史上最完整promise源码手写实现
史上最完整的promise源码实现,哈哈,之所以用这个标题,是因为开始用的标题《手写promise源码》不被收录
promise自我介绍
promise : "君子一诺千金,承诺的事情一定会去执行"
promise的使用场景
- 使用promise能够有效的解决js异步回调地狱问题
- 能够将业务逻辑与数据处理分隔开使代码更优雅,方便阅读,更有利于代码维护
promise的基本用法
function promiseTest() {let promise = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {let r = parseInt(Math.random() * 10)if (r % 2 == 0) {resolve('成功')} else {reject('失败')}})return promise}const promise = promiseTest()promise.then((data) => {console.log(data)}).catch((err) => {console.log(err)})
先来分析一下promise的规范
- promise有三种状态:pending,fulfilled,rejected。pending代表等待的状态,在此状态下,可能执行resolve()的方法,也可能执行reject()方法,fulfilld代表成功态,此状态下执行resolve()方法,rejected代表失败态,此状态下执行reject()方法,一旦成功了就不能失败,反过来也是一样
- 每个promsie都有一个then方法
- 如果new promise 报错了会走失败态(throw new Error('报错')也会走失败态)
// 手写promise源码// 第一步:基础代码class Mypromise {constructor(executor) {this.state = 'pending' //状态值this.value = undefined //成功的返回值this.reason = undefined //失败的返回值// 成功let resolve = (value) => {if (this.state == 'pending') {this.state = 'fullFilled'this.value = value}}// 失败let reject = (reason) => {if (this.state == 'pending') {this.state = 'rejected'this.reason = reason}}try {// 执行函数executor(resolve, reject)} catch (err) {// 失败则直接执行reject函数reject(err)}}then(onFullFilled, onRejected) {// 状态为fulfuilled,执行onFullFilled,传入成功的值if (this.state == 'fullFilled') {onFullFilled(this.value)}// 状态为rejected,执行onRejected,传入失败的值if (this.state == 'rejected') {onRejected(this.reason)}}}const p = new Mypromise((resolve, reject) => {// resolve('success') // 走了成功就不会走失败了throw new Error('失败') // 失败了就走resolvereject('failed') // 走了失败就不会走成功})p.then((res) => {console.log(res)}, (err) => {console.log(err)})
此时九阳神功的第一层就算完成了
但是当碰到异步调用的时候,上面的代码就会卡在pending态,神功初成,还要继续往下修炼,若不能继续突破,则无法上升到第二层境界
如下调用的时候会卡住,无法执行
const p = new Mypromise((resolve, reject) => {setTimeout(function() {resolve('success')}, 1000)})p.then((res) => {console.log(res)}, (err) => {console.log(err)})
此时我们使用一个发布订阅者模式,在pending状态的时候将成功的函数和失败的函数存到各自的回调队列数组中,等一旦reject或者resolve,就调用它们:
在pending态的时候将所有的要在成功态执行的方法都存到onResolveCallbacks数组中

当状态变化的时候,就执行发布他们
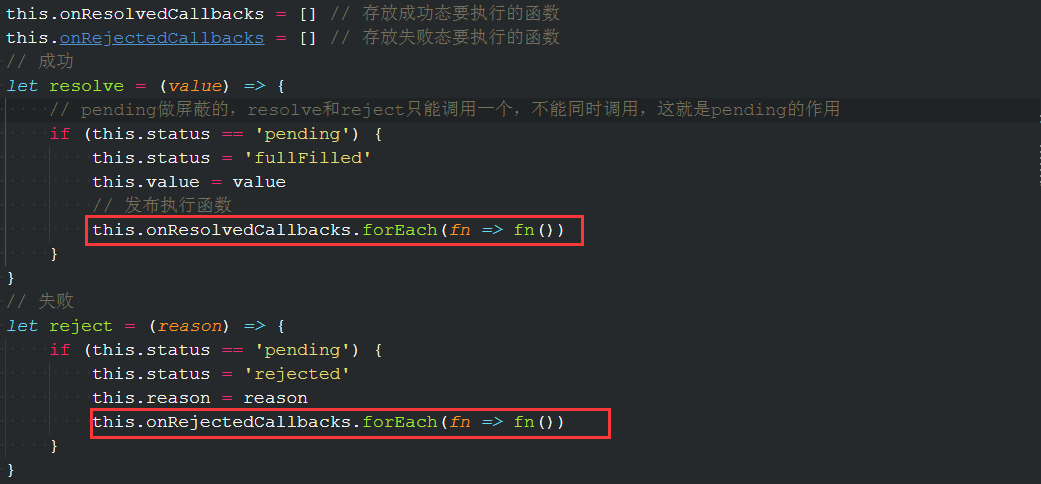
下面是完整的代码
class Mypromise {constructor(executor) {this.status = 'pending' //状态值this.value = undefined //成功的返回值this.reason = undefined //失败的返回值this.onResolvedCallbacks = [] //成功的回调函数this.onRejectedCallbacks = [] //失败的回调函数// 成功let resolve = (value) => {// pending用来屏蔽的,resolve和reject只能调用一个,不能同时调用,这就是pending的作用if (this.status == 'pending') {this.status = 'fullFilled'this.value = value// 发布执行函数this.onResolvedCallbacks.forEach(fn => fn())}}// 失败let reject = (reason) => {if (this.status == 'pending') {this.status = 'rejected'this.reason = reason//失败执行函数this.onRejectedCallbacks.forEach(fn => fn())}}try {// 执行函数executor(resolve, reject)} catch (err) {// 失败则直接执行reject函数reject(err)}}then(onFullFilled, onRejected) {// 同步if (this.status == 'fullFilled') {onFullFilled(this.value)}if (this.status == 'rejected') {onRejected(this.reason)}// 异步if (this.status == 'pending') {// 在pending状态的时候先订阅this.onResolvedCallbacks.push(() => {// todoonFullFilled(this.value)})this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(() => {// todoonRejected(this.reason)})}}}const p = new Mypromise((resolve, reject) => {setTimeout(function() {// resolve('success') // 异步调用的时候,this.status一直是pending状态,不会执行代码了,因此要改装成发布订阅者模式reject('failed')}, 1000)// resolve('success') // 走了成功就不会走失败了// throw new Error('失败') // 失败了也会走resolve// reject('failed')})p.then((res) => {console.log(res)}, (err) => {console.log(err)})p.then((res) => {console.log(res)}, (err) => {console.log(err)})p.then((res) => {console.log(res)}, (err) => {console.log(err)})
恭喜你少年,九阳神功第二层你已经学会了
接下来接续学习神功第三层promise的链式调用
要达到链式调用我们就要采用“老和尚给小和尚讲故事”的递归大法了,也可以说是愚公移山大法,很多同学可能一直对递归函数有点惧怕,其实很简单,想一下小时候听过的老和尚讲故事,以及愚公移山的故事就清楚什么是递归算法了。
我们先来回味一下这两个经典的故事:
“老和尚给小和尚讲故事:从前有座山,山里有座庙,庙里有个老和尚,老和尚给小和尚讲故事,从前有座山,山里有座庙......”
愚公说:“虽我之死,有子存焉;子又生孙,孙又生子;子又有子,子又有孙;子子孙孙无穷匮也,而山不加增,何苦而不平”
递归是不是很简单呢?
不了解规范的同学先去看一下Promises/A+规范文档:
英文规范文档:https://promisesaplus.com/
下面先来分析一下链式调用的用法,以及then里面可能出现的情况
const p = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {resolve(100)})p.then((data) => {return 100 * data}, (err) => {console.log(err)}).then((data) => {return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {console.log(data)resolve(data)})}).then((data) => {console.log('result', data) // 10000})
根据原生promise的then的用法,我们总结一下:
1.then方法如果返回一个普通的值,我们就将这个普通值传递给下一个then
2.then方法如果返回一个promise对象,我们就将这个promise对象执行结果返回到下一个then
普通的值传递很好办,我们将第一次then的onFulfilled函数返回的值存到x变量里面,在然后resolve出去就可以了
then(onFullFilled, onRejected) {// 这样就是一个递归let promise2 = new Mypromise((resolve, reject) => {// 函数里面调函数就跟第一次使用一样,主要的是这里面的this指向怎么变化的// 同步let xconsole.log('this', this)if (this.status == 'fullFilled') {// 箭头函数,无论this一直是指向最外层的对象x = onFullFilled(this.value)resolve(x) // resolve(x) // 这一步x只能处理普通值,但是x可能是一个函数对象,或者promise,所以要对x进行判断// 添加一个resolvePromise()的方法来判断x跟promise2的状态,决定promise2是走成功还是失败}if (this.status == 'rejected') {x = onRejected(this.reason)reject(x)}// 异步if (this.status == 'pending') {// 在pending状态的时候先订阅this.onResolvedCallbacks.push(() => {// todox = onFullFilled(this.value)resolve(x)})this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(() => {// todox = onRejected(this.reason)resolve(x)})}})return promise2 //then方法返回一个promise对象}
复杂的是then里面返回的是一个promise的时候怎么办,因为返回的promise的我们要判断他执行的状态,来决定是走成功态,还是失败态,这时候我们就要写一个判断的函数resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject)来完成这个判断
then(onFullFilled, onRejected) {// 这样就是一个递归let promise2 = new Mypromise((resolve, reject) => {// 箭头函数,无论this一直是指向最外层的对象// 同步let xif (this.status == 'fullFilled') {setTimeout(() => {try {x = onFullFilled(this.value)// 添加一个resolvePromise()的方法来判断x跟promise2的状态,决定promise2是走成功还是失败resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject)} catch (err) { // 中间任何一个环节报错都要走reject()reject(err)}}, 0) // 同步无法使用promise2,所以借用setiTimeout异步的方式// MDN 0>=4ms}if (this.status == 'rejected') {setTimeout(() => {try {x = onRejected(this.value)resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject)} catch (err) { // 中间任何一个环节报错都要走reject()reject(err)}}, 0) // 同步无法使用promise2,所以借用setiTimeout异步的方式}// 异步if (this.status == 'pending') {// 在pending状态的时候先订阅this.onResolvedCallbacks.push(() => {// todosetTimeout(() => {try {x = onFullFilled(this.value)resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject)} catch (err) { // 中间任何一个环节报错都要走reject()reject(err)}}, 0) // 同步无法使用promise2,所以借用setiTimeout异步的方式})this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(() => {// todosetTimeout(() => {try {x = onRejected(this.value)resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject)} catch (err) { // 中间任何一个环节报错都要走reject()reject(err)}}, 0) // 同步无法使用promise2,所以借用setiTimeout异步的方式})}})return promise2}
下面再来实现核心的resolvePromise方法
这个方法的主要作用是用来判断x的值,如果x的值是一个普通的值,就直接返回x的值,如果x的值是一个promise,就要返回x.then() 执行的结果,核心代码如下
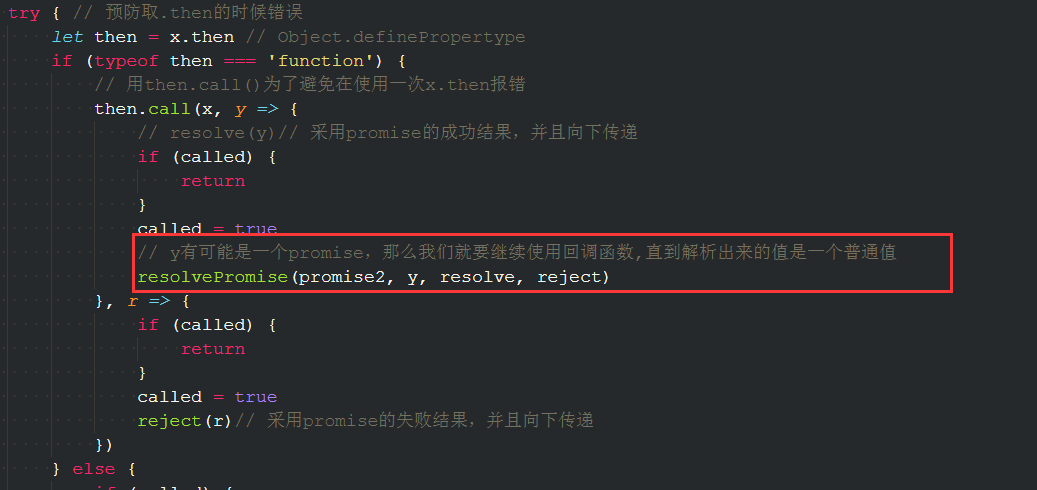
const resolvePromise = (promise2, x, resolve, reject) => {// x和promise2不能是同一个人,如果是同一个人就报错if (promise2 === x) {return reject(new TypeError('Chaining cycle detected for promise #<promise>'))}// 判断如果x是否是一个对象,判断函数是否是对象的方法有:typeof instanceof constructor toStringif (typeof x === 'object' && x != null || typeof x === 'function') {try {let then = x.then // 取then可以报错,报错就走reject()if (typeof then === 'function') {// 用then.call()为了避免在使用一次x.then报错then.call(x, y => {console.log('y', y)resolve(y)// 采用promise的成功结果,并且向下传递}, r => {reject(r)// 采用promise的失败结果,并且向下传递})} else {resolve(x)// x不是一个函数,是一个对象}} catch (err) {reject(err)}} else {// x是一个普通值resolve(x)}}
细节的地方看注释
此时基本的情况都已经实现的差不多了,下面还一种如下的情况,x的值里面包含有promise
const p2 = p.then((data) => {return new Mypromise((resolve, reject) => {resolve(new Mypromise((resolve, reject) => {setTimeout(() => {resolve(data * 1000)}, 1000)}))// 这里很可能又是一个promise函数})})
我们只需要在判断x的值的时候多调用一个回调,就可以解决以上的问题
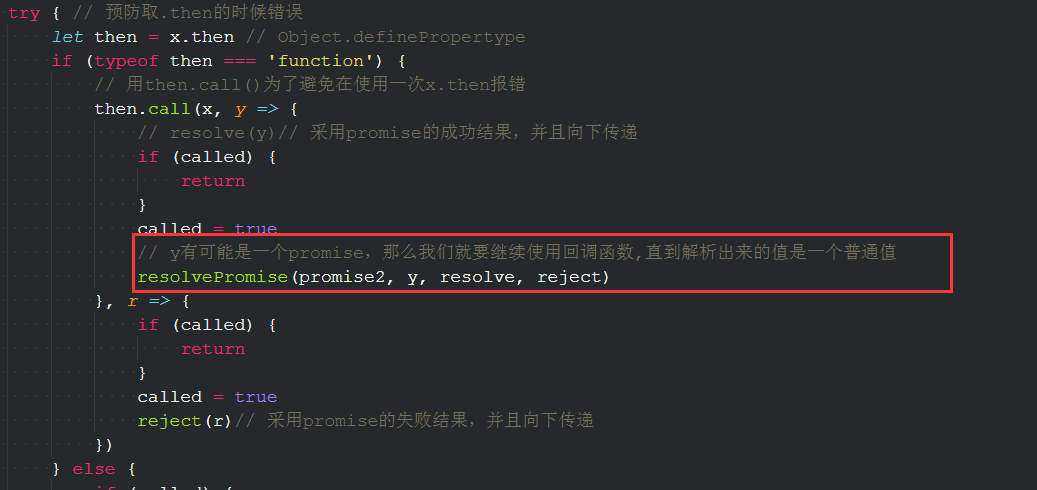
下面是完整的源码:
const isFunction = (value) => typeof value === 'function'const PENDING = 'pending'const RESOLVED = 'fulFilled'const REJECTED = 'rejected'const resolvePromise = (promise2, x, resolve, reject) => {// x和promise2不能是同一个人,如果是同一个人就报错// 加一个开关,防止多次调用失败和成功,跟pending状态值一样的逻辑一样,走了失败就不能走成功了,走了成功一定不能在走失败if (promise2 === x) {return reject(new TypeError('Chaining cycle detected for promise #<promise>'))}// 判断如果x是否是一个对象,判断函数是否是对象的方法有:typeof instanceof constructor toStringif ((typeof x === 'object' && x != null) || typeof x === 'function') {let calledtry { // 预防取.then的时候错误let then = x.then // Object.definePropertypeif (typeof then === 'function') {// 用then.call()为了避免在使用一次x.then报错then.call(x, y => {// resolve(y)// 采用promise的成功结果,并且向下传递if (called) {return}called = true// y有可能是一个promise,那么我们就要继续使用回调函数,直到解析出来的值是一个普通值resolvePromise(promise2, y, resolve, reject)}, r => {if (called) {return}called = truereject(r)// 采用promise的失败结果,并且向下传递})} else {if (called) {return}called = trueresolve(x)// x不是一个函数,是一个对象}} catch (err) {if (called) {return}called = truereject(err)}} else {// x是一个普通值resolve(x)}}class MyPromise {constructor(executor) {this.status = PENDINGthis.value = undefinedthis.reason = undefinedthis.onResolvedCallbacks = []this.onRejectedCallbacks = []// 成功let resolve = (value) => {// pending最屏蔽的,resolve和reject只能调用一个,不能同时调用,这就是pending的作用if (this.status == PENDING) {this.status = RESOLVEDthis.value = value// 发布执行函数this.onResolvedCallbacks.forEach(fn => fn())}}// 失败let reject = (reason) => {if (this.status == PENDING) {this.status = REJECTEDthis.reason = reasonthis.onRejectedCallbacks.forEach(fn => fn())}}try {// 执行函数executor(resolve, reject)} catch (err) {// 失败则直接执行reject函数reject(err)}}then(onFulFilled, onRejected) {// onfulfilled, onrejected 都是可选参数onFulFilled = isFunction(onFulFilled) ? onFulFilled : data => dataonRejected = isFunction(onRejected) ? onRejected : err => {throw err}let promise2 = new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {// 箭头函数,无论this一直是指向最外层的对象// 同步if (this.status == RESOLVED) {setTimeout(() => {try {let x = onFulFilled(this.value)// 添加一个resolvePromise()的方法来判断x跟promise2的状态,决定promise2是走成功还是失败resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject)} catch (err) { // 中间任何一个环节报错都要走reject()reject(err)}}, 0) // 同步无法使用promise2,所以借用setiTimeout异步的方式// MDN 0>=4ms}if (this.status == REJECTED) {setTimeout(() => {try {let x = onRejected(this.reason)resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject)} catch (err) { // 中间任何一个环节报错都要走reject()reject(err)}}, 0) // 同步无法使用promise2,所以借用setiTimeout异步的方式}// 异步if (this.status == PENDING) {// 在pending状态的时候先订阅this.onResolvedCallbacks.push(() => {// todosetTimeout(() => {try {let x = onFulFilled(this.value)resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject)} catch (err) { // 中间任何一个环节报错都要走reject()reject(err)}}, 0) // 同步无法使用promise2,所以借用setiTimeout异步的方式})this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(() => {// todosetTimeout(() => {try {let x = onRejected(this.reason)resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject)} catch (err) { // 中间任何一个环节报错都要走reject()reject(err)}}, 0) // 同步无法使用promise2,所以借用setiTimeout异步的方式})}})return promise2}}
到此核心的代码就写完了,我们用promises-aplus-tests插件来检测一下
安装:npm install promises-aplua-tests -g插件
加上如下代码:
MyPromise.defer = MyPromise.deferred = function() {let dfd = {}dfd.promise = new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {dfd.resolve = resolvedfd.reject = reject})return dfd}module.exports = MyPromise
执行命令:promises-aplus-tests promise.js
ok,非常完美
到此核心的代码都已经实现了,后面的静态方法,catch,all,race,resolve,reject,finally方法就是小试牛刀了,就不在赘述,只贴上代码
catch方法:
// catch方法MyPromise.prototype.catch = function(onReJected) {// 返回一个没有第一个参数的then方法return this.then(undefined, onReJected)}
promise的all方法
// 写一个判断函数是否是一个promise的方法const isPromise = (value) => {if ((value != null && typeof value === 'object') || typeof value === 'function') {if (typeof value.then == 'function') {return true}} else {return false}}// static all方法MyPromise.all = (lists) => {// 返回一个promisereturn new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {let resArr = [] // 存储处理的结果的数组// 判断每一项是否处理完了let index = 0function processData(i, data) {resArr[i] = dataindex += 1if (index == lists.length) {// 处理异步,要使用计数器,不能使用resArr==lists.lengthresolve(resArr)}}for (let i = 0; i < lists.length; i++) {if (isPromise(lists[i])) {lists[i].then((data) => {processData(i, data)}, (err) => {reject(err) // 只要有一个传入的promise没执行成功就走rejectreturn})} else {processData(i, lists[i])}}})}
promise的race方法
// promise的race方法// 两个方法赛跑,哪个赢了就先返回哪个的状态MyPromise.race = (lists) => {return new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {for (let i = 0; i < lists.length; i++) {if (isPromise(lists[i])) {lists[i].then((data) => {resolve(data)// 哪个先完成就返回哪一个的结果return}, (err) => {reject(err)return})} else {resolve(lists[i])}}})}
promise的静态方法resolve()
// 静态resolve方法MyPromise.resolve = (value) => {// 如果是一个promise对象就直接将这个对象返回if (isPromise(value)) {return value} else {// 如果是一个普通值就将这个值包装成一个promise对象之后返回return new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {resolve(value)})}}
promise的reject()方法
// 静态reject方法MyPromise.reject = (value) => {return new MyPromise((resolve, reject) => {reject(value)})}
promise的finally方法
// 终极方法finally finally其实就是一个promise的then方法的别名,在执行then方法之前,先处理callback函数MyPromise.prototype.finally = function(cb) {return this.then(value => MyPromise.resolve(cb()).then(() => value),reason => MyPromise.reject(cb()).then(() => { throw reason }))}
少年,恭喜你promise神功已经修炼大成,是不是以为自己很牛逼,可以下山去行走江湖,劫富济贫,铲奸除恶了,莫急,修炼成promise大法,还只是刚刚开始,前面还有很多大法等着你呢,还有很多怪等你去打完,升级,学不会,就别先想着下山去吧,无论什么时候都要记住,山外有山,天外有天,技术精进一刻也不能怠慢。
史上最完整promise源码手写实现的更多相关文章
- HashMap源码分析(史上最详细的源码分析)
HashMap简介 HashMap是开发中使用频率最高的用于映射(键值对 key value)处理的数据结构,我们经常把hashMap数据结构叫做散列链表: ObjectI entry<Key, ...
- 这一次,彻底理解Promise源码思想
关于Promise的源码实现,网上有太多答案,我也看过很多资料,但都不是很明白.直到有一天我学完函数式编程之函子的概念,才对Promise源码有了更深刻的认识.今天,就让我们来重新认识一下Promis ...
- JAVAWEB贵美网上商城完整项目源码(SSH2)
JAVAWEB贵美网上商城完整项目源码(SSH2) 贵美网上商城原是北大青鸟的一个内部项目,项目采用 struts2+spring4+hibernate4+MySQL等技术实现,数据库连接池采用c3p ...
- 在Ubuntu Server14.04上编译Android6.0源码
此前编译过Android4.4的源码,但是现在Android都到了7.0的版本,不禁让我感叹Google的步伐真心难跟上,趁这周周末时间比较充裕,于是在过去的24小时里,毅然花了9个小时编译了一把An ...
- 从.src.rpm包中提取出完整的源码的方法
1 什么是完整的源码 就是说,最初始的源码加上打了所有的patch后的源码,即最新的源码. 2 过程 2.1 从.src.rpm中提取完整的rpm工程文件 2.1.1 rpm to cpio rpm2 ...
- Git 把码云上被fork项目源码merge到fork出来的分支项目
Git 把码云上被fork项目源码merge到fork出来的分支项目 By:授客 QQ:1033553122 需求描述 被fork的项目有更新代码,希望把更新的代码merge到fork分支项目 解决方 ...
- Promise源码实现与测试
const PENDING = 'pending', FULFILLED = 'fulfilled', REJECTED = 'rejected' class MyPromise { construc ...
- 【commons-pool2源码】写前思考
写作的初衷 工作4年多, 一直没有系统的阅读过优秀的开源代码, 所以从今年开始做一些尝试, 阅读源码并且试着将自己的理解以文章的形式输出, 从而达到以下目的: 通过阅读源码提升自身的技术水准, 通过写 ...
- 设计比较好,有助于学习的Github上的iOS App源码 (中文)
Github版 中文 : TeamTalk 蘑菇街. 开源IM. 电商强烈推荐. MyOne-iOS 用OC写的<一个> iOS 客户端 zhihuDaily 高仿知乎日报 Coding ...
随机推荐
- Win10最详细的优化设置 完美解决磁盘100%占用
1.用360优化win10后开不了机的问题原因是禁用了三个服务:在360应用软件服务里dmwappushsvc.diagnsticsTrackingservice.coreMessaging这三个要开 ...
- .NET Core sdk和runtime区别
SDK和runtime区别 .net core Runtime[跑netcore 程序的] (CoreCLR) .net core SDK (开发工具包 [runtime(jre) + Rolysn( ...
- Java进阶——Java中的字符串常量池
转载. https://blog.csdn.net/qq_30379689/article/details/80518283 字符串常量池 JVM为了减少字符串对象的重复创建,其内部维护了一个特殊的内 ...
- C++ 二叉搜索树原理及其实现
首先是概念:二叉搜索树又称二叉排序树,它具有以下的性质: 若是左子树不为空,则左子树上所有节点的值小于根节点的值 若是右子树不为空,则右子树上所有结点的值大于根节点的值 二叉搜索树的左右子树也是二叉搜 ...
- DS 红黑树详解
通过上篇博客知道,二叉搜索树的局限在于不能完成自平衡,从而导致不能一直保持高性能. AVL树则定义了平衡因子绝对值不能大于1,使二叉搜索树达到了严格的高度平衡. 还有一种能自我调整的二叉搜索树, 红黑 ...
- Windows 上的应用程序在运行期间可以给自己改名(可以做 OTA 自我更新)
原文:Windows 上的应用程序在运行期间可以给自己改名(可以做 OTA 自我更新) 程序如何自己更新自己呢?你可能会想到启动一个新的程序或者脚本来更新自己.然而 Windows 操作系统允许一个应 ...
- java之 代理设计模式
1. 设计一个案例来实现租房功能.分析:在租房的过程中涉及到了3个对象,房东,中介,房客. 中介和房客具有相同的功能--租房. 可以设计如下: 2.上图的设计实际上就是一个代理设计模式---静态代理设 ...
- Java中Date、String、Calendar类型之间的转化
1.Calendar 转化 String //获取当前时间的具体情况,如年,月,日,week,date,分,秒等 Calendar calendat = Calendar.getInstanc ...
- mysql 5.7 非正常安装,无法启动 服务没有报告任何错误
以前,完整安装mysql5.7程序时,由于程序太大,可以将安装缓存目录中的安装文件(较小)复制出来后,留以后使用. mysql--win32.msi 2 mysql-5.7.17-winx64.msi ...
- 利用nfs-client-provisioner动态提供Kubernetes后端存储卷
原文:https://www.kubernetes.org.cn/3894.html 利用NFS client provisioner动态提供Kubernetes后端存储卷 本文翻译自nfs-clie ...
