NUMA node.
- Multiple receive IPs
Since the hashing algorithm on our NIC is pretty limited, the only way to distribute the packets across RX queues is to use many IP addresses. Here's how to send packets to different destination IPs:
sender$ taskset -c 1,2 ./udpsender 192.168.254.1:4321 192.168.254.2:4321
ethtool confirms the packets go to distinct RX queues:
receiver$ watch 'sudo ethtool -S eth2 |grep rx'
rx-0.rx_packets: 8.0/s
rx-1.rx_packets: 0.0/s
rx-2.rx_packets: 0.0/s
rx-3.rx_packets: 355.2k/s
rx-4.rx_packets: 0.5/s
rx-5.rx_packets: 297.0k/s
rx-6.rx_packets: 0.0/s
rx-7.rx_packets: 0.5/s
rx-8.rx_packets: 0.0/s
rx-9.rx_packets: 0.0/s
rx-10.rx_packets: 0.0/s
The receiving part:
receiver$ taskset -c 1 ./udpreceiver1 0.0.0.0:4321
0.609M pps 18.599MiB / 156.019Mb
0.657M pps 20.039MiB / 168.102Mb
0.649M pps 19.803MiB / 166.120Mb
Hurray! With two cores busy with handling RX queues, and third running the application, it's possible to get ~650k pps!
We can increase this number further by sending traffic to three or four RX queues, but soon the application will hit another limit. This time the rx_nodesc_drop_cnt is not growing, but the netstat "receiver errors" are:
receiver$ watch 'netstat -s --udp'
Udp:
437.0k/s packets received
0.0/s packets to unknown port received.
386.9k/s packet receive errors
0.0/s packets sent
RcvbufErrors: 123.8k/s
SndbufErrors: 0
InCsumErrors: 0
This means that while the NIC is able to deliver the packets to the kernel, the kernel is not able to deliver the packets to the application. In our case it is able to deliver only 440kpps, the remaining 390kpps + 123kpps are dropped due to the application not receiving them fast enough.
- Receive from many threads
We need to scale out the receiver application. The naive approach, to receive from many threads, won't work well:
sender$ taskset -c 1,2 ./udpsender 192.168.254.1:4321 192.168.254.2:4321
receiver$ taskset -c 1,2 ./udpreceiver1 0.0.0.0:4321 2
0.495M pps 15.108MiB / 126.733Mb
0.480M pps 14.636MiB / 122.775Mb
0.461M pps 14.071MiB / 118.038Mb
0.486M pps 14.820MiB / 124.322Mb
The receiving performance is down compared to a single threaded program. That's caused by a lock contention on the UDP receive buffer side. Since both threads are using the same socket descriptor, they spend a disproportionate amount of time fighting for a lock around the UDP receive buffer. This paper describes the problem in more detail.
Using many threads to receive from a single descriptor is not optimal.
- SO_REUSEPORT
Fortunately, there is a workaround recently added to Linux: the SO_REUSEPORT flag. When this flag is set on a socket descriptor, Linux will allow many processes to bind to the same port. In fact, any number of processes will be allowed to bind and the load will be spread across them.
With SO_REUSEPORT each of the processes will have a separate socket descriptor. Therefore each will own a dedicated UDP receive buffer. This avoids the contention issues previously encountered:
receiver$ taskset -c 1,2,3,4 ./udpreceiver1 0.0.0.0:4321 4 1
1.114M pps 34.007MiB / 285.271Mb
1.147M pps 34.990MiB / 293.518Mb
1.126M pps 34.374MiB / 288.354Mb
This is more like it! The throughput is decent now!
More investigation will reveal further room for improvement. Even though we started four receiving threads, the load is not being spread evenly across them:

Two threads received all the work and the other two got no packets at all. This is caused by a hashing collision, but this time it is at the SO_REUSEPORT layer.
Final words
I've done some further tests, and with perfectly aligned RX queues and receiver threads on a single NUMA node it was possible to get 1.4Mpps. Running receiver on a different NUMA node caused the numbers to drop achieving at best 1Mpps.
To sum up, if you want a perfect performance you need to:
Ensure traffic is distributed evenly across many RX queues and
SO_REUSEPORTprocesses. In practice, the load usually is well distributed as long as there are a large number of connections (or flows).You need to have enough spare CPU capacity to actually pick up the packets from the kernel.
To make the things harder, both RX queues and receiver processes should be on a single NUMA node.
While we had shown that it is technically possible to receive 1Mpps on a Linux machine, the application was not doing any actual processing of received packets - it didn't even look at the content of the traffic. Don't expect performance like that for any practical application without a lot more work.
Interested in this sort of low-level, high-performance packet wrangling? CloudFlare is hiring in London, San Francisco and Singapore.
How to receive a million packets per second的更多相关文章
- 【Network】高性能 UDP 应该怎么做?
参考资料: EPOLL-UDP-GOLANG golang udp epoll - Google 搜索 go - golang: working with multiple client/server ...
- How To Capture Packets with TCPDUMP?
http://linux-circles.blogspot.com/2012/11/how-to-capture-packets-with-tcpdump.html See the list of i ...
- Intel DPDK的一些参资料
dpdk.org What it is Intel® DPDK is a set of libraries and drivers for fast packet processing on x86 ...
- Man手册--nmap
目录 nmap使用手册 附录: nmap使用手册 附录: NMAP(1) Nmap Reference Guide NMAP(1) NAME nmap - Network exploration to ...
- JDWP Agent
JDWP Agent Implementation Description Revision History Disclaimer 1. About this Document 1.1 Purpose ...
- 嵌入式Linux驱动学习之路(二十六)DM9000C网卡驱动程序
基于DM9000C的原厂代码修改dm9000c的驱动程序. 首先确认内存的基地址 iobase. 确定中断号码. 打开模块的初始化函数定义. 配置内存控制器的相应时序(结合DM9000C.C的手册). ...
- 浅谈UDP(数据包长度,收包能力,丢包及进程结构选择)
UDP数据包长度 UDP数据包的理论长度 udp数据包的理论长度是多少,合适的udp数据包应该是多少呢?从TCP-IP详解卷一第11章的udp数据包的包头可以看出,udp的最大包长度是2^16-1的个 ...
- 每天一个linux命令(56):netstat命令
netstat命令用于显示与IP.TCP.UDP和ICMP协议相关的统计数据,一般用于检验本机各端口的网络连接情况.netstat是在内核中访问网络及相关信息的程序,它能提供TCP连接,TCP和UD ...
- linux 网卡接收多播MAC(01:08开头)
调用: int dev_set_allmulti(struct net_device *dev, int inc) 打上IFF_ALLMULTI标记 #define IFF_ALLMULTI ...
随机推荐
- ASP.NET Core中返回 json 数据首字母大小写问题
ASP.NET Core中返回 json 数据首字母大小写问题 在asp.net core中使用ajax请求动态绑定数据时遇到该问题 后台返回数据字段首字母为定义的大写,返回的数据没有问题 但是在前台 ...
- Thinkphp5.1允许uni-app的H5跨域请求接口解决方法
情景: uni-app使用vue框架开发混合APP,虽然APP或者小程序没有跨域,但希望就是写完这个既有H5,又有APP,小程序等,所以能通过后端解决跨域最好.但是不知道是vue的原因还是什么,在PH ...
- js修改页面标题 title
如果对你有帮助的话麻烦点个[推荐]~最好还可以follow一下我的GitHub~感谢观看! /* * *添加首页description元数据meta标签 *创建一个meta元素,sName为该meta ...
- js检测页面触底
<script> function getDocumentTop() { var scrollTop = 0, bodyScrollTop = 0, documentScrollTop = ...
- Linux下设置Nginx开机自启
1.本地环境 [root@dev ~]#cat /etc/redhat-release CentOS Linux release 7.5.1804 (Core) 2.在/etc/init.d创建ngi ...
- SQL注入之Sqlmap使用
我们都知道,对于网络渗透最重要的一步是要拿到后台数据库管理员的密码与用户名,那么怎么得到这个用户名和密码呢?就要用到今天所说的Sqlmap,它不仅适用于内网环境,在外网环境也是非常受欢迎的,并且在Ka ...
- NumPy简单入门教程
# NumPy简单入门教程 NumPy是Python中的一个运算速度非常快的一个数学库,它非常重视数组.它允许你在Python中进行向量和矩阵计算,并且由于许多底层函数实际上是用C编写的,因此你可以体 ...
- Mincut 最小割 (BZOJ1797+最小割+tarjan)
题目链接 传送门 思路 根据题目给定的边跑一边最大流,然后再在残留网络上跑\(tarjan\). 对于每一条边有: 如果它是非满边,那么它一定不是最小割集里面的边: 如果\(c[u[i]] \not= ...
- Bootstrap 学习笔记1
<img src="..." class="img-responsive" alt="响应式图像"> 通过添加 img-resp ...
- Q-learning之一维世界的简单寻宝
Q-learning的算法: (1)先初始化一个Q table,Q table的行数是state的个数,列数是action的个数. (2)先随机选择一个作为初始状态S1,根据一些策略选择此状态下的动作 ...
